What is the best treatment for thalassemia?
Many times people with thalassemia are prescribed a supplemental B vitamin, known as folic acid, to help treat anemia. Folic acid can help red blood cells develop. Treatment with folic acid is usually done in addition to other therapies. How do blood transfusions affect my body?
What is the life expectancy of someone with thalassemia?
How Is Alpha Thalassemia Treated? Treatment depends on what kind of alpha thalassemia someone has. Children with alpha thalassemia trait or who are carriers don't need treatment. Children and adults with alpha thalassemia major need lifelong medical care that includes: blood transfusions about every 2–4 weeks
Is there any natural treatment for thalassemia?
Individuals with mild forms of alpha thalassemia may not require specific treatment except as needed for management of low hemoglobin levels. In …
How do you treat beta thalassemia?
Jul 29, 2015 · Treatment of alpha-thalassemia often includes blood transfusions to provide healthy blood cells that have normal hemoglobin. Bone marrow transplant has helped to cure a small number of individuals with severe alpha-thalassemia.

Can alpha thalassemia be treated?
Does alpha thalassemia trait require treatment?
What happens when you have alpha thalassemia?
What is the treatment for alpha thalassemia minor?
Is alpha thalassemia serious?
How do you test for alpha thalassemia?
- Complete blood count (CBC). This test checks the size, number, and maturity of different blood cells in a set volume of blood.
- Hemoglobin electrophoresis. ...
- Ferritin. ...
- DNA testing.
How common is thalassemia Alpha?
What is the life expectancy of thalassemia patients?
What is the difference between alpha thalassemia and beta thalassemia?
Which type of alpha thalassemia is not survivable?
If I Have Thalassemia, How Does It Affect My body?
Since your body has fewer red blood cells when you have thalassemia, you may have symptoms of a low blood count, or anemia. When you have anemia, y...
How Is Thalassemia Treated?
The type of treatment a person receives depends on how severe the thalassemia is. The more severe the thalassemia, the less hemoglobin the body has...
How Do Blood Transfusions Affect My body?
People who receive a lot of blood transfusions are at risk for iron overload. Red blood cells contain a lot of iron, and over time, the iron from a...
What is the alpha thalassemia?
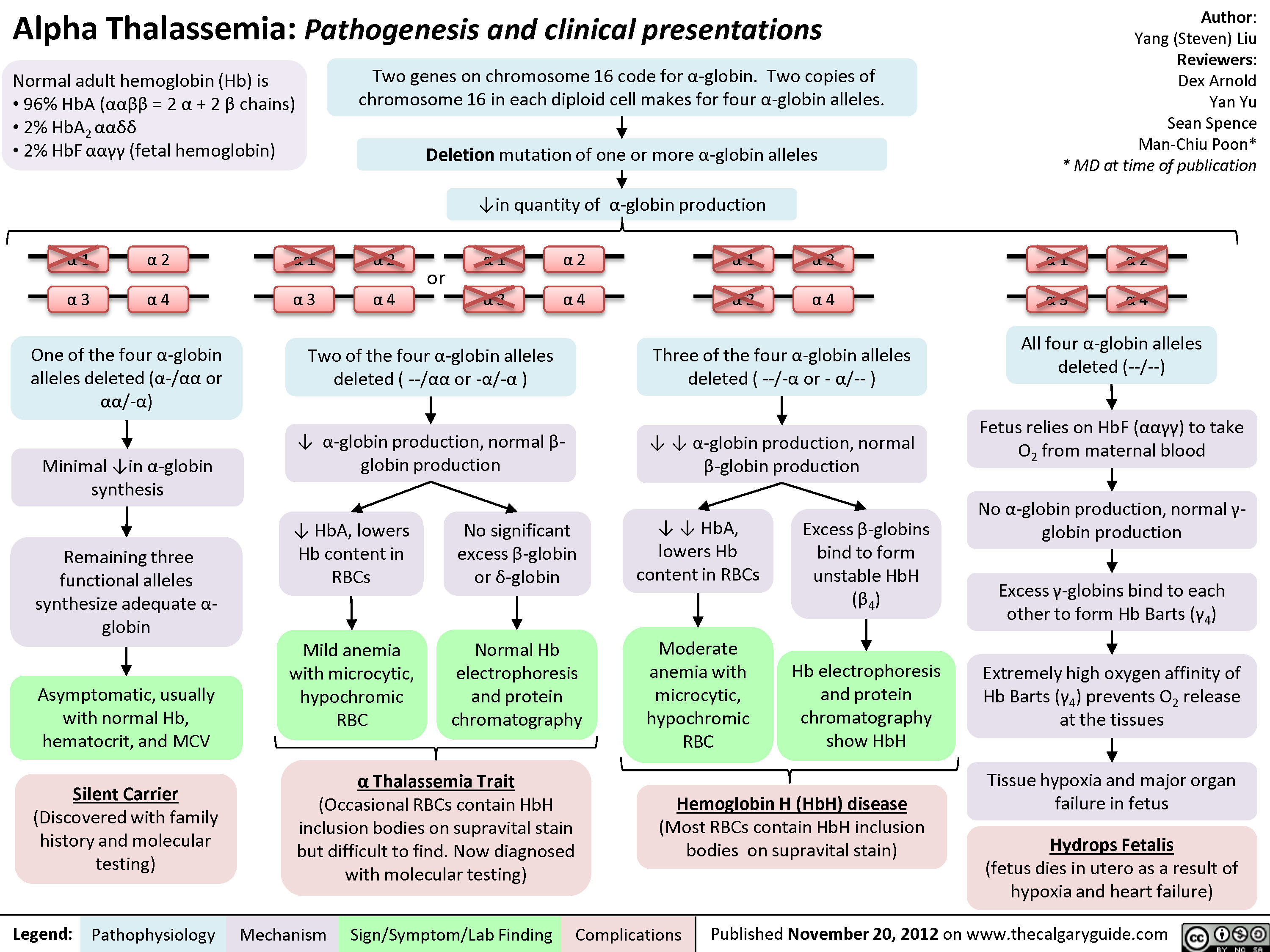
Key points about alpha thalassemia. A thalassemia is an inherited blood disorder. It causes the body to make less hemoglobin than normal. There are 4 different types of alpha thalassemia. This condition causes mild to severe anemia, based on the type of alpha thalassemia that is inherited.
What is the purpose of DNA testing for alpha thalassemia?
This test is done to rule out iron-deficiency anemia. All of these tests can be done using a single blood sample. In a pregnant woman, the baby is diagnosed using CVS ( chorionic villus sampling) or amniocentesis. A DNA test is needed to make a diagnosis of alpha thalassemia.
What is the name of the disease where the alpha-globin gene is missing?
Alpha thalassemia occurs when some or all of the 4 genes that make hemoglobin (the alpha-globin genes) are missing or damaged. There are 4 types of alpha thalassemia: Alpha thalassemia silent carrier. One gene is missing or damaged, and the other 3 are normal. Blood tests are usually normal. Your red blood cells may be smaller than normal.
What is thalassemia inherited?
Thalassemia (thal-uh-SEE-mee-uh) is a blood disorder that is inherited. This means it is passed down from one or both parents through their genes. When you have thalassemia, your body makes less hemoglobin than normal. Hemoglobin is an iron-rich protein in red blood cells. It carries oxygen to all parts of the body.
How many types of thalassemia are there?
There are 2 main types of thalassemia: alpha and beta. Different genes are affected for each type.
Where is Alpha Thalassemia most commonly found?
Alpha thalassemia is most commonly found in these parts of the world: Africa. Middle East. India. Southeast Asia. Southern China. Mediterranean region. The following tests may help to tell if you are a carrier, and can pass the disorder on to your children: Complete blood count (CBC).
Is silent alpha thalassemia carrier a symptom?
Silent alpha thalassemia carrier. This type has no symptoms.
What is Alpha Thalassemia?
Updated on January 24, 2020. Alpha thalassemia is an inherited anemia where the body is unable to produce a normal amount of hemoglobin. Hemoglobin A (the major hemoglobin in adults) contains two alpha globin chains and two beta globin chains. In alpha thalassemia, there is a reduced amount of alpha globes. Andrew Brookes / Getty Images.
Why is Alpha thalassemia minima called silent carrier?
Alpha thalassemia minima causes no laboratory changes on CBC. This is why it is called silent carrier. This is usually suspected after a child is born with Hemoglobin H disease. This can only be determined by genetic testing.
What is it called when two alpha globin genes are lost on the same chromosome?
When the two alpha globin genes lost are on the same chromosome 16 is called cis , but when one alpha globin gene is missing on each copy of chromosome 16 this is called trans. Hemoglobin H disease (or alpha thalassemia intermedia) occurs when three alpha globin genes do not function. In this case, there are an excessive amount of beta globins.
What is the treatment for hemoglobin H?
Iron chelation therapy : Patients with Hemoglobin H disease may develop iron overload even in the absence of blood transfusions secondary to increased absorption of iron in the small intestine. They can be treated with medications called chelators to help rid the body of excess iron.
Is alpha thalassemia inherited?
Alpha thalassemia is an inherited condition and requires both parents to be carriers. A person without alpha thalassemia should have four alpha globin genes. The risk of having a child with alpha thalassemia disease is dependent on the status of the parents. The trans form of alpha thalassemia minor is more common in people of African descent.
Can alpha thalassemia be detected on newborn screen?
Occasionally alpha thalassemia minor is identified on newborn screen, but not in all cases. The test is positive for Hemoglobin Bart's or fast bands. Many people with alpha thalassemia minor I have no idea. This usually comes to light during a routine complete blood count (CBC).
How to manage thalassemia?
You can help manage your thalassemia by following your treatment plan and adopting healthy-living habits. Avoid excess iron. Unless your doctor recommends it, don't take vitamins or other supplements that contain iron. Eat a healthy diet. Healthy eating can help you feel better and boost your energy.
What is the best treatment for thalassemia in children?
Stem cell transplant. Also called a bone marrow transplant, a stem cell transplant might be an option in some cases. For children with severe thalassemia, it can eliminate the need for lifelong blood transfusions and drugs to control iron overload.
How to tell if a child has thalassemia?
If your doctor suspects your child has thalassemia, he or she can confirm a diagnosis with blood tests. Blood tests can reveal the number of red blood cells and abnormalities in size, shape or color.
When should a baby be tested for thalassemia?
Testing can be done before a baby is born to find out if he or she has thalassemia and determine how severe it might be. Tests used to diagnose thalassemia in fetuses include:
Can thalassemia cause excess iron?
Some people with thalassemia who don't have regular transfusions can also develop excess iron. Removing the excess iron is vital for your health. To help rid your body of the extra iron, you might need to take an oral medication, such as deferasirox (Exjade, Jadenu) or deferiprone (Ferriprox).
Does iron supplementation help with alpha thalassemia?
Iron deficiency must be documented carefully with laboratory testing before supplemental iron is given. Iron supplementation does not improve hematologic values in alpha thalassemia. Many patients with apparent iron deficiency actually have iron overload (hemochromatosis), the effects of which can contribute to morbidity and mortality.
Is blood transfusion necessary for HbH?
Guidelines for transfusion in neonates and older children have been established. [ 36] . Blood transfusions should be administered only if necessary.
Can you get iron chelation therapy for HbH?
Transfusion therapy is reserved for patients with severe anemia (usually < 7 g/dL) and symptomatic anemia. If chronic transfusion therapy is needed, iron chelation therapy should be considered to prevent iron overload. Even patients who have not received a large number of transfusions may have elevated total body iron loads and may require chelation therapy.
Is allogeneic stem cell transplantation curative?
In very severe cases, allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation may be considered . This measure is curative because the hematopoietic system of the patient is replaced by that of the donor. A sibling who is fully matched for human leukocyte antigen (HLA) and who is, at most, a carrier for alpha thalassemia (deletion of 2 alpha-globin genes) is the most suitable donor. However, because of the toxicity of the procedure, bone marrow transplantation should be limited to the most severely affected patients.
Can alpha thalassemia be treated?
Approach Considerations. Individuals with mild forms of alpha thalassemia may not require specific treatment except as needed for management of low hemoglobin levels. In some patients, supplementation of iron or folic acid may be useful. Patients with more severe anemia may require lifelong transfusion therapy.
How to treat alpha thalassemia?
Treatment of alpha-thalassemia often includes blood transfusions to provide healthy blood cells that have normal hemoglobin. Bone marrow transplant has helped to cure a small number of individuals with severe alpha-thalassemia. [4]
How many genes are involved in alpha thalassemia?
The inheritance of alpha-thalassemia is complex because the condition involves two genes: HBA1 and HBA2. People have two copies of the HBA1 gene and two copies of the HBA2 gene in each cell. Each copy is called an allele. Therefore, there are 4 alleles that produce alpha-globin, the protein that results from these genes. For each of the 2 genes, one allele is inherited from a person's father, and the other is inherited from a person's mother - so each person inherits 2 alleles from each parent. The different types of alpha-thalassemia result from the loss of some or all of these alleles.
What happens if both parents are missing at least one alpha-globin allele?
If both parents are missing at least one alpha-globin allele, each of their children are at risk of having Hb Bart syndrome or hydrops fetalis, hemoglobin H (HbH) disease, or alpha-thalassemia trait. The precise risk depends on how many alleles are missing and which combination of the HBA1 and HBA2 genes is affected.
What is the name of the disease that causes pale skin, weakness, and fatigue?
Alpha-thalassemia is a blood disorder that reduces the body's production of hemoglobin. Affected people have anemia, which can cause pale skin, weakness, fatigue, and more serious complications. Two types of alpha-thalassemia can cause health problems: the more severe type is known as Hb Bart syndrome; the milder form is called HbH disease.
Can HBH cause anemia?
HbH disease may cause mild to moderate anemia; hepatosplenomegaly; jaundice; or bone changes. Alpha-thalassemia typically results from deletions involving the HBA1 and HBA2 genes. The inheritance is complex, and can be read about here. [1] . No treatment is effective for Hb Bart syndrome.
What is Alpha Thalassemia?
Alpha thalassemia is a genetic condition. Babies inherit it from their biological (birth) parents. To learn more about genetic conditions , visit MedlinePlus Genetics.
Who can help with genetic disorders?
Genetic counselors and medical geneticists can help families learn about this condition and the chance of having children with it. Visit the National Society of Genetic Counselors
Can children with alpha thalassemia have healthier lives?
Children who receive early health care and treatment for Alpha thalassemia can have healthier lives than those who do not receive treatment.
Can a baby with Alpha Thalassemia Major have hemoglobin?
A baby with Alpha thalassemia major does not have any normal alpha globin alleles. Their bodies cannot make any normal hemoglobin. This condition is so serious that damage to their body begins before birth and survival is rare.
What is the characteristic of alpha thalassemia?
The characteristic finding of all forms of alpha thalassemia is anemia, with red blood cells that are small (microcytic), contain low levels of functional hemoglobin (hypochromic), and may break down in prematurely in both the bone marrow (ineffective erythropoiesis) and in the peripheral circulation (hemolysis).
Where is Alpha Thalassemia most common?
Alpha thalassemia is found in most populations worldwide, but is most common in the Middle East, Southeast Asia, and certain Mediterranean countries. Hb Bart’s hydrops fetalis and HbH disease are primarily recognized in Southeast Asia. The estimated incidence of Hb Bart’s hydrops fetalis in Southeast Asia is 1 in 200-2,000 births; its incidence in other parts of the world is unknown. The incidence of HbH disease in these countries is approximately 4-20 individuals per every 1,000 births.
What is the condition that affects two of the four alpha genes?
A mutation (or mutations) that affects two of the four alpha genes results in a condition that is asymptomatic or only very mild symptoms (alpha thalassemia minor). A mutation ( or mutations) that affect three genes results in HbH disease, while defects that affect all four genes result in Hb Bart’s hydrops fetalis.
How are alpha genes inherited?
Mutations in the alpha genes are inherited in an autosomal recessive manner. Recessive genetic disorders become manifest when an individual inherits a mutation of the corresponding gene from each parent. If an individual receives one normal gene and one gene for the disease, the person will be a carrier for the disease, but usually will not show symptoms. The risk that two carrier parents both pass a defective gene to an offspring and producing an affected child, therefore, is 25% for each pregnancy. The risk of bearing a child who is also a carrier (like each parent) is 50% for each pregnancy. The chance that a child will receive a normal gene from both parents and be genetically normal for that particular trait is 25% for each pregnancy. For genes carries on chromosomes 1-22, risk is the same for males and females. The inheritance of alpha thalassemia is somewhat more complicated insofar as each parent contributes two alpha genes to an offspring, rather than only one. The HBA1 and HBA2 genes are inherited in pairs, meaning that both genes from one chromosome are passed on from a parent to a child. Consultation with a genetic counselor is recommended for families or parents who are known or suspected of carrying an alpha thalassemia mutation, even if it does not cause symptoms. Additionally, the organizations listed in the Resources section of this report have more detailed information on the genetics of alpha thalassemia.
How many copies of each gene are there in Alpha Thalassemia?
Alpha thalassemia is caused by mutations in two different genes, the HBA1 and the HBA2 genes. Most individuals inherit two copies of each gene (for a total of four genes); one of each from a person’s father, and one of each gene from a person’s mother.
What is the term for a group of inherited blood disorders characterized by reduced or absent production of alpha-
Alpha thalassemia is a general term for a group of inherited blood disorders characterized by reduced or absent production of alpha-globin subunits, resulting in low levels of hemoglobin that is otherwise fully functional. Hemoglobin is found in red blood cells; it is the red, iron-rich, oxygen-carrying pigment of the blood.
Can HbH be treated with blood transfusions?
Individuals with severe forms of HbH disease are usually treated with regular blood transfusions, which can result in the accumulation of excess iron in the body (iron overload). Although iron overload can damage numerous organs in the body, it can be effectively treated using several highly effective medications.
How many types of alpha thalassemia are there?
There are two different types of alpha thalassemia trait.
What happens if both parents have the trans form of alpha thalassemia?
If both parents have the trans form of alpha thalassemia trait (α-/α-), all of their children will have alpha thalassemia trait.
What is the name of the disease that causes health problems and requires treatment by a physician?
Missing three alpha thalassemia genes (Hemoglobin H disease): (α-/--), this disease causes health problems and requires treatment by a physician.
Which type of thalassemia has two missing alpha genes on the same chromosome?
The second type of alpha thalasse mia trait has two missing alpha genes on the same chromosome (αα/--). This is called the cis form of alpha thalassemia trait.
Is alpha thalassemia common in African Americans?
The trans form of alpha thalassemia trait (α-/α-) is common in African-Americans (20-30%) and in people of African descent. It is rare for African-Americans to have the cis form of alpha thalassemia, but it can happen. The second type of alpha thalassemia trait has two missing alpha genes on the same chromosome (αα/--).
Can thalassemia cause low red blood cells?
Alpha thalassemia can cause low red blood cell levels (mild anemia) and should not be confused with not having enough iron in the blood. Tell the doctor if your child’s newborn screening test showed Bart’s hemoglobin. If a small amount of Bart’s hemoglobin is present at birth, it will usually disappear shortly after birth.
Do people with alpha thalassemia develop H cell disease?
People with alpha thalassemia trait do not develop hemoglobin H cell disease or hydrops fetalis later in life.

Symptoms
Who's at Risk
- Alpha thalassemia is an inherited condition that requires both parents to be carriers. Therefore, the risk of having a child with alpha thalassemia disease depends on the status of the parents. People have four alpha-globin proteins that form the HBA1 and the HBA2 genes (called alleles). When some or all of these alleles are missing, alpha thalassemia occurs. The risk is as follows: …
Treatments
- No treatment is needed for people who are silent carriers (minima) or for alpha thalassemia minor. Although, people with alpha thalassemia minor will have lifelong mild anemia. Those with more moderate to severe cases may require blood transfusions or chelation therapy.
Summary
- Alpha thalassemia is an inherited disorder in which the body can not produce enough hemoglobin. The condition ranges from asymptomatic to severe. Sometimes, a person can be a carrier (silent alpha thalassemia) with no sign of disease. Others may have very mild disease, known as having alpha thalassemia trait. The two types of alpha thalassemia that cause health problems are Hb …
A Word from Verywell
- Remember that both parents must be carriers for a child to be born with alpha thalassemia. Doctors can diagnose alpha thalassemia with blood tests; however, a blood test won't detect it if someone is a silent carrier. Genetic testing can confirm if you are a silent carrier. Talk to your doctor if you are concerned about alpha thalassemia. They may recommend genetic testing an…
Diagnosis
- Most children with moderate to severe thalassemia show signs and symptoms within their first two years of life. If your doctor suspects your child has thalassemia, he or she can confirm a diagnosis with blood tests. Blood tests can reveal the number of red blood cells and abnormalities in size, shape or color. Blood tests can also be used for DNA analysis to look for mutated genes.
Treatment
- Mild forms of thalassemia trait don't need treatment. For moderate to severe thalassemia, treatments might include: 1. Frequent blood transfusions.More severe forms of thalassemia often require frequent blood transfusions, possibly every few weeks. Over time, blood transfusions cause a buildup of iron in your blood, which can damage your heart, liver and other organs. 2. Ch…
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
- You can help manage your thalassemia by following your treatment plan and adopting healthy-living habits. 1. Avoid excess iron.Unless your doctor recommends it, don't take vitamins or other supplements that contain iron. 2. Eat a healthy diet. Healthy eating can help you feel better and boost your energy. Your doctor might also recommend a folic ac...
Coping and Support
- Coping with thalassemia, your own or your child's, can be challenging. Don't hesitate to ask for help. If you have questions or would like guidance, talk with a member of your health care team. You might also benefit from joining a support group, which can provide both sympathetic listening and useful information. Ask a member of your health care team about groups in your area.
Preparing For Your Appointment
- People with moderate to severe forms of thalassemia are usually diagnosed within the first two years of life. If you've noticed some of the signs and symptoms of thalassemia in your infant or child, see your family doctor or pediatrician. You may then be referred to a doctor who specializes in blood disorders (hematologist). Here's some information to help you get ready for your appoin…