
The treatment of breech presentation includes: The healthcare provider shall initially attempt to reverse the breech position by giving relaxation medication and then turning the baby’s head down The procedure of turning the baby into the correct position is referred to as external cephalic version.
What are the treatment options for breech birth?
Treatment options include external cephalic version to increase the likelihood of vaginal birth or a planned cesarean section, the optimal gestation being 37 and 39 weeks, respectively. Planned cesarean section is considered the safest form of delivery for infants with a persisting breech presentation at term.
What is breech presentation and how to treat it?
The treatment of breech presentation includes: The healthcare provider shall initially attempt to reverse the breech position by giving relaxation medication and then turning the baby’s head down. The procedure of turning the baby into the correct position is referred to as external cephalic version.
What are the symptoms of breech presentation and breech birth?
Common signs and symptoms associated with breech presentation include: Kicking may be felt in the lower abdomen in women with breech presentation How is Breech Presentation and Breech Birth Diagnosed? Diagnosis of breech presentation includes: Breech presentation is diagnosed through physical examination along with evaluation of medical history
Can breech presentation be corrected in late pregnancy?
Interventions to correct breech presentation (to cephalic) before labour and birth are important for the woman’s and the baby’s health. The aim of this review is to determine the most effective way of managing a breech presentation in late pregnancy.
What is the management option for breech delivery?
At term, the options for management of breech presentation are (i) external cephalic version; (ii) Caesarean section; or iii) vaginal breech birth.
What is the most common cause of breech presentation?
Prematurity, multiple gestations, aneuploidies, congenital anomalies, Mullerian anomalies, uterine leiomyoma, and placental polarity as in placenta previa are most commonly associated with a breech presentation.
How serious is a breech birth?
In general, breech pregnancies aren't dangerous until it's time for the baby to be born. With breech deliveries, there is a higher risk for the baby to get stuck in the birth canal and for the baby's oxygen supply through the umbilical cord to get cut off.
Why do babies become breech?
It is known, though, that breech presentation is more common when other factors are present: The mother has had more than one pregnancy. There is more than one fetus (twins or more) in the uterus. The uterus holds too much or too little amniotic fluid (the liquid that surrounds the baby inside the uterus)
Are breech babies more painful to carry?
Giving birth to a breech baby vaginally is not usually any more painful than a head-down position, as you'll have the same pain relief options available to you, although it does carry a higher risk of perinatal morbidity (2:1000 compared to 1:1000 with a cephalic baby).
Do breech babies have problems later in life?
An interim analysis found that breech babies born vaginally were three to four times more likely to die at birth, and more likely to have serious health problems in the first six weeks of life, than those born by C-section.
Is it worth having an ECV?
Results. ECV was successful in 32 out of 52 patients with overall success of 61.5%. Out of the 32 successful ECVs, 24 patients delivered vaginally (75%) (p value 0.00), 6 patients delivered by caesarean section, and 2 patients were lost to follow-up. Transverse lie had 100% success rate for ECV (p value 0.005).
How successful is ECV?
External cephalic version is a procedure that externally rotates the fetus from a breech presentation to a vertex presentation. External version has made a resurgence in the past 15 years because of a strong safety record and a success rate of about 65 percent.
What causes a breech birth?
The causes of breech presentations are not fully understood. However, the data show that breech birth is more common: 1 In subsequent pregnancies 2 In pregnancies of multiples 3 When there is a history of premature delivery 4 When the uterus has too much or too little amniotic fluid 5 When there is an abnormally shaped uterus or a uterus with abnormal growths, such as fibroids 6 With women who have placenta previa
What is the purpose of fetal monitoring during breech delivery?
In a vaginal breech delivery, electronic fetal monitoring will be used to monitor the baby’s heartbeat throughout the course of labor.
What is the Webster Breech Technique?
A more relaxed uterus makes it easier for a breech baby to turn naturally. His technique is known as the Webster Breech Technique. The July/August issue of the Journal of Manipulative and Physiological Therapeutics reported and 82% success rate for the Webster Technique.
What are the conditions for a vaginal birth?
The following conditions are considered necessary in order to attempt a vaginal birth: The baby is full-term and in the frank breech presentation. The baby does not show signs of distress while its heart rate is closely monitored. The process of labor is smooth and steady with the cervix widening as the baby descends.
What can be used to confirm a breech position?
If it appears that the baby might be in a breech position, they can use ultrasound to confirm the position. Special x-rays can also be used to determine the baby’s position and the size of the pelvis to determine if a vaginal delivery of a breech baby can be safely attempted.
Why is it unlikely for a premature baby to stretch the cervix?
Since premature babies are small and more fragile, and because the head of a premature baby is relatively larger in proportion to its body , the baby is unlikely to stretch the cervix as much as a full-term baby. This means that there might be less room for the head to emerge.
How to get a baby to move towards the sound?
Consequently, many women have used music or taped recordings of their voice to try to get their baby to move towards the sound. Placing headphones on the lower part of your abdomen and playing either music or sounds of your voice can encourage babies to move towards the sounds and out of a breech position.
What does breech birth mean?
In breech birth the baby is positioned to deliver feet or bottom first. There are a few types of breech 1): Complete breech means the baby is bottom-first, with knees bent. Frank breech means the baby’s legs are stretched up, with feet near the head. Footling breech means one leg is lowered over the mother’s cervix.
How early can a breech baby be delivered?
The safest way for a breech baby to be born is by C-section. If a C-section is planned, it will most often be scheduled for no earlier than 39 weeks.
How to turn a baby from a breech to a head down?
These include postural exercises, acupuncture, moxibustion and chiropractic treatment.
What to do if your baby breaks out of water?
If that happens, call your provider right away and go to the hospital. It is important to go in right away if you have a breech baby and your bag of water breaks. This is because there is a higher chance that the umbilical cord will come out even before you are in labor. This can be very dangerous for the baby.
Why is my baby in a breech position?
Often it is unclear why a baby remains in a breech position, however, some of the common reasons include: too much or too little amniotic fluid around the baby. the length of the umbilical cord. multiple pregnancy – for example, often one twin will be in a cephalic position and the other in a breech position.
Why is a breech baby dangerous?
The danger of breech birth is mostly due to the fact that the largest part of a baby is its head. When the breech baby’s pelvis or hips deliver first, the woman’s pelvis may not be large enough for the head to be delivered also. This can result in a baby getting stuck in the birth canal, which can cause injury or death.
Why is my baby small?
your baby is presenting as a footling breech. your baby is large (>3800g) your baby is small (<2000g) other reasons preventing a vaginal birth, such as low lying placenta. your doctor or hospital do not have the necessary skills and resources for a vaginal breech birth.
Definition
Breech presentation in pregnancy occurs when a baby presents with the buttocks or feet rather than the head first (cephalic presentation) and is associated with increased morbidity and mortality for both the mother and the baby. [1] Cunningham F, Gant N, Leveno K, et al. Williams obstetrics. 21st ed.
Contributors
NN has received salary support from Australian National Health and a Medical Research Council Career Development Fellowship; she is an author of a number of references cited in this topic.
How to diagnose breech presentation?
Breech presentation is diagnosed through physical examination along with evaluation of medical history. The diagnosis may be confirmed by an ultrasound examination of the abdomen. Many clinical conditions may have similar signs and symptoms.
What is breech presentation?
Breech presentation is common in women with multiple pregnancies (multiple babies in the womb) Healthcare providers generally maneuver the fetus to change the position from breech to vertex (‘head down’ position) The prognosis of breech presentation is generally good.
What are the complications of breech presentation?
Complications associated with breech presentation include: Birth hypoxia: Insufficient supply of oxygen to baby’s brain and other organs after birth. Compression of umbilical cord results in obstruction of blood through the umbilical cord.
When is a baby breech?
A pregnancy is referred to as breech when the baby is not in a ‘head down’ position by the 36thweek of pregnancy. The exact cause of breech presentation is unknown. The breech presentation (also called butt down position) is common throughout pregnancy; however, it is not the ideal position for vaginal delivery.
Can you have a vaginal delivery if you are still in a breech position?
In some cases, vaginal delivery is possible even if the baby is still in a breech position. In these cases forceps, a special tool used to pull the baby out, will more than likely be used. Generally, if the baby is still in breech position at the time of labor, a cesarean section will be performed.
How to diagnose a breech birth?
Your doctor will diagnose a breech presentation a few weeks before your due date by placing their hands on your lower abdomen and locating the baby’s head, butt, and back. If they feel that your baby may be lying in a breech presentation, they may use an ultrasound to confirm it.
What causes a breech birth?
What causes a breech presentation isn’t fully understood, but the American Pregnancy Association states that a breech birth has a tendency to occur more frequently in the following situations: 1 if the pregnant woman has a history of several pregnancies 2 if a woman is pregnant with multiples 3 if a woman has a history of delivering prematurely 4 if a woman has placenta previa 5 if the uterus contains either too little or too much amniotic fluid 6 if the woman’s uterus has an abnormal shape or other problems such as fibroids
What is the Webster Breech technique?
This technique of turning a breech baby is referred to as the Webster Breech Technique. According to a study published in the Journal of Manipulative and Physiological Therapeutics, the technique was found to have an 82 percent success rate.
What is a breech baby?
Breech baby positions. A breech presentation happens when a baby doesn’t move into a delivery position before birth and instead stays in a bottom-down position. There are three types of breech baby positions: complete, footling, and frank breech.
What are the different types of breech positions?
There are three types of breech baby positions, depending on the position of the baby in your uterus: complete, footling, and frank breech position.
Why is it so hard for a premature baby to emerge?
This is because premature babies are smaller and more fragile. Their heads are also relatively larger than their bodies, so in breech position, they can’t stretch the cervical opening as much as a full-term baby can. This makes it even more difficult for the head to emerge.
What is it called when a baby's butt is positioned in such a way that they get delivered
When this doesn’t happen, the baby’s feet and/or butt are positioned in such a way that they get delivered first. This position is known as a breech presentation . Breech births are rare but occur in about 1 out of 25 full-term pregnancies.
Why do they do episiotomies for breech delivery?
Episiotomies are often performed for assisted vaginal breech deliveries, even in multiparous women, to prevent soft tissue dystocia. View Media Gallery. Wrap the legs with a towel to aid in grasping the fetus (see image below). Assisted vaginal breech delivery.
What are the different types of breech delivery?
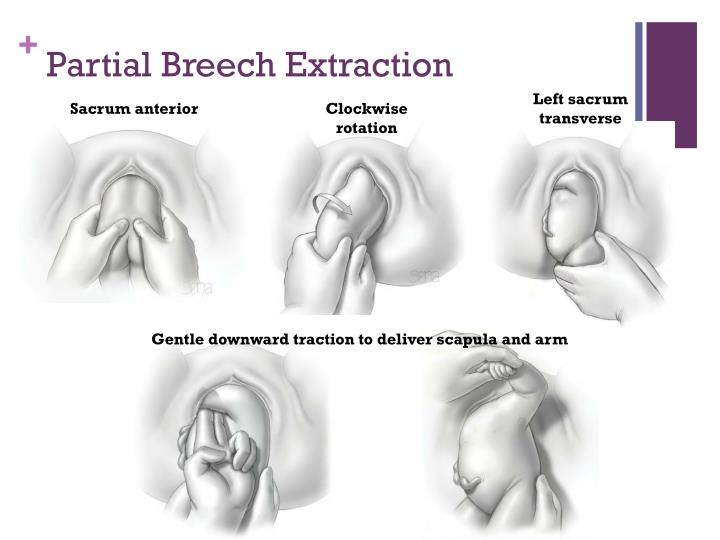
Three types of vaginal breech delivery exist: Spontaneous breech (rare): No manipulation of the infant is necessary, other than supporting the infant. Partial breech extraction (most common): Fetus descends spontaneously to the point where the umbilicus is at the vaginal introitus; then, the fetus is further extracted.
When is downward traction applied?
No downward or outward traction is applied to the fetus until the umbilicus has been reached. Assisted vaginal breech delivery. With a towel wrapped around the fetal hips, gentle downward and outward traction is applied in conjunction with maternal expulsive efforts until the scapula is reached.
Where to take mother in second stage of labor?
If the mother is in the second-stage of labor or if amniotic membranes have ruptured, take the mother to the nearest hospital or urgent care center for emergency delivery. Administer supportive oxygen and IV fluids. Transport the mother in a comfortable position or in the left lateral decubitus position.
How to get a fetus to rotate?
At this point, the fetus's back should rotate anteriorly. Adjust grip so that the thumbs overlay the sacrum. With the fingers over the hips, continue gentle downward traction with a left and right rotation ( to reduce any nuchal arms).
When is a baby breech?
Bottom first or feet first (breech baby) If your baby is lying bottom or feet first, they are in the breech position. If they're still breech at around 36 weeks' gestation, the obstetrician and midwife will discuss your options for a safe delivery.
What happens if a baby is breech?
What happens if your baby is breech? Babies often twist and turn during pregnancy, but most will have moved into the head-down (also known as head-first) position by the time labour begins.
What to expect if baby is still breech?
The Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists (RCOG) website has more information on what to expect if your baby is still breech at the end of pregnancy . The RCOG advises against a vaginal breech delivery if: your baby's feet are below its bottom – known as a "footling breech".
How to turn a baby into a head down position?
This is when a healthcare professional, such as an obstetrician, tries to turn the baby into a head-down position by applying pressure on your abdomen. It's a safe procedure, although it can be a bit uncomfortable. Around 50% of breech babies can be turned using ECV, allowing a vaginal birth.
Why do you have to be admitted to hospital when you are transverse?
This is because of the very small risk of the umbilical cord coming out of your womb before your baby is born ( cord prolapse).
What does it mean when your baby is in a certain position?
your baby is in a certain position – for example, their neck is very tilted back, which can make delivery of the head more difficult. you have a low-lying placenta (placenta praevia) you have pre-eclampsia.
What position do babies go in during pregnancy?
Babies often twist and turn during pregnancy, but most will have moved into the head-down (also known as head-first) position by the time labour begins. However, that does not always happen, and a baby may be: 1 bottom first or feet first (breech position) 2 lying sideways (transverse position)
