Medication
The anti-arteriosclerotic properties of other substances are actively investigated, including calcium channel blockers, betablockers, and novel drug classes. From the medical point of view, a broader use of the well-proven and effective therapies of arteriosclerosis and its complications is clearly warranted. Publication types Review MeSH terms
Procedures
Jun 28, 2018 · Cholesterol Medication Drugs known as statins and fibrates can reduce your LDL (low-density lipoprotein, or "bad") cholesterol, which …
Self-care
Aug 09, 2021 · Treating Arteriosclerosis. Treating arteriosclerosis may involve invasive surgical techniques. Three standard methods include: Balloon Angioplasty; The surgeon places a tiny tube (catheter) into an artery in the leg or groin and threads it …
Nutrition
An angioplasty is used to unblock an artery using a long, thin catheter and a balloon, and an endarterectomy is a procedure used to remove fat from the insides of arteries.
What are the remedies to reverse arteriosclerosis?
Feb 10, 2022 · Arteriosclerosis – Symptoms, Causes & Treatment Hematology Posted by Mia Garnsey Arteriosclerosis is also referred to as cardiovascular arteriosclerosis, which is a heart condition that occurs when the arteries (vessels that carry blood away from the heart) grow stiff and thick, thereby restricting blood flow to vital organs and tissues in ...
How to get rid of arteriosclerosis?
Mar 16, 2021 · These include: Quitting smoking Eating healthy foods Exercising regularly Maintaining a healthy weight Checking and maintaining a healthy blood pressure Checking and maintaining healthy cholesterol and blood sugar levels
Can arteriosclerosis be cured?
Piedmont Heart Institute. The treatment for cerebral arteriosclerosis can include medications or surgery. Physicians may also recommend treatment to help people control high blood pressure, quit cigarette smoking, and reduce the cholesterol level, all of which are risk factors for cerebral arteriosclerosis.
How can arteriosclerosis be prevented?
Feb 19, 2022 · The most common surgical arteriosclerosis treatment is angioplasty. Medical arteriosclerosis treatment may be needed in addition to lifestyle changes to combat underlying diseases and conditions. A doctor can initiate or adjust diabetes medications and prescribe drugs to stabilize blood pressure.

What is the best treatment for atherosclerosis?
Medications for treating atherosclerosis include:cholesterol-lowering drugs, including statins.angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors, which may lower blood pressure.beta-blockers, which “rest” the heart.antiplatelet drugs such as aspirin to prevent blood from clotting and clogging your arteries.
What is the main cause of arteriosclerosis?
Atherosclerosis is thickening or hardening of the arteries caused by a buildup of plaque in the inner lining of an artery. Risk factors may include high cholesterol and triglyceride levels, high blood pressure, smoking, diabetes, obesity, physical activity, and eating saturated fats.
Can you heal arteriosclerosis?
Medical treatment, regular exercise, and dietary changes can be used to keep atherosclerosis from getting worse and stabilize the plaque, but they aren't able to reverse the disease.
What are the 4 stages of atherosclerosis?
Atherogenesis can be divided into five key steps, which are 1) endothelial dysfunction, 2) formation of lipid layer or fatty streak within the intima, 3) migration of leukocytes and smooth muscle cells into the vessel wall, 4) foam cell formation and 5) degradation of extracellular matrix.Dec 8, 2013
What vitamin removes plaque from arteries?
Niacin, or Vitamin B3, is the best agent known to raise blood levels of HDL, which helps remove cholesterol deposits from the artery walls.Nov 28, 2001
What do blocked arteries feel like?
The symptoms of an artery blockage include chest pain and tightness, and shortness of breath. Imagine driving through a tunnel. On Monday, you encounter a pile of rubble. There is a narrow gap, big enough to drive through.Dec 3, 2020
At what age do arteries start clogging?
"Atherosclerosis usually starts in the teens and 20s, and by the 30s we can see changes in most people," says cardiologist Matthew Sorrentino MD, a professor at The University of Chicago Medicine. In the early stages, your heart-related screening tests, like cholesterol checks, might still come back normal.Dec 23, 2015
Can artery plaque be removed?
An atherectomy is a procedure to remove plaque from an artery (blood vessel). Removing plaque makes the artery wider, so blood can flow more freely to the heart muscles. In an atherectomy, the plaque is shaved or vaporized away with tiny rotating blades or a laser on the end of a catheter (a thin, flexible tube).
How to treat arteriosclerosis?
Treatment for arteriosclerosis includes a healthy diet, exercise and medication to control or possibly reverse your condition. If enlarged blood vessels have been diagnosed, our goal is to develop an individualized treatment plan so blood clots do not form.
What are the complications of arteriosclerosis?
Complications of arteriosclerosis include: Coronary Arteriosclerosis (Coronary artery disease): Narrowed arteries near the heart may lead to chest pain, heart attack or heart failure.
What is the process of arteries growing thick and stiff?
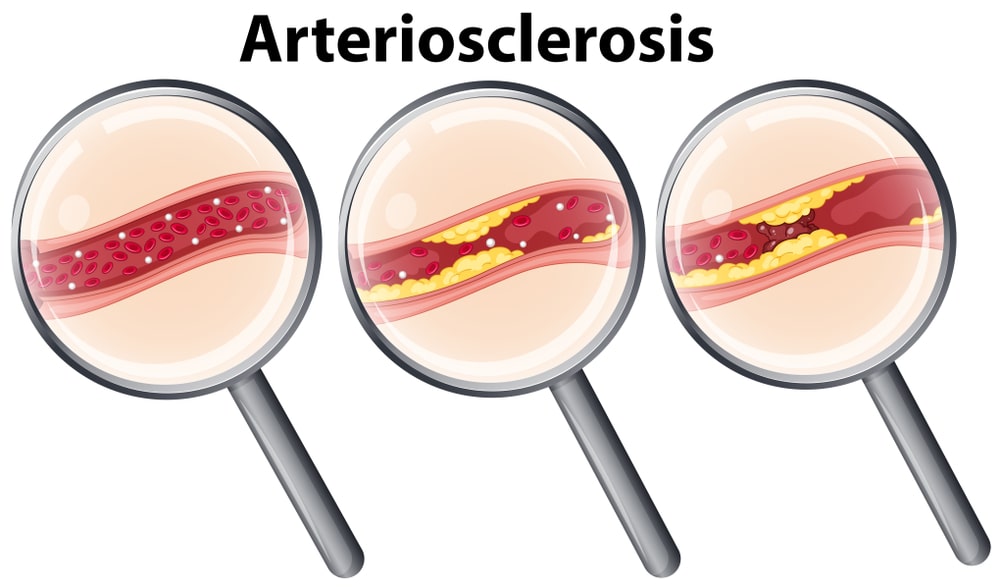
What is Arteriosclerosis? Arteriosclerosis (also known as cardiovascular arteriosclerosis) occurs when arteries grow thick and stiff and restrict blood flow to organs and tissues in the body. This gradual process, also known as hardening of the arteries, weakens arteries and can develop in various organs, most commonly the heart.
How to test blood pressure in the arm?
Exercise makes the heart work hard and beat fast while heart tests are administered. Ultrasound: An ultrasound device can measure blood pressure on various points of the arm or leg, which will help the physician determine if you have any blockages and how quickly blood flows through the arteries.
How to prevent heart disease?
Practice good heart health: Watch what you eat, exercise and avoid smoking. Take your medications as prescribed: If you have high blood pressure, high cholesterol or diabetes, be certain to take your prescribed medications as directed.
What is the best medicine for blood clots?
Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors can lower blood pressure and lower the possibility of heart attack. Calcium channel blockers and diuretics (water pills) can reduce blood pressure. A clot-busting drug may dissolve blood clots. Your physician may also prescribe other medications, based on your needs.
Can a clogged artery cause a heart attack?
As arteriosclerosis progresses, clogged arteries can trigger a heart attack or stroke, with the following symptoms: Chest pain or pressure (angina) Sudden arm or leg weakness or numbness. Slurred speech or difficulty speaking.
What are the treatments for atherosclerosis?
Medically Reviewed. Prescription drugs, surgery, and heart-healthy lifestyle changes are treatment options for atherosclerosis. Shutterstock (2) Atherosclerosis occurs when fat-containing deposits called plaque form in your arteries, causing them to harden and narrow. This can reduce blood flow to different areas of your body, ...
How does a surgeon treat atherosclerosis?
Surgical procedures used to treat atherosclerosis include: Angioplasty In angioplasty, a surgeon inserts a narrow tube into the blocked or narrowed artery and passes a second tube containing a deflated balloon tip through it. The balloon is then inflated, which pushes the blockage open against your artery walls.
What are the medications that help reduce cholesterol?
Cholesterol Medication Drugs known as statins and fibrates can reduce your LDL (low-density lipoprotein, or "bad") cholesterol, which can help stop or even reverse the buildup of plaque in your arteries. In addition to regulating your cholesterol, statins can help stabilize the lining of your heart arteries and prevent atherosclerosis.
How to control risk factors for atherosclerosis?
You can help control risk factors for atherosclerosis and heart disease — such as your weight, blood pressure, and blood cholesterol and glucose levels — by focusing on eating certain foods while avoiding others.
What is the best medicine for blood pressure?
Diuretics (Water Pills) Diuretics help lower your blood pressure by reducing fluid retention throughout your body. Other Drugs Your doctor may prescribe medication to control specific risk factors for atherosclerosis — like diabetes — or symptoms of atherosclerosis, like leg pain during exercise.
How does ACE inhibitor help with atherosclerosis?
Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme (ACE) Inhibitors ACE inhibitors may help slow the progression of atherosclerosis by lowering your blood pressure and relaxing your blood vessels. They also reduce your risk of having multiple heart attacks.
How to stop atherosclerosis?
Stop smoking. Smoking — or using tobacco in another form — damages your arteries. If you’re a smoker, quitting is the single most effective way to stop your atherosclerosis from getting worse and reduce your risk of complications, according to the Mayo Clinic. (2) Get enough exercise.
What happens if you have atherosclerosis in your legs?
If you have atherosclerosis in the arteries in your arms and legs, you may have signs or symptoms of peripheral artery disease, such as leg pain when walking (claudication) or decreased blood pressure in an affected limb. If you have atherosclerosis in the arteries leading to your kidneys, you develop high blood pressure or kidney failure.
What are the complications of atherosclerosis?
Complications. The complications of atherosclerosis depend on which arteries are blocked. For example: Coronary artery disease. When atherosclerosis narrows the arteries close to your heart, you may develop coronary artery disease, which can cause chest pain (angina), a heart attack or heart failure.
What is the name of the buildup of fats, cholesterol, and other substances in and on your artery walls
Atherosclerosis is a specific type of arteriosclerosis. Atherosclerosis is the buildup of fats, cholesterol and other substances in and on your artery walls. This buildup is called plaque. The plaque can cause your arteries to narrow, blocking blood flow. The plaque can also burst, leading to a blood clot.
What happens when an artery is damaged?
Once the inner wall of an artery is damaged, blood cells and other substances often clump at the injury site and build up in the inner lining of the artery. Over time, fatty deposits (plaque) made of cholesterol and other cellular products also build up at the injury site and harden, narrowing your arteries.
How do you know if you have atherosclerosis?
If you have atherosclerosis in the arteries leading to your brain, you may have signs and symptoms such as sudden numbness or weakness in your arms or legs, difficulty speaking or slurred speech, temporary loss of vision in one eye, or drooping muscles in your face.
What happens if you have a blocked artery?
The organs and tissues connected to the blocked arteries then don't receive enough blood to function properly. Eventually, pieces of the fatty deposits may break off and enter your bloodstream. In addition, the smooth lining of the plaque may rupture, spilling cholesterol and other substances into your bloodstream.
What are the symptoms of inadequate blood flow?
Also pay attention to early symptoms of inadequate blood flow, such as chest pain (angina), leg pain or numbness. Early diagnosis and treatment can stop atherosclerosis from worsening and prevent a heart attack, stroke or another medical emergency.
Treatment
Clinical Trials
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
Alternative Medicine
Specialist to consult
Preparing For Your Appointment
- Lifestyle changes, such as eating a healthy diet and exercising, are the first treatment for atherosclerosis — and may be all that you need to treat your atherosclerosis. But sometimes, medication or surgical procedures may be needed.
What Is Arteriosclerosis?
- Explore Mayo Clinic studiestesting new treatments, interventions and tests as a means to prevent, detect, treat or manage this condition.
Symptoms
- Lifestyle changes can help you prevent or slow the progression of atherosclerosis. 1. Stop smoking.Smoking damages your arteries. Quitting smoking is the best thing you can do to keep your arteries healthy and prevent atherosclerosis complications. 2. Exercise most days of the week. Regular exercise improves blood flow, lowers blood pressure, and reduces your risk of co…
Causes
- It's thought that some foods and herbal supplements can help reduce your high cholesterol level and high blood pressure, two major risk factors for developing atherosclerosis. With your doctor's OK, you might consider these supplements and products: 1. Alpha-linolenic acid 2. Barley 3. Beta-sitosterol (found in supplements and some margarines, such as Promise Activ) 4. Blond psylliu…
Diagnosis
- If you think you may have atherosclerosis or are worried about having atherosclerosis because of a strong family history of heart disease, make an appointment with your doctor to have your cholesterol level checked. Here's some information to help you get ready for your appointment and know what to expect from your doctor.
Prevention
- Arteriosclerosis (also known as cardiovascular arteriosclerosis) is a heart condition that occurs when arteries grow thick and stiff and restrict blood flow to organs and tissues in the body. This gradual process, also known as hardening of the arteries, weakens arteries and can develop in various organs, most commonly the heart. Arteries circulate blood throughout the body, but whe…
Treatment
- Even as artery walls gradually thicken and stiffen, there usually are no arteriosclerosis symptoms. Even as the condition worsens into atherosclerosis, mild cases may still show no symptoms. That’s why regular checkups are important. As arteriosclerosis progresses, clogged arteries can trigger a heart attack or stroke, with the following symptoms: 1. Chest pain or pressure (angina) …
Prognosis
- A number of factors can contribute to arteriosclerosis. Arteriosclerosis causes include: 1. High cholesterol 2. High blood pressure 3. High triglycerides 4. Insulin resistance or diabetes 5. Obesity 6. Smoking or use of other tobacco products 7. Inflammation from other diseases
Complications
- Early diagnosis is critical for managing arteriosclerosis. To diagnose the condition, we ask questions about your medical history and do a physical exam. During the physical exam, your physician can use a stethoscope to listen to your arteries for an abnormal whooshing sound called a bruit (broo-E). A bruit may indicate poor blood flow due to plaque buildup.