Explore
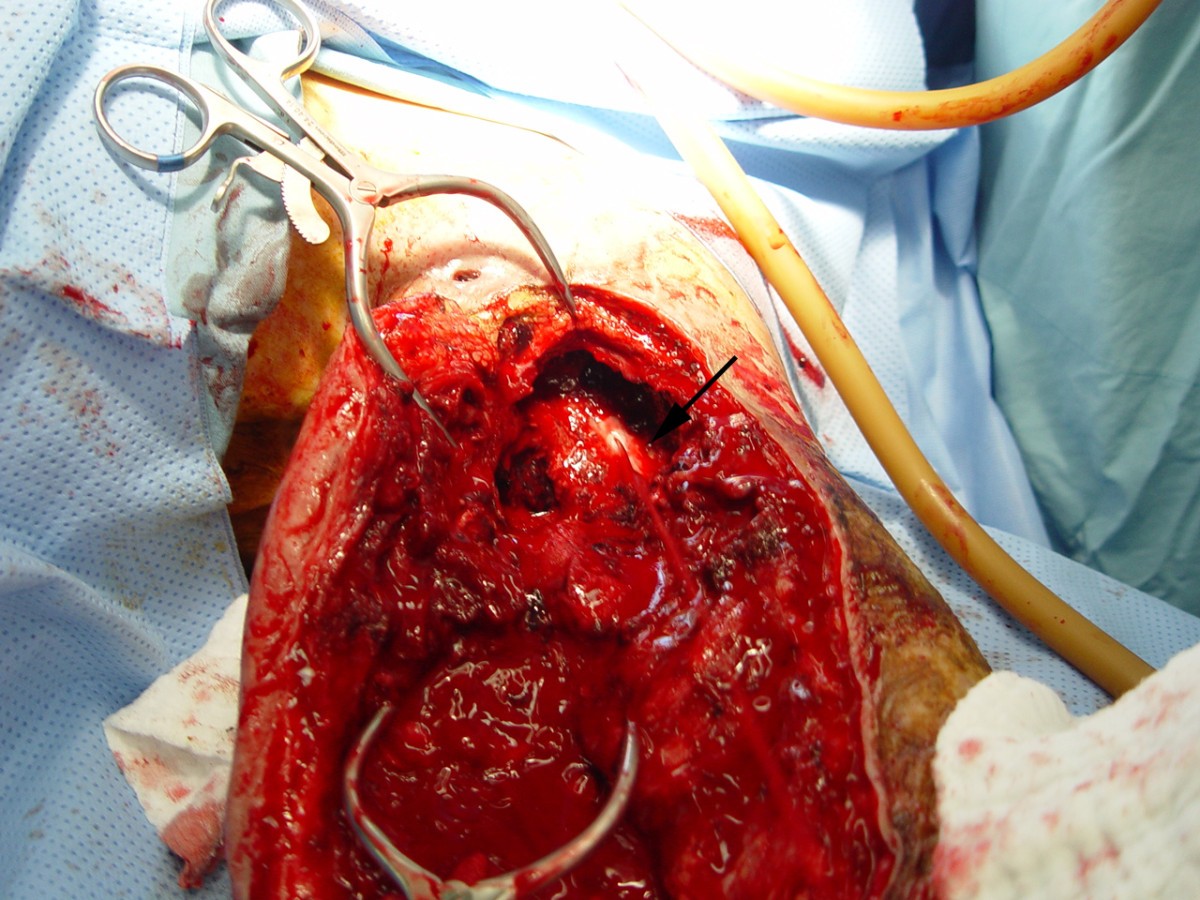
Surgery is sometimes required, but most pseudoaneurysms at arterial puncture sites can be treated with a brief, minimally-invasive procedure performed under local anesthesia. Preparation takes a few minutes. The procedure will be explained and informed consent obtained.
How do you get rid of pseudoaneurysm?
Treatment for femoral pseudoaneurysms The limited evidence base appears to support the use of thrombin injection as an effective treatment for femoral pseudoaneurysm. A pragmatic approach may be to use compression (blind or ultrasound-guided) as first-line treatment, reserving thrombin injection for those in whom the compression procedu …
Why is it important to get a diagnosis of pseudoaneurysm?
Over the past few years, interventional radiological treatment has evolved and taken the place of surgery in management. There are different kinds of percutaneous and endovascular treatment methods in pseudoaneurysm management. Treatment options depend on certain conditions.
How is a pseudoaneurysm treated with thrombin?
These endovascular treatment methods are also used for the pseudoaneurysms (gastroduodenal, pancreaticoduodenal, or splenic artery) associated with chronic pancreatitis . Due to the fact that chronic pancreatitis is a continuous inflammation, surgical approaches are suggested after endovascular embolization to avoid rebleeding [ 63 ].
What is compression for pseudoaneurysm?
14 rows · Mar 21, 2022 · Currently the treatment options for pseudoaneurysms include ultrasound guided compression ...
How serious is a pseudoaneurysm?
Pseudoaneurysms also pose a risk of blood clots that can travel to your heart, lungs, or brain and cause serious health problems such as heart attack or stroke.Nov 10, 2021
Does pseudoaneurysm go away?
Some pseudoaneurysms resolve themselves, though others require treatment to prevent hemorrhage, an uncontrolled leak or other complications. An ultrasound study in the Vascular Laboratory may be requested to evaluate a puncture site if swelling, pain or extensive bruising suggests a pseudoaneurysm may have developed.
What is a pseudoaneurysm and how is it treated?
Once the pseudoaneurysm is found, your doctor presses on it to release the built-up blood. Ultrasound-guided medication. In this treatment, your doctor uses ultrasound imaging to locate and inject a blood clot-forming medication (thrombin) into the pseudoaneurysm. The medication causes the pooled blood to clot.
How long does it take for a pseudoaneurysm to dissolve?
A small pseudoaneurysm may close on its own in about 4 weeks. You may need any of the following to treat a pseudoaneurysm that does not close: Debridement is a procedure used to remove dead tissue. You may need this if the area around your pseudoaneurysm becomes infected.
How long can you live with a pseudoaneurysm?
Methods: 10 patients with postinfarction left ventricular pseudoaneurysm were followed up over a mean (SD) period of 3.8 (5.2) years. Results: In those treated conservatively (n = 9), cumulative survival was 88.9 (10.5)% and 74.1 (16.1)% at one and four years, respectively.
What happens if a pseudoaneurysm ruptures?
It occurs when the wall of a blood vessel is damaged. This can cause blood to leak out of the blood vessel and to collect in the surrounding tissue. If you have a pseudoaneurysm, it's important to get a diagnosis and the appropriate treatment because some pseudoaneurysms, if left untreated, may rupture.Dec 13, 2019
Why is it important to get a diagnosis for a pseudoaneurysm?
If you have a pseudoaneurysm, it’s important to get a diagnosis and the appropriate treatment because some pseudoaneurysms, if left untreated, may rupture. Let’s take a closer look at what causes pseudoaneurysms, where they develop, as well as their symptoms, risk factors, diagnosis, and treatment.
What is a pseudoaneurysm?
As you might guess from the name, a pseudoaneurysm is a false aneurysm. It occurs when the wall of a blood vessel is damaged. This can cause blood to leak out of the blood vessel and to collect in the surrounding tissue. If you have a pseudoaneurysm, it’s important to get a diagnosis and the appropriate treatment because some pseudoaneurysms, ...
What test is used to check for pseudoaneurysms?
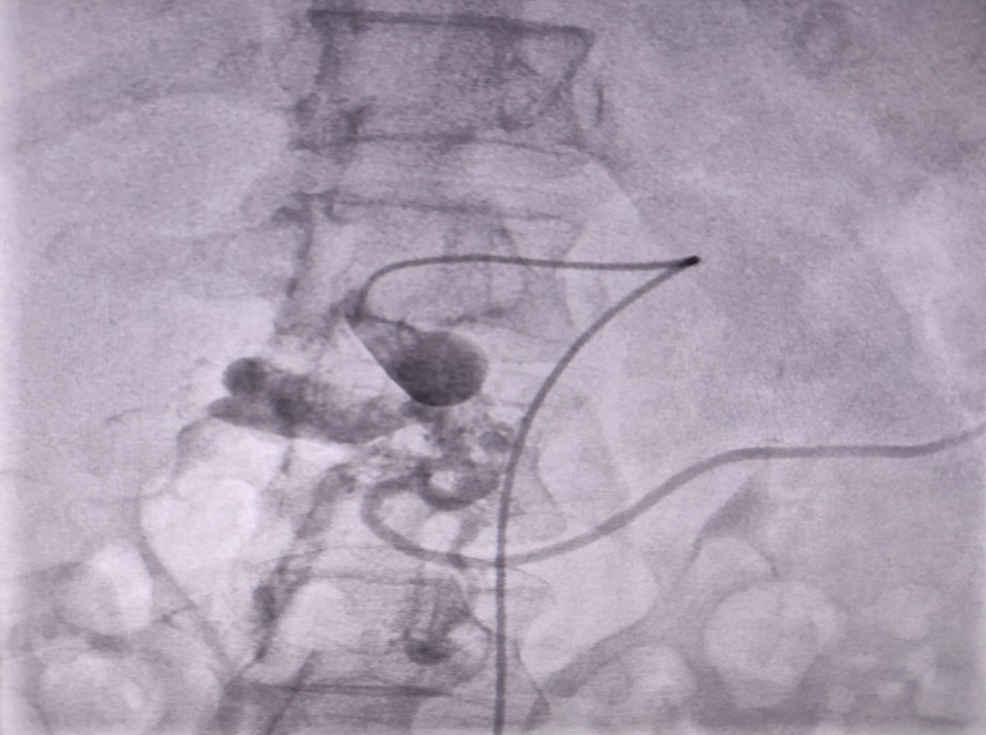
If your healthcare provider suspects you may have a pseudoaneurysm, they’ll probably order an ultrasound or another type of noninvasive test. They may also recommend an angiogram. This test uses X-rays to look at your blood vessels more closely. It involves having a long, thin catheter inserted into your blood stream.
Why do pseudoaneurysms occur?
Trauma. Trauma or damage to the aorta from an accident or wound can cause blood to start leaking, causing a pseudoaneurysm to form in the surrounding tissues. Surgical complication.
What are the symptoms of pseudoaneurysm?
Your healthcare provider might suspect a pseudoaneurysm if you develop the following symptoms: swelling or tenderness in a particular area, especially if you’ve recently undergone a procedure. a painful mass or lump.
Where is a pseudoaneurysm inserted?
A pseudoaneurysm typically develops close to the insertion spot where the narrow, flexible catheterization tube is threaded up toward the heart. If the catheter is inserted in your groin area, the pseudoaneurysm may develop there. The catheter can also be inserted into your neck or arm.
Can a pseudoaneurysm develop after a cardiac catheterization?
It’s not uncommon for a pseudoaneury sm to develop after a person undergoes a cardiac catheterization procedure. In fact, research suggests that a pseudoaneurysm is a common occurrence when the femoral artery (a large artery in your groin area) has been repeatedly punctured during a catheterization.
What is a pseudoaneurysm?
A pseudoaneurysm, or false aneurysm, is swelling of the wall of the artery. The swelling is caused by a small hole that has not sealed. A pseudoaneurysm can happen in any artery. It may become a medical emergency because the pseudoaneurysm can rupture.
How long does it take for a pseudoaneurysm to close?
A small pseudoaneurysm may close on its own in about 4 weeks. You may need any of the following to treat a pseudoaneurysm that does not close: Debridement is a procedure used to remove dead tissue. You may need this if the area around your pseudoaneurysm becomes infected. Compression is a procedure that may be used if the pseudoaneurysm is in your ...
How long to monitor for pseudoaneurysm?
Your healthcare provider may want to monitor the pseudoaneurysm for up to 4 weeks to see if it closes. He may tell you to limit your activity to lower your risk for rupture. Do not smoke. Nicotine and other chemicals in cigarettes and cigars can cause blood vessel and lung damage.
Can you take salt for pseudoaneurysms?
Your healthcare provider may recommend that you limit the amount of sodium (salt) you have every day. You may also need to take your blood pressure and keep a record of the numbers. You may also need to take medicine to control your blood pressure.
What Are the Causes of a Pseudoaneurysm?
A pseudoaneurysm is often a complication of cardiac catheterization. Cardiac catheterization is a procedure for diagnosing heart conditions. Your doctor will insert a flexible tube with a camera into the artery in your leg and thread it through your blood vessels to your heart.
What Are the Symptoms of a Pseudoaneurysm?
The symptoms of a pseudoaneurysm are usually pain and swelling at the site of the blood vessel damage. You might feel a lump under your skin where the blood is pooling in the tissue. It may feel tender or painful to the touch. It may feel like it's throbbing.
What Is the Treatment for a Pseudoaneurysm?
If you suspect you have a pseudoaneurysm, you should talk to your doctor, especially if you’ve recently had a cardiac catheterization. You will need to have an ultrasound of the area to get a firm diagnosis. Your doctor will be able to decide on treatment after seeing the details of the pseudoaneurysm.
Does a Pseudoaneurysm Have Health Risks?
If you think you might have a pseudoaneurysm, you should call your doctor. If you don't have the condition treated, you're at risk of severe complications. The buildup of blood can damage circulation in the area and cause tissue death.
What is PsA in medical terms?
Image Gallery. Pseudoaneurysms (PsA) are defined as a collection of blood between the outer two layers of an artery, the media and adventitia. These lesions are uncommon in the pediatric population. The most common causes are penetrating injuries either traumatic or iatrogenic. In contrast, a true aneurysm involves all three layers ...
Where can a PsA be found?
A PsA can occur in any artery in the body. 4,5 The clinical presentation of a PsA is usually a tender, pulsatile mass in the region of an artery. There is often associated redness, pain with palpation and warmth of the skin. If there is the suspicion of a PsA, confirmation by US with Doppler examination is indicated.
Can a PsA clot spontaneously?
Typically, the US study shows arterial blood flow into the PsA that is chaotic and swirling in its appearance (Figure 1). When a PsA is small it often will spontaneously clot and resolve without therapy; however, larger PAs need therapy since it is unlikely that they will spontaneously resolve. The treatment options for large and/or symptomatic PAs ...
Can a covered stent be used for PsA?
Alternatively, one can use a covered stent to isolate the PsA with or without thrombin injection, however, this is not an ideal approach for small children since there arterial diameter is small and increasing the risk of arterial occlusion and reduction future arterial growth leading to vessel narrowing.
