
Therapy
To help you feel better, you may want to try the following self-care measures:
- Avoid lung irritants. Don't smoke. ...
- Use a humidifier. Warm, moist air helps relieve coughs and loosens mucus in your airways. ...
- Consider a face mask outside. If cold air aggravates your cough and causes shortness of breath, put on a cold-air face mask before you go outside.
Self-care
Viruses that cause bronchiolitis spread easily through the air when someone coughs or sneezes. Germs can stay on hands, toys, doorknobs, tissues, and other surfaces. People can be contagious for several days or even weeks. How Long Does Bronchiolitis Last? Bronchiolitis usually lasts about 1–2 weeks.
See more
- Chest X-ray. Your doctor may request a chest X-ray to look for signs of pneumonia.
- Viral testing. Your doctor may collect a sample of mucus from your child to test for the virus causing bronchiolitis. ...
- Blood tests. Occasionally, blood tests might be used to check your child's white blood cell count. ...
What is the best medicine and treatment for bronchitis?
- Make sure to get good rest and take care of yourself while you’re sick.
- Drink plenty of fluids.
- If you’re stuffy, try a humidifier, saline nasal spray, or breathe in steam from a bowl of hot water or a shower.
- Honey (in hot water or straight) might help soothe a cough or sore throat, but never give honey to a child under 1 year of age.
How long are you contagious with bronchiolitis?
What is included in supportive care for bronchiolitis?
What is the role of antibiotic treatment for bronchitis?
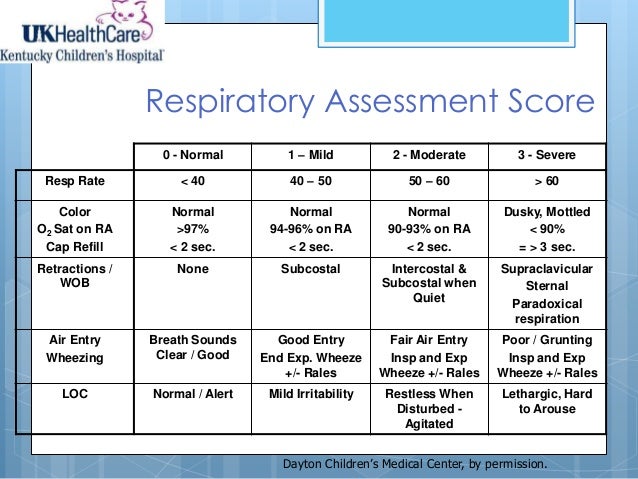
What is the best treatment of bronchitis?
The best treatment for bronchitis includes rest, fluids, a humidifier, honey, lozenges and prescription medications and interventions, if necessary.
How long does bronchiolitis usually last?
Bronchiolitis usually lasts about 1–2 weeks. Sometimes it can take several weeks for symptoms to go away.
How do you treat bronchiolitis in adults?
There's currently no cure for the scarring of bronchiolitis obliterans. Treatment options include: Corticosteroids can help clear the lungs of mucus, reduce inflammation, and open up the airways. You may need oxygen treatments and immunosuppressant medications to regulate your immune system.
Do antibiotics help bronchiolitis?
Because viruses cause bronchiolitis, antibiotics — which are used to treat infections caused by bacteria — aren't effective against it. Bacterial infections such as pneumonia or an ear infection can occur along with bronchiolitis, and your doctor may prescribe an antibiotic for that infection.
Can Covid cause bronchiolitis?
Although in literature there are reported rare cases of acute bronchiolitis caused by SARS‐CoV‐2, 20 , 21 we have found no cases among children admitted to our hospital. This could be due to the reduced spread of the virus in the pediatric population and the use of nonpharmaceutical preventive measures.
What are 3 symptoms of bronchitis?
For either acute bronchitis or chronic bronchitis, signs and symptoms may include:Cough.Production of mucus (sputum), which can be clear, white, yellowish-gray or green in color — rarely, it may be streaked with blood.Fatigue.Shortness of breath.Slight fever and chills.Chest discomfort.
Can bronchiolitis damage lungs?
Bronchiolitis is the result of injury to the small airways in the lung. Bronchiolitis is a general term to describe lung damage. This damage can be caused by many things.
Will an inhaler help bronchiolitis?
In the recent past, children with bronchiolitis were given a trial of inhaled albuterol, which was thought to improve airflow to the lungs. However, recent studies have found that albuterol does not help symptoms and results in uncomfortable side effects.
What antibiotics are prescribed for bronchitis?
Doxycycline and amoxicillin are a couple examples of antibiotics used to treat bronchitis. Macrolide antibiotics such as azithromycin are used for less common cases of bronchitis caused by pertussis (whooping cough). Side effects of antibiotics may include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, or mild skin rash.
Do steroids help bronchiolitis?
Corticosteroids widely used in different routes in the treatment of acute bronchiolitis: Dexamethasone injection used in hospitalized children with acute bronchiolitis showed significantly reduction in the mean respiratory distress duration, mean duration of oxygen therapy and the mean length of hospital stay.
Is Steam Good for bronchiolitis?
Authors' conclusions: Steam inhalation (or cool mist therapy) is commonly used to treat acute bronchiolitis in resource-constrained settings.
Can you catch bronchiolitis from someone else?
Acute bronchitis due to infection is often transmitted through microscopic, airborne droplets that contain a germ and are produced when someone speaks, sneezes, or coughs. It can also be transmitted by shaking hands or other types of physical contact with a person who has the infection.
What are the complications of bronchiolitis?
A common complication of bronchiolitis is an ear infection. Another less common complication is bacterial pneumonia. A small percentage of children may need oxygen therapy or intravenous (IV) fluids, which would be given in the hospital.
What is bronchiolitis in children?
What is bronchiolitis? Bronchiolitis is a viral infection that causes the airways ( bronchioles) in the lungs to become narrow , which makes breathing difficult. It occurs most often in children under age 2 during winter and early spring.
What are the most common viruses that cause bronchiolitis?
The viruses that cause most cases of bronchiolitis are the respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), the rhinovirus and the influenza (flu) virus. These viruses are very contagious and are spread from person to person by touching secretions from the mouth or nose or by respiratory droplets in the air.
What questions do bronchiolitis providers ask?
They will ask you questions like how long your child has been sick, if your child has a fever, and if your child has been around anyone else who has been sick. The provider will examine your child and listen to their lungs.
How long does it take for bronchiolitis to show?
In bronchiolitis, this follows 3 days or so of the first three symptoms. Your child might show more severe signs, including: Making grunting noises. Having trouble sucking and swallowing, which makes feeding difficult on top of having a poor appetite.
How do you know if you have bronchiolitis?
They include: Runny nose. Slight fever (under 101 F). Cough. Rapid or shallow breathing. Wheezing. This might be the first time that your child has wheezing. In bronchiolitis, this follows 3 days or so of the first three symptoms.
Can bronchiolitis be treated with antibiotics?
In most cases, bronchiolitis is not treated. Antibiotics will not help because this is a viral infection. You will be advised to keep your child hydrated as best you can.
What causes bronchiolitis?
Viruses that enter and infect the respiratory tract cause viral bronchiolitis. Viruses are microscopic organisms that can reproduce rapidly and challenge the immune system. The following are common types of viral infections that may cause bronchiolitis:
What age does bronchiolitis occur?
Viral bronchiolitis appears in infants. Most cases of viral bronchiolitis are due to respiratory syncytial virus (RSV). Viral outbreaks occur every winter and affect children under the age of 1 year old.
What is the condition that causes scarring in the bronchioles?
Bronchiolitis obliterans is a rare and dangerous condition seen in adults. This disease causes scarring in the bronchioles. This blocks the air passages creating an airway obstruction that can’t be reversed.
How old is too old to get bronchiolitis?
Viral bronchiolitis affects children up to 2 years old. But it generally occurs in infants 3 to 9 months of age. A few risk factors for viral bronchiolitis in babies and young children are: 1 not being breastfed 2 being born prematurely or born with a heart or lung condition 3 having a depressed immune system 4 being exposed to cigarette smoke 5 being in crowded places where the virus is present, like day care centers
How long does it take for bronchiolitis to show symptoms?
After exposure to certain chemicals, bronchiolitis obliterans symptoms can appear within two weeks to a month. A lung infection can take several months to several years to produce symptoms.
Can bronchiolitis be treated without treatment?
Many cases of viral bronchiolitis are mild and clear up without treatment. For more severe cases in infants, hospitalization may be necessary. A hospital can provide oxygen, a nebulizer, and intravenous fluid treatments. Antibiotic medications don’t work against viruses, but some medications can help open your baby’s airways.
Can bronchiolitis obliterans be treated?
There’s no cure for the scarring of bronchiolitis obliterans. Corticosteroids can help clear the lungs of mucus, reduce inflammation, and open up the airways. You may need oxygen treatments and immunosuppressant medications to regulate your immune system. Breathing exercises and stress reduction can help ease breathing difficulties. Sometimes a lung transplant may be the best option in the most severe cases.
How to help a child with bronchiolitis?
Using a suction bulb to clear your child’s nasal airways is also a simple solution. Your doctor may recommend acetaminophen if they develop a fever. About three percent of children with bronchiolitis will need to be hospitalized. Here the child may be put on humidified oxygen and receive fluids through an IV to prevent dehydration. For the most severe cases, the child may have to have a tube inserted into the windpipe to aid breathing. Most children will be sent home between 2 and 8 days in the hospital.
How to diagnose bronchiolitis?
How Bronchiolitis Is Diagnosed. Doctors will usually start with a basic physical exam when determining if a child has bronchiolitis. Additional tests may be necessary if symptoms are severe. A chest X-ray may be needed to look for signs of pneumonia.
What test is needed to check for infection?
A blood test may be needed to check white blood cell count for signs of infection. A doctor may take a nose swab to test your child’s mucus in an attempt to identify the virus that is causing the infection.
Can bronchiolitis be treated with cold medicine?
There are no vaccines or specific treatments for bronchiolitis. Antibiotics and cold medicine are not effective in treating bronchiolitis. Most cases go away on their own and can be cared for at home. It is key that your child drinks lots of fluids to avoid dehydration.
How long does it take for bronchiolitis to go away?
There is no cure. It usually takes about 2 or 3 weeks for the infection to go away. Antibiotics and cold medicines are not effective in treating it. Most children with bronchiolitis can be treated at home. There, you should watch to see if your child’s symptoms get worse or they have breathing problems.
How many children with bronchiolitis need to go to the hospital?
About 3% of children with bronchiolitis need to go to a hospital. If your child does, the treatments may include:
What is the most common cause of bronchiolitis in children?
Many different viruses can be the culprit, including the flu, but the most common in children is what’s called respiratory syncytial virus, or RSV.
How to get rid of a runny nose?
Use nose drops or sprays to help with a runny nose. Use a bulb syringe, which is an at-home method to remove mucus from the nose. Prop up their head with an extra pillow (but don’t do this if they are under a year old). About 3% of children with bronchiolitis need to go to a hospital.
What to do if your child is having trouble breathing?
If you see signs that your child is having trouble breathing, call their doctor at once or seek medical care if your call isn’t answered. Otherwise, here are some other things to watch for: Call 911 and get emergency medical care if these things happen: Your child has severe trouble breathing.
Is bronchiolitis contagious?
Bronchiolitis is contagious. Viral infections spread through droplets in the air, so you can contract it the same way you get infected with colds or flus. While it’s hard to stop a viral infection, you can lower your child’s chance of getting it if you: Stay away from others who are sick. Practice good handwashing.
Can bronchiolitis be diagnosed with blood tests?
Doctors rarely order X -rays or blood tests for bronchiolitis. But if your child’s symptoms are severe or it’s unclear what’s causing them, they may get these tests:
How to diagnose bronchiolitis?
Exams and tests to diagnose bronchiolitis include: 1 A stethoscope examination of the chest to detect wheezing and crackling sounds. 2 Chest X-ray and blood gases. 3 Samples of nasal fluid may be cultured to determine what virus is present.
What age does bronchiolitis start?
The disease usually affects children under the age of 2, with a peak age of 3 to 6 months, and is a common, sometimes severe illness. Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) is one common cause. Other viruses that can cause bronchiolitis include parainfluenza, influenza, and adenovirus.
What is the medication used in the hospital?
Other medicines used in the hospital may include albuterol (a medication normally used in asthma) or steroids. In extremely ill children, antiviral medications (such as ribavirin) are sometimes used. Antiviral treatment may decrease the severity and duration of the illness.
What is the best treatment for bronchitis?
If you have chronic bronchitis, you may benefit from pulmonary rehabilitation — a breathing exercise program in which a respiratory therapist teaches you how to breathe more easily and increase your ability to exercise.
How long does it take for bronchitis to get better?
Most cases of acute bronchitis get better without treatment, usually within a couple of weeks.
What tests are needed for cough?
If you've ever seen another physician for your cough, let your present doctor know what tests were done, and if possible, bring the reports with you, including results of a chest X-ray, sputum culture and pulmonary function test.
What tests can help you know if you have pneumonia?
In some cases, your doctor may suggest the following tests: Chest X-ray. A chest X-ray can help determine if you have pneumonia or another condition that may explain your cough. This is especially important if you ever were or currently are a smoker. Sputum tests. Sputum is the mucus that you cough up from your lungs.
What to do if you have a cold air cough?
Consider a face mask outside. If cold air aggravates your cough and causes shortness of breath, put on a cold-air face mask before you go outside.
What to do if you have a bacterial infection?
However, if your doctor suspects that you have a bacterial infection, he or she may prescribe an antibiotic. In some circumstances, your doctor may recommend other medications, including: Cough medicine. If your cough keeps you from sleeping, you might try cough suppressants at bedtime. Other medications.
How to avoid lung irritants?
Avoid lung irritants. Don't smoke. Wear a mask when the air is polluted or if you're exposed to irritants, such as paint or household cleaners with strong fumes.
What is bronchitis in the lungs?
What is bronchitis? Bronchitis occurs when the bronchioles (air-carrying tubes in the lungs) are inflamed and make too much mucus. There are two basic types of bronchitis: Chronic bronchitis is defined as cough productive of sputum that persists for three months out of the year for at least two consecutive years.
How long does bronchitis last?
Episodes of acute bronchitis can be related to and made worse by smoking. Acute bronchitis could last for 10 to 14 days, possibly causing symptoms for three weeks. Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center.
How does bronchitis spread?
If bronchitis is caused by a viral or bacterial infection, it is spread the same ways that colds are spread—by germs traveling through the air when someone coughs or sneezes. You can breathe the germs in if you are close enough. You could also touch something that has germs on it, like a door, and then transfer the germs by touching your nose, mouth or eyes. That is why good hand washing practices are important for adults and children.
What is the name of the condition that falls in between the common cold and pneumonia in severity?
Bronchitis . The condition that falls in between the common cold and pneumonia in severity is called bronchitis. Symptoms include a frequent cough that produces mucus, fatigue, fever, and a wheezing sound when breathing. Find out how to treat, or better yet, prevent bronchitis. Appointments 216.444.6503.
How long do you stay contagious after taking antibiotics for bronchitis?
If you have begun taking antibiotics for bronchitis, you usually stop being contagious 24 hours after starting the medication. If you have a viral form of bronchitis, antibiotics will not work. You will be contagious for at least a few days and possibly for as long as a week.
What are the similarities between pneumonia and bronchitis?
Bronchitis can sometimes progress to pneumonia. Despite similarities, the conditions are different. First, bronchitis involves the bronchial tubes, while pneumonia affects the alveoli, or the air sacs in the lungs.
What are the drugs used for COPD?
Anti-inflammatory drugs, such as corticosteroids (also called steroids), to reduce swelling and mucus output.
How to treat bronchitis and bronchiolitis?
Treatment for bronchitis can include: Treatment for bronchiolitis can include: helping your baby sleep with their head slightly raised by putting a pillow under their mattress.
How to help a baby with bronchiolitis?
Treatment for bronchiolitis can include: helping your baby sleep with their head slightly raised by putting a pillow under their mattress.
How long does it take for bronchiolitis to go away?
But if severe bronchiolitis isn’t untreated, it can cause recurrent wheezing and a reduced quality of life. These complications can last into the teenage years. The condition can also be fatal if severe cases aren’t treated. Most children recover at home within three to five days.
What are the risk factors for bronchitis?
Risk factors specific to bronchitis include: gastric reflux, which can irritate your throat. regular exposure to irritants. low immune resistance, especially after a virus or primary infection. High risk factors for developing bronchiolitis include: babies born prematurely. babies with heart, lung, or immune conditions.
What is the difference between bronchitis and bronchitis?
What’s the difference between bronchiolitis and bronchitis. Bronchiolitis and bronchitis are both infections of the lungs. The names may sound similar, but they are two distinct conditions. Bronchitis can affect people of all ages, though it’s most common in older children and adults. It causes inflammation and swelling in ...
What causes bronchitis?
Acute bronchitis is often caused by viruses, especially the flu and the common cold. The most common cause of chronic bronchitis is smoking cigarettes or being around lung irritants. Bronchiolitis is typically caused by a viral infection.
How do you know if you have bronchiolitis?
Symptoms of bronchiolitis include: dry, raspy cough. wheezing. difficulty feeding, especially in infants. slight fever. runny or stuffy nose. If your infant, toddler, or young child displays any of the following symptoms, call your pediatrician for next steps: They are having difficulty breathing .

Diagnosis
Clinical Trials
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
Preparing For Your Appointment