Medication
Procedures
Self-care
Nutrition
How serious is a blocked right coronary artery?
A completely blocked coronary artery will cause a heart attack. The classic signs and symptoms of a heart attack include crushing chest pain or pressure, shoulder or arm pain, shortness of breath, and sweating. Women may have less typical symptoms, such as neck or jaw pain, nausea and fatigue.
What are the 2 ways to treat a blockage in the coronary artery?
One is medication; two is PCI - Percutaneous Coronary Intervention, or Angioplasty; and three is CABG or Coronary Artery Bypass Graft surgery. There are a variety of medications that help you live more comfortably and be able to be more active if your blocked artery is causing symptoms.
What happens if one coronary artery is blocked?
When one or more of the coronary arteries suddenly becomes completely blocked, a heart attack (injury to the heart muscle) may occur. If the blockage occurs more slowly, the heart muscle may develop small collateral blood vessels (or detours) for other coronary arteries to reroute the blood flow, and angina occurs.
Can you fix a blocked artery without surgery?
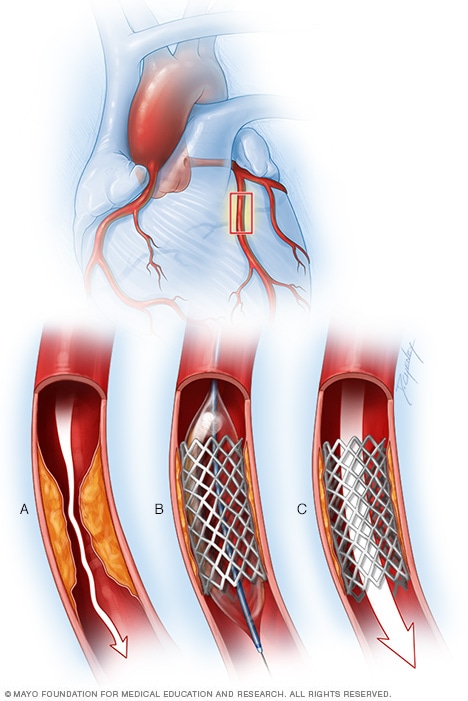
Through angioplasty, our cardiologists are able to treat patients with blocked or clogged coronary arteries quickly without surgery. During the procedure, a cardiologist threads a balloon-tipped catheter to the site of the narrowed or blocked artery and then inflates the balloon to open the vessel.
Can a blocked artery be treated with medication?
In serious cases, medical procedures or surgery can help to remove blockages from within the arteries. A doctor may also prescribe medication, such as aspirin, or cholesterol-reducing drugs, such as statins.
Which artery is the most common to have blockage?
Importance in cardiovascular diseases: The LAD artery is the most commonly occluded of the coronary arteries. It provides the major blood supply to the interventricular septum, and thus bundle branches of the conducting system.
What percentage of artery blockage requires surgery?
If a carotid artery is narrowed from 50% to 69%, you may need more aggressive treatment, especially if you have symptoms. Surgery is usually advised for carotid narrowing of more than 70%. Surgical treatment decreases the risk for stroke after symptoms such as TIA or minor stroke.
What percentage of artery blockage requires a stent?
“For a cardiac stent procedure to qualify as a medical necessity, it is generally accepted that a patient must have at least 70% blockage of an artery and symptoms of blockage,” Justice Department attorneys wrote.
Where is the right coronary artery?
The right coronary artery (RCA) is one of two main coronary vessels that supply the myocardium (the other being the left coronary artery). It originates from the right aortic sinus of the ascending aorta and runs in the right part of atrioventricular groove (coronary sulcus) wrapping around the right side of the heart.
What is the least invasive treatment for coronary artery disease?
Angioplasty. A coronary angioplasty is a type of minimally invasive procedure to treat CAD. For this procedure, a heart doctor threads a small tube, called a catheter, through an artery in your groin or arm.
Can an artery be unblocked without a stent?
The largest research study of its kind has found that drugs can be just as effective as stents and surgery for treating blocked arteries. Results of the study, sponsored by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, were released on November 16.
Can you live a normal life with blocked arteries?
Coronary Artery Disease (CAD) is treatable, but there is no cure. This means that once diagnosed with CAD, you have to learn to live with it for the rest of your life. By lowering your risk factors and losing your fears, you can live a full life despite CAD.
Diagnosis
Treatment
Clinical Trials
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
Specialist to consult
Alternative Medicine
Preparing For Your Appointment
- Treatment for coronary artery disease usually involves lifestyle changes such as not smoking, eating healthy and exercising more. Sometimes, medications and procedures are needed.