
Surgical Care. As with medical care, the need for surgical intervention depends on the cause of biliary obstruction. Cholecystectomy is the recommended treatment in cases of symptomatic cholelithiasis because these patients have an increased risk of developing complications.
What are the symptoms of a Blocked bile duct?
If a bile duct obstruction is left untreated, it can result in:
- Infection
- Liver disease
- Jaundice
- Diabetes
- Pancreatitis
- Vitamin deficiency
- Gastrointestinal problems
- Gallbladder swelling or cholecystitis
- Biliary cirrhosis or cholangitis
What is the treatment for Blocked bile duct?
- Medication to dissolve existing gallstones or prevent more from forming
- Low fat diet to reduce the amount of bile needed to thoroughly digest food
- External radiation or chemotherapy
- Antibiotics and pain management medication or therapy
- Biliary surgery to remove tumors, gallstones, or other blockages
What would cause a blockage in your cecum?
Possible causes and risk factors may include:
- air travel in low cabin pressure
- colon muscle weakness (atonia)
- enlargement of the colon
- Hirschsprung’s disease (where the large intestine becomes inflamed and leads to constipation and obstruction)
- infections
- overexertion
- pelvic tumors
- pregnancy (especially in the third trimester)
- previous abdominal surgeries that caused adhesions
- violent coughing fits
What causes bile obstruction?
The following are some of the most common causes of biliary obstruction:
- gallstones, which are the most common cause
- inflammation of the bile ducts
- trauma
- a biliary stricture, which is an abnormal narrowing of the duct
- cysts
- parasites
- enlarged lymph nodes
- pancreatitis
- an injury related to gallbladder or liver surgery
- tumors that have reached the liver, gallbladder, pancreas, or bile ducts
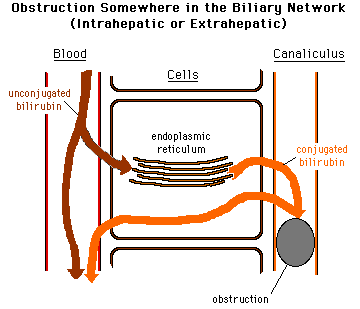
What is the most common cause of biliary obstruction?
The most common etiology of biliary obstruction is gallstones causing common bile duct obstruction, which manifests as pain, nausea/vomiting, and jaundice.
How serious is a bile duct obstruction?
Potential complications of a bile duct obstruction are serious and can be life threatening. This includes infection, which can lead to sepsis, and dangerously high levels of bilirubin in the blood. Long-term bile duct blockages can lead to chronic liver disease, such as biliary cirrhosis.
How long can you live with biliary obstruction?
Death from obstructive jaundice in the first few weeks of its course is quite rare and is only occasionally observed. After a period varying from four to six months, however, patients suffering from occlusion of the common bile duct usually deteriorate rapidly and die.
What causes a blockage of the biliary duct?
In most cases cholangitis is caused by a blocked duct somewhere in your bile duct system. The blockage is most commonly caused by gallstones or sludge impacting the bile ducts. Autoimmune disease such as primary sclerosing cholangitis may affect the system.
Is a blocked bile duct an emergency?
If something is blocking the bile duct, bile can back up into the liver. This can cause jaundice, a condition in which the skin and white of the eyes become yellow. The bile duct might become infected and require emergency surgery if the stone or blockage is not removed.
Can a blocked bile duct be fatal?
Complications of a biliary duct obstruction Without treatment, biliary duct obstructions can be life threatening. Possible complications that can arise without treatment include: infections. sepsis.
How is biliary obstruction diagnosed?
The following tests may be used to investigate a possible blocked bile duct:Abdominal ultrasound.Abdominal CT scan.Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP)Percutaneous transhepatic cholangiogram (PTCA)Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography (MRCP)Endoscopic ultrasound (EUS)
What happens if bile does not drain?
A biliary drain is used when too much bile collects in the bile ducts. If something is blocking the bile duct, bile can back up into the liver. This can cause jaundice, a condition in which the skin and white of the eyes become yellow.
Will a CT scan show blocked bile ducts?
CT scans can show the organs near the bile duct (especially the liver), as well as lymph nodes and distant organs where cancer might have spread to. A type of CT known as CT angiography can be used to look at the blood vessels around the bile ducts.
What are the common signs and symptoms of biliary disease?
Symptoms of possible biliary diseaseJaundice (yellowing of the skin and whites of the eyes)Abdominal pain, especially in the upper right side of the abdomen under the rib cage.Nausea or vomiting.Loss of appetite, which may result in weight loss.Fatigue.Fever or chills.Itching.Light brown urine.More items...
What is a biliary obstruction?
A biliary obstruction is a blockage of the bile ducts. The bile ducts carry bile from the liver and gallbladder through the pancreas to the duodenum, which is a part of the small intestine. Bile is a dark-green or yellowish-brown fluid secreted by the liver to digest fats. After you eat, the gallbladder releases bile to help in digestion ...
What is the treatment for gallstones?
Some of the treatment options include a cholecystectomy and an ERCP. A cholecystectomy is the removal of the gallbladder if there are gallstones. An ERCP may be sufficient to remove small stones from the common bile duct or to place a stent inside the duct to restore bile flow.
What is a biliary radionuclide scan?
Biliary radionuclide scan (HIDA scan) A hepatobiliary iminodiacetic acid scan, or HIDA scan, is also referred to as a biliary radionuclide scan. It uses radioactive material to provide valuable information about the gallbladder and any possible obstructions.
What causes gallstones in the liver?
inflammation of the bile ducts. trauma. a biliary stricture, which is an abnormal narrowing of the duct. cysts. enlarged lymph nodes. pancreatitis . an injury related to gallbladder or liver surgery. tumors that have reached the liver, gallbladder, pancreas, or bile ducts.
Which ducts collect bile?
Intrahepatic ducts: Intrahepatic ducts are a system of smaller tubes within the liver that collect and transport bile to the extrahepatic ducts. Extrahepatic ducts: The extrahepatic ducts begin as two parts, one on the right of the liver and the other on the left.
What is a blood test for cholecystitis?
A blood test includes a complete blood count (CBC) and liver function test. Blood tests can usually rule out certain conditions, such as: cholecystitis, which is an inflammation of the gallbladder. cholangitis, which is an inflammation of the common bile duct.
What happens to the gallbladder after eating?
After you eat, the gallbladder releases bile to help in digestion and fat absorption. Bile also helps clear the liver of waste products. Obstruction of any of these bile ducts is referred to as a biliary obstruction. Many of the conditions related to biliary obstructions can be treated successfully.
What is the best imaging for biliary obstruction?
If blood tests suggest a biliary obstruction, the doctor may recommend one of the following imaging methods to confirm the diagnosis: abdominal ultrasound. abdominal computed tomography (CT) scan.
What is bile duct obstruction?
A bile duct obstruction, also known as biliary obstruction, is when one of the ducts that carry bile from the liver to the intestine via the gallbladder becomes blocked. If left untreated, this blockage can lead to serious complications, including severe infection. This article explores some of the leading causes of bile duct obstruction, ...
What is it called when bile ducts are blocked?
When one or more of the ducts that transport bile become blocked, it is known as a bile duct obstruction. It is also commonly referred to as biliary obstruction. A bile duct obstruction can lead to bile accumulating in the liver and a buildup of bilirubin in the blood.
What happens if you block a gallbladder?
If the blockage occurs between the gallbladder and the common bile duct, a person is at risk of cholecystitis. This is an inflammation of the gallbladder that can lead to a severe infection or the rupturing of the gallbladder. Both of these complications of cholecystitis require emergency surgery to remove the gallbladder.
What is the treatment for choledochal cysts?
They will then treat the cancer with a mix of chemotherapy and radiotherapy, depending on its type, size, and location. If someone has choledochal cysts, a doctor will usually recommend a surgical procedure to correct the enlarged areas of bile ducts.
What happens if you have a blocked drainpipe?
If the “drainpipe” at the bottom of the liver, or the common bile duct, remains blocked, a buildup of bilirubin in the bloodstream can lead to jaundice. This blockage can also lead to bacteria backing up into the liver, which can cause a severe infection known as ascending cholangitis.
Where does bile go when it is needed to digest food?
Bile passes through the bile ducts from the liver to the gallbladder, which stores it. It travels to the small intestine when it is needed to help digest food. This network of ducts is part of the biliary system. When one or more of the ducts that transport bile become blocked, it is known as a bile duct obstruction.
What is biliary obstruction?
Also known as bile duct obstruction, biliary obstruction is a blockage in one of the ducts that transport bile from the liver to the small intestine through the gallbladder. Bile is a liquid produced by the liver that contains bile salts, cholesterol, and waste products like bilirubin ...
What are the complications of biliary duct obstruction?
What Are the Complications Related to Biliary Duct Obstruction? When left untreated, biliary duct obstruction can lead to possible complications such as liver disease like biliary cirrhosis, infections, sepsis, the build-up of bilirubin in the bloodstream, and inflammation of the gallbladder.
How to remove gallstones from bile duct?
Gallstones may be removed from the bile duct using endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP). The doctor may even recommend a cholecystectomy to remove the gallbladder to prevent recurring blockages in the future. If the obstruction is formed because of cancer, surgical procedures may be suggested to stretch and drain the ducts.
How do you know if you have a bile duct obstruction?
Common symptoms experienced by patients include: Jaundice (yellowing of the skin or eyes) due to the build-up of bilirubin in the bloodstream. Itching.
How to prevent gallstones?
Add more fiber to your diet, and lower your intake of saturated fats, cholesterol, and sugar, to prevent gallstones. With the help of exercise and a nutritious diet, work towards achieving a healthy weight. To learn more about biliary obstructions and its preventive measures, contact us. Contact us Call Now.
Where does bile accumulate?
From the liver, the bile passes via a network of bile ducts (also referred to as biliary tree) and accumulates in the gallbladder.
How to treat biliary obstruction?
Here are some of the options you may have for managing your biliary obstruction depending on the underlying cause: Medication to dissolve existing gallstones or prevent more from forming. Low fat diet to reduce the amount of bile needed to thoroughly digest food. External radiation or chemotherapy.
What to do if biliary obstruction is detected?
If your biliary doctor suspects you have a biliary obstruction after performing the appropriate tests, the next step is to treat the cause for the blockage or narrowing of the duct so that you can regain your health as soon as possible.
What is the best test to check for biliary obstruction?
Often used to check for developing pancreatic disease, this test can also look for biliary obstructions. HIDA scan.
Why do you bypass the bile duct?
Bile duct bypass to avoid the blockage and redirect the flow of bile into the small intestine. Full gallbladder removal if gallstones are the prevailing cause and other treatment options have failed to break them up or prevent them from blocking the bile ducts.
How to detect obstructions in the biliary system?
Using x-rays, your biliary surgeon can detect obstructions from the cross-sectional images of your abdomen. This test will provide visuals of your digestive system and the surrounding organs and tissues. Using both x-rays and an endoscope to view your bile ducts internally, this test allows your doctor detects blockages.
What is the biliary tree?
By Dr. Mark Fraiman on April 27, 2017 in Bile Duct Cancer, Bile Duct Disease. The biliary tree is a key component in your digestive system. Delivering bile that is produced in your liver and stored in your gallbladder until it is needed, the bile ducts are the bile’s pathway to the small intestine ...
Why is my bile duct narrowing?
In addition, if you have ever had bile duct inflammation or irritation, the chances of your bile ducts narrowing and becoming restricted increase. Liver Cancer. Some liver cancers that metastasize into the biliary system can cause bile duct obstructions.
What is biliary obstruction?
Biliary obstruction commonly refers to blockage of the bile duct system leading to impaired bile flow from the liver into the intestinal tract. Bile is a substance that contains bile salts, bilirubin, and cholesterol and is continuously synthesized in the liver hepatocytes.
What is the most common cause of biliary obstruction?
Biliary obstruction is common and affects a large portion of the population around the world with significant morbidity and mortality. Gallstones are the most prevalent cause of biliary obstruction; they commonly manifest by dilatating the common bile duct and jaundice.
What hormone controls the release of stored bile from the gallbladder?
The flow of bile into the duodenum is regulated by the release of the hormone Cholecystokinin (CCK) from the duodenum, which controls the release of stored bile from the gallbladder and the relaxation of the sphincter of Oddi. Biliary obstruction is generally referred to as blockage of the extrahepatic biliary system.
What is the term for a disruption of the bile flow due to impairment of the intrahepatic
Disruption in the bile flow due to impairment of the intrahepatic biliary system is generally referred to as cholestasis. Cholestasis can present as abnormalities in serum hepatic enzymes such as elevated bilirubin, alkaline phosphatase levels and can lead to jaundice and pruritis.
Where does bile go in the body?
Fifty percent of the bile flows into the cystic duct and is then stored in the gallbladder, with the rest of the bile flowing through the common bile duct and converging and flowing through the main pancreatic duct in the head of the pancreas to empty into the duodenum through the sphincter of Oddi. Biliary obstruction refers to obstruction in the ...
Where is bile transported?
Bile is then transported via the bile ducts into the second portion of the duodenum to assist with the metabolism of fats. [1]
Which duct joins the gallbladder?
The common hepatic duct then joins the cystic duct arising from the gallbladder to form the common bile duct. The common bile duct then joins the pancreatic duct through its course within the head of the pancreas before opening into the duodenum through the major papilla or ampulla.
