Explore
Treatment: Pilocytic Astrocytoma: These tumors are often removed by surgery alone. ... Diffuse Astrocytoma: If the tumor is accessible and can be completely removed, the only additional care required is follow-up scans. ... Anaplastic Astrocytoma: The first step in treatment of anaplastic astrocytoma is surgery. ... More items...
What is the treatment for high-grade astrocytomas?
Survival rates can vary widely by age, with younger people tending to have a better outlook than older people. The 5-year survival rate for grade 1 and 2 anaplastic astrocytoma in children is almost 90% following surgery. The 5-year survival rate for adults age 20-44 is 58%. The 5-year survival rate for adults age 45-54 is 29%.
How long can you live with anaplastic astrocytoma?
Treatments
- Surgery to remove all of a tumor -- or as much as possible -- is a likely first step. ...
- Radiation often follows in case parts of a tumor could not be removed or surgeons can’t be sure they got all of the cancer.
- Chemotherapy is often used for glioblastoma and anaplastic astrocytoma. ...
How is astrocytoma treated?
- You could experience difficulties with your ability to speak.
- You may also experience changes to your vision, including blurred vision or loss of vision.
- Changes in physical ability are likely to be gradual.
How to diagnose astrocytoma?

How long can you live with an astrocytoma?
Survival rates for more common adult brain and spinal cord tumorsType of Tumor5-Year Relative Survival RateLow-grade (diffuse) astrocytoma73%26%Anaplastic astrocytoma58%15%Glioblastoma22%6%Oligodendroglioma90%69%5 more rows•May 5, 2020
Are astrocytomas curable?
Anaplastic astrocytomas are usually not curable, but are treatable. We do our best to control the tumor and keep it from growing and causing more symptoms using many different tools including surgery, radiation and chemotherapy. Unfortunately these tumors tend to continue to grow and become more aggressive.
Does astrocytoma always come back?
A high-grade astrocytoma is more likely to grow quickly and spread to other parts of the brain or spinal cord. It is common for this tumour to come back after treatment. Further treatment is often needed.
How long can you live with a grade 3 astrocytoma?
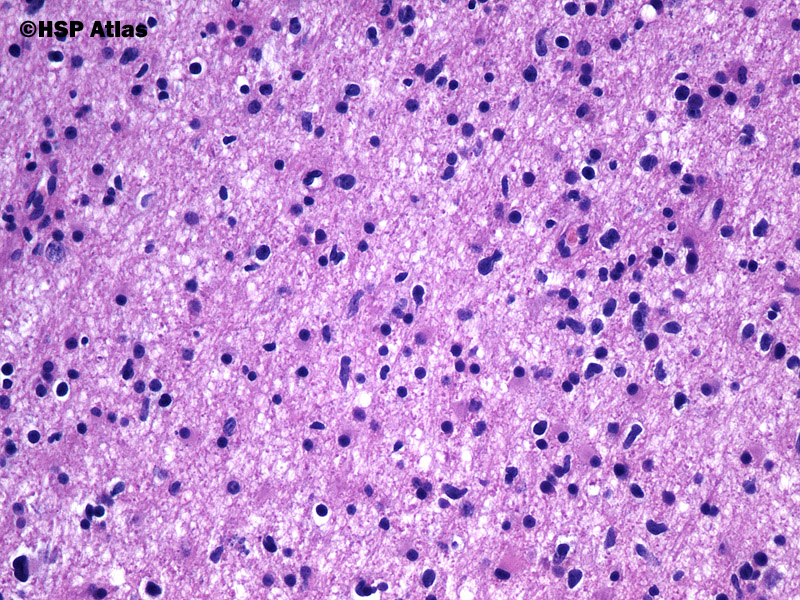
In addition to hypercellularity, grade III astrocytomas, also known as anaplastic astrocytomas, exhibit nuclear atypia and increased mitotic figures. The median survival for patients with grade III tumors is ∼3 years.
What are the stages of astrocytoma?
About this Condition: Astrocytoma Grade 1 astrocytoma (non-infiltrating): Slow-growing tumors that typically do not expand into surrounding tissue. Grade 2 astrocytoma (low grade): Tumors that usually develop slowly, but can expand into surrounding tissue and grow more quickly over time.
What causes an astrocytoma?
Causes. The cause of most astrocytomas is not known. Researchers speculate that genetic and immunologic abnormalities, environmental factors (e.g., exposure to ultraviolet rays, certain chemicals, ionizing radiation), diet, stress, and/or other factors may play contributing roles in causing specific types of cancer.
What happens to the brain after a tumor is removed?
Swelling in the brain is expected after surgery, so recovery will take time and the benefits will not be immediately apparent. Steroids may be prescribed to your loved one to help with the swelling, but they may have their own set of side-effects (difficulty sleeping, sweating, over-eating, agitation).
What does astrocytomas do to the body?
Astrocytoma is a type of cancer that can form in the brain or spinal cord. Astrocytoma begins in cells called astrocytes that support nerve cells. Astrocytoma signs and symptoms depend on the location of your tumor. Astrocytomas that occur in the brain can cause seizures, headaches and nausea.
Is grade 3 astrocytoma a terminal?
Grade 1 and grade 2 astrocytomas grow slowly and are benign, meaning they're not cancerous. Grade 3 and grade 4 astrocytomas grow faster and are malignant, which means they're cancerous. An anaplastic astrocytoma is a grade 3 astrocytoma. While they're rare, they can be very serious if left untreated.
Can you survive a grade 2 astrocytoma?
Grade 1 tumors are largely cured (96% survival rate at 5 years), usually by surgery only. Grade 2 tumors: Overall median survival is 8 years. Presence of IDH1 mutation is associated with longer survival. Grade 4 tumors: Median survival is 15 months.
Is astrocytoma a glioblastoma?
Astrocytomas can develop in adults or in children. High-grade astrocytomas, called glioblastoma multiforme, are the most malignant of all brain tumors. Glioblastoma symptoms are often the same as those of other gliomas. Pilocytic astrocytomas are low-grade cerebellum gliomas commonly found in children.
What are the final stages of a brain tumour?
These symptoms include drowsiness, headaches, cognitive and personality changes, poor communication, seizures, delirium (confusion and difficulty thinking), focal neurological symptoms, and dysphagia. Some patients may have several of these symptoms, while others may have none.
What is the treatment for astrocytoma?
Treatments include surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy and therapeutic electric fields.
What are the different types of astrocytoma?
There are several types of astrocytomas, including: Pilocytic: These tend to not spread and are considered to be noncancerous. Diffuse: These grow slowly. Anaplastic: These are rare but call for aggressive treatment. Glioblastoma: This type grows aggressively and is the most common cancerous primary brain tumor.
How old do you have to be to get astrocytoma?
Most cases of pilocytic astrocytomas are diagnosed by the age of 20. About 1,200 people younger than 19 in the United States will have an astrocytoma diagnosis. The 20-45 year age group accounts for about 60% of all low-grade astrocytoma diagnoses.
What is a star shaped astrocyte?
Star-shaped astrocytes are glial cells (the type of cells that provide the brain's supportive tissues). Astrocytomas are tumors that grow from these cells and that are found in the central nervous system.
Why is astrocytoma not usually a staged disease?
Staging of astrocytomas is not usually done because it is rare that they grow outside the brain. A person being treated for astrocytoma may also need physical therapy and/or occupational therapy.
How long do glioblastoma patients live?
For example, patients with a glioblastoma may have a survival rate of less than one year, although some patients may live five years or more. Patients with a pilocytic astrocytoma may have a survival rate of about ten years.
Where are astrocytes found?
Astrocytomas are tumors found in the central nervous system (CNS) that grow from star-shaped astrocyte cells. Astrocytes are glial cells (the type of cells that provide supportive tissue in the brain). Some types of astrocytomas have small areas of infiltration, while others are more spread out. There are several types of astrocytomas, including:
How to treat astrocytoma?
Astrocytoma treatments include: Surgery to remove the astrocytoma. Your brain surgeon (neursurgeon) will work to remove as much of the astrocytoma as possible. The goal is to remove all of the cancer, but sometimes the astrocytoma is located near sensitive brain tissue that makes that too risky. Even removing some of the cancer may reduce your ...
How to diagnose astrocytoma?
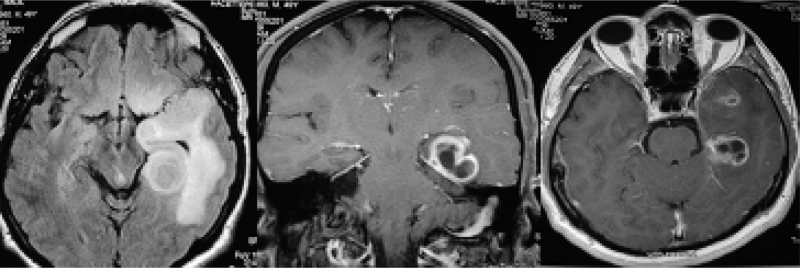
Tests and procedures used to diagnose astrocytoma include: 1 Neurological exam. During a neurological exam, your doctor will ask you about your signs and symptoms. He or she may check your vision, hearing, balance, coordination, strength and reflexes. Problems in one or more of these areas may provide clues about the part of your brain that could be affected by a brain tumor. 2 Imaging tests. Imaging tests can help your doctor determine the location and size of your brain tumor. MRI is often used to diagnose brain tumors, and it may be used along with specialized MRI imaging, such as functional MRI, perfusion MRI and magnetic resonance spectroscopy.#N#Other imaging tests may include CT and positron emission tomography (PET). 3 Removing a sample of tissue for testing (biopsy). A biopsy can be done with a needle before surgery or during surgery to remove your astrocytoma, depending on your particular situation and the location of your tumor. The sample of suspicious tissue is analyzed in a laboratory to determine the types of cells and their level of aggressiveness.#N#Specialized tests of the tumor cells can tell your doctor the types of mutations the cells have acquired. This gives your doctor clues about your prognosis and may guide your treatment options.
What is the name of the cancer that grows in the brain?
Astrocytoma. Astrocytoma. Open pop-up dialog box. Close. Astrocytoma. Astrocytoma. Astrocytoma is a type of cancer that can occur in the brain or spinal cord. It begins in cells called astrocytes that support nerve cells. Some astrocytomas grow very slowly and others can be aggressive cancers that grow quickly.
What is the best treatment for cancer after surgery?
Chemotherapy is often used after surgery to kill any cancer cells that might remain. It can be combined with radiation therapy for aggressive cancers.
How does chemotherapy work?
Chemotherapy. Chemotherapy uses drugs to kill cancer cells. Chemotherapy drugs can be taken in pill form or through a vein in your arm. In certain situations, a circular wafer of chemotherapy medicine can be placed in your brain after surgery where it slowly dissolves and releases the medication.
What is the best way to diagnose brain tumors?
Imaging tests. Imaging tests can help your doctor determine the location and size of your brain tumor. MRI is often used to diagnose brain tumors, and it may be used along with specialized MRI imaging, such as functional MRI, perfusion MRI and magnetic resonance spectroscopy.
What tests are used to diagnose astrocytoma?
Tests and procedures used to diagnose astrocytoma include: Neurological exam. During a neurological exam, your doctor will ask you about your signs and symptoms. He or she may check your vision, hearing, balance, coordination, strength and reflexes.
Why is surgery important for astrocytoma?
Surgery is the first step for the treatment of astrocytomas, as it provides two important benefits: First, it procures tumor tissue to establish a diagnosis. Secondly, it offers the possibility to remove as much tumor is safely possible to relieve mass effect , reduce swelling and facilitate response to adjuvant therapies, when indicated. The decision whether to perform a simple biopsy or a full resection depends on multiple factors, but particularly on the clinical and medical conditions of the patient, as well as the predicted extent of resectability of the tumor.
How long does radiation treatment last for astrocytoma?
Radiotherapy: Radiation has been at the basis of treatment of astrocytomas for the past 50 years and it is extremely effective, at least for the first few months after treatment. Radiation, too, works by damaging DNA of the tumor cells, thus inducing their death. Under standard protocols, the treatment consists of small doses of radiation in the area of the tumor, 5 days a week for 6 weeks. Side effects are local hair loss (usually temporary), and fatigue. Long term side effects are necrosis of the brain around the treated region, and cognitive difficulties.
What is the most common brain tumor?
The brain is made up by many different cells, including neurons, which constitute the electric circuitry responsible for brain functions, and astrocytes, which provide the structure and support for neurons to work properly. Astrocytomas are tumors which originates from astrocytes, and, in adult individuals, they are the most common brain tumors. In the US, about 15,000 new astrocytomas are diagnosed every year. Males are slightly more affected than females, with a ratio of 1.3/1.
What is GBM tumor?
Histologically, it is characterized by very abnormal-appearing cells, proliferation, areas of dead tissue and formation of new vessels. GBM can present either as a malignant progression from a previously existing lower grade astrocytoma (usually in 10% of cases) or originate directly as a grade 4 tumor (90% of cases).
What is the grade of astrocytoma?
According to the World Health Organization (WHO) classifications of brain tumors, astrocytomas range from grade 1 (most benign) to grade 4 (most malignant). This grading, which is made by analyzing the tumor cells under the microscope is based on the following features: 1) how abnormal the cells look like (atypia); 2) how much they grow (mitosis); 3) presence of newly made blood vessels within the tumor (vascular proliferation). This is further integrated by the analysis of tumor’s genetic features, i.e. the DNA analysis of the tumor cells. Generally, with the exception of grade 1 tumors, which are most common in the pediatric population, most astrocytomas affect patients older than 40. Also, the older the patient, the higher the chances of the astrocytoma to be of higher grade.
Where is astrocytoma most common?
Most common in the cerebellum, i.e. the part of the brain located in the back of the head, just above the neck. It does not invade into the surrounding brain, thus when resected completely it is considered cured, and it does not require either chemotherapy or radiotherapy.
Why do doctors do genetic analysis of tumors?
Targeted therapies: Nowadays, the majority of treating centers perform detailed genetic analysis of any tumor tissue removed at surgery, in order to obtain patient-specific molecular signatures which can help establish the best drug for that tumor.
Why are astrocytomas hard to remove?
They are grade III tumors that grow quickly and spread to nearby tissue. They are hard to remove completely because of their tentacle-like fingers, which grow into nearby brain tissue.
What are the different types of astrocytoma?
There are several types of astrocytoma: 1 Anaplastic astrocytomas are rare. They are grade III tumors that grow quickly and spread to nearby tissue. They are hard to remove completely because of their tentacle-like fingers, which grow into nearby brain tissue. 2 Glioblastomas are also called grade IV astrocytomas. Over 50% of astrocytomas are glioblastomas. They grow very quickly and are hard to treat because they are often a mix of different cancer cell types. 3 Diffuse astrocytomas can grow into nearby tissue, but they grow slowly. They are considered low-grade (grade II), but they can develop into higher-grade tumors. 4 Pineal astrocytic tumors can be any grade. They form around the pineal gland. This tiny organ in the cerebrum makes melatonin, which helps control sleep and waking. 5 Brain stem gliomas are rare in adults. It doesn’t happen often, but sometimes gliomas can form in the brain stem, the part that connects to the spinal cord. 6 Pilocytic astrocytomas and subependymal giant cell astrocytomas are more common in children and considered grade I.
What age does astrocytoma show up?
Treatments. Astrocytoma is the most common a type of glioma tumor that can develop in the brain and spinal cord. It’s more common in men than women and most often shows up after age 45. There are several types of astrocytoma, and some grow faster than others.
How does electric field therapy work?
Electric-field therapy uses electrical fields to target cells in the tumor while not damaging normal cells. It's done by putting electrodes directly on the scalp. The device is called Optune.
What is the grade of astrocytoma?
Like other tumors, astrocytomas are graded on a scale of I to IV, based on how abnormal the cells look and how fast they grow. Grade IV tumors are the most aggressive in their growth. Most astrocytomas in adults are high grade. This means the cells look abnormal and grow quickly.
How do you know if you have astrocytoma?
They depend partly on where and how big your tumor is. Early symptoms include: Headaches. Blurry vision. Seizures. Memory loss. Nausea and vomiting.
Is a pineal astrocytic tumor a grade 2 tumor?
They are considered low-grade (grade II), but they can develop into higher-grade tumors. Pineal astrocytic tumors can be any grade. They form around the pineal gland. This tiny organ in the cerebrum makes melatonin, which helps control sleep and waking. Brain stem gliomas are rare in adults.
How to treat astrocytoma?
The treatment for astrocytomas depends on the grade of the tumour, as well as its size and location. Generally the first treatment for astrocytomas is neurosurgery to remove as much of the tumour as possible. This may be followed by radiotherapy and sometimes chemotherapy.
What happens if you have astrocytoma?
If you or someone you know has just been diagnosed with an astrocytoma, you may be in a state of shock. This is a natural way to feel. Our Support and Information team can help answer any questions you may have or provide a listening ear if you need one.
How do astrocytomas affect the brain?
As astrocytomas grow from cells that are vital in processing information in the brain, astrocytomas can disrupt the function of whichever area of the brain they are growing in.
Why are there other brain tumours that don't have astrocytoma?
There are other brain tumours, which don't have astrocytoma in their name, that are still actually astrocytomas because they grow from astrocytes. For example, some types of diffuse midline glioma (previously called DIPGs). Back to the top.
How many types of astrocytoma are there?
There are 4 main types of astrocytoma (pronounced ass-tro-sigh-toe-ma). Grade 1 astrocytomas (pilocytic astrocytoma) They are: slow growing, sometimes very slow growing. relatively contained (have well-defined edges), which can make it easier to remove completely. unlikely to spread to other parts of the brain.
What age do astrocytomas occur?
They occur most often in adults between the ages of 20 and 45. They’re more common in males than females. Grade 3 astrocytomas (anaplastic astrocytoma) Anaplastic means the cells divide rapidly and don’t look like normal cells in structure or function. They are: fast growing.
Where do astrocytomas grow?
Astrocytomas grow from a type of cell in the brain called an astrocyte. These cells support and protect the nerves in the brain (neurons) and help to pass messages between them. As these cells are found throughout the brain, astrocytomas can occur in many different areas of the brain. There are 4 main types of astrocytoma (pronounced ...
What is the treatment for anaplastic astrocytoma?
Treatment depends on the location of the tumor and how far it has progressed. Surgery and radiation therapy, with chemotherapy during or following radiation, are the standard treatments. If surgery is not an option, then the doctor may recommend radiation and/or chemotherapy . Many clinical trials using radiation, chemotherapy, or a combination are available for initial and recurrent anaplastic astrocytomas.
What is grade 3 astrocytoma?
Grade III – Anaplastic Astrocytoma. Back to top. An astrocytoma is a glioma that develops from star-shaped glial cells (astrocytes) that support nerve cells. An anaplastic astrocytoma is classified as a grade III tumor.
Why is chemotherapy given to children?
Chemotherapy may be given to very young children instead of radiation therapy to avoid damage to the developing brain. Some of these tumors can progress to a higher grade, so it is important to be diligent about following up with the medical team after treatment.
What is the most common malignant brain tumor?
Glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) is the most common and deadliest of malignant primary brain tumors in adults and is one of a group of tumors referred to as gliomas. Classified as a Grade IV (most serious) astrocytoma, GBM develops from the lineage of star-shaped glial cells, called astrocytes, that support nerve cells.
How to treat a tumor in the lungs?
Treatment depends on the size and location of the tumor. The doctor will most likely perform a biopsy or surgery to remove the tumor. Partial resections or inoperable tumors may be treated with radiation. Recurring tumors may require additional surgery, radiation and/or chemotherapy.
What is a grade 2 glioma?
Grade II – Low-grade Astrocytoma. An astrocytoma is a type of glioma that develops from star-shaped cells (astrocytes) that support nerve cells. The WHO classifies a low-grade astrocytoma as a grade II tumor.
What are the characteristics of a brain tumor?
Characteristics. Slow growing, with relatively well-defined borders. Grows in the cerebrum, optic nerve pathways, brain stem and cerebellum. Occurs most often in children and teens. Accounts for two percent of all brain tumors.
What are the Causes of Astrocytoma?
Causes of astrocytomas are unknown. Researchers have found that the only solid causes are environmental or hereditary. For example, radiation exposure in early years and certain DNA mutations that are also common causes of other cancers can contribute to heightened risk.
Treatment for Astrocytoma
Grade 1 tumors might be resolved with surgery, but the majority of astrocytomas are incurable. The goal of treatment of astrocytoma is comfort and pain management, keeping the symptoms at bay for as long as possible with:
How to diagnose astrocytoma?
The diagnosis of astrocytoma is based on a thorough clinical evaluation, characteristic physical findings, a careful patient history, and specialized tests, such as blood tests, neuroimaging techniques, and/or other diagnostic studies. Neuroimaging techniques, such as computed tomography (CT) scanning and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the brain assist in evaluating tumor size, location, and other factors. During CT scanning, a computer and x-rays are used to create cross-sectional images of certain tissue structures. MRI uses a magnetic field to create cross-sectional images of particular organs and bodily tissues. Examination of a sample of the tumor (biopsy) and microscopic examination of tumor cells is used to determine the tumor type and grade.
Why do people get astrocytomas?
Researchers speculate that genetic and immunologic abnormalities, environmental factors (e.g., exposure to ultraviolet rays, certain chemicals, ionizing radiation), diet, stress, and/or other factors may play contributing roles in causing specific types of cancer.
What is the most aggressive type of brain tumor?
Anaplastic astrocytoma occurs most often in adults between the ages of 30 and 50, and accounts for 4% of all brain tumors. Grade IV astrocytoma is also called glioblastoma or GBM and is the most aggressive type of nervous system tumor.
What is the name of the tumor that forms from the star-shaped cells?
An astrocytoma is a tumor that arises from the star-shaped cells (astrocytes) that form the supportive tissue of the brain. Other supportive cells of the brain include oligodendrocytes and ependymal cells. Collectively, these cells are known as glial cells and the tissue they form is known as glial tissue. Tumors that arise from the glial tissue, including astrocytomas, are collectively referred to as gliomas.
How many grades of astrocytoma are there?
The World Health Organization (WHO) classifies astrocytomas into four grades depending on how fast they are growing and the likelihood that they will spread (infiltrate) to nearby brain tissue. Non-infiltrating astrocytomas usually grow more slowly than the infiltrating forms.
Where does astrocytoma occur?
Pilocytic astrocytoma occurs most often in the cerebellum, cerebrum, optic nerve pathway and brainstem. This tumor occurs most often in children and teens and accounts for 2% of all brain tumors. Grade II astrocytoma is also called low-grade astrocytoma or diffuse astrocytoma and is usually an infiltrating tumor.
How long does radiation therapy last for astrocytoma?
With the use of CT (computed tomography) and MRI (magnetic resonance imaging), radiation sometimes may be deferred for several months or years while the patient is scanned at regular intervals.
What is the prognosis of astrocytoma?
Astrocytoma prognosis. A prognosis is when your doctor gives you a forecast of the likely outcome of your medical condition. Your doctor cannot be absolutely certain about what will happen to you following a diagnosis of a brain tumour.
How long does astrocytoma last?
About 27% of people diagnosed with a high grade astrocytoma live for five years or more .
How long does a grade 4 glioblastoma patient live?
Grade 4 - Glioblastoma. A grade 4 astrocytoma is called a glioblastoma . The average survival time is 12-18 months - only 25% of glioblastoma patients survive more than one year, and only 5% of patients survive more than five years.
What is brain tumor information pack?
Our Brain Tumour Information Pack can help you better understand your diagnosis and feel confident talking to your medical team.
Can a prognosis be based on your tumor type?
They can give you an estimate, based on your tumour type and current situation, but they may not be able to predict other factors, such as how well you might respond to treatment. This is why prognosis is often an ongoing process, revised at different stages in your journey.