
Nutrition
These are the three treatment options:
- Isoniazid (INH): This is the most common therapy for latent TB. You typically take an isoniazid antibiotic pill daily for 9 months.
- Rifampin ( Rifadin, Rimactane): You take this antibiotic each day for 4 months. ...
- Isoniazid and rifapentine: You take both of these antibiotics once a week for 3 months under your doctor’s supervision.
What drugs are used to treat TB?
The following are the stages of TB:
- Exposure. This happens when a person has been in contact with, or exposed to, another person who has TB. ...
- Latent TB infection. This happens when a person has TB bacteria in his or her body, but does not have symptoms of the disease. ...
- TB disease. This describes the person who has signs and symptoms of an active infection. ...
What are the phases of TB treatment?
With latent TB:
- You cannot spread TB to other people.
- In some people, the bacteria can become active. If this happens, you may become sick, and you can pass the TB germs to someone else.
- Even though you do not feel sick, you need to take medicines to treat latent TB for 6 to 9 months. ...
Why should I take antibiotics for TB?
- Take your medicine exactly as the healthcare provider directed.
- When you cough, sneeze or laugh, cover your mouth with a tissue. ...
- Do not go to work or school until your healthcare provider says it's okay.
- Avoid close contact with anyone. ...
- Air out your room often so the TB germs don't stay in the room and infect someone else.
What are the treatment medications for active tuberculosis?
Which treatment is used for treating active tuberculosis?
The most common treatment for active TB is isoniazid INH in combination with three other drugs—rifampin, pyrazinamide and ethambutol. You may begin to feel better only a few weeks after starting to take the drugs but treating TB takes much longer than other bacterial infections.
How long does it take to treat active TB?
With the proper treatment, tuberculosis (TB, for short) is almost always curable. Doctors prescribe antibiotics to kill the bacteria that cause it. You'll need to take them for 6 to 9 months.
How is active TB diagnosed?
There are two kinds of tests used to detect TB bacteria in the body: the TB skin test (TST) and TB blood tests. A positive TB skin test or TB blood test only tells that a person has been infected with TB bacteria. It does not tell whether the person has latent TB infection (LTBI) or has progressed to TB disease.
How do you know if TB is latent or active?
What is Latent TB Infection?Usually has a skin test or blood test result indicating TB infection.Has a normal chest x-ray and a negative sputum test.Has TB bacteria in his/her body that are alive, but inactive.Does not feel sick,Cannot spread TB bacteria to others.More items...
How long do you have to take antibiotics for tuberculosis?
For active tuberculosis, you must take antibiotics for at least six to nine months. The exact drugs and length of treatment depend on your age, overall health, possible drug resistance and where the infection is in your body.
What is the test for TB?
Sputum tests. If your chest X-ray shows signs of tuberculosis, your doctor might take samples of your sputum — the mucus that comes up when you cough. The samples are tested for TB bacteria. Sputum samples can also be used to test for drug-resistant strains of TB.
How long does ethambutol last?
If you have drug-resistant TB, a combination of antibiotics called fluoroquinolones and injectable medications, such as amikacin or capreomycin (Capastat), are generally used for 20 to 30 months. Some types of TB are developing resistance to these medications as well.
What test is used to test for tuberculosis?
The most commonly used diagnostic tool for tuberculosis is a skin test, though blood tests are becoming more commonplace. A small amount of a substance called tuberculin is injected just ...
Can a TB test be wrong?
Results can be wrong. The TB skin test isn't perfect. Sometimes, it suggests that people have TB when they don't. It can also indicate that people don't have TB when they do. You can have a false-positive result if you've been vaccinated recently with the bacille Calmette-Guerin (BCG) vaccine.
Can TB drugs cause liver damage?
Serious side effects of TB drugs aren't common but can be dangerous when they do occur. All tuberculosis medications can be toxic to your liver. When taking these medications, call your doctor immediately if you have any of the following:
Is TB a serious disease?
TB is a serious disease, and can be fatal if not treated properly. It is important to remember that all medications have risks and benefits. Learn more from CDC’s Dear Colleague letter. Not everyone infected with TB bacteria becomes sick. As a result, two TB-related conditions exist: latent TB infection and TB disease.
Can rifampin be used for TB?
Treatment. impurities in rifampin and rifapentine, two important anti-tuberculosis (TB) medications. People with TB disease or latent TB infection taking rifampin or rifapentine should continue taking their current medication, and should talk with their healthcare provider about any concerns.
What is the best treatment for TB?
The most common treatment for active TB is isoniazid INH in combination with three other drugs—rifampin, pyrazinamide and ethambutol. You may begin to feel better only a few weeks after starting to take the drugs but treating TB takes much longer than other bacterial infections.
How long does it take to treat TB?
The treatment for this type of TB takes much longer, 20 to 30 months to complete, and you may experience more side effects.
What are the side effects of TB?
While you are in treatment for active TB disease, you will need regular checkups to make sure your treatment is working. Everyone is different, but there are side effects associated with taking the medications, including: 1 Upset stomach, nausea and vomiting or loss of appetite 2 Tingling or numbness in the hands or feet 3 Itchy skin, rashes or bruising 4 Changes in your eyesight or blurred visions 5 Yellowish skin or eyes 6 Dark-colored urine 7 Weakness, fatigue or fever that for three or more days
What are the symptoms of TB?
Yellowish skin or eyes. Dark-colored urine. Weakness, fatigue or fever that for three or more days. It is important to tell your doctor or TB nurse immediately if you begin having any unusual symptoms while taking medicine for either preventive therapy or for active TB disease.
Can TB cause liver damage?
TB drugs can be toxic to your liver, and your side effects may be a warning sign of liver damage . If you are having trouble with tingling and numbness, your doctor may prescribe a vitamin B6 supplement while you are in treatment. It may also be possible to change TB medications if your side effects are serious.
Can you get TB from taking too much medicine?
You must finish your medicine and take the drugs exactly as prescribed. If you stop taking the drugs too soon you can become sick again and potentially spread the disease to others. Additionally, by taking the drugs incorrectly, TB germs that are still alive may become drug-resistant, making it harder for you to get better next time.
What is the standard of care for TB?
The standard of care for treatment of active TB is daily administration of medicines from local health department nurses. These nurses meet at regular times with TB patients Monday through Friday to watch them take their medicines and to monitor for any problems. This is called directly observed therapy (DOT).
What are the groups that pass on TB?
Contact with groups known for passing on TB, such as the homeless, injection drug users, and persons with HIV/AIDS. Living or working with people who are at high risk for TB, such as those in hospitals, homeless shelters, prisons, nursing homes, or refugee camps.
Why do people get sick from TB?
People get sick from the TB germs that are alive and active. This means that they are growing and destroying tissues in a person’s body. TB was once the leading cause of death in the United States. Today, we have many medicines to treat and cure TB disease.
How long does it take for TB to go away?
Treatment. TB can be treated by taking several medicines for six to twelve months. It is very important that all medicines are taken exactly as prescribed. If your child stops taking the medicines too soon, the germs that are still alive may become resistant. This makes the TB germs harder to treat.
How does TB spread?
Active TB disease is contagious. That means it can be spread from one person to another. It is most often spread through the air. The germs may enter the air when a person with TB disease of the lungs or throat coughs or sneezes. People nearby may breathe in these germs and get infected.
Can TB be isolated at home?
On weekends and holidays, parents give their child the medicines. Usually, your child will be isolated at home until he or she is determined to no longer be contagious. Once your child is out of isolation, he or she will be seen in the TB clinic monthly, or as needed, until the end of treatment.
Can you take TB medicine with milk?
Take medicines on an empty stomach, either one hour before a meal or two hours after a meal. Do not take the medicines with milk products. Your child will have positive TB skin and blood tests for the rest of his or her life. Therefore, when being evaluated for TB in the future, your child will need a chest x-ray.
What should a clinic decide on TB treatment?
Clinicians should choose the appropriate treatment regimen based on drug susceptibility results of the presumed source case (if known), coexisting medical conditions (e.g., HIV. ), and potential for drug-drug interactions. Consultation with a TB expert is advised if the known source of TB infection has drug-resistant TB.
What is the name of the drug that is used to treat TB?
Isoniazid (INH) Rifapentine (RPT) Rifampin (RIF) These medications are used on their own or in combination, as shown in the table below. CDC and the National Tuberculosis Controllers Association (NTCA) preferentially recommend short-course, rifamycin-based, 3- or 4-month latent TB infection treatment regimens over 6- or 9-month isoniazid ...
Is 6H or 9H better for TB?
Although effective, 6H and 9H have higher toxicity risk and lower treatment completion rates than most short-term treatment regimens. All treatment must be modified if the patient is a contact of an individual with drug-resistant TB disease.
How long do you have to take antibiotics for TB?
In addition, because tuberculosis bacteria grow slowly, it's necessary to take the antibiotics for at least six months. (5, 12) Treatment for active TB will include a combination of three to four of these drugs: Isoniazid (Nydrazid) Rifampin (Rifadin) Pyrazinamide.
What does it mean to have active tuberculosis?
What It Means to Have Active Tuberculosis Disease. In active tuberculosis, the bacteria multiply in the body, causing noticeable symptoms. This is also when the disease can spread to others. The difference between active and latent TB is the amount of organisms in the body, according to Dr. Reichman.
Why is it important to treat latent TB?
That’s why it’s important to identify and treat latent TB. If a latent infection is discovered, treatment is recommended in certain individuals at high risk to prevent that person from developing active disease and to prevent the further spread of tuberculosis.
How many stages of tuberculosis are there?
Most commonly, tuberculosis goes through three stages: Primary TB infection. Latent TB infection. Active TB disease. Millions of people carry latent TB bacteria but never develop active tuberculosis. In fact, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) estimates that as many as 13 million people in the United States have ...
How many stages of TB are there?
Even when it starts to make you sick, symptoms come on very gradually and can often be confused with other conditions. Most commonly, tuberculosis goes through three stages: Primary TB infection. Latent TB infection.
What is the primary cause of tuberculosis?
Primary or Initial Tuberculosis Infection. Infection with M. tuberculosis begins when a person breathes in airborne bacteria. This is more likely to happen if a person is in close contact with one or more infected people with active TB who are coughing or sneezing.
How many antibiotics do you need for tuberculosis?
Because there are so many drug-resistant strains of TB, people with active disease must take more than one antibiotic to ensure that all of the bacteria are killed.
Where is TB common?
From countries where TB is common, including Mexico, the Philippines, Vietnam, India, China, Haiti, and Guatemala, or other countries with high rates of TB. (Of note, people born in Canada, Australia, New Zealand, or Western and Northern European countries are not considered at high risk for TB infection, unless they spent time in a country ...
Why is latent TB important?
Treatment of latent TB infection is essential to controlling TB in the United States because it substantially reduces the risk that latent TB infection will progress to TB disease.
How many people have latent TB?
In the United States, up to 13 million people may have latent TB infection. Without treatment, on average 1 in 10 people with latent TB infection will get sick with TB disease in the future. The risk is higher for people with HIV, diabetes, or other conditions that affect the immune system.
What is a TST reaction?
People with a tuberculin skin test (TST) reaction of 5 or more millimeters who are: HIV-infected persons. Recent contacts to a patient with active TB disease. Persons with fibrotic changes on chest radiograph consistent with old TB. Organ transplant recipients.
Can TB be treated with LTBI?
Persons with no known risk factors for TB may be considered for treatment of LTBI if they have either a positive IGRA result or if their reaction to the TST is 15 mm or larger. However, targeted TB testing programs should only be conducted among high-risk groups.
Can TB spread to others?
People with latent TB infection do not have symptoms, and they cannot spread TB bacteria to others. However, if latent TB bacteria become active in the body and multiply, the person will go from having latent TB infection to being sick with TB disease.

Risk Factors
Signs and Symptoms
Diagnosis
Treatment
Specialist to consult
What to Watch For at Home
- Being in close contact with a person with active TB disease
- People who were born, traveled, or have lived overseas
- Contact with groups known for passing on TB, such as the homeless, injection drug users, and persons with HIV/AIDS
- Living or working with people who are at high risk for TB, such as those in hospitals, homeles…
- Being in close contact with a person with active TB disease
- People who were born, traveled, or have lived overseas
- Contact with groups known for passing on TB, such as the homeless, injection drug users, and persons with HIV/AIDS
- Living or working with people who are at high risk for TB, such as those in hospitals, homeless shelters, prisons, nursing homes, or refugee camps
Activity, Diet and Other Information
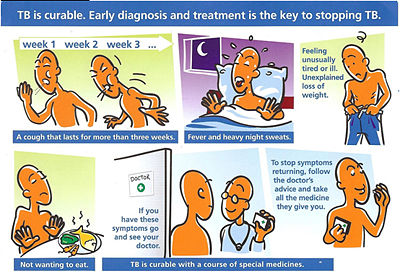
- A cough that lasts two weeks or more
- Pain in the chest, with cough or at rest
- Coughing up blood or thick mucous
- Night sweats