What is adenomyosis and how can it be treated?
Adenomyosis treatment is focused primarily on symptom management, as the cause is not well understood. There are nutrition and lifestyle practices that can help reduce pain, improve hormonal health, lower inflammation, and improve health outcomes. In some cases, surgical intervention may be necessary.
Is there any cure for adenomyosis?
Vitamin B complex and vitamin E play a significant role in the treatment of conditions like adenomyosis. Studies have found that vitamins B1, B6, and E can help reduce menstrual pain (9), (10). You may get the required amounts of these vitamins by consuming eggs, milk, cheese, fish, poultry, almonds, spinach, and kale.
Is dienogest effective for treating symptomatic adenomyosis?
The combination of MEA and postoperative dienogest is useful for treating uterine adenomyosis with menorrhagia and dysmenorrhea. Combination of microwave endometrial ablation and postoperative dienogest administration is effective for treating symptomatic adenomyosis
What techniques are used to diagnose adenomyosis?
These include:
- oral contraceptive pills
- high-dose progestins
- a levonorgestrel-releasing intrauterine device
- danazol
- gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) agonists and antagonists, like elagolix
- endometrial ablation, which is an outpatient procedure that uses a laser or other ablation techniques to destroy the lining of the uterus

How is Adenomyomatosis of the gallbladder treated?
The fundal type gallbladder adenomyomatosis can be treated by partial laparoscopic cholecystectomy. The segmental and diffuse type should undergo a total laparoscopic cholecystectomy. Females over 60 years of age who present gallbladder stones and segmental type gallbladder adenomyomatosis should undergo surgery 13).
How serious is gallbladder adenomyomatosis?
Originally recognized as a precancerous lesion, adenomyomatosis is currently recognized by recent studies as a benign alteration of the gallbladder that is often associated with cholecystitis and cholecystolithiasis. Gallbladder carcinoma is an extremely malignant disease with a 5-year survival rate of less than 5%.
What causes adenomyomatosis of gallbladder?
It occurs as a result of poorly understood hyperplastic changes involving the mucosa and muscular wall of the gallbladder and the formation of intramural sinuses, known as the Rokitansky-Aschoff sinuses, which are characteristic of this disease. Involvement of the gallbladder may be diffuse or segmental.
What are the symptoms of gallbladder adenomyomatosis?
The most common presentation of GAM is pain in the upper right quadrant of the abdomen, which is similar to gallstone pain with or without cholecystitis. This pain is intermittent and mostly self-limiting [5,6]. It is possible that GAM symptoms are secondary to gallstones and inflammation.
Is adenomyomatosis curable?
Can Adenomyosis Be Cured? The only definitive cure for adenomyosis is a hysterectomy, or the removal of the uterus. This is often the treatment of choice for women with significant symptoms.
Does Adenomyomatosis of the gallbladder require surgery?
Adenomyomatosis is a benign condition and frequently asymptomatic, requiring no further treatment. However, elective surgery is often performed in patients with right upper quadrant pain, as in this case, or with inconclusive imaging findings.
How common is gallbladder adenomyomatosis?
1. Gallbladder adenomyomatosis is a common benign lesion (1–9% of the patients).
What does adenomyomatosis mean?
With adenomyosis, the same tissue that lines the uterus (endometrial tissue) is present within and grows into the muscular walls of your uterus. Adenomyosis (ad-uh-no-my-O-sis) occurs when the tissue that normally lines the uterus (endometrial tissue) grows into the muscular wall of the uterus.
What is adenomyomatosis of the liver?
Adenomyomatosis is a benign condition characterized by hyperplastic changes of unknown cause involving the wall of the gallbladder.
Does adenomyomatosis enhance?
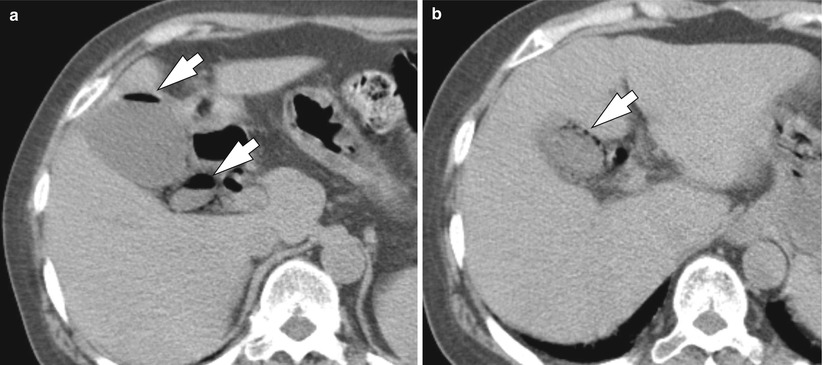
Abnormal gallbladder wall thickening and enhancement are common but nonspecific CT features of adenomyomatosis.
What is the difference between cholesterolosis and adenomyomatosis?
Discussion: Hyperplastic cholecystoses include cholesterolosis and adenomyomatosis. Adenomyomatosis is differentiated from cholesterolosis by the presence of Rokitansky-Aschoff sinuses which represent invagination of hyperplastic gallbladder mucosa into the thickened muscular layer.
Can gallbladder adenomyomatosis cause nausea?
Nausea and vomiting associated with meals and fatty food intolerance are also reported symptoms. The diagnosis can sometimes be made on ultrasound, when there are intramural cystic foci and "comet tail" artifacts.
What are the three forms of ADM?
There are three forms of ADM: segmental, fundal and more rarely, diffuse. Etiology and pathogenesis are not well understood but chronic inflammation of the GB is a necessary precursor.
What is GB ADM?
Gallbladder (GB) adenomyomatosis (ADM) is a benign, acquired anomaly, characterized by hypertrophy of the mucosal epithelium that invaginates into the interstices of a thickened muscularis forming so-called Rokitansky-Aschoff sinuses. There are three forms of ADM: segmental, fundal and more rarely, diffuse.
Can ADM be asymptomatic?
ADM, although usually asymptomatic, can manifest as abdominal pain or hepatic colic, even in the absence of associated gallstones (50% to 90% of cases). ADM can also be revealed by an attack of acalculous cholecystitis.
What is adenomyomatosis?
Adenomyomatosis is a benign condition that is pathologically characterized by hyperplasia of the gallbladder wall mucosa and muscularis propria, with pathognomonic epithelial invaginations forming cystic pockets (Rokitansky-Aschoff sinuses).
Can adenomyomatosis be diagnosed with gallbladder cancer?
Sometimes, mainly when the characteristic imaging findings are not present, ade nomyomatosis can be challenging to distinguish from gallbladder cancer based on the diagnostic imaging finding s. Adenomyomatosis is often asymptomatic and incidentally detected, requiring no specific treatment.
Is adenomyomatosis a benign condition?
Adenomyomatosis is a benign condition that is pathologically char …. Adenomyomatosis, also known as adenomyoma or adenomyomatous hyperplasia of the gallbladder, is one of the two hyperplastic cholecystoses. The other hyperplastic cholecystosis is cholesterolosis, also known as "strawberry gallbladder.". Adenomyomatosis is a benign condition that is ...
How to relieve pain from adenomyosis?
To ease pelvic pain and cramping related to adenomyosis, try these tips: Soak in a warm bath. Use a heating pad on your abdomen. Take an over-the-counter anti-inflammatory medication, such as ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin IB, others).
How to treat adenomyosis after menopause?
Treatment options for adenomyosis include: Anti-inflammatory drugs. Your doctor might recommend anti-inflammatory medications , such as ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin IB, others), to control the pain.
Can endometrial biopsy confirm adenomyosis?
But an endometrial biopsy won 't help your doctor confirm a diagnosis of adenomyosis. Pelvic imaging such as ultrasound and MRI can detect signs of adenomyosis, but the only way to confirm it is to examine the uterus after hysterectomy.
Can an MRI confirm adenomyosis?
But an endometrial biopsy won't help your doctor confirm a diagnosis of adenomyosis.
What can you tell me about a condition called gallbladder adenomyomatosis?
A benign finding: This is a benign finding in many gallbladders. It is associated with cholesterol crystals that build up in a thickened gallbladder wall. Often associa... Read More
I just was diagnosed with adenomyomatosis of gallbladder, i also have 2 small polyps . should i get removed, should i fear of it becoming cancerous!
Up to you: Smaller polyps tend to be benign , size 2 cm or more have higher incidence of malignancy , the one you describing could be observed but need clos... Read More
Gallbladder without gallstones but with a few small hyperechoic nodules along its inner wall largest measuring 0.8 x 0.9 x 0.6 cm compatible with small polyps versus adenomyomatosis. no sxs. treat?
Up to you: General recommendation for polyps is observation and repeat ultrasound in 6-12 months if less than 1cm. If you're having pain, and you think it could ... Read More
My ultrasound reported: gallbladder exhibits features of adenomyomatosis. there is no cholelithiasis or billiard tract dilatation. what it could be?
Hyperplastic gb: Adenomyomatosis denotes 3 hyperplastic changes in the gallbladder--overgrowth of the mucous membrane, thickening of the muscle layer, & intramural... Read More
What to do if i have been told i have adenomyomatosis of the gall bladder has anyone else heard of this?
Polyps?: If you have adenomatous changes or polyps of the gall bladder you should be evaluated by a surgeon for removal of the gall bladder.
I have a hyperechoic nodule on the right hepatic lobe measuring 0.750.820.39 cm that is stable.focal fat sparing in the periportal region noted. gall bladder adenomyomatosis detected. should i go for a further scan or it is just normal? this is my ultra
Maybe: You should discuss this with your doctor. Do you have underlying liver disease and would be at risk of a problem in the liver? Liver cysts are usuall... Read More
What is an extended gallbladder and what is the treatment?
DIStended?: The gallbladder's function is to store bile. A distended gallbladder is simply one filled with bile. We can see distention in many different condition... Read More
What is focal adenomyomatosis?
This can lead to focal cholelithiasis or cholecystitis involving only the fundus of the gallbladder. Focal adenomyomatosis manifesting as a mass is sometimes referred to as an adenomyoma.
What is adenomyomatous hyperplasia?
Adenomyomatosis of the gallbladder, also referred to as adenomyomatous hyperplasia and intramural diverticulosis, is an acquired, hyperplastic lesion of the gallbladder characterized by excessive proliferation of surface epithelium with invaginations into the thickened, hypertrophied muscularis propria. 215 The intramural diverticula formed by epithelial invaginations into the muscularis are referred to as Rokitansky-Aschoff sinuses (RAS) and dilated RAS are a prominent feature of this disorder. The pathophysiology of this disorder is not entirely certain. This is not usually associated with cholesterolosis, indicating a separate pathophysiology. Pathogenesis has been postulated to result from mechanical obstruction of the gallbladder (from stones, cystic duct kinking or congenital septum), chronic inflammation and anomalous pancreaticobiliary ductal union. 215 The functional obstruction to bile outflow causes increased pressure within the gallbladder lumen and results in invagination of the mucosa through the muscularis, forming the dilated RAS. The reported incidence of adenomyomatosis in cholecystectomy specimens is up to 8%. 219 The association of this disorder with clinical findings is controversial The disorder may be asymptomatic or associated with symptoms of chronic cholecystitis. Over 90% of cases are associated with gallstones which may be responsible for biliary symptoms. 2 Adenocarcinoma of the gallbladder has been found in association with adenomyomatosis, however, a causal link has not been established. 215 In a surgical series of 3,000 resected gallbladders, there was a higher frequency of gallbladder carcinoma (6.4%) in gallbladders with segmental adenomyomatosis than those without. 219
What is the term for the overgrowth of the mucosa, hypertrophy of the muscularis layer,
Gallbladder adenomyomatosis is characterized by overgrowth of mucosa, hypertrophy of the muscularis layer, and extension of mucosa into the thickened gallbladder wall, forming intramural diverticula known as Rokitansky-Aschoff sinuses.178 Adenomyomatosis is present more often in women than in men, has a mean age of presentation of 50 years, and is revealed incidentally in up to 20% of patients who undergo cholecystectomy for biliary symptoms such as right upper quadrant pain. 179,180
Can focal adenomyomatosis be missed?
Focal adenomyomatosis is more difficult to diagnose and can be missed ; this is supported by the pathological examination of gallbladders in which focal changes are seen more frequently than shown on imaging studies. Ultrasound scan shows gallbladder wall thickening and occasionally may show sinus formation.
Is adenomyomatosis a focal or segmental?
Adenomyomatosis may be generalized, segmental or focal and the focal form is most common. 220 Diffuse adenomyomatosis causes thickening and irregularity of the mucosa and muscular layer with associated RAS, which on gross inspection appear as collections of bile in the gallbladder wall.
Is adenomyomatosis a form of cholecystosis?
Adenomyomatosis is one of two forms of hyperplastic cholecystoses (cholesterolosis is the other). Like cholesterolosis, the etiology is unknown. Pathologically, adenomyomatosis is characterized by mucosal hyperplasia and thickening of the muscular layer of the gallbladder. Mucosal herniations into the muscular layer are called Rokitansky-Aschoff ...
Is cholecystectomy asymptomatic?
Many patients are asymptomatic. Treatment of symptomatic patients is controversial. There is evidence to suggest, however, that symptomatic patients who receive cholecystectomy frequently experience abatement of symptoms. Cholesterolosis has been described in the previous section.
How to diagnose adenomyosis?
Until recently, the only definitive way to diagnose adenomyosis was to perform a hysterectomy and examine the uterine tissue under a microscope. However, imaging technology has made it possible for doctors to recognize adenomyosis without surgery.
What hormones cause adenomyosis?
Though the cause of adenomyosis isn't known, studies have suggested that various hormones -- including estrogen, progesterone, prolactin, and follicle stimulating hormone -- may trigger the condition.
What is the procedure that destroys the lining of the uterus?
Endometrial ablation. This minimally invasive procedure destroys the lining of the uterus. Endometrial ablation has been found to be effective in relieving symptoms in some patients when adenomyosis hasn't penetrated deeply into the muscle wall of the uterus.
Can ultrasound diagnose adenomyosis?
An ultrasound can allow a doctor to see the uterus, its lining, and its muscular wall. Though ultrasound cannot definitively diagnose adenomyosis, it can help to rule out other conditions with similar symptoms. Another technique sometimes used to help evaluate the symptoms associated with adenomyosis is sonohysterography.
Is adenomyosis a benign condition?
The condition can be located throughout the entire uterus or localized in one spot. Though adenomyosis is considered a benign ( not life-threatening) condition, the frequent pain and heavy bleeding associated with it can have a negative impact on a woman's quality of life.
Is adenomyosis the same as fibroids?
However, the two conditions are not the same. While fibroids are benign tumors growing in or on the uterine wall, adenomyosis is less of a defined mass of cells within the uterine wall. An accurate diagnosis is key in choosing the right treatment.
Gallbladder Disorders
Adenomyomatosis can be classified as a type of gallbladder disorder, but this condition is not dangerous. There are several types of gallbladder disorders, and most of them are caused by gallstones. Gallstones are small formations that can develop anywhere in the biliary tract; however, most gallstones do not form inside the gallbladder.
Adenomyomatosis of Gallbladder
Adenomyomatosis is quite similar to cholesterol. Sometimes, it is very hard to tell whether a person is suffering from cholesterol or adenomyomatosis of the gallbladder.