Explore
How Is Acute Respiratory Failure Treated? The goal of any treatment for respiratory failure is to improve airflow to the lungs, with an eye to reestablishing a healthy equilibrium of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the blood. This may include: Pain-relief medications to make breathing easier
What are the guidelines for acute respiratory failure?
The main goal of treating respiratory failure is to get enough oxygen to your lungs and organs and remove carbon dioxide. Treatments for respiratory failure include the following: Inhaled medications: Medicines administered either through an inhaler device or through a nebulizer machine can also open up airways, allowing your lungs to pick up oxygen and remove carbon …
What are the early signs of respiratory failure?
Mar 05, 2021 · The most common clinical presentation of all types of acute respiratory failure is acute hypoxia.79 Early identification and appropriate management are critical in limiting adverse outcomes. In the non-intubated patient, evaluation includes a physical examination, a review of recent events, an inspection of any supplemental oxygen equipment, arterial blood analysis, …
What medications are used for respiratory failure?
In the presence of an exacerbation the treatment of airway obstruction with bronchodilators ( Bach et al 2001 ), and the administration of systemic steroids ( Niewoehner et al 1999) and antibiotics are basic in the management of acute respiratory failure.
Can You recover from respiratory failure?
Mar 24, 2022 · If you are diagnosed with a serious lung disease such as respiratory failure, you may need extra oxygen through tubes in your nose or support with a breathing machine called a ventilator. Book traversal links for What Is Respiratory Failure?
What is the most appropriate treatment for a patient in respiratory failure?
A patient with acute respiratory failure generally should be admitted to a respiratory care unit or intensive care unit (ICU). Most patients with chronic respiratory failure can be treated at home with oxygen supplementation and/or ventilatory assist devices along with therapy for their underlying disease.Apr 7, 2020
What medication is used for respiratory failure?
Respiratory Failure MedicationDiuretics, Other.Nitrates.Opioid Analgesics.Inotropic Agents.Beta2 Agonists.Xanthine Derivatives.Anticholinergics, Respiratory.Corticosteroids.Apr 7, 2020
Can you recover from acute respiratory failure?
It is important to note that most people survive ARDS. They will not require oxygen on a long-term basis and will regain most of their lung function. Others will struggle with muscle weakness and may require re-hospitalization or pulmonary rehabilitation to regain their strength.Apr 15, 2020
What does it mean to be in acute respiratory failure?
Acute respiratory failure is defined as the inability of the respiratory system to meet the oxygenation, ventilation, or metabolic requirements of the patient.
What is the nursing diagnosis for acute respiratory failure?
Commonly used NANDA-I nursing diagnoses for patients experiencing decreased oxygenation and dyspnea include Impaired Gas Exchange, Ineffective Breathing Pattern, Ineffective Airway Clearance, Decreased Cardiac Output, and Activity Intolerance.
Is Lasix used for respiratory failure?
Purpose: Furosemide is often used to reduce edema in patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS).
How long can a person be on a ventilator in an ICU?
Some people may need to be on a ventilator for a few hours, while others may require one, two, or three weeks. If a person needs to be on a ventilator for a longer period of time, a tracheostomy may be required.Jun 2, 2020
Is respiratory failure painful?
Surrogates indicated that one out of four patients died with severe pain and one out of three with severe confusion. Families of 42% of the patients who died reported one or more substantial burden.
Can you survive respiratory failure?
Most people who survive ARDS go on to recover their normal or close to normal lung function within six months to a year. Others may not do as well, particularly if their illness was caused by severe lung damage or their treatment entailed long-term use of a ventilator.
How long does respiratory failure last?
Breathing problems. Many people with ARDS recover most of their lung function within several months to two years, but others may have breathing problems for the rest of their lives. Even people who do well usually have shortness of breath and fatigue and may need supplemental oxygen at home for a few months.Jun 13, 2020
What are the early signs of respiratory failure?
The symptoms of respiratory failure depend on the cause and the levels of oxygen and carbon dioxide in your blood. A low oxygen level in the blood can cause shortness of breath and air hunger (the feeling that you can't breathe in enough air). Your skin, lips, and fingernails may also have a bluish color.
What can cause acute respiratory failure?
An injury to your chest or ribs. A drug or alcohol overdose, which can harm your brain and breathing. Lung damage from breathing in fumes or smoke. Lung disease or infection, like chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), cystic fibrosis, or pneumonia.Jan 31, 2021
How is respiratory failure treated?
The main goal of treating respiratory failure is to get enough oxygen to your lungs and organs and remove carbon dioxide.
How to treat respiratory failure?
Treatments for respiratory failure include the following: Inhaled medications: Medicines administered either through an inhaler device or through a nebulizer machine can also open up airways, allowing your lungs to pick up oxygen and remove carbon dioxide more effectively.
Why do we need fluids?
Fluids: Having the correct amount of fluid in the body supports proper blood flow and transportation of nutrition throughout the body, without causing fluid to build up in the lungs. You may be given fluids intravenously to ensure you have just the right amount. This is usually done if you are in the hospital.
How to help shortness of breath?
Oxygen therapy can help reduce shortness of breath and allow patients to be more active. Tracheostomy: involves surgically creating a hole in the front of your neck and into your windpipe. A tube called a tracheostomy is put into the hole to improve your breathing.
What is NPPV in sleep?
It blows air into your airways and lungs. Non-invasive Positive Pressure Ventilation (NPPV): is a noninvasive treatment that helps to keep your airways open while you sleep. NPPV involves wearing a mask that creates mild air pressure to keep the airways open.
What is acute respiratory failure?
Acute respiratory failure occurs when the lungs fail to oxygenate arterial blood adequately and it is one of the commonest postoperative complications. The preoperative identification of risk factors for postoperative acute respiratory failure allows identification of those patients who may benefit from preoperative optimization ...
What is the role of bronchoscopy?
The role of bronchoscopy is limited to the retrieval of large particulate matter. The acidic aspirate is neutralized by pulmonary secretions within minutes of aspiration, therefore bronchoscopy and saline lavage are not required for the aspiration of nonparticulate matter.
Is atelectasis asymptomatic or asymptomatic?
Clinically, atelectasis ranges from asymptomatic to severe hypoxemia and acute respiratory failure. The variability in presentation depends on the rapidity of onset, the degree of lung involvement, and the presence of an underlying pulmonary infection.
What are the two types of acute respiratory failure?
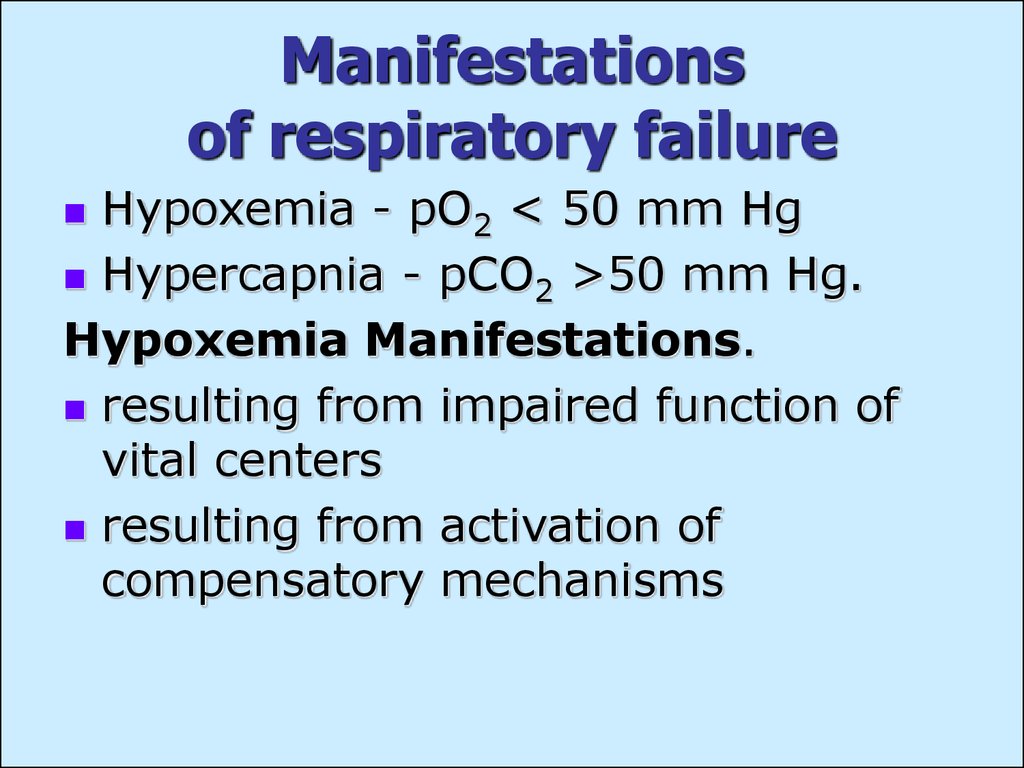
There are two types of acute respiratory failure, hypoxemia or hypercapnia. Hypoxemia is the result of a lack of oxygen in the blood. Hypercapnia is an elevated level of carbon dioxide. Acute respiratory failure has two classifying types, Type 1 and Type 2.
Why do I have respiratory failure?
The underlying cause of respiratory failure comes from the lungs, specifically the alveolus in the lungs when gases cannot be exchanged properly. This is mainly from not getting enough oxygen in the lungs or being able to release enough carbon dioxide out of the lungs.
What is the oxygen exchange?
Oxygen Exchange. Everyday, hour by hour, minute by minute, second by second there is an amazing exchange that happens within our body. Oxygen, the vital living element for all cells in our bodies is breathed in and used for everything from muscles to bones to our heart and brain. Oxygen is taken in and carbon dioxide is then released out ...
How does oxygen get released?
Oxygen is taken in and carbon dioxide is then released out through exhalation. Our lungs are at the center of this fascinating exchange we call respiration. Although this happens every time we take a breath, we never give it much thought, so long as everything is functioning normally.
What is the name of the condition where the respiratory system fails to properly exchange gases?
The condition known as acute respiratory failure occurs when the respiration system fails to properly exchange gases. That can either mean the oxygenation process or the carbon dioxide release. There are two types of acute respiratory failure , hypoxemia or hypercapnia. Hypoxemia is the result of a lack of oxygen in the blood. Hypercapnia is an elevated level of carbon dioxide. Acute respiratory failure has two classifying types, Type 1 and Type 2. Type 1 represents respiratory failure with hypoxemia without hypercapnia. Type 2 is noted if both hypoxemia and hypercapnia are present. Acute respiratory failure can be a serious complication that arises from any number of inflammatory respiratory conditions including, pneumonia and bronchitis.
How to diagnose hypercapnia?
The two most common ways to diagnose acute respiratory failure are physical examination and chest x-ray. Pulse oximetry and arterial blood gas tests can also be used. The most common and most successful treatment option is mechanical ventilation.
What are the symptoms of hypoxemia?
For those with hypoxemia, symptoms usually include difficulty breathing, blueish or pale skin, known as cyanosis, anxiety and restlessness. Symptoms for hypercapnia usually include rapid breathing and confusion. Both types can cause trouble sleeping, profuse sweating and irregular heartbeats.
Does COPD cause shallow breathing?
In the chronic setting, patients with COPD often show a rapid shallow breathing. This presumably represents a key protective mechanism to prevent respiratory muscle fatigue, however at the price of an insufficient alveolar ventilation (Roussos et al 2003).
Is COPD a high risk for death?
Patients with advanced COPD and acute or chronic respiratory failure are at high risk for death . Beyond pharmacological treatment, supplemental oxygen and mechanical ventilation are major treatment options. This review describes the physiological concepts underlying respiratory failure and its therapy, as well as important treatment outcomes.
What is respiratory failure?
Respiratory failure occurs when the breathing system fails to keep adequate blood oxygen levels. There may also be difficulties in removing waste gases, mainly blood carbon dioxide. Respiratory Failure.
What is the most common cause of respiratory failure?
There are various causes of respiratory failure, the most common being due to the lungs or heart.
Why do I feel tired after exertion?
Tiredness - this is due to a lack of oxygen getting to the body's organs.
What happens when you breathe in oxygen?
Every time we take a breath in we are taking oxygen from the air down to the lungs. This crosses over into the blood and is then transported to the various organs. At the same time carbon dioxide, which is the waste gas produced by organs, crosses from the blood and into the lungs - we then breathe this out.
What is the difference between Type I and Type II respiratory failure?
Type I respiratory failure - the blood oxygen is low and the carbon dioxide is normal or low. Type II respiratory failure - the blood oxygen is low and the carbon dioxide is high. Respiratory failure can also be described according to the time it takes to develop: Acute - happens within minutes or hours; usually, ...
What is chronic lung disease?
Chronic - occurs over days and usually there is an underlying lung disease . Acute on chronic - this is usually a sudden or quick worsening of the respiratory function in someone who already has chronic respiratory failure.
What is the purpose of a thyroid function test?
Spirometry: this is used to measure the lung volumes and capacity and is useful in the evaluation of chronic cases.
How long does it take for a respiratory system to develop?
The decrease in oxygen and the buildup of carbon dioxide can happen at the same time. Acute respiratory failure may develop in minutes, hours, or days.
What causes ARF in the lungs?
What causes ARF? Pneumonia, fluid buildup in the lungs from heart failure, or acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) A condition such as Guillain-Barré syndrome or myasthenia gravis that affects nerves or muscles used for breathing. A blood clot in your lungs (pulmonary embolism, or PE) or brain (stroke)
Why is ventilator important?
Ventilation helps get oxygen into your lungs and carbon dioxide out. Ventilation also makes the work of breathing easier. Some systems, such as a CPAP or BiPAP, may only be needed while you sleep. A mechanical ventilator may be needed some or all of the time. It is attached to a mask or breathing tube.
What is ARF in medical terms?
What is acute respiratory failure (ARF)? ARF is a condition that happens when your lungs cannot get enough oxygen into your blood. ARF can also happen when your lungs cannot get the carbon dioxide out of your blood. A buildup of carbon dioxide in your blood can cause damage to your organs. The decrease in oxygen and the buildup ...
How to get oxygen out of your system?
Use pursed-lip breathing any time you feel short of breath. Take a deep breath in through your nose. Slowly breathe out through your mouth with your lips pursed for twice as long as you inhaled.
Can you smoke e-cigarettes?
Ask your healthcare provider for information if you currently smoke and need help to quit. E-cigarettes or smokeless tobacco still contain nicotine.
What does it mean when you feel drowsy?
Feeling drowsy or sleepy during the day, confusion, or mood changes. Swelling of your hands and feet. A bluish color on your skin, fingernails, and lips, or pale skin. Vision problems, seizures, or loss of consciousness.
How much oxygen is needed for AHRF?
Underlying conditions must be addressed as discussed elsewhere. AHRF is initially treated with high flows of 70 to 100% oxygen by a nonrebreather face mask. If oxygen saturation > 90% is not obtained, mechanical ventilation probably should be instituted. Specific management varies by condition.
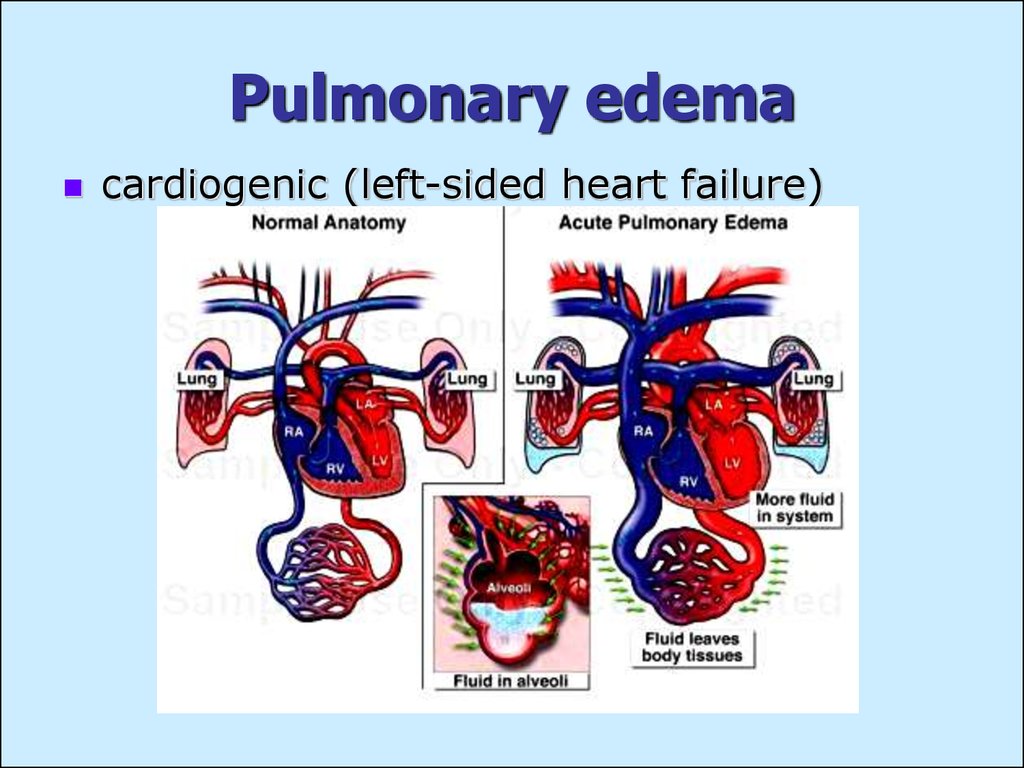
What is acute hypoxemia?
Acute hypoxemic respiratory failure is severe arterial hypoxemia that is refractory to supplemental oxygen. It is caused by intrapulmonary shunting of blood resulting from airspace filling or collapse (eg, pulmonary edema due to left ventricular failure, acute respiratory distress syndrome) or by intracardiac shunting of blood from ...
How high is the mortality rate in ARDS?
Overall, mortality in ARDS was very high (40 to 60%) but has declined in recent years to 25 to 40%, probably because of improvements in mechanical ventilation and in treatment of sepsis. However, mortality remains very high (> 40%) for patients with severe ARDS (ie, those with a PaO2:FIO2 < 100 mm Hg). Most often, death is not caused by respiratory dysfunction but by sepsis and multiorgan failure. Persistence of neutrophils and high cytokine levels in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid predict a poor prognosis. Mortality otherwise increases with age, presence of sepsis, and severity of preexisting organ insufficiency or coexisting organ dysfunction.
What are the different types of ARDS?
ARDS is divided into 3 categories of severity: mild, moderate, and severe based on oxygenation defects and clinical criteria (see table Berlin Definition of ARDS ). The mild category corresponds to the previous category termed acute lung injury (ALI).
What are the effects of cytokines on the lungs?
The cytokines activate alveolar macrophages and recruit neutrophils to the lungs, which in turn release leukotrienes, oxidants, platelet-activating factor, and proteases. These substances damage capillary endothelium and alveolar epithelium, disrupting the barriers between capillaries and airspaces.
What is the early phase of ARDS?
This early phase of ARDS is termed exudative. Later, there is proliferation of alveolar epithelium and fibrosis, constituting the fibro-proliferative phase. Causes of ARDS may involve direct or indirect lung injury. Common causes of direct lung injury are. Acid aspiration.
What is Merck and Co?
Merck & Co., Inc., Kenilworth, NJ, USA is a global healthcare leader working to help the world be well. From developing new therapies that treat and prevent disease to helping people in need, we are committed to improving health and well-being around the world. The Merck Manual was first published in 1899 as a service to the community. The legacy of this great resource continues as the Merck Manual in the US and Canada and the MSD Manual outside of North America. Learn more about our commitment to Global Medical Knowledge.