Medication
The main treatment for most types of AML is chemotherapy, sometimes along with a targeted therapy drug. This might be followed by a stem cell transplant. Other drugs (besides standard chemotherapy drugs) may be used to treat people with acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL).
Procedures
Mar 16, 2022 · Most patients with AML who undergo intensive therapy are treated with an anthracycline. Anthracyclines have been associated with increased risk of congestive heart failure (CHF). [ 9] Anthracycline cardiotoxicity is dose-dependent.
Self-care
The goals of treatment for patients diagnosed with AML are: Cure The goal of induction therapy is remission. Patients who are in remission should be treated with post-remission therapy 4 AML has a greater chance of being cured in younger patients than in older patients 5 Palliation 6
Nutrition
Feb 22, 2021 · Progress in the understanding of the biology and therapy of acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is occurring rapidly. Since 2017, nine agents have been approved for various indications in AML. These included several targeted therapies like venetoclax, FLT3 inhibitors, IDH inhibitors, and others.
What are the current treatment options for AML?
How Is Leukemia Treated? The types of treatment used most often to treat childhood cancer are: Surgery Chemotherapy Radiation therapy Bone marrow transplantation The goal of treatment is to destroy the cancer cells.
Can AML leukemia be cured?
Dec 09, 2021 · Most people with AML receive chemotherapy treatments. These medications rapidly kill dividing cells, such as cancer cells. Chemotherapy can lead to remission, which means a person doesn’t have...
What is the natural cure for leukemia?
Many new and better treatments for AML have become available in recent years. So the prognosis for people diagnosed with AML today is likely better. In fact, treatment advances have almost doubled the 5-year survival rate for leukemias as a combined group.
What would be the most likely treatment for leukemia?
See more
Can you be cured from AML leukemia?
Although AML is a serious disease, it is treatable and often curable with chemotherapy with or without a bone marrow/stem cell transplant (see the Types of Treatment section). It is important to remember that statistics on the survival rates for people with AML are an estimate.
How long is treatment for AML leukemia?
Treatment for AML is a long-term process. Chemotherapy and other treatment for the disease may take 6 to 12 months to complete. Some, but not all, patients are eligible for induction therapy.
How long do you live with AML leukemia?
The 5-year overall survival rate for AML is 29.5 percent , according to the National Cancer Institute (NCI). This means that an estimated 29.5 percent of people in America living with AML are still living 5 years after their diagnosis.
What is the latest treatment for acute myeloid leukemia?
The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) recently approved two new treatments for some adult patients with acute myeloid leukemia (AML): enasidenib (Idhifa®), a drug that targets aberrant forms of the IDH2 protein; and liposomal cytarabine-daunorubicin CPX-351 (Vyxeos™), a two-drug chemotherapy combination encapsulated ...Aug 28, 2017
How many rounds of chemo is normal for AML?
Most people have 2 rounds of induction chemotherapy. The treatment will be carried out in hospital or in a specialist centre, as you'll need very close medical and nursing supervision. You may be able to go home between treatment rounds.
Why is AML so hard to treat?
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML): the pervasive aggressor Generally a disease impacting older people, the average age of an AML patient is 68 at the time of diagnosis. Because it's so aggressive, treatment for AML is considered harder on the body, especially for older patients with other health challenges.Apr 19, 2018
Is AML the worst leukemia?
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is a cancer of the blood and bone marrow. It is the most common type of acute leukemia in adults. This type of cancer usually gets worse quickly if it is not treated.Mar 4, 2022
Can you live 20 years with leukemia?
Most people live for about 10 years, but this varies depending on how CLL behaves. People in stages 0 to II may live for 5 to 20 years without treatment. CLL has a very high incidence rate in people older than 60 years.Nov 16, 2021
Is AML a death sentence?
AML is one of the more common types of leukemia among adults and is rarely diagnosed in people under age 40. As Dr. Wang explains in this video, AML is no longer considered a death sentence.Jun 1, 2020
Is AML painful?
Bone or joint pain Some people with AML have bone pain or joint pain caused by the buildup of leukemia cells in these areas.Aug 21, 2018
What are the end stage symptoms of AML?
What are the symptoms of the final stages of AML?cool, dry skin.slow or labored breathing.blurry vision.decreased urination or incontinence.restlessness or involuntary muscle movements.decreased movements or weakness.loss of appetite and decreased fluid intake.increased drowsiness and sleepiness.More items...•Nov 23, 2021
How is AML treated in the elderly?
Current therapeutic options for elderly individuals with AML include intensive chemotherapy with a cytarabine and anthracycline backbone, hypomethylating agents (decitabine and azacitidine), low-dose cytarabine, investigational agents, and supportive care with hydroxyurea and transfusions.Dec 5, 2014
How long does it take for leukemia to go down?
This is called leukostasis. Chemo can take a few days to lower the number of leukemia cells in the blood.
What is APL post remission?
Consolidation (post-remission therapy) The acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL) subtype of AML is treated differently. Treatment for AML usually needs to start as quickly as possible after it is diagnosed because it can progress very quickly. Sometimes another type of treatment needs to be started even before the chemo has had a chance to work.
What happens when blood cells recover from leukemia?
When the blood cell counts recover, the doctor will again check cells in a bone marrow sample to see if the leukemia is in remission. Remission induction usually does not destroy all the leukemia cells, and a small number often remain.
How long does it take for blood count to go down after chemo?
Blood counts tend to stay low for a few weeks. About a week after chemo is done, the doctor will do a bone marrow biopsy. It should show few bone marrow cells ( hypocellular bone marrow) and only a small portion of blasts (making up no more than 5% of the bone marrow) for the leukemia to be considered in remission.
How old do you have to be to get chemo?
How intense the treatment is can depend on a person’s age and health. Doctors often give the most intensive chemo to people under the age of 60, but some older patients in good health may benefit from similar or slightly less intensive treatment.
Can you take midostaurin with chemo?
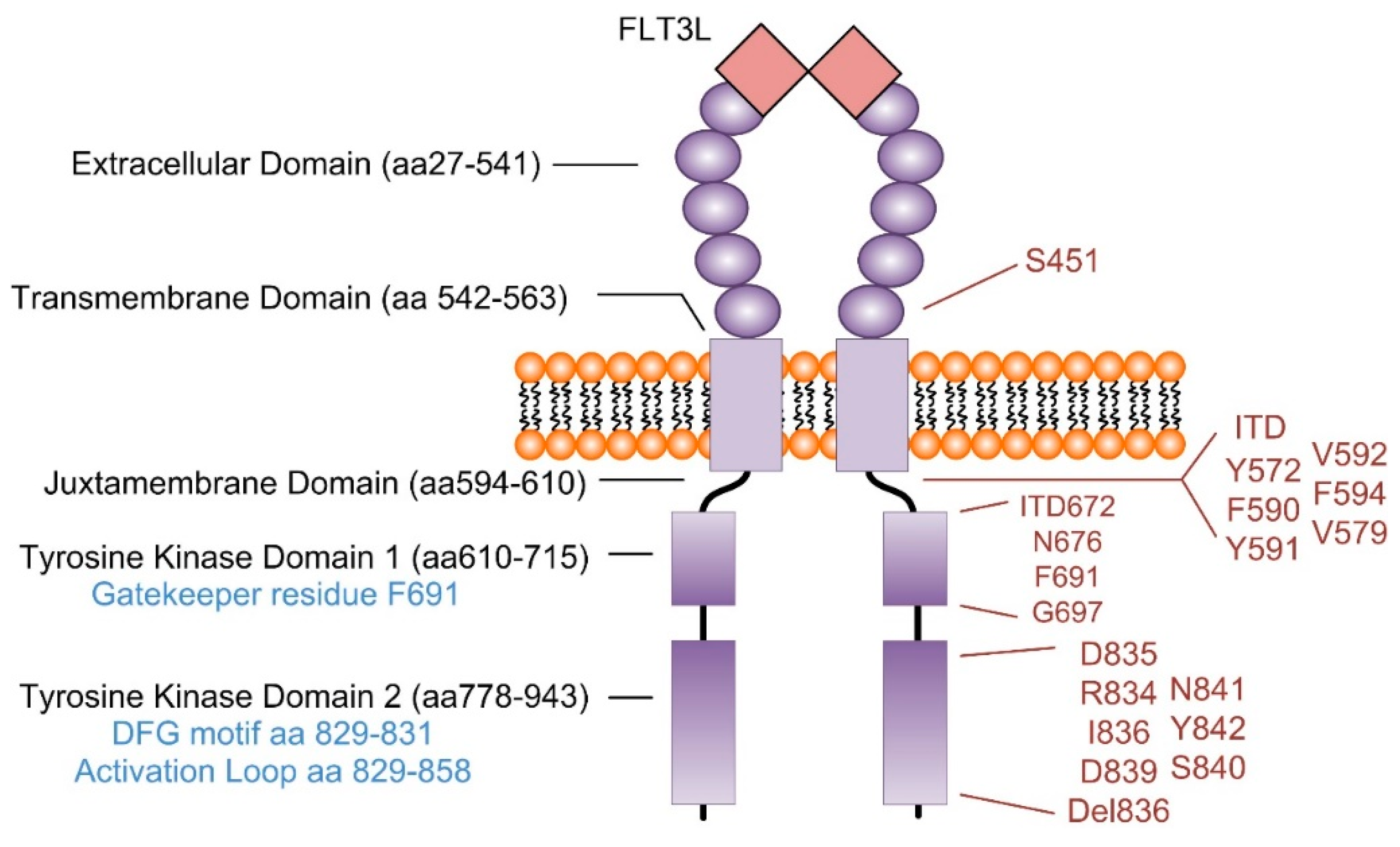
For patients whose leukemia cells have an FLT3 gene mutation, the targeted therapy drug midostaurin (Rydapt) might be given along with chemo. This drug is taken twice daily as a pill. For patients whose leukemia cells have the CD33 protein, the targeted drug gemtuzumab ozogamicin (Mylotarg) might be added to chemo.
Should stem cells be given for leukemia?
Still others feel that stem cell transplants should be given if the leukemia is likely to come back based on certain gene or chromosome changes. Research in this area continues to study which AML patients get the most benefit from stem cell transplant and which type of transplant is best in each situation.
What is the treatment for AML?
The main treatment for most types of AML is chemotherapy, sometimes along with a targeted therapy drug. This might be followed by a stem cell transplant. Other drugs (besides standard chemotherapy drugs) may be used to treat people with acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL). Surgery and radiation therapy are not major treatments for AML, ...
What do people with cancer need?
People with cancer need support and information, no matter what stage of illness they may be in. Knowing all of your options and finding the resources you need will help you make informed decisions about your care.
Why is it important to discuss all of your treatment options?
It’s important to discuss all of your treatment options and their goals and possible side effects, with your treatment team to help make the decision that best fits your needs. Some important things to consider include:
What kind of doctor treats cancer?
Based on your treatment options, you may have different types of doctors on your treatment team. These doctors could include: 1 A hematologist: a doctor who treats disorders of the blood 2 A medical oncologist: a doctor who treats cancer with medicines
What is complementary medicine?
Complementary methods refer to treatments that are used along with your regular medical care. Alternative treatments are used instead of a doctor’s medical treatment.
What are the services offered by the American Cancer Society?
These might include nursing or social work services, financial aid, nutritional advice, rehab, or spiritual help. The American Cancer Society also has programs and services – including rides to treatment, lodging, and more – to help you get through treatment.
Can AML be treated?
In most cases AML can progress quickly if not treated, so it's important to start treatment as soon as possible after the diagnosis is made.
What is AML classification?
The classification of acute myeloid leukemia (AML) has been revised by a group of pathologists and clinicians under the auspices of the WHO. [ 1] While elements of the French-American-British (FAB) classification have been retained (i.e., morphology, immunophenotype, cytogenetics, and clinical features), [ 2, 3] the WHO classification incorporates and interrelates morphology, cytogenetics, molecular genetics, and immunologic markers, which construct a classification that is universally applicable and has prognostic and therapeutic relevance. [ 1, 3, 4] Each criterion has prognostic and treatment implications but, for practical purposes, initial antileukemic therapy is similar for all subtypes.
What is myelodysplasia in AML?
AML with myelodysplasia-related features is characterized by 20% or more blasts in the blood or bone marrow and dysplasia in two or more myeloid cell lines, generally including megakaryocytes. [ 5] To make the diagnosis, dysplasia must be present in 50% or more of the cells of at least two lineages and must be present in a pretreatment bone marrow specimen or must have the presence of an MDS-related cytogenetic abnormality. [ 5] AML with myelodysplasia-related features may occur de novo or after MDS or a myelodysplastic/myeloproliferative neoplasm overlap. (Refer to the PDQ summaries on Myelodysplastic Syndromes Treatment and Myelodysplastic/Myeloproliferative Neoplasms Treatment for more information.) The diagnostic terminology AML with myelodysplasia-related features evolving from a myelodysplastic syndrome should be used when an MDS precedes AML. [ 5] In the presence of a mutation in NPM1 or biallelic mutations of CEBPA, the presence of multilineage dysplasia alone will not classify a case as AML with myelodysplasia-related changes. [ 5]
What is a myeloid sarcoma?
Myeloid sarcoma (also known as extramedullary myeloid tumor, granulocytic sarcoma, and chloroma) is a tumor mass that consists of myeloblasts or immature myeloid cells, occurring in an extramedullary site. [ 5] Development of myeloid sarcoma has been reported in 2% to 8% of patients with AML. [ 77] Clinical features include occurrence common in subperiosteal bone structures of the skull, paranasal sinuses, sternum, ribs, vertebrae, and pelvis; lymph nodes, skin, mediastinum, small intestine, and the epidural space; and occurrence de novo or concomitant with AML or a myeloproliferative disorder. [ 10, 77, 78]
What is a T-MN?
Therapy-related myeloid neoplasms (t-MN) include AML (t-AML) and MDS (t-MDS) that arise secondary to cytotoxic chemotherapy and/or radiation therapy. [ 5] The therapy-related (or secondary) MDS are included because of their close clinicopathologic relationships to therapy-related AML. Although these therapy-related disorders can be distinguished by the specific mutagenic agents involved, this distinction may be difficult to make because of the frequent overlapping use of multiple potentially mutagenic agents in treating cancer. [ 68] Because the associated cytogenetic abnormality, not the mutagenetic agent, determines prognosis and treatment it should be noted in the diagnosis. [ 10]
What translocation produces RBM15-MKL1?
The t (1;22) (p13;q13) translocation that produces RBM15-MKL1 is an uncommon driver of pediatric AML (<1% of pediatric AML) and is restricted to acute megakaryocytic leukemia. (Refer to the PDQ summary on Childhood Acute Myeloid Leukemia/Other Myeloid Malignancies Treatment for more information.)
What is acute leukemia?
Acute leukemias of ambiguous lineage are rare types of acute leukemia in which the morphologic, cytochemical, and immunophenotypic features of the blast population do not allow classification in myeloid or lymphoid categories; or the types have morphologic and/or immunophenotypic features of both myeloid and lymphoid cells or both B and T lineages (i.e., acute bilineal leukemia and acute biphenotypic leukemia). [ 10, 83, 84]
How long does it take for mutagenic agents to cause acute leukemia?
The alkylating agent/radiation-related acute leukemias and myelodysplastic syndromes typically occur 5 to 6 years after exposure to the mutagenic agent, with a reported range of approximately 10 to 192 months. [ 70, 71] The risk of occurrence is related to both the total cumulative dose of the alkylating agent and the age of the patient.
What is leukemia in the body?
What Is Leukemia (ALL and AML)? Leukemia is cancer of the tissues of the body which make the blood cells and the bone marrow. When leukemia strikes, the body makes an abundance of abnormal white cells that do not perform their proper functions. They invade the marrow and crowd out the normal healthy blood cells, ...
What is the most common type of childhood leukemia?
There are two main types of childhood leukemia: Acute lymphocytic leukemia (ALL) Acute myelocytic leukemia (AML) ALL accounts for 80 percent of all leukemia in children and AML accounts for 20 percent.
How does chemotherapy work?
Chemotherapy drugs slow or stop cancer cells from growing and making more abnormal cells. While these drugs may affect normal healthy cells, these can repair and return to normal. Radiation Therapy is the treatment of cancer and other diseases with high-energy rays to damage or destroy cancer cells.
What is the best treatment for childhood cancer?
The types of treatment used most often to treat childhood cancer are: Surgery. Chemotherapy. Radiation therapy. Bone marrow transplantation. The goal of treatment is to destroy the cancer cells. Your child may have one kind of treatment or a combination of treatments and may have to have a variety of tests and procedures during treatment.
What is clinical trial?
A clinical trial is a research study in which physicians find ways to improve cancer treatment. The goals of these studies are to answer scientific questions about preventing, diagnosing and treating cancer. A clinical trial for cancer treatment occurs in three phases.
What is the treatment for AML?
Most people with AML receive chemotherapy treatments. These medications rapidly kill dividing cells, such as cancer cells. Chemotherapy can lead to remission, which means a person doesn’t have symptoms of the disease and their blood cell counts are in a normal range.
What is the prognosis for AML?
The outlook and prognosis for AML varies widely. Doctors consider many factors when giving someone a prognosis, such as the person’s age or type of AML. Much of it is based on the outcomes and analysis of blood tests, imaging studies, cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) examinations, and bone marrow biopsies.
What is AML in medical terms?
What is acute myeloid leukemia (AML)? Acute myeloid leukemia, or AML, is a type of cancer that affects the bone marrow and blood. It’s known by a variety of names, including acute myelogenous leukemia and acute non-lymphocytic leukemia. AML is the second most common leukemia type in adults. Doctors call AML “ acute ” because ...
Why is AML called acute?
Doctors call AML “ acute ” because the condition can progress rapidly. The term “ leukemia ” refers to cancers of the bone marrow and blood cells. The word myeloid, or myelogenous, refers to the cell type it affects. Myeloid cells are precursors to other blood cells.
How many people go into remission after chemo?
Around 90 percent of people with an AML type known as acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL) will go into remission after “induction” (first round) of chemo. This is according to the American Cancer Society (ACS). For most other types of AML, the remission rate is around 67 percent.
What are some examples of AML?
Some cell mutation types are known to be more responsive to treatments. Examples include mutated CEBPA and inv (16) CBFB-MYH11 cells. Some cell mutations can be very treatment-resistant.
How long does it take for AML to go away?
Some people who go into remission stay in remission. Still, for many, AML can return over time. The five-year overall survival rate for AML is 27.4 percent. Trusted Source. , according to the National Cancer Institute (NCI).
How to diagnose AML?
Your prognosis depends mainly on: 1 The subtype of AML 2 Your age and overall health 3 Your health history (such as if you've had a blood disease or have had chemotherapy for another cancer in the past) 4 Gene or chromosome changes in the leukemia cells 5 If you have a very high white blood cell (WBC) count at diagnosis (greater than 100,000) 6 If there are leukemia cells in your brain and spinal cord (called CNS or central nervous system involvement). This is very rare. 7 If you have a bad infection when you're diagnosed 8 How well your leukemia responds to treatment
What does a doctor look for in AML?
Your doctor will look at risk estimates about the exact type of leukemia you have. These estimates are based on what results researchers have seen over decades in many people with the same type of leukemia. If your AML is likely to respond well to treatment, your doctor will say you have a favorable prognosis.
What is the subtype of AML?
The subtype of AML. Your age and overall health. Your health history (such as if you've had a blood disease or have had chemotherapy for another cancer in the past) Gene or chromosome changes in the leukemia cells. If you have a very high white blood cell (WBC) count at diagnosis (greater than 100,000)
How long do you live after cancer diagnosis?
Most often, the numbers used refer to the 5-year survival rate. That’s how many people live at least 5 years after being diagnosed.
Can leukemia shorten your life?
If your leukemia is likely to be hard to control, your prognosis may be less favorable. In this case, the leukemia may shorten your life. It’s important to keep in mind that a prognosis states what’s likely or probable. It is not a prediction of what will definitely happen. No doctor can be fully certain about an outcome.
Treating Leukostasis
Induction
Consolidation
Treating Frail Or Older Adults
Specialist to consult
What Is AML?
- Some people with AML have very high numbers of leukemia cells in their blood when they are first diagnosed, which can cause problems with normal blood circulation. This is called leukostasis. Chemo can take a few days to lower the number of leukemia cells in the blood. In the meantime, leukapheresis (sometimes just called pheresis) might be used be...
What Influences Aml Survival Rate?
- This first phase of treatment is aimed at quickly getting rid of as many leukemia cells as possible. How intense the treatment is can depend on a person’s age and health. Doctors often give the most intensive chemo to people under the age of 60, but some older patients in good health may benefit from similar or slightly less intensive treatment. People who are much older or are in poo…
Coping and Support
- Induction is considered successful if remission is achieved. Further treatment (called consolidation) is then given to try to destroy any remaining leukemia cells and help prevent a relapse.
Summary
- Treatment of AML in people under 60 is fairly standard. It involves cycles of intensive chemo, sometimes along with a stem cell transplant (as discussed above). Many patients older than 60 are healthy enough to be treated in the same way, although sometimes the chemo may be less intense. People who are much older or are in poor health may not be able to tolerate this intens…
A Word from Verywell
- AML is a type of cancer of the body’s blood cells. The blood contains multiple types of cells, including red blood cells (which carry oxygen to the body’s tissues) and white blood cells(which fight off invaders). These cells are made in the spongy tissue inside the bones, called bone marrow. Our bodies continually make them by stem cells that are constantly dividing and maturi…