
Medication
Top 7 Natural Treatments for Alzheimer Disease
- Seeds Containing Lots of Essential Nutrients. The intake of certain seeds such as sesame seeds, pumpkin seeds and sunflower seeds. ...
- Turmeric. Turmeric is a common household spice. ...
- Ashwagandha Herb. ...
- Gotukola Herb. ...
- Sesame Oil. ...
- Green Leafy Vegetables. ...
- Fatty Acids. ...
Self-care
Options include:
- Aripiprazole (Abilify)
- Brexpiprazole ( Rexulti)
- Haloperidol ( Haldol)
- Olanzapine ( Zyprexa)
See more
How to care for someone with Alzheimer's disease
- Learn about Alzheimer's disease. Alzheimer's symptoms worsen as the disease progresses, which brings new challenges for caregivers. ...
- Create a routine. Caregivers can help someone feel more comfortable by establishing a constant daily routine. ...
- Plan activities. ...
- Promote ongoing communication. ...
- Help them eat a nutritious diet. ...
- Boost their self-esteem. ...
What are some natural remedies for Alzheimers?
As not everyone with Alzheimer’s will experience the disease the same way, treatment plans might look different as well. Although there is no cure right now, finding a cure for Alzheimer’s disease and a treatment that stops disease progression is an active area of biomedical research. Available treatments for Alzheimer's
What therapies are used to treat Alzheimer's disease?
How to help care for someone with Alzheimer's disease?
Is there a cure for Alzheimer's?
See more
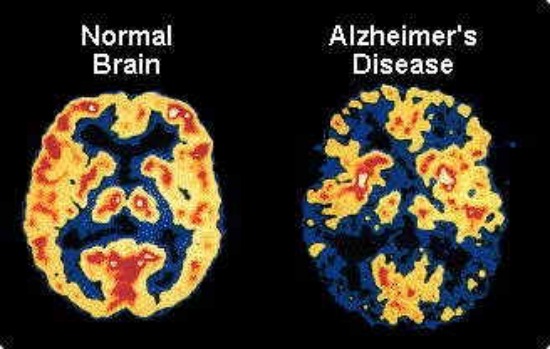
What are 3 treatments for Alzheimer's?
Three cholinesterase inhibitors are commonly prescribed:Donepezil (Aricept) is approved to treat all stages of the disease. It's taken once a day as a pill.Galantamine (Razadyne) is approved to treat mild to moderate Alzheimer's. ... Rivastigmine (Exelon) is approved for mild to moderate Alzheimer's disease.
Is there any treatment for Alzheimer's?
There's currently no cure for Alzheimer's disease. But there is medicine available that can temporarily reduce the symptoms. Support is also available to help someone with the condition, and their family, cope with everyday life.
What is the standard treatment for Alzheimer's?
There are three drugs of this type: donepezil (Aricept), galantamine (Razadyne), and rivastigmine (Exelon). Aricept is the only treatment approved by the FDA for all stages of Alzheimer's disease: mild, moderate, and severe.
How Alzheimer's treatment works?
Donepezil, rivastigmine and galantamine all prevent an enzyme called acetylcholinesterase from breaking down acetylcholine. This means there is a higher concentration of acetylcholine in the brain, which leads to better communication between nerve cells. This may ease some symptoms of Alzheimer's disease for a while.
How is Alzheimer's treated early?
Although Alzheimer disease has no cure, you can make the best of a bad situation by keeping your mind and your body as healthy as possible. This can include eating a healthy diet, getting regular exercise, cutting down on alcohol, and using relaxation techniques to reduce stress.
What are the 10 warning signs of Alzheimer's?
Ten Warning Signs of Alzheimer's DiseaseMemory loss. ... Difficulty performing familiar tasks. ... Problems with language. ... Disorientation to time and place. ... Poor or decreased judgment. ... Problems with abstract thinking. ... Misplacing things. ... Changes in mood or behavior.More items...
Can Alzheimer's go away?
There's no cure for Alzheimer's, but there are treatments that may change disease progression, and drug and non-drug options that may help treat symptoms. Understanding available options can help individuals living with the disease and their caregivers to cope with symptoms and improve quality of life.
What is the life expectancy of someone with Alzheimer's?
The symptoms of Alzheimer's disease worsen over time, although the rate at which the disease progresses varies. On average, a person with Alzheimer's lives four to eight years after diagnosis, but can live as long as 20 years, depending on other factors.
Can Alzheimer cause death?
Alzheimer's disease is ultimately a fatal form of dementia. It is the sixth leading cause of death in the United States, accounting for almost 4% of all deaths in 2014.2,3 The number of Alzheimer's deaths has increased, in part, because of a growing population of older adults.
What is the main cause of Alzheimer's disease?
Alzheimer's disease is thought to be caused by the abnormal build-up of proteins in and around brain cells. One of the proteins involved is called amyloid, deposits of which form plaques around brain cells. The other protein is called tau, deposits of which form tangles within brain cells.
What's the difference between dementia and Alzheimer's?
Dementia is a general term for a decline in mental ability severe enough to interfere with daily life. Alzheimer's is the most common cause of dementia. Alzheimer's is a specific disease. Dementia is not.
How is Alzheimer's diagnosed?
To diagnose Alzheimer's dementia, doctors conduct tests to assess memory impairment and other thinking skills, judge functional abilities, and identify behavior changes. They also perform a series of tests to rule out other possible causes of impairment.
What are the plaques in Alzheimer's?
Plaques are a characteristic sign of Alzheimer's disease. Strategies aimed at beta-amyloid include: Recruiting the immune system. Several drugs — known as monoclonal antibodies — may prevent beta-amyloid from clumping ...
What is the acronym for the Coalition against Major Diseases?
To help accelerate discovery, the Coalition Against Major Diseases (CAMD), an alliance of pharmaceutical companies, nonprofit foundations and government advisers, has forged a first-of-its-kind partnership to share data from Alzheimer's clinical trials.
What are the strategies under investigation?
Strategies under investigation include: Current drugs for heart disease risk factors. Researchers are investigating whether drugs such as blood pressure medications now used to treat vascular disease may also be beneficial for people with Alzheimer’s or may reduce the risk of developing dementia.
What is the drug used to treat Alzheimer's disease?
Researchers are studying ways to treat inflammatory processes at work in Alzheimer's disease. The drug sargramostim (Leukine) is currently in research. It's thought that the drug may stimulate the immune system to protect the brain from harmful proteins.
What is the best way to reduce beta-amyloid?
Production blockers. These therapies may reduce the amount of beta-amyloid formed in the brain. Research has shown that beta-amyloid is produced from a "parent protein" in two steps performed by different enzymes. Several experimental drugs aim to block the activity of these enzymes.
Is Donanemab a monoclonal antibody?
Donanemab is another monoclonal antibody that showed promise in phase 2 trials and is moving into phase 3. In studies, the monoclonal antibody solanezumab did not demonstrate any benefit for individuals with mild or moderate Alzheimer's disease. It's possible that solanezumab may be more effective when given earlier in the course of the disease. ...
Is lecanemab approved by the FDA?
Experts also need to identify which patients may benefit from the drug. The monoclonal antibody lecanemab shows promise in removing amyloid and has moved into phase 3 clinical trials.
When is Alzheimer's Awareness Month?
June is Alzheimer’s & Brain Awareness Month — the perfect time to join the fight to end Alzheimer’s. Help us provide compassionate care and support and advance critical research with a generous gift today.
Is there a cure for Alzheimer's?
There's no cure for Alzheimer’s, but one treatment may potentially delay decline from the disease, and there are drug and non-drug options that may help treat symptoms. Understanding available options can help individuals living with the disease and their caregivers to cope with symptoms and improve quality of life.
How to help someone with memory loss?
If you're worried about memory loss or related symptoms, ask a close relative or friend to go with you to a doctor's appointment. In addition to providing support, your partner can provide help in answering questions.
How to help a patient with constipation?
Regular exercise is an important part of a treatment plan. Activities such as a daily walk can help improve mood and maintain the health of joints, muscles and the heart. Exercise can also promote restful sleep and prevent constipation — and it's beneficial for care partners, too.
How to support a person's sense of well-being and continued ability to function?
You can take these steps to support a person's sense of well-being and continued ability to function: Always keep keys, wallets, mobile phones and other valuables in the same place at home, so they don't become lost. Keep medications in a secure location. Use a daily checklist to keep track of dosages.
What are some ways to prevent Alzheimer's?
Alternative medicine. Various herbal remedies, vitamins and other supplements are widely promoted as preparations that may support cognitive health or prevent or delay Alzheimer's. Clinical trials have produced mixed results with little evidence to support them as effective treatments.
What is the purpose of a CT scan?
A CT scan, a specialized X-ray technology, produces cross-sectional images (slices) of your brain. It's usually used to rule out tumors, strokes and head injuries. Imaging of disease processes can be performed with positron emission tomography (PET).
How to help someone with Alzheimer's?
For someone with Alzheimer's, establishing and strengthening routine habits and minimizing memory-demanding tasks can make life much easier .
What is FDG in a PET scan?
Fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) PET scans show areas of the brain in which nutrients are poorly metabolized. Identifying patterns of degeneration — areas of low metabolism — can help distinguish between Alzheimer's disease and other types of dementia. Amyloid PET imaging can measure the burden of amyloid deposits in the brain.
What are the side effects of a syringe?
Common side effects are usually mild for these medications and include diarrhea, vomiting, nausea, fatigue, insomnia, loss of appetite, and weight loss. There are three drugs of this type: donepezil ( Aricept ), galantamine ( Razadyne ), and rivastigmine ( Exelon ). Aricept is the only treatment approved by the FDA for all stages ...
How long does acetylcholine last?
They may slow down how fast symptoms get worse for about half of people who take them. The effect lasts for a limited time, on average 6 to 12 months.
What is the FDA approved drug for?
The FDA has approved the drug aducanumab-avwa (aduhelm) as the first therapy that targets the fundamental pathophysiology of the disease by reducing amyloid beta plaques in the brain. It is not without controversy because of concerns it may cause swelling of bleeding in the brain.
How to choose a treatment plan for a syphilis?
Your doctor will help you choose the best treatment based on a few things about you, including: 1 Your age, overall health, and medical history 2 How severe your disease is 3 How well a medicine or therapy will work for you and your lifestyle 4 Your preferences or those of your family or caregivers
Is Aricept a mild or severe drug?
Aricept is the only treatment approved by the FDA for all stages of Alzheimer’s disease: mild, moderate, and severe. You can take it as a tablet that you swallow or that dissolves in your mouth. Razadyne (formerly called Reminyl) is also for mild to moderate Alzheimer’s.
Does Namenda work better with Exelon?
It may improve how well the brain works and how well some people can do everyday tasks. The drug may work even better when you take it with Aricept, Exelon, or Razadyne. Namenda’s side effects include tiredness, dizziness, confusion, constipation, and headache. Namzaric. This drug is a mix of Namenda and Aricept.
Does vitamin E help with Alzheimer's?
But so far, there’s no evidence that they have any effect.
Alzheimer's Disease & Related Dementias
Current treatment approaches focus on helping people maintain mental function, manage behavioral symptoms, and slow or delay the symptoms of disease.
Next Steps After an Alzheimer's Diagnosis
Get information and resources about what to do and expect after a diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease.
How Is Alzheimer's Disease Treated?
Learn about prescription drugs and other strategies to treat the symptoms of Alzheimer's disease. Find out about medicines to avoid and take with caution.
What is the most common cause of dementia?
Alzheimer’s disease is the most common cause of dementia (accounting for 60 percent to 80 percent of cases). Alzheimer’s disease is the sixth leading cause of death in the United States. One in 10 people older than 65 and nearly half of people older than 85 have Alzheimer’s disease.
What causes Alzheimer's disease?
Alzheimer’s disease is caused by the abnormal build-up of proteins in the brain. The build-up of these proteins — called amyloid protein and tau protein — leads to cell death. The human brain contains over 100 billion nerve cells as well as other cells.
How does acetylcholinesterase work?
These drugs work by blocking the action of acetylcholinesterase, the enzyme responsible for destroying acetylcholine. Acetylcholine is one of the chemicals that helps nerve cells communicate. Researchers believe that reduced levels of acetylcholine cause some of the symptoms of Alzheimer's disease.
What is the slow and ongoing death of the nerve cells in the brain?
The slow and ongoing death of the nerve cells, starting in one area of the brain (usually in the area of the brain that controls memory) then spreading to other areas, results in the symptoms seen in patients with Alzheimer’s disease.
How does Alzheimer's affect memory?
The disease severely affects memory, thinking, learning and organizing skills and eventually affects a person’ s ability to carry out simple daily activities . Alzheimer’s disease is not a normal part of the aging process. Alzheimer’s is a disease whose symptoms worsen over time.
How long does Alzheimer's disease last?
Alzheimer’s disease gets worse over time and is ultimately fatal. Persons with Alzheimer’s disease live, on average, four to eight years after diagnosis. Some patients can live as long as 20 years after diagnosis. The course of the disease varies from person to person.
How many people will have Alzheimer's by 2050?
According to the Alzheimer's Association, with the aging of the population and without successful treatment, there will be 14 million Americans and 106 million people worldwide with Alzheimer’s disease by 2050.
Why is FDA accelerating approval important?
The FDA instituted its Accelerated Approval Program to allow for earlier approval of drugs that treat serious conditions, and that fill an unmet medical need. Approval is based on a surrogate or intermediate clinical endpoint (in this case reduction of amyloid plaque in the brain).
What is a surrogate endpoint?
A surrogate endpoint is a marker, such as a laboratory measurement, radiographic image, physical sign or other measure that is thought to predict clinical benefit but is not itself a measure of clinical benefit. The use of a surrogate endpoint can considerably shorten the time required prior to receiving FDA approval.
What is the FDA approved drug for Alzheimer's?
Today FDA approved Aduhelm (aducanumab) to treat patients with Alzheimer’s disease using the Accelerated Approval pathway, under which the FDA approves a drug for a serious or life-threatening illness that may provide meaningful therapeutic benefit over existing treatments when the drug is shown to have an effect on a surrogate endpoint ...
What is Aduhelm treatment?
Perhaps more significantly, Aduhelm is the first treatment directed at the underlying pathophysiology of Alzheimer’s disease, the presence of amyloid beta plaques in the brain. The clinical trials for Aduhelm were the first to show that a reduction in these plaques—a hallmark finding in the brain of patients with Alzheimer’s—is expected to lead ...
Does Aduhelm help with amyloid beta?
Although the Aduhelm data are complicated with respect to its clinical benefits, FDA has determined that there is substantial evidence that Aduhelm reduces amyloid beta plaques in the brain and that the reduction in these plaques is reasonably likely to predict important benefits to patients. As a result of FDA’s approval ...
Does the FDA monitor Aduhelm?
FDA will continue to monitor Aduhelm as it reaches the market and ultimately the patient’s bedside. Additionally, FDA is requiring Biogen to conduct a post-approval clinical trial to verify the drug’s clinical benefit. If the drug does not work as intended, we can take steps to remove it from the market.
What is the best medication for dementia?
There are several classes of medications proven to work at treating symptoms and reducing the effects of dementia, which include: Cholinesterase inhibitors: Aricept (donepezil), Razadyne (galantamine) and Exelon (rivastigmine).
Why are antidepressants used for dementia?
A high percentage of dementia sufferers are afflicted by depression, so antidepressants are used to increase wellbeing and quality of life.
What is the effect of cholinesterase inhibitors on Alzheimer's?
Cholinesterase inhibitors alleviate symptoms of Lewy-body dementia and Alzheimer's disease by slowing the breakdown of Acetylcholinesterase, which plays a role in learning, memory, and cognitive skills.
What are the side effects of dementia medication?
Side effects of medications used to alleviate dementia symptoms include nausea, dizziness, vomiting, slowed heart rate and diarrhea. A doctor or healthcare professional can prescribe the medication that best fits an individual's condition and situation.
How does behavioral therapy help dementia?
Behavioral therapy involves tackling the triggers or causes of unwanted behaviors like aggression or wandering in order to alleviate and provide outlets for these behaviors without medication. For example, a trained caregiver may find that feelings of restlessness or stress cause their patient to wander away from home, and can implement an exercise regimen to manage this restlessness.
How to manage dementia?
Dementia hugely affects everyday functioning both for sufferers and for their loved ones, and coping with dementia can require major lifestyle and environmental changes. A comprehensive management system includes therapy and counseling to manage possible stress, anxiety, and depression.
What are the best supplements for reversible dementia?
Medication and supplements that can completely cure reversible dementias include: Vitamin B12 supplements for pernicious anemia. Hormonal supplements for hyperthyroidism, hypothyroidism, or other imbalances. SSRIs or other antidepressants for depression symptoms which may mimic dementia.

Diagnosis
Treatment
Clinical Trials
Alternative Medicine
Specialist to consult
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
Coping and Support
- Drugs
Current Alzheimer's medications can help for a time with memory symptoms and other cognitive changes. Two types of drugs are currently used to treat cognitive symptoms: 1. Cholinesterase inhibitors. These drugs work by boosting levels of cell-to-cell communication by preserving a ch… - Creating a safe and supportive environment
Adapting the living situation to the needs of a person with Alzheimer's disease is an important part of any treatment plan. For someone with Alzheimer's, establishing and strengthening routine habits and minimizing memory-demanding tasks can make life much easier. You can take thes…
Preparing For Your Appointment
- Explore Mayo Clinic studiestesting new treatments, interventions and tests as a means to prevent, detect, treat or manage this condition.