Explore
Mar 24, 2020 · Replacement therapy will increase blood levels of AAT, but it is not clear that it leads to longer-term improvements in lung function or survival. Replacement therapy is given intravenously. Some patients with advanced lung disease may be referred for lung volume reduction surgery (LVRS) and lung transplantation. More information
What are the symptoms of alpha 1?
Serum levels below the putative protective threshold level of 11 micromolar (mumol/L) increase the risk of emphysema. In addition to the usual treatments for emphysema, infusion of purified AAT from pooled human plasma represents a specific therapy for AAT deficiency and raises serum and epithelial lining fluid levels above the protective threshold.
Should I be tested for alpha 1 deficiency?
Mar 24, 2022 · There is no cure for AAT deficiency, but there are treatments to slow the lung damage it causes. You may need a lifelong treatment called augmentation therapy. This treatment raises the levels of the AAT protein in your lungs, using ATT protein taken from the blood of donors. This helps slow down lung damage.
Is alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency the same as cystic fibrosis?
Jan 04, 2012 · Treatment of alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency (AATD) is based on a person's symptoms. There is currently no cure. The major goal of AATD management is preventing or slowing the progression of lung disease. Treatments include bronchodilators and prompt treatment with antibiotics for upper respiratory tract infections.
What are the symptoms of alpha - 1 disease?
In addition, there’s a specific treatment for alpha-1: protease inhibitor augmentation therapy, which helps slow or stop the progression of lung damage by replacing the deficient protein. This treatment is administered via weekly intravenous infusions. Doreen’s Story I was in my mid-20s when I was diagnosed with asthma.
What is the best treatment for alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency?
The only specific therapy for alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency (AATD) is augmentation therapy. During this therapy, preparations of alpha-1 antitrypsin protein that have been isolated from pooled blood of healthy donors are given by weekly intravenous infusion.Feb 1, 2021
Is there a treatment for alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency?
Although there's no cure for AAT deficiency, you can raise the amount of AAT protein in your blood, which protects you against more lung damage. Doctors call this augmentation therapy. You may also have this treatment if you get emphysema. Augmentation therapy is also called replacement therapy.Nov 17, 2019
What is the life expectancy of someone with alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency?
How does Alpha-1 lung disease affect my life expectancy? People who continue to smoke and have Alpha-1 lung disease, have an average life expectance of about 60 years of age.Nov 1, 2017
Is AAT treatable?
Currently, AAT deficiency has no cure, but a treatment called augmentation therapy may help slow lung damage. You may also need oxygen therapy, pulmonary rehabilitation, or medicines to treat complications.Mar 18, 2020
Is Alpha-1 a terminal illness?
The rare disorder disorder called alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency (Alpha-1) can lead to potentially life-threatening lung and liver diseases, including emphysema and cirrhosis.Dec 24, 2019
Is Alpha-1 an autoimmune disease?
Alpha-1 antitrypsin (AAT) deficiency is an under-recognized hereditary disorder associated with the premature onset of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, liver cirrhosis in children and adults, and less frequently, relapsing panniculitis, systemic vasculitis and other inflammatory, autoimmune and neoplastic ...Mar 24, 2014
What are the odds of having alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency?
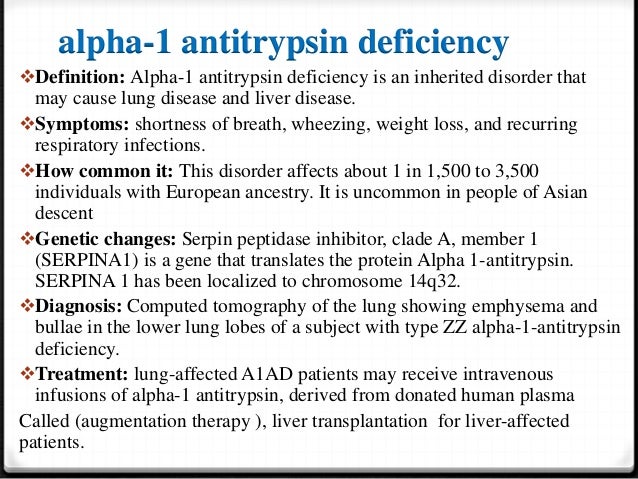
Alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency occurs worldwide, but its prevalence varies by population. This disorder affects about 1 in 1,500 to 3,500 individuals with European ancestry.Sep 15, 2021
What is a normal alpha-1 antitrypsin level?
Most hospital laboratories report serum alpha1-antitrypsin levels in milligrams per decimeter, with a reference range of approximately 100-300 mg/dL. Levels less than 80 mg/dL suggest a significant risk for lung disease.Sep 11, 2020
How do you know if you have alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency?
When the liver is affected by AAT deficiency, symptoms may include tiredness, loss of appetite, weight loss, swelling of the feet or belly, yellowish discoloration of the skin (jaundice) or white part of the eyes, vomiting of blood, or blood in stools.Mar 24, 2020
What does alpha-1 do to the lungs?
Alpha-1 antitrypsin (AAT) deficiency is a rare genetic disorder that is passed on in families and can affect the lungs, liver and/or skin. When this condition affects the lungs, it causes COPD (chronic obstructive pulmonary disease).
Why does a1 antitrypsin destroy lungs?
Alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency (AATD) is an inherited disorder characterized by low serum levels of alpha-1 antitrypsin (AAT). Loss of AAT disrupts the protease-antiprotease balance in the lungs, allowing proteases, specifically neutrophil elastase, to act uninhibited and destroy lung matrix and alveolar structures.
Do both parents have to have alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency?
Both parents must have at least one copy of the abnormal alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency gene in order for their child to inherit the disease.
What is the treatment for alpha 1?
Augmentation Therapy. There's only one specific treatment to fight alpha 1: augmentation therapy. It's also called replacement therapy. It’s been around for 25 years, but it's attracting more attention.
How does alpha 1 affect the lungs?
If you have alpha-1, you don't have enough of a protein that normally protects the lungs from damage. Augmentation therapy raises your levels of that protein. You get it through an IV tube into a vein in your arm. The extra alpha-1 moves through your blood to your lungs and may slow down the damage.
What is the best treatment for a lung infection?
These may include inhaled drugs called bronchodilators that open up the airways. Inhaled steroids can reduce the swelling in the lungs. Antibiotics. Alpha-1 makes it more likely to get a lung infection. Your doctor may prescribe antibiotics to head off problems.
What is Alpha 1 Antitrypsin?
About Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency. Alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency is an inherited condition that causes low levels of, or no, alpha-1 antitrypsin in the blood.
Where is antitrypsin made?
Alpha-1 antitrypsin (AAT) is a protein that is made in the liver. The liver releases this protein into the bloodstream.
What is the AATD?
Alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency (AATD) can present as lung disease in adults and can be associated with liver disease in a small portion of affected children. In affected adults, the first symptoms of AATD are shortness of breath with mild activity, reduced ability to exercise and wheezing.
What is the alpha 1 gene?
Alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency (AATD) is inherited in families in an autosomal co dominant pattern. Codominant inheritance means that two different variants of the gene (alleles) may be expressed, and both versions contribute to the genetic trait. The M gene is the most common allele of the alpha-1 gene. It produces normal levels of the alpha-1 ...
What is codominant inheritance?
Codominant inheritance means that two different variants of the gene (alleles) may be expressed, and both versions contribute to the genetic trait. The M gene is the most common allele of the alpha-1 gene. It produces normal levels of the alpha-1 antitrypsin protein. The Z gene is the most common variant of the gene.
What is the S allele?
The S allele is another, less common variant that causes ATTD. If a person inherits one M gene and one Z gene or one S gene ('type PiMZ' or 'type PiMS'), that person is a carrier of the disorder. While such a person may not have normal levels of alpha-1 antitrypsin, there should be enough to protect the lungs.
What are the symptoms of AATD?
Other signs and symptoms can include repeated respiratory infections, fatigue, rapid heartbeat upon standing, vision problems and unintentional weight loss. Some Individuals with AATD have advanced lung disease and have emphysema, in which the small air sacs (alveoli) in the lungs are damaged.
What is Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency?
Alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency is a rare inherited condition that can lead to serious lung disease in adults. At least 100,000 people in the United States – from all populations and ethnic groups – have the condition.
What is the treatment for Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency?
There is no cure for alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency, but medications are available to address inflammation and improve breathing.
What is the treatment for alpha 1?
Treatment. The specific therapy for the treatment of Alpha-1-related lung disease is augmentation therapy – also called replacement therapy. Augmentation therapy is the use of alpha-1 antitrypsin protein (AAT) from the blood plasma of healthy human donors to augment (increase) the alpha-1 levels circulating in the blood and lungs ...
What is the best intervention for a port or other central catheter infection?
Prevention is the best intervention. The best intervention for a port or other central catheter infection is prevention . Preventing infection should be the priority of everyone who has a port or other central device, as well as a top priority for those healthcare providers who access these devices.
How many augmentations are there in the US?
Currently available therapy. There are four augmentation therapy products approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and available in the United States, and more potential therapies are on the horizon.
What is the goal of augmentation therapy?
The basic goal of augmentation therapy is to increase the level of alpha-1 protein in the lungs. Alpha-1 antitrypsin protects the lungs from the destructive effects of neutrophil elastase, an enzyme released by our body’s white blood cells as they respond to inflammation or infection. The ultimate goal is to slow or stop the progression ...
What is an IgA?
A: IgA is one of the most common hereditary immune deficiencies. IgA deficiency, like Alpha-1, can be associated with lung and allergic symptoms. People with either of these conditions (IgA deficiency or Alpha-1) can lead normal, healthy lives without ever knowing they have one of these conditions.
Does augmentation therapy help with pulmonary exacerbations?
There is also some evidence that augmentation therapy can reduce the frequency and severity of pulmonary exacerbations (flare-ups of lung disease) and it appears to be an effective treatment for the Alpha-1 related skin disease, Necrotizing Panniculitis.
What is AAT deficiency?
Alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency ( A1AD or AATD) is an inherited genetic disorder that occurs due to the mutation of the gene, Serpina1. This results in insufficient levels of alpha-1 antitrypsin ( A1AT or AA ), which is a protein that protects the lungs.
What is the best treatment for a lung infection?
Bronchodilators may be prescribed to widen the airway and improve lung symptoms. Oxygen therapy and pulmonary rehabilitation may be required in some cases. Antibiotics are administered whenever there is any infection. Vaccinations against lung infections like pneumonia and annual flu shots are usually advised.
Why is AAT important?
AAT is required to protect the lungs. With AAT deficiency, infections of the lungs and environmental irritants like tobacco smoke cause lung damage much faster than usual. AAT deficiency can cause chronic obstructive pulmonary disease ( COPD ). COPD is a group of diseases causing an inflammatory reaction and irreversible damage in the lungs.
Is there a cure for AAT?
There is no cure for AAT deficiency, but various treatment options are available to manage the disease. Patients typically require lifelong treatment and lifestyle modifications to live a normal life and prevent complications. Treatment options include.
What is the name of the disease that affects the alveoli?
Emphysema is a disease of the alveoli (the tiny air sacs in the lungs). Chronic bronchitis is a disease of the bronchus (the tubes through which air passes in the lungs). The trachea can also be involved. During inhalation, air travels through the nose and/or mouth into the trachea (windpipe).
What are the two tubes that separate the trachea?
The trachea further divides into two tubes called bronchi. The bronchi branch out into smaller tubes called bronchioles. The ends of bronchioles open into little air sacs called alveoli, which aid in gaseous exchange.
Is there a cure for alpha 1 antitrypsin deficiency?
Life expectancy in alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency. There is no cure for the disease, but various treatment options are available to manage the disease and associated lung and liver problems. With appropriate treatment, most patients would be able to live a good life with normal life expectancy, work, play sports and exercise.
