Full Answer
Who is the author of the treatment of Acute anuria?
The Treatment of Acute Anuria *† With Evaluation of Peritoneal Lavage Irving A. Fields, Helen Eastman Martin, D. G. Simonsen, Maxine Wertman, and Leola Westover Author informationCopyright and License informationDisclaimer *Submitted for publication, February, 1949.
What is anuria or anuresis?
Anuria or anuresis occurs when the kidneys aren’t producing urine. A person may first experience oliguria, or low output of urine, and then progress to anuria.
What is the outlook for anuria?
Overall, the outlook for anuria depends on: Because anuria is related to numerous potential causes, you can’t self-diagnose your condition. Your best bet is to see your doctor right away if you notice any changes in urination and urine output. The earlier anuria is detected, the better the outlook.
Can you self-diagnose anuria?
Because anuria is related to numerous potential causes, you can’t self-diagnose your condition. Your best bet is to see your doctor right away if you notice any changes in urination and urine output. The earlier anuria is detected, the better the outlook.

What is the treatment of anuria?
The exact treatment for anuria depends on the underlying condition that's causing it. Kidney disease may be treated with dialysis to remove fluids and waste. Ureteral stents may also help collect urine. A kidney transplant is considered a last resort.
Is anuria a medical emergency?
Anuria or not urinating is a symptom itself and not a medical condition. Sometimes, a person may also have signs of the condition that is causing the poor urine output. The symptoms of kidney disease can include: swelling in the legs, feet, ankles, face.
What is the treatment of oliguria?
Increasing Fluid Intake A simple way to treat oliguria is by increasing the amount of fluids you take in. This can often be done at home by drinking more water or rehydration solutions that include electrolytes.
What do you do if a patient has no urine output?
Oliguria is likely to need medical treatment unless your urine output is low because you haven't been taking in enough fluids. You may be able to treat yourself in that case by drinking more fluids, such as plain water or rehydration solutions that contain electrolytes.
Can anuria cause death?
Outcomes of patients with anuric AKI The in-hospital mortality rate was 44.8%, with 18.7% of discharged patients being dependent on dialysis. Patients with anuric AKI had a higher rate of in-hospital death (60.5% vs. 40.6%, P=0.025) and a higher rate of long-term dependence on RRT among the survivors (41.2% vs.
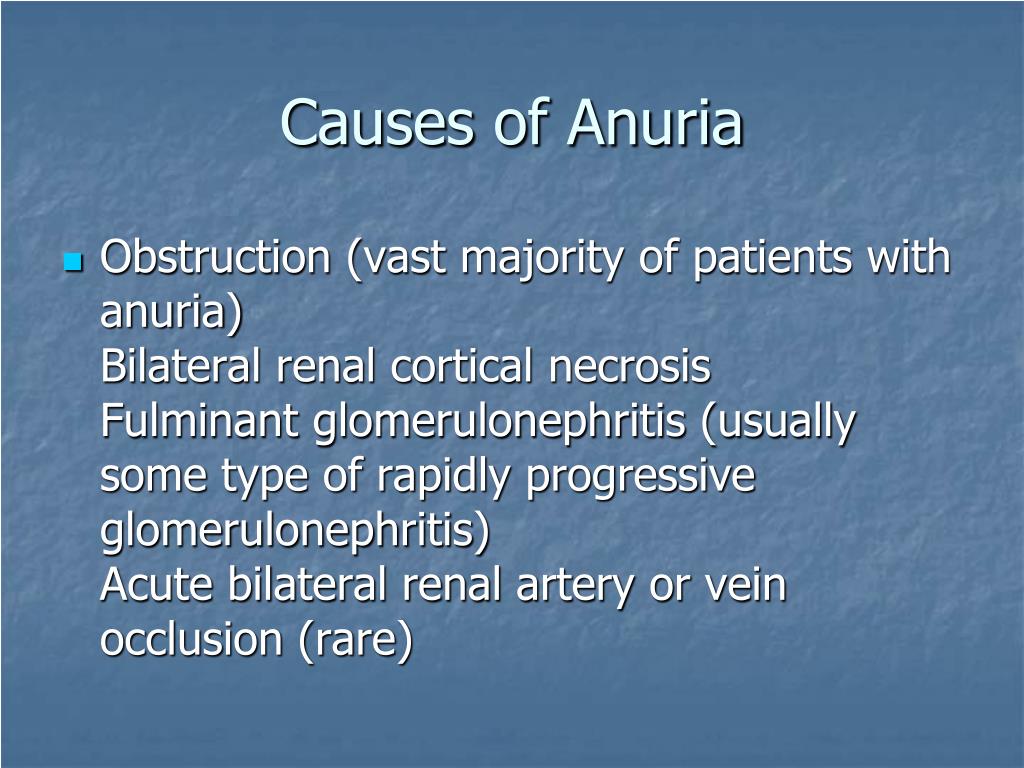
What is the most common cause of anuria?
Symptoms and Causes Ultimately, anuria can be caused by obstruction or abnormalities in the normal urine flow after the blood has been filtered and processed by the kidneys. These post-renal causes include bladder outlet obstruction, kidney stones or an enlarged prostate gland.
How do you increase urine output for a kidney?
Treatment may include:Hospitalization.Administration of intravenous (IV) fluids in large volumes (to replace depleted blood volume)Diuretic therapy or medications (to increase urine output)Close monitoring of important electrolytes such as potassium, sodium, and calcium.Medications (to control blood pressure)More items...
How can I increase my urine output?
Nine ways to induce urinationTapping the area between navel and pubic bone. ... Bending forward. ... Placing a hand in warm water. ... Running water. ... Drinking while trying to urinate. ... Trying the Valsalva maneuver. ... Exercising. ... Massaging the inner thigh.More items...•
How can I increase my urine flow?
Do Kegel exercises. Stand at or sit on the toilet and contract the muscle that allows you to stop and start the flow of pee. Hold it for 5 to 10 seconds. Do this 5 to 15 times, 3 to 5 times a day to help with bladder control and function.
What drugs increase urine output?
Diuretics are used to induce urine output in acute tubular necrosis (ATN) and to treat edema and hypertension. They increase urine excretion by inhibiting sodium and chloride reabsorption at different sites in the nephron.
What level of urine output is considered anuria?
Anuria: It is characterized by reduced urine output (<100mL urine per day), reflecting renal injury. Oliguria: It is defined as reduced urine output below 400mL/day. Such urinary volume is insufficient to excrete the daily osmolar load.
What drugs can cause urinary retention?
Pharmacologic Agents Associated with Urinary RetentionClassDrugsAntipsychoticsChlorpromazine (Thorazine*); fluphenazine (Prolixin*); haloperidol (Haldol); prochlorperazine (Compazine*); thioridazine (Mellaril*); thiothixene (Navane)Hormonal agentsEstrogen; progesterone; testosterone10 more rows•Mar 1, 2008
Overview
Anuria literally means no urine, or without urine. In practical terms, it means that your kidneys aren’t producing urine (pee) or that you aren’t peeing (anuresis). Anuria’s the most severe form of oliguria, which means that your kidneys aren’t producing enough urine. Your healthcare provider might refer to this condition as anuria or anuresis.
Symptoms and Causes
Anuria is when your kidneys don’t have enough blood or fluid supply from conditions like extreme dehydration, blood loss, severe infection, shock, or heart and liver failure. Anuria can also be caused by something affecting your kidney’s normal filtering of your blood.
Management and Treatment
Treatment for anuria depends on why you have the condition in the first place. Anuria must be treated by a healthcare professional.
Prevention
If you have any type of chronic illness, like diabetes or heart failure, follow your healthcare provider’s instructions on staying well. This may include instructions on what and how much to eat or drink and keeping track of your weight to recognize signs of water retention early.
How to treat anuria in kidneys?
Surgery is typically used as a treatment option for managing the underlying cause of anuria. It is most commonly recommended for individuals with either kidney stones or a tumor blocking the urine from exiting the kidneys. Surgery for patients with kidney stones normally involves a doctor passing a scope up the urethra or making a small incision so they can reach the stone and break it into smaller pieces that are easy to pass. Surgical treatments for tumors are a little more involved and typically require the doctor to make a slightly larger incision, cut out the tumor, close off any blood vessels linked to the tumor, and suture up the incision. Recovery times may vary depending on what sort of surgical process is performed. Some individuals may be able to leave the hospital in a few days while others may be bed bound for a couple of weeks.
How does radiation help with anuria?
It can be used for treating both benign and malignant tumors putting pressure on the kidneys and keeping them from properly releasing urine. The radiation therapy process is not invasive like surgeries. Instead, the doctor will direct beams of radiation at the area from outside the patient's body. The radiation therapy itself is very short, but it will have some side effects that linger for a while. Patients may feel nauseous, fatigued, and have skin problems wherever the radiation beam was directed. However, it is very effective because the radiation can kill off cells in the tumor and make it shrink. This turns larger tumors into a more manageable size that can either be removed during a surgical treatment or just left to sit out of the way of the kidneys.