What diseases are caused by Bacillus bacteria?
Sep 16, 2021 · B. cereus produces beta-lactamases and is resistant to beta-lactam antibiotics. When antibiotics are required, treatment with vancomycin, gentamicin, chloramphenicol, or carbapenems should be considered. Clindamycin, tetracycline, and erythromycin have had variable results with susceptibility testing and are not considered first-line agents.
What disease is caused by Bacillus subtilis?
Jan 11, 2022 · The following antibiotics are recommended in Bacillus cereus infections: Ciprofloxacin. Gentamicin. Rifampicin. Chloramphenicol. Gatifloxacin. Levofloxacin. Streptomycin. Tetracycline. Linezolid. Vancomycin. Moxifloxacin. Tigecycline.
What is the difference between bacillus, coccus, and Spirillum?
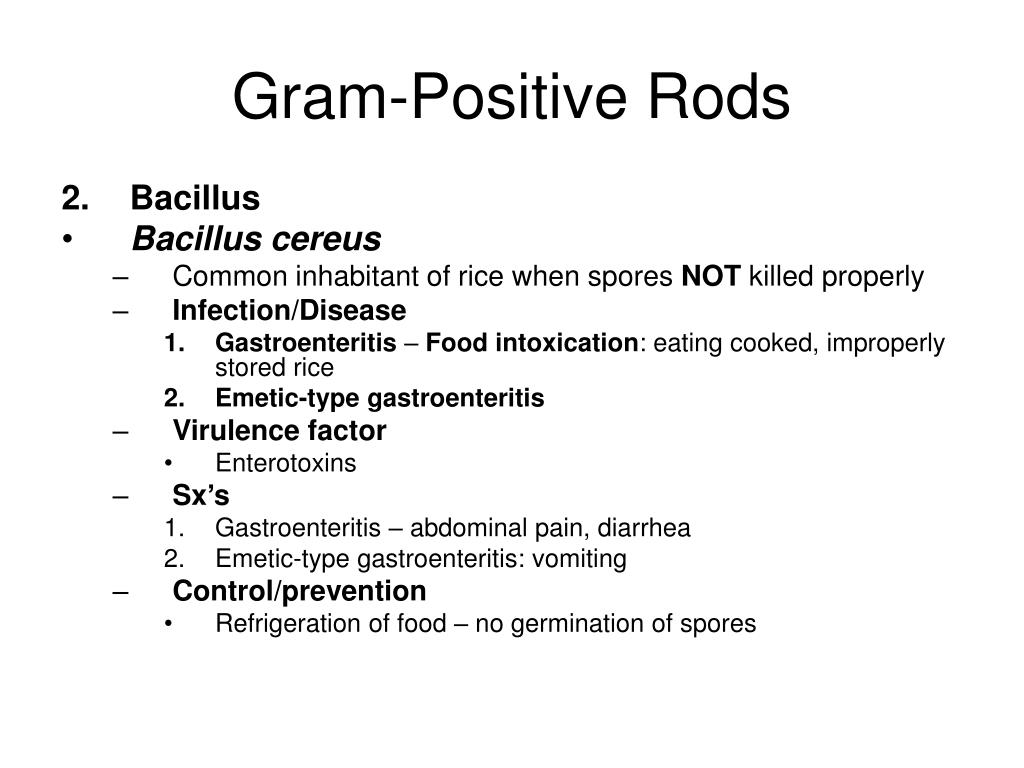
Jul 17, 2019 · Bacillus cereus (B. cereus) is a Gram-positive, facultatively aerobic sporeformer whose cells are large rods. Two different clinical syndromes appear to be associated with B. cereus food poisoning, which correspond to two different toxins produced by the bacteria. The onset of symptoms, such as watery diarrhea, abdominal cramps, and pain, in ...
Is Bacillus an antibiotic?
Jun 29, 2021 · The MYP agar has been the standard media for plating B. cereus, but it has little selectivity so background flora is not inhibited and can mask the presence of B. cereus. Bacara is a chromogenic...

What is the treatment for Bacillus?
Antibiotics which appear especially useful in the treatment of Bacillus infections are clindamycin and vancomycin, to which the vast majority of strains are susceptible in vitro. Beta-lactam antibiotics, including the new cephalosporins and penicillins, are of little value in this setting.
Which antibiotic is best for Bacillus cereus?
Vancomycin appears to be the most suitable treatment of choice for B. cereus bacteremia. However, carbapenem antibiotics are reported to be as effective as glycopeptide group [2, 5].Apr 19, 2016
What happens if you get Bacillus cereus?
Definition. Bacillus cereus is a foodborne pathogen that can produce toxins, causing two types of gastrointestinal illness: the emetic (vomiting) syndrome and the diarrhoeal syndrome. When the emetic toxin (cereulide) is produced in the food, vomiting occurs after ingestion of the contaminated food.
Can Bacillus cereus go away on its own?
cereus occur each year within the U.S., according to a 2019 article published in the journal Frontiers in Microbiology. However, the vast majority of cases go unreported, because the symptoms are generally mild and subside on their own with rest and hydration.May 1, 2019
Does doxycycline treat Bacillus?
A patient who developed severe wound infection with bacteremia caused by B. cereus was treated successfully with ciprofloxacin 750 mg every q 12 hours for almost 3 months (22). Doxycycline has been used in the treatment of bacteremia associated with Hickman catheters caused by B.
Can penicillin treat Bacillus cereus?
Bacillus cereus s.s. is typically resistant to penicillin and other β-lactam antibiotics [22] and can furthermore acquire resistance to commonly used antibiotics such as ciprofloxacin, cloxacillin, erythromycin, tetracycline and streptomycin [22, 23].Nov 9, 2019
What are the symptoms associated with Bacillus cereus?
The symptoms of B. cereus diarrheal type food poisoning include abdominal pain, watery diarrhea, rectal tenesmus, moderate nausea that may accompany diarrhea, seldom vomiting and no fever. Symptoms develop within 6-15 hrs and can persist for 24 hrs.Apr 25, 2007
How long does it take Bacillus cereus to grow?
cereus can double in size within 20 minutes if kept at 30˚C. The routine reheating of your food will not help to deactivate the toxin or kill the bacteria. Since this bacteria and its toxin are so resistant to heat your only hope of dodging food poisoning is to avoid allowing the bacteria to germinate.Jul 11, 2019
What diseases are caused by bacilli bacteria?
Although anthrax remains the best-known Bacillus disease, in recent years other Bacillus species have been increasingly implicated in a wide range of infections including abscesses, bacteremia/septicemia, wound and burn infections, ear infections, endocarditis, meningitis, ophthalmitis, osteomyelitis, peritonitis, and ...
What are the symptoms of bacilli?
Signs and symptoms include:Nausea.Vomiting.Abdominal pain.Headache.Loss of appetite.Fever.Severe, bloody diarrhea in the later stages of the disease.Sore throat and difficulty swallowing.More items...•May 15, 2020
How do you test for Bacillus cereus?
Abstract. An egg yolk-polymyxin medium (KG) for rapid enumeration of Bacillus cereus is described. The test is presumptive in that differentiation of B. cereus (and closely related organisms) from other species is based on the formation of turbidity in the agar surrounding the colonies of the cereus group organisms.
What causes Bacillus cereus?
Bacillus cereus is caused by the ingestion of food contaminated with enterotoxigenic B. cereus or the emetic toxin. In non-gastrointestinal illness, reports of respiratory infections similar to respiratory anthrax have been attributed to B.Sep 16, 2021
What are the toxins in Bacillus cereus?
Among these secreted toxins are four hemolysins, three distinct phospholipases, an emesis-inducing toxin, and proteases.[1][2] Bacillus cereus is a toxin-producing facultatively anaerobic gram-positive ...
Where is Bacillus cereus found?
The bacteria is commonly found in the environment, is often found in soil and vegetation, and can be present in foods.
What is the name of the bacteria that causes nausea and vomiting?
2SFH Evanston. Last Update: September 11, 2020. Continuing Education Activity. Bacillus cereus is a facultatively anaerobic, toxin-producing gram-positive bacteria that can be found in soil vegetation and even food. This may cause two types of intestinal illness, one diarrheal, and one causing nausea and vomiting.
What is a CME/CE?
Earn continuing education credits (CME/CE) on this topic. Introduction. Bacillus cereusis a toxin-producing facultatively anaerobic gram-positive bacteria. The bacteria is commonly found in the environment, is often found in soil and vegetation, and can be present in foods. It can quickly multiply at room temperature.
How long does it take for rice to incubate?
Incubation for the first type is 6 to 15 hours. In the second type, affected food, most often starchy food, and classically, rice, contains a different type of toxin (cereulide, an ionophoric low-molecular-weight dodecadepsipeptide that is pH-stable and heat and protease-resistant).
How long does it take to recover from endophthalmitis?
Treatment / Management. Treatment is symptomatic. Most patients recover within 24 hours after symptom onset. However, in severe cases, intravenous fluid hydration is necessary.
Can bacillus cereus be confused with colitis?
However, the symptoms can be confused with C.difficile colitis.
What is the name of the chromogenic agar used to detect Bacillus cereus?
January 2012: The Bacillus Chapter has been updated with the inclusion of a new optional chromogenic agar, Bacara agar, for the detection and enumeration of Bacillus cereus in foods. Bacillus cereus is an aerobic spore-forming bacterium that is commonly found in soil, on vegetables, and in many raw and processed foods.
What foods are contaminated with B. cereus?
Foods incriminated in past outbreaks include cooked meat and vegetables, boiled or fried rice, vanilla sauce, custards, soups, and raw vegetable sprouts. Two types of illness have been attributed to the consumption of foods contaminated with B. cereus.
Is Bacara a selective agar?
Bacara is a chromogenic selective and differential agar that promotes the growth and identification of B. cereus, but inhibits the growth of background flora. The chromogenic agar has been suggested for the enumeration of B. cereus group as a substitute for MYP 1,2 .
Can B. cereus be tested for emetic toxin?
However, results with atypical strains of B. cereus are quite variable, and further testing may be necessary to identify the isolates. Test for cereulide (emetic toxin). Intoxication is caused by the pre-formed cereulide produced by B. cereus spores after germinating in food that has not been stored properly.
Why do Bacillus cereus endospores survive?
Because B. cereus endospores are extremely heat resistant, they are likely to survive cooking at temperatures that would otherwise destroy foodborne pathogen cells. Heat resistance increases with increasing salinity (presence of salt) and decreases with increasing acidity. Bacillus cereus spores can germinate when exposed to heat or improper handling; therefore, the 2013 Food Code recommends that hot foods be maintained at a temperature of 135ºF (57ºC) or above and cold foods be maintained at a temperature of 41ºF (5ºC) or below (FDA 2013a).
Where is B. cereus found?
Due to its ubiquity in the environment, B. cereus is easily spread to many types of fresh and processed food products. It is found in the environment and on many foods, including meat, cereal dishes, vegetables, milk, products,