Medication
How to use garlic as one of the strongest home remedies for bacterial vaginosis:
- Make a mixture of some drops of garlic oil with a half teaspoon of coconut and vitamin E oil. ...
- Add garlic to your cooking daily as well as consume few cloves of garlic on a daily basis.
- Take garlic supplementary pills after consulting the doctor.
Self-care
Clindamycin isn’t practical because you’re not treating the cause of bacterial vaginosis; you’re only treating the frustrating symptoms you’re experiencing. Another problem you’ll find with using clindamycin to treat bacterial vaginosis is that some women are allergic to this antibiotic.
Nutrition
Can bacterial vaginosis go away on its own? BV will often go away on its own within a few days, but it also tends to come back. If you take antibiotics to treat BV, the symptoms may disappear within a day or two, but it’s important to take the full course of pills, which is usually seven days.
How to treat bacterial vaginosis naturally at home?
Treatment. To treat bacterial vaginosis, your doctor may prescribe one of the following medications: Metronidazole (Flagyl, Metrogel-Vaginal, others). This medicine may be taken as a pill by mouth (orally). Metronidazole is also available as a topical gel that you insert into your vagina.
Does clindamycin really treat bacterial vaginosis?
Can BV go away on its own?
What is the best medicine for vaginal bacteria?

Can bacterial vaginosis be cured?
BV will sometimes go away without treatment. But if you have symptoms of BV you should be checked and treated. It is important that you take all of the medicine prescribed to you, even if your symptoms go away. A health care provider can treat BV with antibiotics, but BV may recur even after treatment.
Resources for Clinicians
Vaginitis Self-Study Module external icon – An online learning experience that helps users learn how to manage vaginitis. Free CME/CNE available. (November 1, 2017)
What is BV in vagina?
Both bacterial vaginosis (BV) and yeast infections are vaginal infections that increase discharge. Here’s how you can tell the difference:
How to avoid bacterial vaginosis?
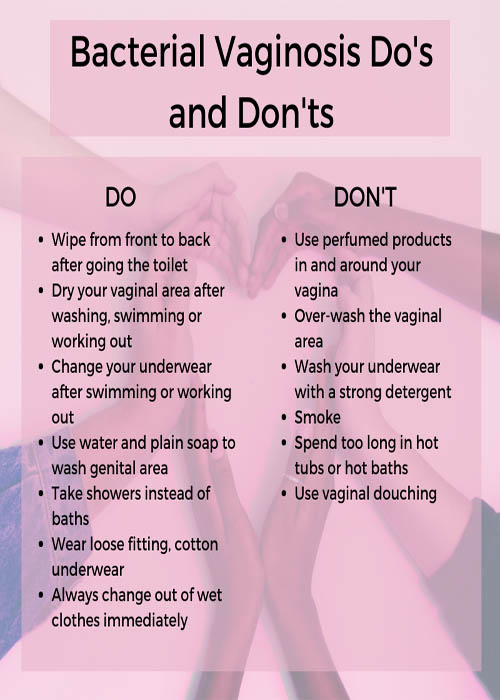
Because bacterial vaginosis (BV) isn’t fully understood, there are no foolproof ways of avoiding it. These steps may reduce your risk: Avoid douching. It changes the natural balance of bacteria in your vagina. Instead, practice healthy vaginal and vulvar care.
What is a BV?
Bacterial Vaginosis. Bacterial vaginosis (BV) is a common vaginal infection that happens when some normal bacteria that lives in the vagina overgrows, causing a bacterial imbalance. Symptoms include an off-white or grey vaginal discharge that smells “fishy.”. In some women, BV goes away without treatment, in others, ...
Why does my vagina smell fishy?
Bacterial vaginosis may cause a "fishy" odor and cause vaginal irritation in some women. Others may not have any symptoms. Bacterial vaginosis is associated with poor obstetrics ...
What is the name of the system that produces bacteria in the vagina?
Your vagina is home to multiple types of bacteria (called a microbiome), just like your digestive system. Bacterial vaginosis (BV) happens when some of the vaginal bacteria grow more quickly than others. Too much of one type of bacteria leads to an imbalance.
What age do women get BV?
Bacterial vaginosis (BV) is the most common vaginal problem for women ages 15 to 44. In fact, an estimated one in three American women will get BV. The rate is higher in black women.
How many people with BV don't have symptoms?
Up to 84% of people with bacterial vaginosis (BV) don’t have symptoms. If you do, you may have:
What is BV in vagina?
Bacterial vaginosis (BV) is a common vaginal infection caused by too much of a certain type of bacteria in your vagina. Left untreated, it can raise your risk for several serious health problems. Bacterial vaginosis doesn’t always cause symptoms. But if it does, they can include:
What is the best medicine for a vaginal infection?
These might include: Clindamycin, a cream you use in your vagina. It sells under the brand names Cleocin and Clindesse. Metronidazole, available as a pill you swallow or a gel you insert in your vagina.
What If My BV Comes Back?
It’s common for this infection to come back within a year. If that happens, talk to your doctor about treatments. They may prescribe extended-use metronidazole.
What are the different types of bacteria that grow in the vagina?
There are at least seven types of bacteria that grow in the vagina. Lactobacillus is one of them. BV is linked to a decrease of lactobacillus, which is found in yogurt and acidophilus milk.
How long does it take for BV to come back?
Clindamycin can weaken latex condoms not only while you’re using the medication, but for at least 3 days after you stop.
Does yogurt cause BV?
BV is linked to a decrease of lactobacillus, which is found in yogurt and acidophilus milk. Some studies suggest that eating foods that contain lactobacillus may be beneficial, but more research is needed. Do not douche with yogurt or any other product. Vaginal douching is a risk factor for BV.
What is the best treatment for BV?
Currently, the only effective treatments for BV are prescribed antibiotics, including metronidazole (pronounced met-roh-NIH-duh-zohl) and clindamycin (pronounced klin-duh-MY-sin ). 1, 2, 3, 4 These are prescribed as oral medications, which are taken by mouth, or as a gel or cream, both of which are inserted into the vagina with an applicator.
Why is it important to complete the entire course of a prescription for BV?
Even if symptoms start to disappear, it is important to complete the entire course of a prescription for BV because of the likelihood of recurrence.
How much weight can a pregnant woman have with BV?
Risks of BV during pregnancy include delivering an infant preterm (before 37 weeks of pregnancy) and delivering an infant with a low birth weight (generally, 5.5 pounds or less). The CDC recommends that pregnant women be tested—and treated if necessary—if they have symptoms of BV.
Does BV reduce preterm birth?
Some research shows that treating BV in pregnant women does not reduce the risk of preterm birth. Further study is needed to better understand these outcomes. 5
How to diagnose BV?
BV can be diagnosed by using clinical criteria (i.e., Amsel’s diagnostic criteria) ( 999) or by determining the Nugent score from a vaginal Gram stain ( 1000 ). Vaginal Gram stain, considered the reference standard laboratory method for diagnosing BV, is used to determine the relative concentration of lactobacilli (i.e., long gram-positive rods), small gram-negative and gram-variable rods (i.e., G. vaginalis or Bacteroides ), and curved gram-negative rods (i.e., Mobiluncus) characteristic of BV. A Nugent score of 0–3 is consistent with a Lactobacillus -predominant vaginal microbiota, 4–6 with intermediate microbiota (emergence of G. vaginalis ), and 7–10 with BV. Clinical diagnosis of BV by Amsel criteria requires at least three of the following four symptoms or signs:
What is the best test for BV?
In addition to the Amsel criteria, multiple POC tests are available for BV diagnosis. The Osom BV Blue test (Sekisui Diagnostics) detects vaginal sialidase activity ( 1003, 1004 ). The Affirm VP III (Becton Dickinson) is an oligonucleotide probe test that detects high concentrations of G. vaginalis nucleic acids (>5 x 10 5 CFU of G. vaginalis/ mL of vaginal fluid) for diagnosing BV, Candida species, and T. vaginalis. This test has been reported to be most useful for symptomatic women in conjunction with vaginal pH measurement and presence of amine odor (sensitivity of 97%); specificity is 81% compared with Nugent. Finally, the FemExam Test Card (Cooper Surgical) measures vaginal pH, presence of trimethylamine (a metabolic by-product of G. vaginalis ), and proline aminopeptidase ( 1005 ). Sensitivity is 91% and specificity is 61%, compared with Nugent. This test has primarily been studied in resource-poor settings ( 1005 ), and although it has been reported to be beneficial compared with syndromic management, it is not a preferred diagnostic method for BV diagnosis.
What is the Max Vaginal Panel?
The Max Vaginal Panel provides results by an algorithmic analysis of molecular DNA detection of Lactobacillus species ( L. crispatus and L. jensenii) in addition to G. vaginalis, A. vaginae, BVAB2, and Megasphaera type 1. This test has 90.5% sensitivity and 85.8% specificity for BV diagnosis, compared with Amsel criteria and Nugent score. It also provides results for Candida species and T. vaginalis. The Aptima BV detects G. vaginalis, A. vaginae, and certain Lactobacillus species including L. crispatus, L. jensenii, and L. gasseri, with sensitivity and specificity ranging from 95.0% to 97.3% and 85.8% to 89.6%, respectively (using either clinician- or patient-collected vaginal swabs). The three laboratory-developed tests (NuSwab VG, OneSwab BV Panel PCR with Lactobacillus Profiling by qPCR, and SureSwab BV) have to be internally validated before use for patient care yet have good sensitivity and specificity, similar to FDA-cleared assays. BV NAATs should be used among symptomatic women only (e.g., women with vaginal discharge, odor, or itch) because their accuracy is not well defined for asymptomatic women. Despite the availability of BV NAATs, traditional methods of BV diagnosis, including the Amsel criteria, Nugent score, and the Affirm VP III assay, remain useful for diagnosing symptomatic BV because of their lower cost and ability to provide a rapid diagnosis. Culture of G. vaginalis is not recommended as a diagnostic tool because it is not specific. Cervical Pap tests have no clinical utility for diagnosing BV because of their low sensitivity and specificity.
Is oral clindamycin better than topical clindamycin?
Oral therapy has not been reported to be superior to topical therapy for treating symptomatic BV in effecting cure or preventing adverse outcomes of pregnancy. Pregnant women can be treated with any of the recommended regimens for nonpregnant women, in addition to the alternative regimens of oral clindamycin and clindamycin ovules.
Is BV treatment recommended for women?
Treatment for BV is recommended for women with symptoms. Established benefits of therapy among nonpregnant women are to relieve vaginal symptoms and signs of infection. Other potential benefits of treatment include reduction in the risk for acquiring C. trachomatis, N. gonorrhoeae, T. vaginalis, M. genitalium, HIV, HPV, and HSV-2 ( 971, 986 – 988, 990, 1010 ). No data are available that directly compare the efficacy of oral and topical medications for treating BV.
Can you douch for BV?
Douching might increase the risk for relapse , and no data support use of douching for treatment or symptom relief.
Should women with BV be tested for HIV?
All women with BV should be tested for HIV and other STIs.
What is the best medicine for bacterial vaginosis?
Boric acid capsules can be used to treat bacterial vaginosis.
What is the quickest way to treat bacterial vaginosis?
The fastest way to treat BV is to visit your doctor and get a prescription to treat the condition.
How long does bacterial vaginosis last?
After seeing your doctor and starting treatment with a prescribed medication, your symptoms will likely start improving within 2 to 3 days.
What is the difference between a yeast infection and bacterial vaginosis?
BV and vaginal yeast infections have similar symptoms but different causes and treatments. Both cause inflammation of the vagina, also known as vaginitis.
What is a vaginal infection caused by an overgrowth of bacteria?
Bacterial vaginosis is a vaginal infection caused by an overgrowth of bacteria.
What to wear for bacterial vaginosis?
According to the University of New Hampshire’s Department of Health and Wellness, to help your bacterial vaginosis heal quickly and to prevent future cases, wear cotton underwear that’s breathable.
Can bacterial vaginosis be prevented?
Bacterial vaginosis is a common condition that many women can get, regardless of whether they’ve had sex. Home remedies can be used to treat and prevent it. Some may be more effective than others.
How to prevent BV?
These include wearing breathable cotton underwear, which may help prevent the growth of bacteria around the genital s by preventing moisture from building up in the area.
What is BV in medical terms?
Medical treatment. When to see a doctor. Diagnosis. Summary. Bacterial vaginosis (BV) is an infection that develops due to an imbalance in the natural bacteria in the vagina. It occurs when “bad” bacteria, which do not need oxygen to survive, outnumber “good” bacteria, known as lactobacilli. BV is the most common.
How long does metronidazole take to treat BV?
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommend antibiotics to treat BV. Oral metronidazole: 500 milligrams twice a day for 7 days. Metronidazole 0.75% gel: One full 5-gram (g) applicator intravaginally once a day for 5 days.
How do you know if you have BV?
The symptoms of BV include: a thin vaginal discharge that is white or gray. a bad-smelling discharge, which may become worse before a period or after having sex. pain when having sex. itchy or discolored genitals. a burning sensation when urinating.
What is the normal pH level for a vagina?
A healthcare professional can test the vaginal fluid to check its pH level. According to the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence, a pH level of 3.5–4.5 is normal for people of reproductive age.
When to see a doctor for BV?
A doctor or gynecologist will check that BV is the cause of the symptoms and not another condition. If a person develops BV during pregnancy , they should see a doctor for appropriate treatment.
Can BV reoccur?
BV can sometimes clear up by itself, but treatment is often necessary. In either case, BV can reoccur. Factors that can make a person more likely to develop BV include: having sex with more than one person. using vaginal douches or other hygiene products on the vagina, such as scented soaps or washes.
