Medication
Ipratropium, an anticholinergic, is effective in acute COPD exacerbations and should be given concurrently or alternating with beta-agonists. Dosage is 0.25 to 0.5 mg by nebulizer or 2 to 4 inhalations (17 to 18 mcg of drug delivered per puff) by metered-dose inhaler every 4 to 6 hours.
Procedures
Mar 31, 2015 · If the COPD attack is very severe, you may need to spend time in the hospital to receive treatment. At the hospital, chest X-rays and blood tests help doctors decide the best way to treat the flare-up. While in the hospital, you may be treated with: 2,3 IV medicines and antibiotics Supplemental oxygen Ventilator to help with breathing
Therapy
Oct 20, 2021 · Respiratory infections should be treated with antibiotics, if appropriate. Supplemental oxygen. A portable oxygen tank may be needed if blood oxygen levels are low. Symptoms of COPD include: Frequent coughing or wheezing Excess phlegm or sputum Shortness of breath Trouble taking a deep breath If you have any of these symptoms, talk to your doctor.
Nutrition
May 29, 2020 · At a hospital, your doctor may provide additional treatments to support your breathing. One example is the use of a continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) device to help keep your lungs open....
What is the best treatment for COPD patients?
Antibiotic Guidance for Treatment of Acute Exacerbations of COPD (AECOPD) in Adults Antibiotics are not recommended for all patients with AECOPD as bacterial infection is implicated in less than one-third of AECOPD. Procalcitonin (PCT) may be helpful in determining if antibiotics are necessary or the duration of treatment.
What medicines are used to treat COPD?
Jul 06, 2017 · Most people with COPD are given a treatment plan to follow if the symptoms get any worse. This often includes having a supply of steroid tablets (prednisolone) to start as soon as any increased breathlessness starts to affect your activities. You will also often be given an antibiotic to take as soon as your phlegm (sputum) changes colour.
How do you cure COPD?
Apr 25, 2018 · Without quick and careful treatment, these symptoms could make it necessary to seek emergency treatment. COPD flares can be frightening and uncomfortable, but their effects go beyond the attack ...
What is the latest medication for COPD?
Treatment for COPD COPD Complications If you’re living with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, you can control it with the help of the right kind …
What do you do if you have an attack with COPD?
At the first sign of a flare-up:DO NOT panic. ... Take medicines as directed for flare-ups. ... Take antibiotics as directed if your provider prescribes them.Use oxygen if prescribed.Use pursed lip breathing to save energy, slow your breathing, and help you relax.More items...•Oct 1, 2019
What is the first treatment of choice for an acute COPD exacerbation?
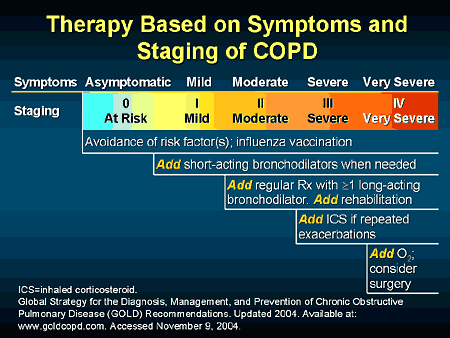
SHORT-ACTING BRONCHODILATORS 6,9 The first step in treating a COPD exacerbation is increasing the dosage of albuterol delivered via metered dose inhaler or nebulizer.Mar 1, 2010
How do you calm a COPD flare-up?
4 steps to manage your COPD flareUse a quick-acting inhaler. Relief or rescue inhalers work by sending a powerful stream of medicine straight to your constricted lungs. ... Take oral corticosteroids to reduce inflammation. ... Use an oxygen tank to get more oxygen into your body. ... Shift to a mechanical intervention.
What medications are given for COPD exacerbation?
For people who have frequent COPD exacerbations despite being on bronchodilators and inhaled steroids, two medications are sometimes used—roflumilast and long-term use of the antibiotic, azithromycin. Both are taken by mouth as pills and have been shown to decrease the number of exacerbations you have.
Which is the most appropriate choice of therapy in the treatment of a mild acute COPD exacerbation in a 42 year old man?
Key Points. Most patients with exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) require oxygen supplementation during an exacerbation. Inhaled short-acting beta-agonists are the cornerstone of drug therapy for acute exacerbations.
When do you give antibiotics for COPD exacerbation?
Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease (GOLD) guidelines recommend using antibiotics to treat exacerbations in patients with moderate or severe COPD who: have increased dyspnea, sputum volume, and sputum purulence; have 2 of these 3 symptoms if increased sputum purulence is one of the symptoms; or.
When should you go to the hospital for COPD?
Call 999 if you're struggling to breathe or have sudden shortness of breath and: your chest feels tight or heavy. you have a pain that spreads to your arms, back, neck and jaw. you feel or are being sick.
How long does an exacerbation of COPD last?
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) exacerbations may last for two days or even two weeks, depending on the severity of the symptoms. Sometimes, COPD exacerbations may require antibiotics, oral corticosteroids and hospitalization.May 6, 2021
What triggers COPD flare ups?
A flare-up is the worsening of your COPD symptoms. They are the main reason people with COPD go to the hospital. Flare-ups should be taken very seriously. They are usually caused by a trigger such as air pollution or allergens, or a chest infection from a virus (cold or flu) or bacteria.Nov 21, 2019
What medications should be avoided with COPD?
COPD, such as antibiotics, antimuscarinics, beta-agonists, roflumilast, steroids, and theophylline. Cystic fibrosis, such as antibiotics, cystic fibrosis trans- membrane regulator modulators, mucolytics, and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.Apr 30, 2018
How to stop COPD?
Quitting smoking. The most essential step in any treatment plan for COPD is to quit all smoking. Stopping smoking can keep COPD from getting worse and reducing your ability to breathe. But quitting smoking isn't easy. And this task may seem particularly daunting if you've tried to quit and have been unsuccessful.
What is the best medication for COPD?
Theophylline. When other treatment has been ineffective or if cost is a factor, theophylline (Elixophyllin, Theo-24, Theochron), a less expensive medication, may help improve breathing and prevent episodes of worsening COPD.
What is a spirometer?
A spirometer is a diagnostic device that measures the amount of air you're able to breathe in and out and the time it takes you to exhale completely after you take a deep breath. COPD is commonly misdiagnosed. Many people who have COPD may not be diagnosed until the disease is advanced. To diagnose your condition, ...
How to diagnose COPD?
To diagnose your condition, your doctor will review your signs and symptoms, discuss your family and medical history, and discuss any exposure you've had to lung irritants — especially cigarette smoke. Your doctor may order several tests to diagnose your condition.
What tests are done to determine if you have a pulmonary disease?
Your doctor may order several tests to diagnose your condition. Tests may include: Lung (pulmonary) function tests. These tests measure the amount of air you can inhale and exhale, and whether your lungs deliver enough oxygen to your blood.
How does pulmonary rehabilitation help COPD?
Pulmonary rehabilitation after episodes of worsening COPD may reduce readmission to the hospital, increase your ability to participate in everyday activities and improve your quality of life.
Do bronchodilators help with shortness of breath?
This can help relieve coughing and shortness of breath and make breathing easier . Depending on the severity of your disease, you may need a short-acting bronchodilator before activities, a long-acting bronchodilator that you use every day or both.
What is the best medicine for COPD?
Special kinds of medications called “inhaled bronchodilators” can be useful for immediately treating the symptoms when a COPD attack hits. Healthcare providers should prescribe their COPD patients with the right kind of inhalers to have on hand for treating COPD attacks.
What are the symptoms of COPD?
2 These symptoms can include: Feeling short of breath or breathless. Coughing. Fever. Increased amount of mucus. Change in color of the mucus: from clear to yellow, green, brown, or red.
How to tell if you have COPD?
During a COPD attack, a patient has symptoms that are much worse than usual. 2 These symptoms can include: 1 Feeling short of breath or breathless 2 Coughing 3 Fever 4 Increased amount of mucus 5 Change in color of the mucus: from clear to yellow, green, brown, or red
How does air pollution affect COPD?
Air pollution. Infections and air pollution trigger COPD attacks by causing the lungs to become irritated and inflamed. However, around 30% of exacerbations have an unknown cause. 3,4. Some COPD patients are more likely than others to have COPD attacks, for reasons that are not understood. Patients who have two or more COPD attacks in ...
How to treat COPD?
Treating your COPD can greatly improve your quality of life. Treatment options that your doctor may consider include: 1 Quitting smoking. For people who smoke, the most important aspect of treatment is to stop smoking. 2 Avoiding tobacco smoke and other air pollutants at home and at work. 3 Medication. Symptoms such as coughing or wheezing can be treated with medication. 4 Pulmonary rehabilitation, a personalized treatment program that teaches you how to manage your COPD symptoms to improve quality of life. Plans may include learning to breathe better, how to conserve your energy, and advice on food and exercise. 5 Avoiding lung infections. Lung infections can cause serious problems in people with COPD. Certain vaccines, such as flu and pneumonia vaccines, are especially important for people with COPD. Learn more about vaccination recommendations. Respiratory infections should be treated with antibiotics, if appropriate. 6 Supplemental oxygen from a portable oxygen tank may be needed if blood oxygen levels are low.
How many people have COPD?
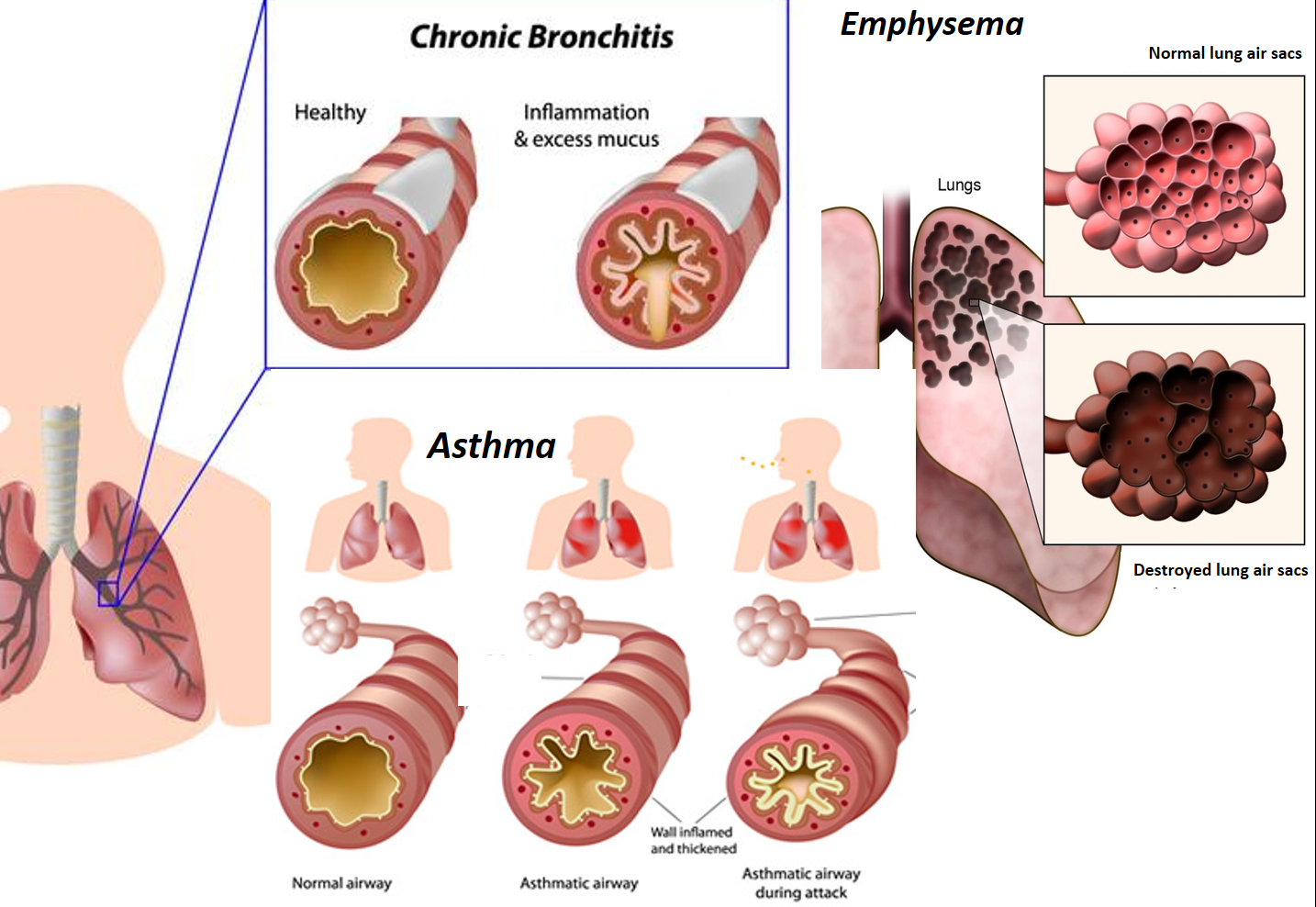
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), which includes emphysema and chronic bronchitis, makes breathing difficult for the 16 million Americans who have been diagnosed with COPD. Millions more suffer from COPD, but have not been diagnosed and are not being treated.
What is pulmonary rehabilitation?
Pulmonary rehabilitation, a personalized treatment program that teaches you how to manage your COPD symptoms to improve quality of life. Plans may include learning to breathe better, how to conserve your energy, and advice on food and exercise. Avoiding lung infections.
Can COPD cause lung infections?
Lung infections can cause serious problems in people with COPD. Certain vaccines, such as flu and pneumonia vaccines, are especially important for people with COPD. Learn more about vaccination recommendations. Respiratory infections should be treated with antibiotics, if appropriate.
Can you get COPD from smoking?
Could you have COPD? The main cause of COPD is tobacco smoke, so if you smoke or used to smoke, you are at a higher risk of having COPD. Exposure to air pollution in the home or at work, family history, and respiratory infections like pneumonia also increase your risk.
What is COPD exacerbation?
What is a COPD exacerbation? A person with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) experiences long-term, progressive damage to their lungs. This affects airflow to the lungs. Doctors sometimes call this condition emphysema or chronic bronchitis.
How many exacerbations of COPD are there in a year?
This is known as an acute exacerbation. They may need to seek medical help at a hospital. The average person with COPD has between 0.85 and 1.3 exacerbations a year.
How does COPD affect you?
depression, as having COPD can affect your ability to do things you enjoy. heart problems, such as heart disease and an increased risk of heart attack. pulmonary arterial hypertension, or high blood pressure in the arteries of the lungs. lung cancer, as those with COPD often were or are smokers.
How many stages of COPD are there?
Doctors classify COPD into four stages, from Group A to Group D. Group A has fewer symptoms and a low risk of exacerbations, while Group D has more symptoms and a higher risk of exacerbations. Because the condition is chronic, you may progress through each of the stages. However, this usually occurs over many years.
Why do people with COPD have difficulty breathing?
A person with COPD has more difficulty making this exchange because their lungs don’t work as well. This could lead to a buildup of carbon dioxide and reduced oxygen levels.
What does it mean when you cough?
coughing. experiencing shortness of breath at rest or with minimal activity, such as walking from one room to another. feeling excessively sleepy or confused. having lower oxygen levels than normal. noticing increasing amounts of mucus, which is often yellow, green, tan, or even blood-tinged. wheezing more than usual.
What happens if you have too much carbon dioxide?
Symptoms of too much carbon dioxide in your body include: confusion. severe headache. difficulty walking even short distances. having a hard time catching your breath.
What is COPD in medical terms?
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) is a progressive respiratory disease characterized by inflammation and structural changes leading to decreased airflow. The most common symptoms of COPD include chronic cough, dyspnea, and sputum production. The disease includes emphysema and obstructive bronchiolitis. Chronic bronchitis may be present in patients with COPD, but it is considered to be a separate disease state. COPD affects millions of patients in the United States and exacerbations account for a significant proportion of healthcare expenditures each year.
Can you take antibiotics for AecoPD?
Antibiotics are not recommended for all patients with AECOPD as bacterial infection is implicated in less than one-third of AECOPD. Procalcitonin (PCT) may be helpful in determining if antibiotics are necessary or the duration of treatment. All antibiotic dosages listed below are based on normal renal and hepatic function. The typical duration of therapy for AECOPD is 5 days.
Is AECOPD a preventative antibiotic?
As bacteria are known to cause exacerbations, there have been several trials conducted to determine if preventative antibiotics could decrease the exacerbation frequency and define the population that might derive greatest benefit from such therapy. Azithromycin has been studied as it has shown benefit in other pulmonary conditions.
How to control COPD?
Controlling your COPD symptoms as best you can. This includes: Not smoking. Taking your medications as directed by your doctor or nurse. Attending regular check-ups to make sure your COPD is well controlled. See the separate leaflet called Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) for further information.
When should antibiotics be used for COPD?
Antibiotics should only be used if there is any evidence of a bacterial infection. You should act quickly as soon as you realise that your symptoms are getting any worse. Most people with COPD are given a treatment plan to follow if the symptoms get any worse.
What is an acute exacerbation of COPD?
An acute exacerbation is more commonly known as a 'flare-up'. An acute exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a sudden worsening of COPD symptoms compared with the usual severity of symptoms. This often means a worsening of breathlessness and an increase in coughing, with more phlegm (sputum).
How old do you have to be to get COPD?
COPD symptoms are usually difficult to spot at first. Most people are not diagnosed until they are 50 years of age or older. The number of people with COPD increases with their age and varies significantly by area of the country.
What causes a person to have difficulty breathing?
Exacerbations of COPD can cause: Increased breathlessness and difficulty with breathing - being less able to do any physical exercise or do your usual daily activities. Increased cough. Increased amount of phlegm (sputum) and a change in colour of the sputum. This may become green or dirty brownish.
Can you take antibiotics for chest infection?
You should only take a course of an antibiotic medicine if your sputum changes colour or if your doctor thinks you may have a chest infection. A sample of your sputum is usually sent to the hospital microbiology laboratory to check whether you are taking the right antibiotic for your infection.
What does it mean when you feel drowsy?
Increased wheeze heard from your chest. Feeling very tired and generally unwell. Severe exacerbations of COPD may cause a bluish colour (cyanosis) in your lips and tongue and make you feel drowsy and confused.
What happens when you have COPD?
During a COPD exacerbation, your airway and lung functions change quickly and dramatically. You may suddenly experience more mucus clogging your bronchial tubes, or the muscles around your airways may constrict significantly, cutting off your air supply. Symptoms of a COPD flare are: or shortness of breath.
How to manage a flare?
It likely outlines specific actions, doses, or medications around these steps to manage a flare. 1. Use a quick-acting inhaler. Relief or rescue inhalers work by sending a powerful stream of medicine straight to your constricted lungs.
Can you take oxygen during a COPD flare?
If you use supplemental oxygen at home, you may want to take advantage of the supply during a flare. It’s best to follow the COPD action plan designed by your doctor and attempt to relax to control your breathing while you’re breathing in oxygen.
What does it mean when you can't breathe?
or shortness of breath. Either feeling like you can’t. breathe deeply or gasping for air. Increase. in coughing attacks. Coughing helps to. rid your lungs and airways of blockages and irritants. Wheezing. Hearing a wheeze or whistling noise when you breathe means that air is being.
How long do corticosteroids last?
If you don’t already include them in your treatment plan, your doctor may prescribe corticosteroids for a week or more after a flare to help get the inflammation under control.
Can oxygen therapy help with exacerbation?
In some situations, rescue medication, anti-inflammatory steroids, and oxygen therapy won’t bring your exacerbation symptoms back down to a manageable state. In this instance, you may need a machine to help you breathe through a process known as a mechanical intervention.
What does it mean when you hear a wheeze?
Hearing a wheeze or whistling noise when you breathe means that air is being. forced through a narrower passageway. Increase. of mucus. You may begin to cough up more mucus, and it may be a different. color than usual. Fatigue. or sleep problems. Sleep disturbances or exhaustion.
How to treat COPD?
If you’re living with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, you can control it with the help of the right kind of food, exercise, and plenty of sleep . No matter how careful you are, though, your COPD may act up from time to time. When you have a flare-up like this, you may hear a doctor or nurse call this an ...
How to stop COPD?
Avoid secondhand smoke. And if you smoke -- the cause behind many cases of COPD -- ask your doctor for help in quitting. Be careful outdoors. If cold air bothers you, pull up your scarf around your mouth and nose, and breathe through your nose. During hot, humid weather, stay inside with air conditioning.
How to know if you have a COPD flare up?
Awareness is key with COPD flare-ups. You know how you feel on a typical day with your breathing and how much you cough. If you get an infection in your lungs or if something else irritates them -- secondhand smoke, for instance -- you might be headed for a flare-up.
How to prevent a flare up in the lungs?
Start with your lifestyle, because a healthier body has the best chance to fight off germs. Eat nutritious food. Exercise. Get plenty of sleep.
How to tell if you have a flare up?
Signs of a COPD Flare-up. You might be more short of breath or wheeze and cough more than you usually do. Other symptoms include: Fatigue. Fever. Scratchy throat or other signs of a cold. Coughing up more mucus than usual, or it turns green, tan, or bloody. Swollen ankles.
What is the difference between Salmeterol and Fluticasone?
Aminophylline can be used for mild to moderate cases of acute asthma. Salmeterol is a long-acting beta 2 agonist that is indicated for maintenance treatment , not acute episodes. Fluticasone is an inhaled corticosteroid; montelukast is a leukotriene receptor antagonist (LTRA).
Is Advair a long acting inhaler?
In combination, they are used for the maintenance treatment of asthma and COPD. As a long-acting inhaler, Advair is not appropriate for treatment of acute bronchospasms. The other statements are incorrect. The nurse is reviewing medications for the treatment of asthma.
Can you use a spacer with a metered dose inhaler?
ANS: CThe use of a spacer may be indicated with metered-dose inhalers, especially if success with inhalation is limited. The other options are not appropriate interventions. The nurse is providing instructions about the Advair inhaler (fluticasone propionate and salmeterol).

Diagnosis
Treatment
Clinical Trials
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
Specialist to consult
Coping and Support
Preparing For Your Appointment
- Many people with COPDhave mild forms of the disease for which little therapy is needed other than smoking cessation. Even for more advanced stages of disease, effective therapy is available that can control symptoms, slow progression, reduce your risk of complications and exacerbations, and improve your ability to lead an active life.