
What is the best diet for bile reflux?
What to Eat to Absorb Bile in Stomach
- All About Bile. Bile acids are derivatives of cholesterol and about 500 milligrams are used every day to make bile in your liver, according to Colorado State University.
- Soluble Fiber and Bile. ...
- Sources of Soluble Fiber. ...
- Avoid Fatty Foods. ...
- Bile Reflux Diet Ideas. ...
What are the symptoms of too much bile?
- GERD. This condition, which causes irritation and inflammation of the esophagus, is most often due to excess acid, but bile may be mixed with the acid. ...
- Barrett's esophagus. This serious condition can occur when long-term exposure to stomach acid, or to acid and bile, damages tissue in the lower esophagus. ...
- Esophageal cancer. ...
What medications reduce bile production?
Some common bile acid binders include:
- cholestyramine (Questran)
- colestipol (Colestid)
- colesevelam (Welchol)
What causes too much bile in stool?
- Stop smoking.
- Eat smaller meals.
- Stay upright after eating.
- Limit fatty foods.
- Avoid problem foods and beverages.
- Limit or avoid alcohol.
- Lose excess weight.
- Raise your bed.
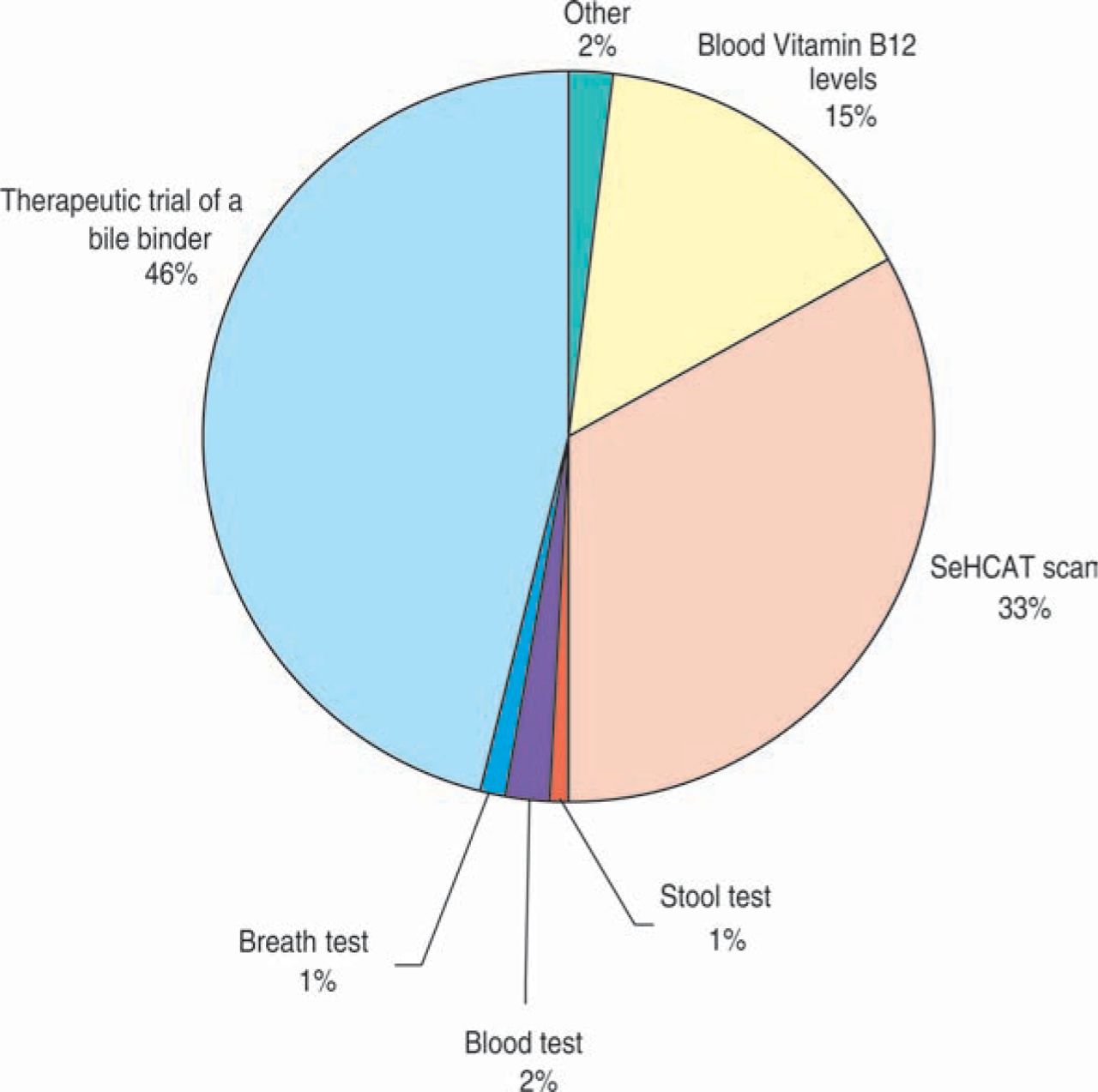
How serious is bile acid malabsorption?
Bile salt malabsorption may also cause cramp-like pains in your abdomen. These can be very severe. You may also suffer from very smelly wind and very erratic bowel movements. Very occasionally, if too much bile salt is lost, sufferers start to lose weight.
What is the best medicine for bile acid malabsorption?
Medicines that bind to bile acids in your gut (bowel) are usually very effective. Examples of bile acid binder medicines are colestyramine, colestipol or colesevelam. Colestyramine is the medicine most often used and is usually very effective.
How is bile acid malabsorption treated?
Medication. Bile acid binders are prescribed to people who are affected by the malabsorption of bile acids. They work by binding to bile acids in the small intestine, preventing them from irritating the lining of the gut as they move through the gastrointestinal tract.
What happens if bile acid malabsorption is left untreated?
Untreated bile salt malabsorption can increase your risk of forming gallstones and kidney stones. Vitamin B12 is another vital nutrient which is absorbed into the body at the end of the small bowel.
What home remedy gets rid of bile?
Lifestyle and home remediesStop smoking. Smoking increases the production of stomach acid and dries up saliva, which helps protect the esophagus.Eat smaller meals. ... Stay upright after eating. ... Limit fatty foods. ... Avoid problem foods and beverages. ... Limit or avoid alcohol. ... Lose excess weight. ... Raise your bed.More items...•
Is there a pill form of cholestyramine?
Is there a pill form of cholestyramine (Prevalite)? Cholestyramine (Prevalite) is currently only available as a powder form. There are other bile acid type medications, such as colestipol (Colestid) and colesevelam (Welchol), that are available in a pill form.
Can bile acid malabsorption go away by itself?
Some patients with Type II bile acid malabsorption can naturally improve and no longer require medications. However, many patients may need to remain on medications for long term.
What does malabsorption poop look like?
When there is inadequate absorption of fats in the digestive tract, stool contains excess fat and is light-colored, soft, bulky, greasy, and unusually foul-smelling (such stool is called steatorrhea). The stool may float or stick to the side of the toilet bowl and may be difficult to flush away.
What foods increase bile acids?
Bitter foods are great at stimulating bile production. You can choose from all dark green leafy vegetables, as well as beetroot, artichokes and pickles. Drinks such as roasted dandelion root tea, lemon tea, celery juice and coffee all stimulate bile production.
How common is bile acid malabsorption?
The resulting condition is bile acid malabsorption (BAM). It is also sometimes called bile acid diarrhea (BAD). BAM can cause significant gut problems. Experts report that roughly 1 out of 100 people may have BAM.
Does omeprazole help bile reflux?
In summary, omeprazole significantly reduces reflux of both acid and duodenal contents into the oesophagus. In addition, the delivery of duodenal contents to the upper stomach is significantly reduced, although not to such a dramatic extent as in the oesophagus.
How do you know if you have bile acid malabsorption?
Excess bile acids entering the colon can cause the classic signs and symptoms of bile acid malabsorption (BAM), including watery stool, urgency and fecal incontinence. Although BAM has been associated with diarrhea for nearly 50 years, it remains an underrecognized and underdiagnosed cause of chronic diarrhea.
Expert Q&A
Include your email address to get a message when this question is answered.
About This Article
This article was medically reviewed by Erik Kramer, DO, MPH. Dr. Erik Kramer is a Primary Care Physician at the University of Colorado, specializing in internal medicine, diabetes, and weight management. He received his Doctorate in Osteopathic Medicine (D.O.) from the Touro University Nevada College of Osteopathic Medicine in 2012. Dr.
What is the treatment for bile acid malabsorption?
The main treatment options available for bile acid malabsorption are medication and diet changes. Because type 1 and type 3 are caused by underlying health conditions, it may be necessary to treat them first, which may improve the symptoms associated with bile acid malabsorption.
How much fat should I eat a day for bile acid malabsorption?
Individuals diagnosed with bile acid malabsorption may be referred to a dietician to help control their symptoms. In many cases, it is advised to eat less than 40g of fat per day and make healthy swaps, such as whole milk for skimmed or semi-skimmed varieties.
What does it mean when bile acids are not retained?
If the results show fewer radiolabeled bile acids, then it indicates that bile acids are not being retained normally, which is a sign of bile acid malabsorption.
What causes bile acid diarrhoea?
Research shows that the idiopathic form (type 2) of bile acid diarrhoea may be caused by low serum fibroblast growth factor 19 (FGF19) , which impairs the normal bile acid cycle. There is also evidence of increased weight being associated with bile acid malabsorption and low FGF19 levels.
What is the condition called when the large intestine releases more water?
This condition is also known as bile acid diarrhoea (BAD), and bile salt malabsorption. In bile acid malabsorption, too much bile acid enters the colon, which causes the large intestine to release more water. The increase in fluids results in a faster transit time of waste through the gut and chronic watery diarrhoea.
How do bile acid binders work?
They work by binding to bile acids in the small intestine, preventing them from irritating the lining of the gut as they move through the gastrointestinal tract.
What are bile acids made of?
Bile acids are made from cholesterol, and they are vital for the absorption and transportation of fats, nutrients, and vitamins. Primary bile acids, like cholic acid and chenodeoxycholic acid, participate in a few critical processes: 1 the breakdown and absorption of fats and fat-soluble vitamins 2 the removal of waste products from the body that are secreted into bile
How do bile acids help the body?
Bile acids help the body break down fats and absorb key nutrients. The liver makes them, the gallbladder stores them, and they eventually go to work in the small intestine. These bile acids are a great example of recycling in nature. After digestion, the body usually reabsorbs the bile acids, and the whole process starts again.
What causes BAM in the bowel?
Inflammatory bowel conditions, such as Crohn’s disease, can also cause type 1 BAM. Type 2: Type 2 BAM is also called primary or idiopathic BAM, which means it has no obvious cause. Type 3: This third form of BAM develops as a result of other conditions, such as chronic diseases, radiation treatment, or celiac disease.
What happens to the body after digestion?
After digestion, the body usually reabsorbs the bile acids, and the whole process starts again. However, sometimes, the small intestine does not absorb the 95 percent of bile acids it is supposed to. The resulting condition is bile acid malabsorption (BAM). It is also sometimes called bile acid diarrhea (BAD).
How effective is BAM treatment?
Effective treatment for BAM depends on what form of the condition a person is experiencing. For example, those with Crohn’s disease who develop BAM may see their symptoms substantially disappear once they find the right treatment combination to control the underlying condition.
What causes bloating and stomach cramps?
BAM can cause stomach cramps, flatulence, and bloating. There are three different kinds of BAM, based on what causes the condition: Type 1: This form of BAM can happen after the surgical removal of part of the small intestine. Inflammatory bowel conditions, such as Crohn’s disease, can also cause type 1 BAM .
What percentage of people have bile acid malabsorption?
For example, around 50% of people who have chronic or recurrent diarrhea, also called functional diarrhea, experience bile acid malabsorption. Around 35% of people with large intestine inflammation, also called microscopic colitis, are affected by bile acid malabsorption.
What is the function of bile?
Bile helps break down fats in your stomach when food is digested. It also carries waste out of your digestive system. There's a salt component in bile that breaks down fat from food, absorbs it, and moves it into your stool for removal.
What acid is associated with diarrhea?
If you have chronic diarrhea, you’re likely to have higher levels of primary bile acids, cholic acid , and chenodeoxycholic acid, each associated with irritable bowel syndrome with diarrhea.. Serum 7αC4 test.
How does the gallbladder work?
When you eat, your gallbladder should release the right amount of bile into your stomach to break down fat content. Your gallbladder manages the amount of bile that gets released based on how much your stomach needs for digestion. Diagnosing Bile Acid Malabsorption. Bile acid malabsorption affects around 1% to 2% of people in the U.S.
What is bile acid 2021?
Medically Reviewed by Dan Brennan, MD on June 09, 2021. Bile acid is a liquid substance your liver produces to aid in food digestion. Your body usually releases bile at the correct levels based on the food you eat. But sometimes your body produces too much bile or isn’t able to use it correctly, resulting in bile acid malabsorption (BAM).
What is the best medicine for diarrhea?
Cholestyramine is the primary medication prescribed for conditions like bile acid malabsorption. It's designed to break down in your colon to improve symptoms of chronic diarrhea.. Surgery. If lifestyle changes and medication don’t help your symptoms, your doctor may recommend surgery to remove your gallbladder.
What are gallstones in the gallbladder called?
Gallstones in your gallbladder, also known as cholelithiasis. Gallstones in your bile duct, also known as choledocholithiasis. Gallbladder inflammation, also known as cholecystitis. Persistent polyps impacting the tissue that surrounds your gallbladder . Pancreas inflammation, also known as pancreatitis.
What are the symptoms of bile acid malabsorption?
What are the usual symptoms of bile acid malabsorption? Diarrhoea: this is the main symptom. When bile acids are not properly re-absorbed from the ileum, they pass instead into the large intestine (colon), irritating the lining of the colon and stimulating salt and water secretion.
What is the purpose of bile acids?
Firstly, in the breakdown and absorption of fats and vitamins from food as it passes through the gut and, secondly, to aid with the removal of waste products. Bile acids are made in the liver, stored in the gallbladder and released into the small intestine (gut) when food is eaten. Virtually all (97%) of the bile acids are then re-absorbed in the final section of the small intestine (ileum) and returned to the liver. This cycle repeats itself and is called the enterohepatic circulation. When this cycle is disturbed, this is termed bile acid malabsorption. Bile acid malabsorption is sometimes called bile salt malabsorption or bile acid diarrhoea and these two terms mean exactly the same thing. Bile acid malabsorption affects up to 1 in 100 people in the UK.
How does bile acid sequestrant work?
These work by binding to the bile acid in the small intestine and preventing them from irritating the large intestine. These are called ‘bile acid sequestrants’ and can help symptoms and improve the quality of the life of sufferers. They will affect the absorption of other drugs so must be taken four hours before or after other medications.
What happens if you lose too much bile acid?
If too much bile acid is lost from the body due to diarrhoea, there is an increased risk of the formation of gallstones and kidney stones. The impact over time depends on the underlying cause of your bile acid malabsorption.
Where are bile acids stored?
Bile acids are made in the liver, stored in the gallbladder and released into the small intestine (gut) when food is eaten. Virtually all (97%) of the bile acids are then re-absorbed in the final section of the small intestine (ileum) and returned to the liver. This cycle repeats itself and is called the enterohepatic circulation.
Can colestipol cause constipation?
The main medications include: Colestyramine and colestipol – these medications only come in powder form. Unfortunately, some people may find them unpalatable and if the dose is too high, it can cause constipation, so it is important to adjust the dose according to symptoms.
Is radiation necessary for bile acid test?
The overall result can establish how much bile acid is lost from the body and whether malabsorption is taking place. The amount of radiation in the test is very small and extra precautions are not necessary.
Where do bile acids go when you eat?
As soon as you eat something, bile acids are expelled from the gallbladder into the bile duct. Bile Acids then enter your small intestine and break down food so your body can absorb the nutrients. 97% of these bile acids are then reabsorbed in the terminal ileum, the very end of the small intestine, to be used repeatedly.
What happens when you have too much bile acid in your colon?
When you have too much bile acid lingering in your colon, you can get watery stools and diarrhea (aka bile acid diarrhea).
What is the best way to reduce the amount of water in your bowels?
1. Fiber. Soluble fiber supplements like psyllium or slippery elm act as a natural bile acid binder, They can help reduce the amount of water in the bowels. 2. Low FODMAP Diet. Some people with BAM find a low FODMAP diet, (a diet low in fermentable carbs), helpful in reducing excess gas and fluid in the gut.
What are the deficiencies caused by BAM?
If you have chronic Bile Acid Malabsorption symptoms, it is crucial to treat nutritional deficiencies caused by diarrhea, such as low iron, zinc, potassium, and magnesium.
Where is bile produced?
Bile is a fluid that is produced in the liver . Bile acids are critical molecules that help us digest and absorb fat and nutrients from our food. The common bile duct moves bile acids from your liver into your gallbladder (see video below), where they remain until you eat something.
What is the liver responsible for?
The liver is responsible for processing vitamins and nutrients from your food into forms that can be utilized by your body. Many holistic practitioners include liver supporting herbs and supplements as part of a protocol to treat BAM.
What causes watery diarrhea?
Another name it is frequently referred to is Bile Acid Diarrhea. The condition results in extra bile buildup in your intestines, which causes watery diarrhea. Bile acid malabsorption is a common but often incorrectly diagnosed cause of chronic diarrhea.
What is the best treatment for bile acid malabsorption?
Such medications include cholestyramine (Questran), colesevelam (WelChol) and colestipol (Colestid). These medications require a prescription and may lead to side effects such as abdominal pain and bloating.
Why is bile acid malabsorption important?
As bile acid malabsorption can result in many intestine-related problems, including chronic cases of diarrhea, it is important to treat the symptoms effectively to prevent doing damage to the body. As with many health conditions, you may be able to work with a doctor to identify an underlying condition that may be causing bile acid malabsorption.
How to reduce diarrhea from bile acid?
Following a bile acid malabsorption diet may be one of the most important ways to help control and reduce the episodes of diar rhea if you have bile acid malabsorption. Because bile is required for fat digestions, your body has to release more bile acids when you consume foods that are high in fat. Following a low-fat diet can help reduce ...
What is bile acid malabsorption?
Bile acid malabsorption is also known as bile acid diarrhea. It can result in many intestine-related problems, including chronic cases of diarrhea. It occurs due to the malabsorption of bile caused by gastrointestinal disease, or it can be a primary disorder in itself, associated with excessive bile acid production.
Why is bile acid not reabsorbed?
This might occur due to disease or malfunction of the area of the small intestine responsible for reabsor ption.
Why does bile acid cause diarrhea?
This leads to an excessive amount of bile acid in the intestinal tract not being reabsorbed, and in effect, it causes excess amounts of fluid to be pumped into the colon, causing diarrhea. This often means that those who have this condition will need to find a bathroom urgently during times of bile acid malabsorption.
How to reduce bile acid in the colon?
Following a low-fat diet can help reduce the amount of bile acid in the body, causing less of it to make its way to the colon. This, in turn, will lessen your chances of suffering from diarrhea if you have bile acid malabsorption. Avoid foods high in fats, including butter/dairy, fried foods, lunch meats, mayonnaise, and baked goods.
