
Chemotherapy followed by radical cystectomy
Cystectomy
Cystectomy is a medical term for surgical removal of all or part of the urinary bladder. It may also be rarely used to refer to the removal of a cyst. The most common condition warranting removal of the urinary bladder is bladder cancer.
What causes a cyst on the bladder?
Interstitial cystitis. Interstitial cystitis is a poorly understood bladder condition that causes long-term pelvic pain and problems peeing. It's also known as painful bladder syndrome or bladder pain syndrome. The condition tends to first affect people in their 30s and 40s, and is much more common in women than men.
Can cyst be treated without having surgery?
While it may be tempting, you should not try to remove a cyst on your own. Most cysts on the skin are harmless and resolve without treatment. While there are a few home remedies, some cysts do require medical treatment. It’s best to see a doctor for diagnosis and treatment recommendations.
Is bleeding normal after cyst removal?
If you have undergone ovarian cyst removal or other critical procedures, you may experience bleeding after laparoscopy for a few weeks. Consult with your GP about your energy and comfort levels so that you know when you can perform certain jobs.
How to treat bladder cyst?
- Urine analysis. For a suspected bladder infection, your doctor may ask for a urine sample to determine whether bacteria, blood or pus is in your urine. ...
- Cystoscopy. During this test, your doctor inserts a cystoscope — a thin tube with a light and camera attached — through the urethra into your bladder to view your urinary ...
- Imaging. ...

How serious is a tumor in the bladder?
Bladder cancer can be benign or malignant. Malignant bladder cancer may be life threatening, as it can spread quickly. Without treatment, it can damage tissues and organs. In this article, we cover everything you need to know about bladder cancer, including types, symptoms, causes, and treatments.
Can a tumor be removed from the bladder?
A trans urethral resection of bladder tumour (TURBT) is usually the first treatment you have for early bladder cancer. Your surgeon removes the tumour in your bladder through the urethra. The urethra is the tube that carries urine from the bladder to the outside of your body.
What happens if tumor in bladder is not removed?
Untreated bladder cancer produces significant morbidity, including the following: Hematuria. Dysuria. Irritative urinary symptoms.
Does a bladder tumor mean cancer?
Bladder tumors are abnormal growths that occur in the bladder. If the tumor is benign, it's noncancerous and won't spread to other parts of your body. This is in contrast to a tumor that's malignant, which means it's cancerous. There are several types of benign tumors that can develop within the bladder.
How long does it take to remove tumor from bladder?
Most people with non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer have an operation called transurethral resection of bladder tumour (TURBT). This is done under general anaesthetic using a rigid cystoscope. A TURBT takes 15–40 minutes and does not involve any cuts to the outside of the body.
How long is recovery from bladder tumor surgery?
It will take 6 weeks from the date of surgery to fully recover from your operation. This can be divided into two parts -- the first 2 weeks and the last 4 weeks. During the first 2 weeks from the date of your surgery, it is important to be "a person of leisure".
How do they remove tumor from bladder?
A type of thin, rigid cystoscope called a resectoscope is put into your bladder through your urethra. The resectoscope has a wire loop at the end that's used to remove any abnormal tissues or tumors. The removed tissue is sent to a lab for testing.
Does size of bladder tumor matter?
CONCLUSIONS: Larger tumor size (>5 cm) is associated with greater length of stay, reoperation, readmission, and death following TURBT. Patients should be counseled appropriately and likely warrant vigilant observation prior to and following hospital discharge.
How long does bladder surgery take?
In the Operating Room Just before surgery, you will be connected to monitors, given blood thinners to prevent clots if needed, and given antibiotics to prevent infection. Then, the anesthesiologist will put you to sleep with a general anesthetic. Usually, surgery takes four to six hours.
What causes a cyst on your bladder?
Bladder cysts can be caused by a rare condition called cystitis cystica. It is associated with persistent inflammation in the urinary tract, possibly due to irritation or bacteria in the bladder.
What are the 5 warning signs of bladder cancer?
Here are five warning signs to watch for:Blood in the urine (hematuria). This is the most common early symptom of bladder cancer and typically the first sign of bladder cancer that is seen. ... UTI-like symptoms. ... Unexplained pain. ... Decreased appetite. ... Postmenopausal uterine bleeding.
What are the symptoms of stage 1 bladder cancer?
SymptomsBlood in urine (hematuria), which may cause urine to appear bright red or cola colored, though sometimes the urine appears normal and blood is detected on a lab test.Frequent urination.Painful urination.Back pain.
Treating Stage 0 Bladder Cancer
Stage 0 bladder cancer includes non-invasive papillary carcinoma (Ta) and flat non-invasive carcinoma (Tis). In either case, the cancer has not inv...
Treating Stage I Bladder Cancer
Stage I bladder cancers have grown into the connective tissue layer of the bladder wall but have not reached the muscle layer.Transurethral resecti...
Treating Stage II Bladder Cancer
These cancers have invaded the muscle layer of the bladder wall. Transurethral resection (TURBT) is typically the first treatment for these cancers...
Treating Stage III Bladder Cancer
These cancers have reached the outside of the bladder and might have grown into nearby tissues or organs.Transurethral resection (TURBT) is typical...
Treating Stage IV Bladder Cancer
These cancers have reached the abdominal or pelvic wall (T4b tumors) or have spread to nearby lymph nodes or distant parts of the body. Stage IV ca...
Treating Bladder Cancer That Progresses Or Recurs
If cancer continues to grow during treatment (progresses) or comes back (recurs), your treatment options will depend on where and how much the canc...
Which Treatments Are Used For Bladder Cancer?
Depending on the stage of the cancer and other factors, treatment options for people with bladder cancer can include: 1. Surgery 2. Intravesical th...
Which Doctors Treat Bladder Cancer?
Depending on your options, you can have different types of doctors on your treatment team. The types of doctors who treat bladder cancers include:...
Making Treatment Decisions
It’s important to discuss all of your treatment options, including their goals and possible side effects, with your doctors to help make the decisi...
Help Getting Through Treatment
Your cancer care team will be your first source of information and support, but there are other resources for help when you need it. Hospital- or c...
What is the first treatment for bladder cancer?
Chemo (with or without radiation) is typically the first treatment when bladder cancer has spread to distant parts of the body (M1). After this treatment the cancer is rechecked. If it looks like it's gone, a boost of radiation to the bladder may be given or cystectomy might be done.
What is stage 0 bladder cancer?
Stage 0 bladder cancer includes non-invasive papillary carcinoma (Ta) and flat non-invasive carcinoma (Tis or carcinoma in situ). In either case, the cancer is only in the inner lining layer of the bladder. It has not invaded (spread deeper into) the bladder wall.
What is the treatment for T3 tumors?
An option for some patients with single, small tumors (some T3) might be treatment with a second (and more extensive) transurethral resection (TURBT) followed by a combination of chemo and radiation. If cancer is still found when cystoscopy is repeated, cystectomy might be needed.
What to do if you have cancer that hasn't been removed?
(Less often, close follow-up alone might be an option.) If all of the cancer wasn't removed, options are intravesical BCG or cystectomy (removal of part or all of the bladder).
How to get rid of stage IV cancer?
The tumor is then rechecked. If it appears to be gone, chemo with or without radiation or cystectomy are options.
What is the treatment for cancer that recurs in distant parts of the body?
Cancers that recur in distant parts of the body can be harder to remove with surgery, so other treatments, such as chemotherapy, immunotherapy, targeted therapy, or radiation therapy , might be needed. For more on dealing with a recurrence, see Understanding Recurrence.
Can you get a partial cystectomy for bladder cancer?
Lymph nodes near the bladder are often removed as well. If cancer is in only one part of the bladder, a partial cystectomy may be done instead. But this is possible in only a small number of patients . Radical cystectomy may be the only treatment for people who are not well enough to get chemo.
What is the procedure to check for cysts in the bladder?
Cystoscopy. This allows a doctor or urologist to look inside the bladder and inspect cysts. It involves inserting a tube with a tiny camera through the urethra and into the bladder. A cystoscopy may be performed under local, regional, or general anesthesia.
What is a CT scan for bladder cysts?
A CT scan can be used to diagnose a bladder cyst . A doctor may begin by asking questions about recent symptoms and a person’s individual and familial medical history. They may also test the urine for infection. Receiving a correct diagnosis is key.
What causes cysts in the bladder?
The following factors can increase a person’s risk of developing bladder cysts: 1 catheter use 2 a history of surgery near the bladder 3 a history of kidney stones or bladder stones 4 frequent UTIs
How long does it take to biopsy a bladder cyst?
A tube containing a camera and needle reaches the cyst by passing through the urethra. The process usually takes less than an hour.
What are the symptoms of a swollen bladder?
If symptoms appear, they can include: pain when urinating. blood or off-colored streaks in the urine. a painful need to urinate. a continuous, urgent need to urinate. inability to control the bladder, which is known as incontinence. excessive urination at night. pain in the lower back or pelvic region.
When should I seek an evaluation for bladder cysts?
When a person has symptoms of bladder cysts or frequently experiences UTIs, they should seek an evaluation. Receiving a diagnosis and treatment early can prevent complications and put the mind at ease. Last medically reviewed on May 15, 2018. Urinary Tract Infection.
Where do cysts form?
They may appear anywhere on the body, internally or externally. Bladder cysts tend to form in the lining of the bladder. They are relatively rare in people who have a normally functioning urinary tract. These cysts tend to form as small, benign growths that can go unnoticed.
What is the treatment for bladder cancer?
Depending on the stage of the cancer and other factors, treatment options for people with bladder cancer can include: Bladder Cancer Surgery. Intravesical Therapy for Bladder Cancer. Chemotherapy for Bladder Cancer. Radiation Therapy for Bladder Cancer. Immunotherapy for Bladder Cancer. Targeted Therapy Drugs for Bladder Cancer.
What are the things to consider when considering cancer treatment?
Some important things to consider include: Your age and expected life span. Any other serious health conditions you have. The stage and grade of your cancer. The likelihood that treatment will cure your cancer (or help in some other way) Your feelings about the possible side effects from treatment.
What kind of doctor treats cancer?
Based on your treatment options, you might have different types of doctors on your treatment team. These doctors could include: 1 Urologists: surgeons who specialize in treating diseases of the urinary system and male reproductive system 2 Radiation oncologists: doctors who treat cancer with radiation therapy 3 Medical oncologists: doctors who treat cancer with medicines such as chemotherapy and immunotherapy
What do people with cancer need?
People with cancer need support and information, no matter what stage of illness they may be in. Knowing all of your options and finding the resources you need will help you make informed decisions about your care.
Is treatment information given here official policy of the American Cancer Society?
The treatment information given here is not official policy of the American Cancer Society and is not intended as medical advice to replace the expertise and judgment of your cancer care team. It is intended to help you and your family make informed decisions, together with your doctor.
Can you continue cancer treatment?
Whether or not you continue treatment, there are still things you can do to help maintain or improve your quality of life.
Can bladder cancer be removed?
Surgery, alone or with other treatments, is used to treat most bladder cancers. Early-stage bladder tumors can often be removed. But a major concern in people with early-stage bladder cancer is that new cancers often form in other parts of the bladder over time.
How long after a bladder surgery can you take Tylenol?
Take them on a regular basis the first 2-3 days after the procedure. For pain not relieved by these medications, use the prescription Tylenol with Codeine or Vicodin that was prescribed for you. We may also occasionally give you a few days of bladder spasm medication.
How long does it take for urine to clear up after a TURBT?
Again, these usually tend to be minor issues, and resolve within 1-2 days after the procedure. Definitely rest up for a day or two after a TURBT. Drink at least 6-8 glasses of water to wash out your system. Within a day or two, your urine will begin to clear up and look ‘normal’.
How long does it take for a foley bag to drain after surgery?
It is not unusual to have a sensation of wanting to urinate, or to have bladder spasms after surgery. This usually goes away within 1-2 days.
How to get rid of a bowel movement?
Do not strain when having a bowel movement. Expect irregular bowel habits until fully recovered. Increase fiber in your diet. You may need a stool softener or laxative. Do not take blood thinners or aspirin products for one week or as directed by your physician.
Can you pull a bladder tumor out?
Just like weeds, there are weeds with superficial roots that you can pluck right out, and there are weeds with deep roots that despite pulling, you can’t completely pull them out.
Can bladder cancer be managed?
The great news is that bladder cancer, when detected early, and managed properly, can be managed with good outcomes.
Can a bladder tumor come back?
The only problem with bladder tumors, is that just like weeds, they have a nasty habit of coming back. The problem is that the source of the bladder tumor, which 90% of the time is associated with smoking, has affected the entire bladder. And those effects are long lasting.
How to treat a cyst in the kidney?
Options include: Puncturing and draining the cyst, then filling it with alcohol. Rarely, to shrink the cyst, your doctor inserts a long, thin needle through your skin and through the wall ...
How to remove a cyst?
Surgery to remove the cyst. A large or symptomatic cyst may require surgery to drain and remove it. To access the cyst, the surgeon makes several small incisions in your skin and inserts special tools and a small video camera.
What tests are used to diagnose kidney cysts?
Tests and procedures used to diagnose simple kidney cysts include: Imaging tests. Imaging tests, such as an ultrasound, a computerized tomography (CT) scan and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), are often used to investigate simple kidney cysts. Imaging tests can help your doctor determine whether a kidney mass is a cyst or a tumor.
Can a cyst in the kidney be treated?
Treatment may not be necessary. If your simple kidney cyst causes no signs or symptoms and doesn't interfere with your kidne y function, you may not need treatment. Instead, your doctor may recommend that you have an imaging test, such as ultrasound, periodically to see whether your kidney cyst has enlarged.
What is the most common surgery for bladder cancer?
Surgery. Transurethral resection of bladder tumor (TURBT, also known as transurethral resection, or TUR) is the most common surgery for bladder cancer that’s in the early stages. It’s a procedure used to take samples of tissue from inside your bladder to find out if you have cancer there or if a tumor has spread, or to take out a tumor.
What type of surgery removes the bladder?
Cystectomy. In this type of surgery, your doctor removes part of your bladder (a partial cystectomy ) or all of it (a radical cystectomy ). If cancer has spread to the muscle layer of your bladder and is still small, your doctor may be able to perform a partial cystectomy.
How does immunotherapy help bladder cancer?
This treatment uses your immune system to attack the cancer. It helps your immune system recognize cancer cells as dangers and launch a stronger response against them. That can shrink tumors or stop them from growing. Several immunotherapy drugs are used to treat bladder cancer that has spread.
What is the tube called after a bladder surgery?
After the procedure, you’ll have a tube in your bladder called a catheter. It takes pee out of your body and into a bag. You may need to have it in for a few days before you can go on your own. You can get up and walk when you have a catheter, but as the anesthesia wears off, it may feel uncomfortable.
How long do you have to stay in the hospital after a bladder surgery?
But if your tumor was large, you may need to stay in the hospital overnight. You may see blood in your pee for up to 3 days after your surgery. Drink lots of fluid to help flush out your bladder -- aim for eight to 10 glasses per day.
What is the name of the germ that is injected into the bladder?
In this method, your body’s own immune system attacks the cancer cells. Your doctor will inject a germ called Bacillus Calmette-Guerin (BCG) into your bladder through a catheter. This germ is related to the one that causes tuberculosis. This draws your body’s immune cells to your bladder.
How does a pee tube get to the bladder?
They get to your bladder through your urethra, the tube that pee goes through as it passes out of your body. Before the surgery, you’ll have either general anesthesia -- which puts you to sleep -- or regional anesthesia that numbs just the lower part of your body. The procedure starts once that medicine starts to work.
How to treat a benign bladder tumor?
Treatment for your tumor will depend on what type of tumor you have. First, your doctor may diagnose the tumor via biopsy or endoscopy. An endoscopy will provide a visual look, while a biopsy will provide a tissue sample of the tumor. After diagnosing the tumor, your doctor will develop a treatment plan ...
What is bladder tumor?
What are bladder tumors? Bladder tumors are abnormal growths that occur in the bladder. If the tumor is benign, it’s noncancerous and won’t spread to other parts of your body. This is in contrast to a tumor that’s malignant, which means it’s cancerous.
How to tell if bladder tumor is a tumor?
Bladder tumors are typically diagnosed by a biopsy or a urine analysis. However, certain symptoms can indicate that a tumor or bladder issue is the possible cause, including: blood in the urine. pain while urinating. inability to urinate. having the urge to urinate more frequently. blockage of the urine stream.
What is a tumor that grows fat cells?
Lipomas are tumor growths of fat cells. They’re often caused by an overgrowth of such cells. Lipomas are fairly common and usually don’t cause any pain unless they press against other organs or nerves.
What is a wart in the bladder?
Papillomas ( warts) are common viral skin growths. They’re usually harmless. Papillomas in the bladder typically start in the urothelial cells, which make up the lining of your bladder and urinary tract. Inverted papillomas have smooth surfaces and tend to grow into the bladder wall.
What to do after a tumor is diagnosed?
After diagnosing the tumor, your doctor will develop a treatment plan that best suits your condition. If the tumor is positioned so the risk of surgery damaging blood vessels, nerves, and the surrounding area is relatively low, they’ll most likely recommend removing the tumor.
Can a bladder tumor be removed?
Your doctor will be able connect you to the right specialists for diagnosis and determine the best course of treatment for your bladder tumor. If the tumor isn’t cancerous, it’s likely that your doctor will recommend either removal or waiting and monitoring the tumor.
How to treat cystitis in the bladder?
Take a sitz bath. Soak in a bathtub of warm water (sitz bath) for 15 to 20 minutes to help relieve pain or discomfort. For recurrent bladder infections, work with your doctor to develop a strategy to reduce recurrences and the discomfort that cystitis can cause.
How to get rid of a swollen bladder?
Stay hydrated. Drink plenty of fluids to keep yourself hydrated. Avoid coffee, alcohol, soft drinks with caffeine and citrus juices — as well as spicy foods — until your infection clears.
What is a cystoscope?
Cystoscopy allows your doctor to view your lower urinary tract to look for abnormalities, such as a bladder stone. Surgical tools can be passed through the cystoscope to treat certain urinary tract conditions.
How to treat bladder distention?
Procedures that manipulate your bladder to improve symptoms, such as stretching the bladder with water or gas ( bladder distention) or surgery. Nerve stimulation, which uses mild electrical pulses to relieve pelvic pain and, in some cases, reduce urinary frequency.
What is the procedure to check for bacterial culture in urine?
If so, he or she may request a urine bacterial culture. Cystoscopy. During this test, your doctor inserts a cystoscope — a thin tube with a light and camera attached — through the urethra into your bladder to view your urinary tract for signs of disease.
Why are bladder infections so difficult to treat?
Hospital-acquired bladder infections can be a challenge to treat because bacteria found in hospitals are often resistant to the common types of antibiotics used to treat community-acquired bladder infections. For that reason, different types of antibiotics and different treatment approaches may be needed.
How to prepare for a cystitis appointment?
To prepare for your appointment: Ask if there's anything you need to do in advance, such as collect a urine specimen. Write down your symptoms, including any that seem unrelated to cystitis. Make a list of all the medications, vitamins or other supplements that you take.
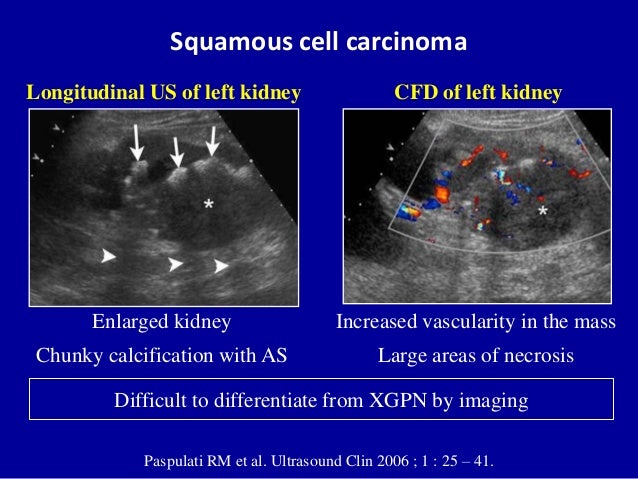
Treatment
- No incisions! Thats the good part. The entire procedure is done under general anesthesia (asleep) via the urethra (penis). We now utilize state-of-the-art high definition cameras to visualize the bladder. We then use plasma-vaporization devices to basically remove the bladder tumor.The best way to think of a bladder tumor is that it is a weed. Just...
Symptoms
- It is not unusual to have a sensation of wanting to urinate, or to have bladder spasms after surgery. This usually goes away within 1-2 days. You may occasionally notice a small amount of urine leak around the catheter, and this is normal.
Results
- After the procedure, patients may have a variety of minor issues. Although many patients may do fine with no issues, some patients may experience minor, temporary issues such as noticing burning with urination, frequent urination, small clots, or pink/red colored urine, or occasional discomfort that radiates from the kidney to the bladder. Again, these usually tend to be minor iss…
Administration
- For pain, Advil®, Motrin®, or prescription Toradol® work great dependent upon your doctors advice. Never take a medication without clearing it with your doctor first. These are non-narcotic, so you dont get sleepy, constipated or have other issues; however they are great anti-inflammatories. Take them on a regular basis the first 2-3 days after the procedure. For pain not …
Preparation
- You will need a catheter to drain your bladder, depending upon the extent of your surgery. Catheters generally are removed within a few days in the Urology Clinic. Wash around the catheter with soap and water and rinse well. You may shower, but avoid baths until the catheter is removed.
Prevention
- Avoid coffee, tea, carbonated beverages, alcoholic beverages,citrus juices, spicy foods and smoking for the first month week following surgery.Increase your intake of fluids, particularly water at least 6-8 glasses of water are typically recommended during the first two weeks of your recovery.
Prognosis
- The only problem with bladder tumors, is that just like weeds, they have a nasty habit of coming back. The problem is that the source of the bladder tumor, which 90% of the time is associated with smoking, has affected the entire bladder. And those effects are long lasting. That means that we place each of our patients through a very rigorous, scientifically validated protocol for surveil…