
What is the most common treatment for cardiomyopathy?
- Lifestyle changes. Stopping alcohol use. Monitoring salt intake.
- Medicines. Lower blood pressure. ...
- Surgically implanted device that helps maintain proper heart rhythm.
- Ablation procedure. Removes extra heart tissue to reduce thickening. ...
- Heart transplant (for a severely damaged heart)
Is LVNC heart failure?
What is the life expectancy of someone with left ventricular hypertrophy?
How is left ventricular failure treated?
Can you live a long life with LVNC?
What is the treatment for non compaction cardiomyopathy?
Your doctor might prescribe certain drugs to treat LVNC. These include: Blood thinners to reduce the risk of blood clots. Beta blockers to help control heart beats and lower blood pressure.
How serious is left ventricular enlargement?
What happens if left ventricular hypertrophy is left untreated?
Is an enlarged left ventricle to heart life threatening?
Can the left ventricle repair itself?
Does a pacemaker help congestive heart failure?
What is the most common cause of left ventricular failure?
What is the left ventricle called?
In left ventricular non-compaction cardiomyopathy (LVNC) the lower left chamber of the heart, called the left ventricle, contains bundles or pieces of muscle that extend into the chamber. These pieces of muscles are called trabeculations. During development, the heart muscle is a sponge-like network of muscle fibers.
What is the term for the piece of muscle that is a sponge-like network of muscle fibers?
These pieces of muscles are called trabeculations. During development, the heart muscle is a sponge-like network of muscle fibers. As normal development progresses, the trabeculations become compacted transforming the heart muscle from sponge-like to smooth and solid. LVNC occurs when compaction does not occur.
What is the heart muscle?
During development, the heart muscle is a sponge-like network of muscle fibers. As normal development progresses, the trabeculations become compacted transforming the heart muscle from sponge-like to smooth and solid. LVNC occurs when compaction does not occur. These trabeculations typically occur at the bottom of the heart called ...
Where does LVNC occur?
LVNC occurs when compaction does not occur. These trabeculations typically occur at the bottom of the heart called the apex but can be seen anywhere in the left ventricle. Individuals with LVNC may also have another type of heart muscle disease (hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, dilated cardiomyopathy or restrictive cardiomyopathy).
Where are trabeculations found in the heart?
These trabeculations typically occur at the bottom of the heart called the apex but can be seen anywhere in the left ventricle. Individuals with LVNC may also have another type of heart muscle disease (hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, dilated cardiomyopathy or restrictive cardiomyopathy). LVNC is being diagnosed more frequently in both children ...
Is LVNC a secondary condition?
LVNC is being diagnosed more frequently in both children and adults secondary to increased awareness of the condition. The initial diagnosis may be made at any age and many patients often go undiagnosed until later in life. Symptoms. Many individuals with LVNC experience no symptoms.
How do you know if you have LVNC?
Symptoms. Many individuals with LVNC experience no symptoms. For those who have heart failure or an abnormal heart rhythm, symptoms can include: Older children and adults. Shortness of breath and fatigue. Feeling dizzy or light-headed. Fainting or passing out (syncope)
What tests can show dilated cardiomyopathy?
Exercise testing can help reveal the cause and severity of dilated cardiomyopathy. If you're unable to exercise, you may be given medication to mimic the effect of exercise on your heart. CT or MRI scan. These imaging tests can show the size and function of your heart's pumping chambers. Cardiac catheterization.
How to manage dilated cardiomyopathy?
If you have dilated cardiomyopathy, these self-care strategies may help you manage your symptoms: Exercise. Talk to your doctor about what activities would be safe and beneficial for you. In general, competitive sports aren't recommended because they can increase the risk of the heart stopping and causing sudden death.
What is the name of the device that doctors use to test your heart?
Your doctor will perform a physical exam and ask questions about your personal and family medical history. He or she will use a device called a stethoscope to listen to your heart and lungs. You may be referred to a heart specialist (cardiologist) for testing.
What does a chest xray tell you about your heart?
Chest X-ray. Your doctor may order a chest X-ray to check your heart and lungs for changes or problems in the heart's structure and size, ...
What is the purpose of chest X-rays?
Chest X-ray. Your doctor may order a chest X-ray to check your heart and lungs for changes or problems in the heart's structure and size, and for fluid in or around your lungs. Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG). An electrocardiogram records electrical signals as they travel through your heart.
What is the purpose of an electrocardiogram?
An electrocardiogram records electrical signals as they travel through your heart. Your doctor can look for patterns that may be a sign of an arrhythmia or problem with the left ventricle. Your doctor may ask you to wear a portable ECG device (Holter monitor) to record your heart rhythm for a day or two. Echocardiogram.
How to tell if left ventricle is enlarged?
Sound waves produce images of the heart, allowing your doctor to see whether your left ventricle is enlarged. An echocardiogram can also reveal how much blood is pumped out of the heart with each beat and whether blood is flowing in the right direction. Exercise stress test.
What is the most recently classified form of cardiomyopathy?
Left ventricular non-compaction cardiomyopathy . Left ventricular non-compaction, the most recently classified form of cardiomyopathy, is characterised by abnormal trabeculations in the left ventricle, most frequently at the apex.
What is left ventricular non-compaction?
Left ventricular non-compaction, the most recently classified form of cardiomyopathy, is characterised by abnormal trabeculations in the left ventricle, most frequently at the apex. It can be associated with left ventricular dilation or hypertrophy, systolic or diastolic dysfunction, or both, or various forms of congenital heart disease.
Can heart failure be induced by exercise?
Affected individuals are at risk of left or right ventricular failure, or both. Heart failure symptoms can be induced by exercise or be persistent at rest, but many patients are asymptomatic. Patients on chronic treatment for compensated heart failure sometimes present acutely with decompensated heart failure.
Is there a treatment for left ventricular noncompaction?
There are no specific treatment guidelines for left ventricular noncompaction (LVNC). Medical management varies depending on clinical manifestations, left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF), the p resence or absence of arrhythmias , and the risk of thromboembolism.
What is the treatment for arrhythmia?
Depending on the above factors, treatment might include: medications including diuretics , ACE inhibitors or Angiotensin II Receptor Blockers (ARBs), anticoagulants, and beta-blockers; an implantable cardioverter-defibrillator (ICD) or a pacemaker if an arrhythmia is present; and cardiac transplantation. [2] [3] [4]
What is LVNC in heart?
Listen. Left ventricular noncompaction (LVNC) is a rare heart condition. In LVNC the inside wall of the heart is spongy or grooved, instead of smooth. Signs and symptoms of LVNC vary, but may cause life-threatening abnormal heart rhythms and weakness of the heart muscle.
What are the symptoms of LVNC?
Signs and symptoms of LVNC vary, but may cause life-threatening abnormal heart rhythms and weakness of the heart muscle. Treatments, such as blood thinning medication and defibrillators, are available to control these heart symptoms. In rare cases, heart transplantation is needed. [1]
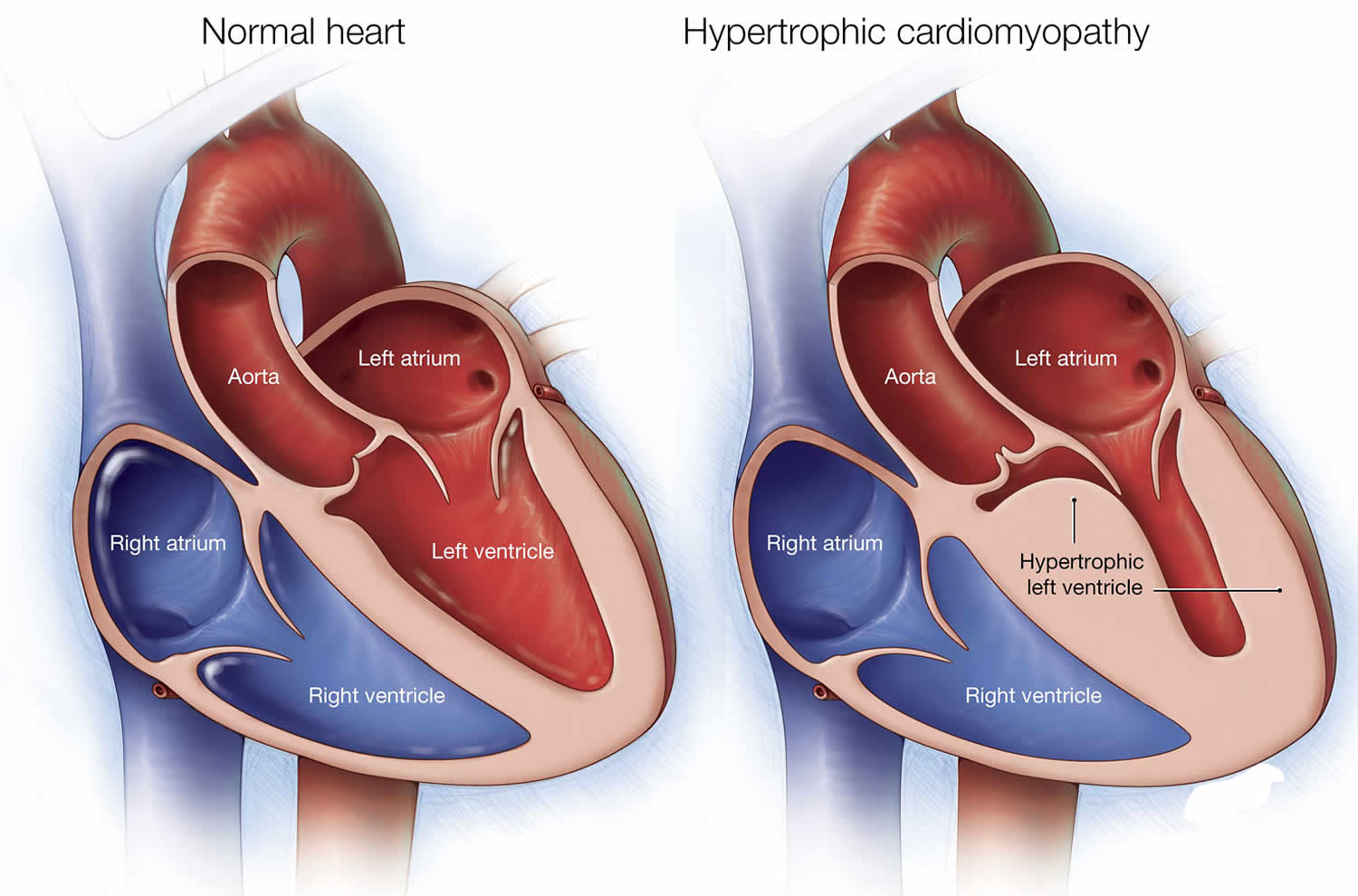
Diagnosis
Treatment
- If you have dilated cardiomyopathy, your doctor might recommend treatment for the underlying cause, if known. Treatment may help relieve symptoms, improve blood flow and prevent further damage to your heart.
Clinical Trials
- Explore Mayo Clinic studiestesting new treatments, interventions and tests as a means to prevent, detect, treat or manage this condition.
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
- If you have dilated cardiomyopathy, these self-care strategies may help you manage your symptoms: 1. Exercise.Talk to your doctor about what activities would be safe and beneficial for you. In general, competitive sports aren't recommended because they can increase the risk of the heart stopping and causing sudden death. 2. Quit smoking.Your doctor...
Preparing For Your Appointment
- If you think you may have dilated cardiomyopathy or are worried about your risk because of a family history, make an appointment with your family doctor. Your doctor may refer you to a cardiologist, if necessary. Here's information to help you get ready for your appointment.