
Medication
- the heart
- the windpipe
- the food pipe (oesophagus)
- major blood vessels
Procedures
Method 3 Method 3 of 3: Soothing Throat Nodules
- Drink plenty of water. While drinking water is always important, it's especially important if you have throat nodules.
- Limit your alcohol and caffeine intake. Both of these can irritate your throat and make nodules worse.
- Quit smoking or don’t start at all. ...
- Treat any underlying health issues you have that could cause nodules. ...
Therapy
What are lung nodules and what sneaky thing causes them? Lung nodules are small growths found in lung tissue. Pulmonary nodules can be benign or cancerous. Benign nodules are caused by diseases which cause inflammation of lung tissue. Infections and autoimmune diseases are the most common causes of benign nodules on lungs.
Nutrition
Overall, the likelihood that a lung nodule is cancer is 40 percent. However, a person's actual risk depends on a variety of factors, such as age: In people younger than 35, the chance that a lung nodule is malignant is less than 1 percent, while half of lung nodules in people over 50 are cancerous.
How do you remove a lung nodule?
How to dissolve nodules naturally?
What are lung nodules and what sneaky thing causes them?
What are the chances a lung nodule or spot is cancer?
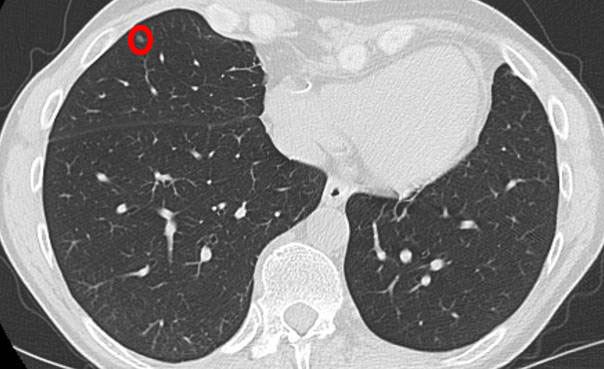
How serious is a nodule on your lung?
If the nodule on earlier images hasn't changed in size, shape or appearance in two years, it's probably noncancerous. Noncancerous lung nodules are often caused by previous infections. Noncancerous lung nodules usually require no treatment.
How do doctors treat lung nodules?
Treatment for a cancerous nodule A doctor may request a thoracotomy to remove a cancerous nodule. This surgical procedure involves removing the nodule through an incision in the chest wall. Additional treatments for cancerous lung nodules may include chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and other surgical interventions.
Can nodules in the lung go away?
What causes lung nodules? In the vast majority of cases, lung nodules turn out to be small benign scars, indicating the site of a previous small area of infection. These nodules may be permanent or may even spontaneously disappear by the time of the next scan. Most are of absolutely no consequence.
When should I worry about lung nodules?
If the CT scan shows small nodules (less than a centimeter wide, or about the size of a green pea), the probability of them being cancerous is low. Larger nodules are more worrisome. Rounded nodules are less likely to be cancerous than spiculated (having jagged edges) ones.
Can lung nodules be treated without surgery?
Small, noncancerous lung nodules don't usually require treatment. You may need treatments, such as antibiotics or antifungal medications, if you have an infection. If the nodule grows, causes problems or is cancerous, you may need surgery.
Does a pulmonologist treat lung nodules?
Our experienced team of pulmonary specialists have advanced expertise in the diagnosis and treatment of all types of lung nodules. They are highly skilled at identifying both benign pulmonary nodules that can be treated conservatively and suspicious nodules that may signal lung cancer.
Do lung nodules affect breathing?
Nodules are found in up to half of adults who get a chest x-ray or CT scan. Do nodules cause any symptoms? In general, small nodules don't cause any noticeable problems. They're too small to cause pain or breathing problems.
How painful is a lung biopsy?
Lung biopsy procedures are not usually painful and have few risks that doctors associate with them. A doctor will only recommend a lung biopsy procedure to support their diagnosis. For example, if a person has smaller lung nodules, a biopsy may be too risky and difficult to justify.
Why do I have lung nodules?
The most common causes of lung nodules are inflamed tissue due to an infection or inflammation (called granulomas) or benign lung tumors (such as hamartomas). Less common, malignant lung nodules are typically caused by lung cancer or other cancers that have spread to the lungs (metastatic cancer).
How is a nodule removed from the lung?
Remove the nodule. In general, a lung nodule can be removed very safely and using a minimally invasive surgical approach. Your surgeon may want to perform a bronchoscopy to take a closer look at your nodules and take a biopsy. A biopsy involves removing a piece of your lung to look at it under a microscope.
At what size should a lung nodule be removed?
Nodules between 6 mm and 10 mm need to be carefully assessed. Nodules greater than 10 mm in diameter should be biopsied or removed due to the 80 percent probability that they are malignant. Nodules greater than 3 cm are referred to as lung masses.
Can a CT scan tell if a tumor is benign?
Cysts that appear uniform after examination by ultrasound or a computerized tomography (CT) scan are almost always benign and should simply be observed. If the cyst has solid components, it may be benign or malignant and should have further evaluation.
What Are Pulmonary Nodules?
A pulmonary nodule is a small round or oval-shaped growth in the lung. It may also be called a “spot on the lung” or a “coin lesion.” Pulmonary nod...
How Common Are Pulmonary Nodules?
Countless pulmonary nodules are discovered each year during chest X-rays or CT scans. Most nodules are noncancerous (benign). A solitary pulmonary...
What Causes Pulmonary Nodules?
There are two main types of pulmonary nodules: malignant (cancerous) and benign (noncancerous). Over 90% of pulmonary nodules that are smaller than...
What Are The Symptoms of Pulmonary Nodules?
Usually there are no symptoms associated with pulmonary nodules. If present, symptoms would be related to the condition that led to the nodule deve...
What to do if you have a pulmonary nodule?
You may need treatments, such as antibiotics or antifungal medications, if you have an infection. If the nodule grows, causes problems or is cancerous, you may need surgery. Surgical procedures to remove noncancerous and cancerous pulmonary nodules include:
How does a thoracotomy remove a lung nodule?
Thoracotomy: Your provider removes the lung nodule through a larger incision between your ribs, below your shoulder blade. For several days after the surgery, a tube drains excess fluid from your chest.
What is a granuloma in the lung?
When an infection or illness inflames lung tissue, a small clump of cells (granuloma) can form. Over time, a granuloma can calcify or harden in the lung, causing a noncancerous lung nodule. A neoplasm is an abnormal growth of cells in the lung. Neurofibromas are a type of noncancerous neoplasm.
What is a lung nodule?
A lung (pulmonary) nodule is an abnormal growth that forms in a lung. You may have one nodule on the lung or several nodules. Nodules may develop in one lung or both. Most lung nodules are benign (not cancerous). Rarely, pulmonary nodules are a sign of lung cancer. Lung nodules show up on imaging scans like X-rays or CT scans.
What percentage of lung nodules are benign?
About 95% of lung nodules are benign. Many things can cause benign lung nodules, including infections and scarring. If you have a pulmonary nodule, your healthcare provider may want to perform additional tests to determine the cause and rule out lung cancer.
What causes a non-cancer lung nodule?
Types of malignant (cancerous) neoplasms include lung cancer and carcinoid tumors. Other causes of noncancerous lung nodules include: Air irritants or pollutants. Autoimmune diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis and sarcoidosis.
How long does it take for a lung nodule to show up on a CT scan?
The findings are often a surprise. If an imaging test shows a lung nodule, your healthcare provider may recommend active surveillance. In six to 12 months, you get another CT scan. Nodules that stay the same size during a two-year surveillance period are not likely to be cancer.
What does a pathologist do when a person has lung nodules?
A pathologist will examine the tissue under a microscope to look for cancerous cells. A doctor will not always need to perform a biopsy when a person shows lung nodules. If an individual is low risk, and the features of the nodule suggest a low likelihood of cancer, a biopsy may cause more harm than good.
What does it mean when a doctor finds a lung nodule?
After finding a lung nodule, the doctor will assess its size, shape, and appearance. Certain features may suggest that the nodule is more likely to be cancerous. For example, larger nodules are more likely to be cancer. The location, shape, and size of the nodule may increase its risk of malignancy.
What to do if nodule is low risk?
If the nodule has characteristics that suggest a low risk of cancer, the doctor may recommend watchful waiting. This approach involves monitoring the nodule with regular CT scans over time to identify any potentially malignant changes, such an increase in size.
Why do I have nodules in my lungs?
Noncancerous lung nodules can have a variety of causes, including: Infection: Inflammation in the lungs might occur due to a range of infections, such as tuberculosis (TB) or fungal infections. A group of cells called a granuloma may develop around the inflamed area in the lung.
What is a lung nodule?
What to know about lung nodules. A lung nodule is a small growth on the lung and can be benign or malignant. The growth usually has to be smaller than 3 centimeters to qualify as a nodule. Benign nodules are noncancerous, typically not aggressive, and do not spread to other parts of the body.
What is the outlook for people with malignant lung nodules?
The outlook for people with a malignant lung nodule varies, depending on the stage of the disease. In many cases, early detection and treatment improve a person’s long term outlook.
What is a lung nodule on a CT scan?
A lung nodule will often be visible on one of these scans. The nodule will show as a spot or shadow on the X-ray. If an X-ray shows signs of a nodule, the doctor may request a follow-up CT scan.
What is the best way to check if a lung nodule is cancerous?
Positron emission tomography (PET) scan – A PET scan can help your doctor determine if a lung nodule is non-cancerous or cancerous, because it allows them to get a more detailed look. Biopsy – During a biopsy, your doctor removes a small amount of tissue from the nodule to examine closely under a microscope.
How to diagnose a lung nodule?
To start, your doctor will discuss your medical history with you, perform a physical exam and a chest X-ray or CT scan.
What are the risk factors for lung cancer?
However, certain risk factors can increase the likelihood that a lung nodule is malignant. These can include: Being over the age of 50. A nodule larger than 3 centimeters. Smoking. Having a family history of lung cancer. Having symptoms of lung cancer. Growth or irregular borders. Having multiple nodules.
What is a spot on your lung?
The good news is that these “spots” are typically small, benign (non-cancerous) lung nodules. We’re here to diagnose, monitor and guide you through treatment.
What can a doctor see with a lung scan?
These scans can help your doctor see the size, shape and location of the lung nodule, as well as other characteristics, like calcium deposits. From there, they may recommend additional tests to rule out cancer or to determine another underlying cause. These can include:
What causes granuloma in the lungs?
Infections: When your immune system acts against an infection, it will form a granuloma. Infections can be bacterial, fungal or parasitic.
Can a lung nodule be malignant?
Lung nodules are common, mostly in those who smoke, and are typically benign (non-cancerous) but can also be malignant (cancerous). You may have a single lung nodule or several.
What is the best way to determine if a pulmonary nodule is cancerous?
Biopsy. If a pulmonary nodule is considered highly suspicious for lung cancer, it will need to be biopsied to determine if it is cancerous. This will be based on its size, shape and appearance on chest X-ray or CT scan, as well as considering other risk factors.
How to get a sample from a pulmonary nodule?
The biopsy is a simple procedure of getting a sample from the pulmonary nodule for microscopic exam. It can be done surgically, through a bronchoscope or by placing a needle through the chest wall under radiographic guidance.
What doctor examines pulmonary nodules?
A sample is taken and immediately examined by a pathologist (a doctor who identifies diseases by studying cells and tissue under a microscope). The pathologist will determine if the pulmonary nodule is cancerous or benign.
Do you need surgery for a benign lung nodule?
Benign (non-cancerous) lung nodules do not need treatment. Lung cancer, if localized, is usually removed surgically. If part of the cancer has spread to other parts of the body, you may need chemotherapy, radiation therapy, surgery, alone or in various combinations.
Can you come back with a benign nodule?
If it is benign (not cancerous), your doctor will ask you to come back in the future to re-examine the spot with another X-ray. Your doctor will watch the nodule for any changes and catch it early if it becomes cancerous. If the nodule is cancerous, a few more samples will be taken or other tests performed to determine if the cancer has spread. ...
