Medication
- Fractures of the affected bone
- Stunted growth in children (if the infection has involved the growth plate)
- Gangrene infection in the affected area
Procedures
Tooth abscess
- Diagnosis. Tap on your teeth. A tooth that has an abscess at its root is generally sensitive to touch or pressure.
- Treatment. The goal of treatment is to get rid of the infection. ...
- Lifestyle and home remedies. Rinse your mouth with warm salt water. ...
- Preparing for your appointment. You're likely to start by seeing your dentist. ...
Self-care
Surgery can incorporate:
- Draining any pus or fluid that has developed in response to the infection.
- Removing an infected bone or any surrounding tissue with signs of infection.
- Restoring blood flow to the damaged bone by placing a piece of bone tissue or skin from another part of the body.
Nutrition
Description
- Eat Vitamin A, E, and C rich food. They will enhance the immunity and prevent the infections.
- Eat probiotics. They contain good bacteria and provide strength to the intestines.
- Eat immunity booster Herbs like Garlic, Goldenseal, Ginseng Siberian, Echinacea and Astragulus. These Herbs will increase the immunity and ability to fight with infections.
What is the best antibiotic for a bone infection?
What is the best treatment for an infected tooth?
How to cure bone infection?
What is the cure for a bone infection?
See more

Can bone infection be treated?
Most cases of osteomyelitis are treatable. Chronic infections of the bone, however, may take longer to treat and heal, especially if they require surgery. Treatment should be aggressive because an amputation can become necessary sometimes. The outlook for this condition is good if the infection is treated early.
How long does bone infection take to heal?
The infection may clear up faster if you start treatment within three to five days of first noticing symptoms. Treatments include: Antibiotics: Antibiotics kill infection-causing bacteria. You may need antibiotics for four to eight weeks, starting with intravenous (IV) antibiotics in the hospital for a week or two.
What is the most common cause of bone infection?
Bone infection is most often caused by bacteria. But it can also be caused by fungi or other germs. When a person has osteomyelitis: Bacteria or other germs may spread to a bone from infected skin, muscles, or tendons next to the bone.
Can bone infection be cured without surgery?
Non-Surgical Treatment for Osteomyelitis Non-surgical treatment of osteomyelitis requires a multidisciplinary team approach including primary care, infectious disease specialist care, nutritionist care and wound care. These wounds will require antibiotic therapy for a duration of six to eight weeks.
How serious is a bone infection?
An infection in your bone can impede blood circulation within the bone, leading to bone death. Areas where bone has died need to be surgically removed for antibiotics to be effective. Septic arthritis. Sometimes, infection within bones can spread into a nearby joint.
What is the strongest antibiotic for bone infection?
The classic antibiotic combination for bone infections caused by Staphylococcus aureus and P. aeruginosa is levofloxacin plus rifampicin. It is difficult to assess how long it will take for an infection to clear following the treatment of bone infection.
How fast does a bone infection spread?
Acute osteomyelitis develops rapidly over a period of seven to 10 days. The symptoms for acute and chronic osteomyelitis are very similar and include: Fever, irritability, fatigue. Nausea.
How is a bone infection diagnosed?
A bone biopsy can reveal what type of germ has infected your bone. Knowing the type of germ allows your doctor to choose an antibiotic that works particularly well for that type of infection. An open biopsy requires anesthesia and surgery to access the bone.
How painful is a bone infection?
This pain is usually described as dull or aching and may worsen during activity. The person may also experience fever and night sweats. In addition to pain, some cancerous bone lesions can cause stiffness, swelling, or tenderness in the affected area. The pain may come and go and may be worse or better at night.
What happens if a bone infection goes untreated?
If the infection is left untreated, a ball of pus (abscess) may develop in the bone and surrounding tissue. In time, this may burst on to the skin and leave a track (sinus) between the infected bone and the surface of the skin. Blood infection (sepsis) which can cause serious illness.
How long do you take IV antibiotics for osteomyelitis?
Traditionally, antibiotic treatment of osteomyelitis consists of a 4- to 6-week course. Animal studies and observations show that bone revascularization following debridement takes about 4 weeks. However, if all infected bone is removed, as in forefoot osteomyelitis, antibiotic therapy can be shortened to 10 days.
Is osteomyelitis an emergency?
Osteomyelitis can present to the emergency department as an acute, subacute, or chronic orthopedic concern.
Who Is Affected by Osteomyelitis?
Osteomyelitis can affect both adults and children. The bacteria or fungus that can cause osteomyelitis, however, differs among age groups. In adult...
What Causes Osteomyelitis?
It can be caused by a variety of microbial agents (most common in staphylococcus aureus) and situations, including: 1. An open injury to the bone,...
What Are The Symptoms of Osteomyelitis?
The symptoms of osteomyelitis can include: 1. Pain and/or tenderness in the infected area. 2. Swelling, redness and warmth in the infected area. 3....
Why is it important to treat osteomyelitis?
The objective of treating osteomyelitis is to eliminate the infection and prevent the development of chronic infection. Chronic osteomyelitis can lead to permanent deformity, possible fracture, and chronic problems, so it is important to treat the disease as soon as possible.
What is the disease that can cause bone tissue death?
Osteomyelitis. Osteomyelitis is an infection of the bone that can affect both adults and children. If left untreated, it can lead to bone tissue death over time. Appointments 216.444.2606. Appointments & Locations. Contact Us. Overview. Symptoms and Causes. Diagnosis and Tests.
What is osteomyelitis infection?
What is osteomyelitis? Osteomyelitis is a bacterial, or fungal, infection of the bone. Osteomyelitis affects about 2 out of every 10,000 people. If left untreated, the infection can become chronic and cause a loss of blood supply to the affected bone.
How do you know if you have osteomyelitis?
The symptoms of osteomyelitis can include: Pain and/or tenderness in the infected area. Swelling, redness and warmth in the infected area. Fever. Nausea, secondarily from being ill with infection. General discomfort, uneasiness, or ill feeling. Drainage of pus (thick yellow fluid) through the skin.
How do antibiotics help the body?
Antibiotics help the body get rid of bacteria in the bloodstream that may otherwise re-infect the bone. The dosage and type of antibiotic prescribed depends on the type of bacteria present and the extent of infection.
Why are antibiotics ineffective?
The reason for this is that antibiotics are ineffective at reaching pockets of infected fluid as they have no blood supply. Antibiotic medications: Prescribing antibiotics is the first step in treating osteomyelitis. Antibiotics help the body get rid of bacteria in the bloodstream that may otherwise re-infect the bone.
What causes a bone to break out?
It can be caused by a variety of microbial agents (most common in staphylococcus aureus) and situations, including: An open injury to the bone, such as an open fracture with the bone ends coming out through the skin.
What is the treatment for bone infection?
Bone infections are treated with antibiotics . The specific antibiotic you’ll get will depend on which bacteria is causing the infection. Antibiotics are typically given intravenously (IV). In this case, you need a temporary IV catheter placed in the arm to receive the antibiotics.
What is bone infection?
What is a bone infection? A bone infection, also called osteomyelitis, occurs when bacteria invade and infect the bones. Cuts, wounds, and traumatic injuries can lead to a bone infection. Bacteria enter the body through the broken skin of the wound and infect nearby bones. The infection can also spread through the bloodstream and infect bones ...
What happens if you have an untreated bone infection?
Other complications of untreated bone infections include bone fracture, deformity, and bone death. In bone death, also known as osteonecrosis, the infected bone needs to be removed. Untreated bone infection in children can result in stunted growth.
How to prevent bone infection in diabetics?
For people with diabetes, the best ways to prevent bone infections are to wear comfortable shoes and check your feet often for ulcers .
What is the most severe form of infection that can cause death?
Sepsis is when an infection is so bad that the body becomes overwhelmed and major organs start to fail. In the most severe cases, this can result in death. —Dr. Grand. Bone infections can occur in children without obvious wounds, broken bones, diabetes, or other risk factors that are common in adults.
How long does it take for a bone to hurt when you stand still?
The bone may hurt when you move or even when standing still. If you have a new infection, the symptoms may worsen over a few days. In chronic infections, symptoms may develop over weeks or months and worsen as the infection progresses.
How to tell if a child has a bone infection?
Other symptoms in children include fever and redness and swelling at the site of the affected bone or joint. Infants and toddlers may also be irritable and lethargic. Early treatment is very successful in curing bone infections in children.
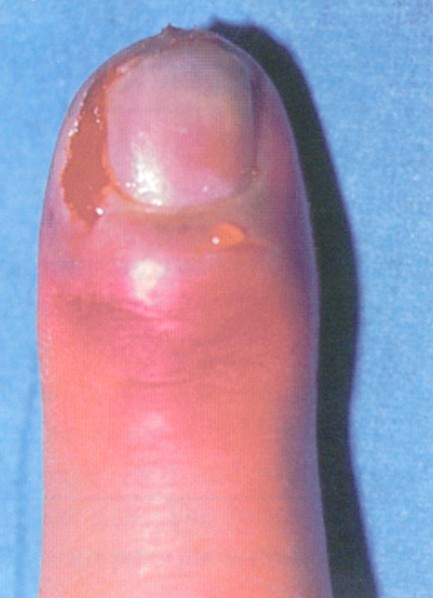
What are the symptoms of bone infection?
Bone infections can become a severe condition if not treated properly. If you have any of the following signs, you should reach out to your doctor right away: 1 Chronic infections of bone 2 Infections around or involving orthopaedic implants 3 Infected fractures 4 Infections of original (native) and prosthetic joints
Can bone infections be severe?
Bone infections can become a severe condition if not treated properly. If you have any of the following signs, you should reach out to your doctor right away: Infections around or involving orthopaedic implants. Infections of original (native) and prosthetic joints.
Why do I get bone infections?
Causes. Bone infection is most often caused by bacteria. But it can also be caused by fungi or other germs. When a person has osteomyelitis: Bacteria or other germs may spread to a bone from infected skin, muscles, or tendons next to the bone. This may occur under a skin sore.
How long do you take antibiotics for bone marrow infection?
Antibiotics are taken for at least 4 to 6 weeks, often at home through an IV (intravenously, meaning through a vein). Surgery may be needed to remove dead bone tissue if the above methods fail:
How do you know if you have osteomyelitis?
Main symptoms include: Bone pain. Excessive sweating. Fever and chills. General discomfort, uneasiness, or ill feeling (malaise) Local swelling, redness, and warmth. Open wound that may show pus.
Is osteomyelitis a good outcome?
Outlook (Prognosis) With treatment, the outcome for acute osteomyelitis is often good. The outlook is worse for those with long-term (chronic) osteomyelitis. Symptoms may come and go for years, even with surgery. Amputation may be needed, especially in people with diabetes or poor blood circulation.
Is an amputation necessary for diabetes?
Amputation may be needed, especially in people with diabetes or poor blood circulation. The outlook for people with an infection of a prosthesis depends partly on: The person's health. The type of infection.
Can you remove dead bone tissue?
Surgery may be needed to remove dead bone tissue if the above methods fail: If there are metal plates near the infection, they may need to be removed. The open space left by the removed bone tissue may be filled with bone graft or packing material. This promotes resolution of the infection.
Can you get infection after joint replacement?
Infection that occurs after joint replacement may require surgery. This is done to remove the replaced joint and infected tissue in the area. A new prosthesis may be implanted in the same operation. More often, doctors wait until the antibiotic course is finished and the infection has gone away.
What is the procedure to treat a bone infection?
I. Surgical procedure: A) Mild infection can be treated with debridement, a surgical procedure that removes all of the infected bone and tissue. B) Locally administered antibiotics: Because the bone infection damages the blood supply to the area, oral and IV antibiotics often can’t reach the infected area.
Why is bone infection so hard to treat?
Bone infection can be difficult to treat because bacteria are constantly changing to fight the new antibiotics that are used to kill them. Some bacteria have been extremely difficult to kill, including methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus species and vancomycin-resistant enterococci.
How long can you live with bone infection?
Bone infection should be treated to try to save the limb and avoid the following possible complications: Systemic infection: People can live with bone infection for years as long as the bacteria do not enter the bloodstream and cause the rest of the body to become sick. Signs of systemic infection include fever, chills, rapid heartbeat, ...
What is the cause of bone infection?
Bone infection is most often caused by Staphylococcus aureus, a type of bacteria. Bone infection occurs when the bacteria invade bone, either through the bloodstream or by contact with the outside environment—usually from an open fracture or surgery.
What is the term for a skin cancer that is caused by bacteria in the joints?
This type of skin cancer is called a Marjolin ulcer.
What causes swelling and redness in the limb?
Bone infection often causes redness, swelling and pain in the affected limb. Sometimes, fluid exits through the skin; this is called a draining sinus tract. Occasionally the infection weakens the bone so much that the bone breaks.
How to treat orthopedic infection?
The first step to treating an orthopedic infection is to evaluate, and if necessary, optimize the patient’s immune system. If a patient is diagnosed with immune system deficiencies, the patient is referred to an immunologist for treatment to try to boost the immune system.
What is the term for a chronic infection of the bone and bone marrow?
Antibiotics for treating chronic bone infection in adults. Osteomyelitis is an inflammation of the bone and bone marrow caused by pus-forming bacteria, mycobacteria or fungi. All bone infection that is long-standing is called chronic osteomyelitis.
How long does osteomyelitis last?
Despite advances in both antibiotic and surgical treatment, the long-term recurrence rate remains around 20%.
Can you have surgical debridement before antibiotics?
All trials mentioned surgical debridement before starting on antibiotic therapy as part of treatment, but it was unclear in four trials whether all participants underwent surgical debridement.
Does oral antibiotics affect remission?
Limited and low quality evidence suggests that the route of antibiotic administration (oral versus parenteral) does not affect the rate of disease remission if the bacteria are susceptible to the antibiotic used. However, this and the lack of statistically significant differences in adverse effects need confirmation.
Does antibiotic treatment affect remission?
This evidence suggests that the way antibiotics are given does not impact on the disease remission rate if the bacteria causing the infection are sensitive to the antibiotic used. However, confirmation is needed. There was either no or insufficient evidence on which to base judgements about the optimum length of antibiotic treatment or ...
Why is it important to treat osteomyelitis early?
In cases of acute osteomyelitis, early treatment prevents the condition from becoming a chronic problem that requires ongoing treatment . Besides the pain and inconvenience of repeated infections, getting osteomyelitis under control early provides the best chance for recovery.
What is the disease of the bone?
Osteomyelitis. By Joanne Barker. Medically Reviewed by Jennifer Robinson, MD on May 11, 2019. Osteomyelitis is an infection of the bone, a rare but serious condition. Bones can become infected in a number of ways: Infection in one part of the body may spread through the bloodstream into the bone, or an open fracture or surgery may expose ...
How long does it take for osteomyelitis to develop?
Symptoms of Osteomyelitis. Acute osteomyelitis develops rapidly over a period of seven to 10 days. The symptoms for acute and chronic osteomyelitis are very similar and include: Osteomyelitis in the vertebrae makes itself known through severe back pain, especially at night.
What is the cause of osteomyelitis?
In most cases, a bacteria called Staphylococcus aureus, a type of staph bacteria, causes osteomyelitis. Certain chronic conditions like diabetes may increase your risk for osteomyelitis.
How to prevent osteomyelitis?
Preventing Osteomyelitis. The best way to prevent osteomyelitis is to keep things clean. If you or your child has a cut, especially a deep cut, wash it completely.
How many people get osteomyelitis?
Only 2 out of every 10,000 people get osteomyelitis. The condition affects children and adults, although in different ways. Certain conditions and behaviors that weaken the immune system increase a person's risk for osteomyelitis, including: Diabetes (most cases of osteomyelitis stem from diabetes) Sickle cell disease.
Can osteomyelitis be chronic?
In adults, osteomyelitis can be either acute or chronic. People with diabetes, HIV, or peripheral vascular disease are more prone to chronic osteomyelitis, which persists or recurs, despite treatment. Whether chronic or acute, osteomyelitis often affects an adult's pelvis or vertebrae of the spine.
Drugs used to treat Bone infection
The following list of medications are in some way related to, or used in the treatment of this condition.
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.

Causes
Symptoms
Exams and Tests
Treatment
Specialist to consult
Outlook
- Bone infection is most often caused by bacteria. But it can also be caused by fungi or other germs. When a person has osteomyelitis: 1. Bacteria or other germs may spread to a bone from infected skin, muscles, or tendons next to the bone. This may occur under a skin sore. 2. The infection can start in another part of the body and spread to the bone through the blood. 3. The i…
When to Contact A Medical Professional
- Symptoms of osteomyelitis are not specific and vary with age. Main symptoms include: 1. Bone pain 2. Excessive sweating 3. Fever and chills 4. General discomfort, uneasiness, or ill feeling (malaise) 5. Local swelling, redness, and warmth 6. Open wound that may show pus 7. Pain at the site of infection