Medication
What is the Treatment for Spermatocele?
- Spermatocele Treatment
- Medications. If the patient experiences pain or swelling, then the doctor may provide some over-the-counter medicines.
- Surgery. When oral medications do not give any relief, then the doctor recommends surgery to remove the cyst.
- Aspiration. ...
- Sclerotherapy. ...
- Other Treatment Options. ...
Procedures
Thus, Spermatocele does not go away on its own but treatment is not always necessary since this condition is quite benign and asymptomatic.
Nutrition
Spermatocele Prognosis. Spermatic cysts usually do not cause any short-term or long-term problems. In more serious cases, the prognosis is generally positive with early diagnosis and proper treatment. The condition does not affect the fertility of the patient. Timely treatment allows the patient to live a long and normal life. Spermatocele ...
How to treat spermatocele at home naturally?
- feel comfortable in their actions
- avoid sexual activities that cause pain
- adopt safer sex strategies
Do Spermatoceles go away on their own?
What is the prognosis of spermatocele following treatment?
How to reduce spermatocele?

What is the best treatment for spermatocele?
Surgical therapy known as spermatocelectomy is the most common treatment for a symptomatic spermatocele. The aim is to remove the cyst from the epididymis while, at the same time, preserve the genital system. This surgery is done as an outpatient procedure. That means you won't need to stay in a hospital overnight.
How is a spermatocele cyst treated?
Spermatocelectomy is the standard treatment for spermatoceles that cause symptoms. The goal of surgery is to remove the spermatocele from the epididymal tissue and preserve the reproductive tract. This outpatient procedure is often done with local or general anesthesia. It usually takes less than 1 hour.
Do spermatocele need to be removed?
Most spermatoceles remain small in size and cause few or no symptoms. If a spermatocele doesn't bother you, you may not need treatment. In more severe cases, a spermatocele can cause long-term pain or other uncomfortable symptoms. Your provider may recommend surgery to remove the cyst.
How long can a spermatocele last?
The mean duration of symptoms was 48 months. At the time of excision, the average size of spermatoceles was 4.2 cm in greatest diameter, and most (71%) were right sided. Men who experienced pain as an isolated symptom were younger by approximately 10 years compared to those who experienced mass.
How can I get rid of spermatocele without surgery?
You cannot get rid of a spermatocele naturally....Another, although less effective, alternative surgery is sclerotherapy.This involves injecting a substance that shrinks the spermatocele (a sclerosing agent).Common sclerosing agents include alcohol, phenol, tetracycline and fibrin glue.More items...•
How can I shrink my spermatocele naturally?
For spermatocele treatment, natural remedies can also be used. Maintaining a balanced diet with less fat and more iodine content is vital. A deficiency of iodine can cause cyst formation. Also, the topical application of iodine, magnesium and chromium chloride can also be used for the spermatocele treatment.
Can you live with a spermatocele?
Although your spermatocele probably won't go away on its own, most spermatoceles don't need treatment. They generally don't cause pain or complications.
Can antibiotics treat spermatocele?
No specific medical therapy is indicated for treatment of a simple spermatocele. Oral analgesics may be prescribed for symptomatic relief. If an underlying epididymitis is responsible for discomfort, antibiotics may be indicated. Observation is usually used for simple, small asymptomatic spermatoceles.
How big can spermatocele get?
They can get to be as large as 15 cm, and some patients will present with concern that they “have a third testicle.” The consistency of a large spermatocele is, in fact, similar to that of a normal testis. Spermatoceles rarely cause pain.
At what size should a spermatocele be removed?
Men on average will seek surgical correction of spermatoceles once the lesion has reached the size of a normal testicle, around 4 centimeters.
When is a spermatocele too big?
If it becomes large enough, however, you might feel: Pain or discomfort in the affected testicle. Heaviness in the testicle with the spermatocele. Fullness behind and above the testicle.
Does spermatocele affect sperm?
In some cases, spermatoceles grow large in size causing heaviness and pain. They also can grow large enough to push the testes up into the groin. Though this happens rarely, in such cases, spermatocele causes infertility.
What is a spermatocele?
Spermatocele is a common growth that develops right above or behind the testicle. It is also called a testicular or epididymal cyst. Spermatoceles are benign (not cancer). Healthcare providers usually recommend treatment only when a large spermatocele hurts or bothers you. Ask your provider how cyst removal surgery could affect fertility.
What is spermatocelectomy surgery?
Spermatocelectomy is another name for spermatocele cyst removal surgery. It is an outpatient procedure. You go home after surgery instead of staying in the hospital. During a spermatocelectomy, a provider makes an incision in the scrotum or groin area. Then the provider carefully removes the spermatocele.
Why do spermatocele go undiagnosed?
Spermatoceles are a common condition. They usually cause few or no symptoms. Many times, a spermatocele goes undiagnosed because people don’t realize it’s there. The condition doesn’t generally lead to further health problems or pose a serious threat. Larger spermatoceles may be painful or uncomfortable.
Where is the spermatocele located?
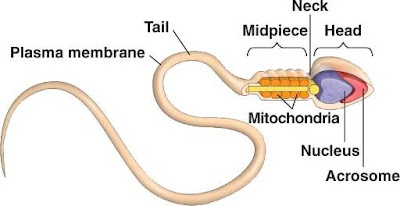
A spermatocele is a fluid-filled cyst (growth) located above or behind the testicle. Inside each spermatocele is a clear or cloudy fluid that may also contain sperm. Healthcare providers sometimes call these growths spermatic cysts or epididymal cysts. Spermatoceles develop along the epididymis, which is part of the male reproductive system.
How accurate are sonograms for spermatoceles?
Sonograms are nearly 100% accurate in diagnosing spermatoceles. Lab tests: If you have testicular pain, your provider may recommend blood tests (such as a complete blood count or CBC test) or urine tests (such as urinalysis ). These tests check for possible inflammation or infection.
Where does sperm build up?
Spermatoceles happen when sperm builds up somewhere in the epididymis. Healthcare providers don’t fully understand the factors that lead to this sperm buildup. Some medical experts point to a blockage in the epididymal duct or inflammation as potential causes.
Can spermatocele damage your reproductive system?
However, certain spermatocele treatments have the potential to damage reproductive tissues. Surgery poses a small risk, as does a rarely used therapy called aspiration and sclerotherapy [JS1] . Your provider can explain your treatment options, including how a therapy may affect your reproductive future.
Medications
If the patient experiences pain or swelling, then the doctor may provide some over-the-counter medicines. Medicines like Tylenol or ibuprofen help in reducing the pain and swelling caused due to spermatocele.
Surgery
When oral medications do not give any relief, then the doctor recommends surgery to remove the cyst. The patient will be given general anesthesia and a small cut is made in the scrotum and the cyst is separated from the epididymis and removed.
Aspiration
This is a minimally invasive therapy in which the doctor inserts a needle into the epididymis and the fluid is drained from the cyst.
Sclerotherapy
After the aspiration therapy, if the spermatocele reoccurs, then sclerotherapy is done. In this technique, the fluid is drained out from the sac and it is filled with an irritating agent that forms the scar tissue. This actually lowers the chance of reoccurrence. Sclerotherapy can cause damage to epididymis which can lead to infertility.
Other Treatment Options
For spermatocele treatment, natural remedies can also be used. Maintaining a balanced diet with less fat and more iodine content is vital. A deficiency of iodine can cause cyst formation. Also, the topical application of iodine, magnesium and chromium chloride can also be used for the spermatocele treatment.
What is the best treatment for a spermatocele?
Surgical therapy . Surgical therapy known as spermatocelectomy is the most common treatment for a symptomatic spermatocele. The aim is to remove the cyst from the epididymis while, at the same time, preserve the genital system. This surgery is done as an outpatient procedure.
How to diagnose spermatocele?
Diagnosis. A spermatocele can be diagnosed through a detailed examination of the genital area. Your doctor will feel your testicles to search for masses, or areas that are tender or painful to the touch. You can expect to feel some pain when your doctor touches the affected areas.
What is a cyst in the testicle called?
A spermatocele is an often pain-free benign cyst that occurs close to a testicle. It may also be known as a spermatic or epididymal cyst. The cyst forms in the epididymis. The epididymis is a coiled tube behind each testicle. The cyst is filled with fluid and may contain dead sperm.
Where is the spermatocele found?
They can be felt, however. A spermatocele feels like a smooth, but separate, firm lump. The lump is found near the top of, or behind, a testicle. Spermatoceles are most likely to be discovered during your yearly physical when your doctor checks for any signs of a testicular growth.
How to check for cysts in scrotum?
Any spermatocele should be clearly seen. Ultrasound. If transillumination isn’t successful, an ultrasound can be used by your doctor to look inside the scrotum to search for a cyst.
What does it mean when you have a mass in your testicle?
You may also experience heaviness, as well as a feeling of fullness in the testicle. A mass in your scrotum could signal another issue as well. Talk to your doctor about any unexplained lumps in your scrotum. That way they can rule out more serious causes and come up with a treatment plan.
Can spermatocele come back after surgery?
It’s also possible that your spermatocele might come back, even after surgery.
How long does it take to remove spermatocele?
This outpatient procedure is often done with local or general anesthesia. It usually takes less than 1 hour. Sometimes all or a part of the epididymis may need to be removed as well.
Where are spermatoceles found?
They tend to be benign (not cancerous). These cysts are found near the top and behind the testicle, but are separate from the testicle.
What is the difference between sclerotherapy and aspiration?
Aspiration and sclerotherapy are 2 treatments that are available, but are not often used. Aspiration involves puncturing the spermatocele with a needle and drawing out its contents. Sclerotherapy involves injecting an irritating agent into the spermatocele sac. This causes it to heal or scar closed.
How long does scrotal swelling last after surgery?
A follow up visit with your surgeon is often scheduled between 1 and 3 weeks later. Scrotal swelling is normal and typically lasts for 2 to 21 days.
What does it mean when spermatocele is light shining?
Light can be shined through a spermatocele. This generally shows if the mass looks like a solid tumor or a benign (not cancerous) cyst.
What is the function of the male reproductive tract?
The male reproductive tract handles the growth, maturation and delivery of sperm. Faults in the male reproductive tract can cause a mass to grow. If a mass forms in the scrotum, it may mean nothing or it could be a sign of something serious.
Can sperm tubes be used for fertility?
These options have been shown to work but in general, they are not recommended and rarely used. There is a risk of harm to the epididymis (tube that stores sperm), which can lead to fertility problems. Another common problem with both of these methods is that the spermatoceles can come back.
Where is the spermatocele located?
A spermatocele (SPUR-muh-toe-seel) is an abnormal sac (cyst) that develops in the epididymis — the small, coiled tube located on the upper testicle that collects and transports sperm. Noncancerous and generally painless, a spermatocele usually is filled with milky or clear fluid that might contain sperm.
What to do if you find a lump in your testicles?
Regular self-examination is an important health habit. But it can't substitute for a doctor's examination. Your doctor normally checks your testicles whenever you have a physical exam. By Mayo Clinic Staff.
How to examine testicles?
How to examine your testicles. A good time to examine your testicles is during or after a warm bath or shower. The heat from the water relaxes your scrotum, making it easier for you to detect anything unusual. Then follow these steps: Stand in front of a mirror. Look for any swelling on the skin of the scrotum.
Can spermatocele cause testicular cancer?
Because a spermatocele usually doesn't cause symptoms, you might discover it only during a testicular self-exam, or your doctor might find it during a routine physical exam. It's a good idea to have your doctor evaluate any scrotal mass to rule out a serious condition, such as testicular cancer. Also, call your doctor if you experience pain ...
What does it feel like to have a large testicle?
If it becomes large enough, however, you might feel: Pain or discomfort in the affected testicle. Heaviness in the testicle with the spermatocele. Fullness behind and above the testicle.
Is spermatocele a risk factor?
There aren't many known risk factors for developing a spermatocele. Men whose mothers were given the drug diethylstilbestrol (DES) during pregnancy to prevent miscarriage and other pregnancy complications appear to have a higher risk of spermatoceles.
Is the testicle a part of the scrotum?
Also, the cord leading upward from the top of the testicle (epididymis) is a normal part of the scrotum. By regularly performing this exam, you'll become more familiar with your testicles and aware of any changes that might be of concern. If you find a lump, call your doctor as soon as possible.
Symptoms
Spermatoceles cannot be seen during a visual exam. That’s because they’re contained within the scrotum. They can be felt, however. A spermatocele feels like a smooth, but separate, firm lump. The lump is found near the top of, or behind, a testicle.
Causes
Researchers don’t know what causes spermatoceles. Spermatoceles are neither cancerous nor do they increase your risk of testicular cancer.
Diagnosis
A spermatocele can be diagnosed through a detailed examination of the genital area. Your doctor will feel your testicles to search for masses, or areas that are tender or painful to the touch. You can expect to feel some pain when your doctor touches the affected areas.
Treatment
Spermatoceles aren’t cancerous and are usually pain-free. Most people won’t need treatment. Instead, your doctor will monitor the cyst during regular doctor appointments.
Outlook
Most people won’t experience any symptoms from a spermatocele. If you do experience pain or discomfort, spermatocelectomy should provide relief, though there is a risk for complications that may affect fertility. It’s also possible that your spermatocele might come back, even after surgery.
What is a spermatocele and what are its causes
The epididymal cyst or spermatocele is a retention of spermatic fluid in the epididymis tubule that distends forming a bulge or cyst, therefore it is a benign cyst and it turns out to be the most common of those that form in the testicular area. . Generally, within this cyst this whitish or even transparent liquid contains dead sperm cells.
Symptoms of spermatocele
The epididymal cyst does not usually present noticeable symptoms by the sufferer. Normally when they are small, which happens in the vast majority of cases, these internal lumps of retention of spermatic fluid do not cause any pain .
Diagnosis of spermatocele
To detect and diagnose a benign cyst in this area of the male body, it is essential that a man perform a testicular self-examination on a regular basis, we remember that it is recommended by specialists to do it every month, or that he also go to the urologist on a regular basis to check himself completely.
Treatment of spermatocele and spermatocelectomy
In most cases, as they are small cysts that do not produce pain or discomfort, no specific medical treatment is required.
Frequently asked questions about spermatocele
In addition to knowing what it is, the causes, symptoms and its possible treatments, there are some frequent doubts about sperm cysts that we answer below:
How big should a spermatocele be for sclerotherapy?
Generally, the spermatocele should be at least 1.5 cm to be amenable to treatment. The first step is a diagnosis, which can be done by an ultrasound in the office.
What is a spermatocele cyst?
A spermatocele or spermatic cyst is an abnormal sac in the upper part of the epididymis (the epididymis is a coiled tube in the testicle that collects and transports sperm). In most cases, a spermatocele is a smooth, soft mass that contains clear or milky fluid, and sometimes, sperm. The exact reason why spermatoceles develop is unknown ...
What is sclerotherapy in surgery?
Sclerotherapy is an outpatient procedure performed in the office that involves removing the fluid collection (aspiration) through a small tube followed by injection of a medication (sclerotherapy) that helps close the cavity that was containing the fluid. Our specialist applies a local anesthetic to make the procedure essentially pain-free. There is no nerve block or anesthesia required otherwise. There is no downtime, stitches or incisions. You will walk out of the office after the procedure.
What are the complications of spermatocelectomy?
Possible complications include continued pain, recurrence of the spermatocele, hematoma, and infection. Damage to the epididymis and/or vas deferens during the surgery can affect fertility. In one study, nearly 20% of patients who underwent surgical spermatocelectomy experienced postoperative complications such as treatment failure, chronic pain, ...
Is spermatoceles a problem?
Spermatoceles are a relatively common problem and are often discovered by chance. Incidental spermatoceles are found in 30% of patients undergoing ultrasound of the scrotum for other complaints.
Can spermatocele be removed with aspiration?
Aspiration alone will not be sufficient. If your specialist only removes the fluid it will only be a matter of time that the spermatocele will return causing your symptoms again. Sclerotherapy is important as it closes the cavity, preventing the fluid from returning.
Is scrotal spermatocele surgery invasive?
Sclerotherapy is a minimally-invasive, non-surgical, outpatient treatment for scrotal spermatocele. It is quick, safe, and effective, and it avoids the expense and potential complications of surgery. There are no major incisions, no stitches, and no downtime. You can return to work immediately after the treatment.
