Explore
There are many different factors that can lead to a block of the first degree. These include, the presence of an AV nodal disease and an enhanced vagal tone. In cases of people, who have an enhanced vagal tone, the block may be physiologic in nature, as is seen in well trained athletes.
What can cause 1st degree AV block?
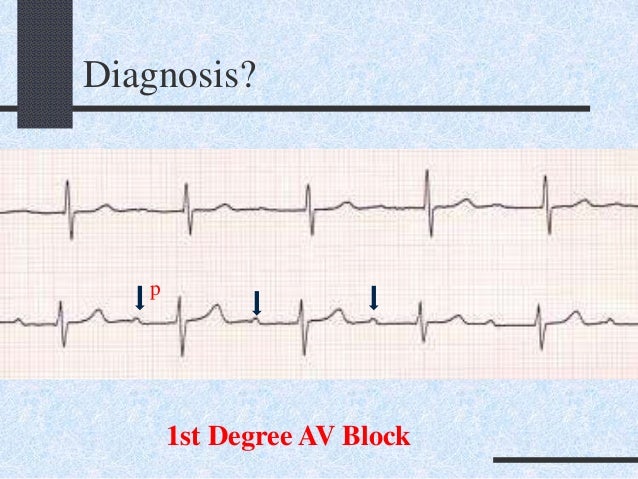
What Are ECG Characteristics of First-Degree AV Block?
- P wave for every QRS complex
- Prolonged PR interval that is greater than 0.20 seconds
- If the PR interval is greater than 0.30 seconds, a P wave may appear to be buried in the previous T wave
- If the PR interval is extended for more than 0.30 seconds, it is considered “marked”
- No beats are dropped in this rhythm
What are the symptoms of a 1st degree AV block?
In addition, this is what will be present with a 1 st Degree AV Heart Block:
- Regular P-waves and R-waves
- P-wave always accompanying the QRS complex
- QRS complex will measure normal
- PR INTERVAL WILL BE PROLONGED
How to identify 1st degree AV block?
First-degree atrioventricular block (AV block) is a disease of the electrical conduction system of the heart in which electrical impulses conduct from the cardiac atria to the ventricles through the atrioventricular node (AV node) more slowly than normal. First degree AV block does not generally cause any symptoms, but may progress to more severe forms of heart block such as second- and third ...
What exactly is a 1st degree AV block?
What is the treatment for AV block?
Permanent pacing is the therapy of choice in patients with symptomatic atrioventricular (AV) block with bradycardia. Temporary transcutaneous or transvenous pacing is required if a slow heart rate (or asystole) caused by AV block requires correction and permanent pacing is not immediately indicated or not available.
How serious is a first-degree AV block?
Traditionally, first-degree AV block has been considered a benign condition. However, epidemiologic data from the Framingham Study have shown that first-degree AV block is associated with increased risk of all-cause mortality in the general population.
What is the drug of choice for first degree heart block?
First-degree AV block occurs in <1.5% of patients with AMI admitted to hospital. Generally, it does not require specific treatment. If it is associated with signs of excessive vagal tone (i.e., severe hypotension), administration of atropine may be helpful.
What medication is given for heart block?
Medications that may be used in the management of third-degree AV block (complete heart block) include sympathomimetic or vagolytic agents, catecholamines, and antidotes.
Does first-degree heart block need treatment?
You generally don't need any treatment for first-degree heart block. Second-degree heart block. This means that the electrical signals between your atria and ventricles can intermittently fail to conduct.
What is the most common cause of heart block?
Coronary artery disease with and without a heart attack is one of the most common causes of heart block. Cardiomyopathies which are diseases that weaken the heart muscle can also result in wire damage.
Is first-degree heart block normal?
First-degree atrioventricular (AV) block is a delay within the AV conduction system and is defined as a prolongation of the PR interval beyond the upper limit of what is considered normal (generally 0.20 s). Up until recently, first-degree AV block was considered an entirely benign condition.
Can you give atropine for 1st degree heart block?
Atropine is useful for treating symptomatic sinus bradycardia and may be beneficial for any type of AV block at the nodal level. The recommended atropine dose for bradycardia is 0.5 mg IV every 3 to 5 minutes to a maximum total dose of 3 mg.
How can I improve my AV block?
Carotid sinus massage increases vagal tone, which worsens the block at the AV node. In contrast, carotid sinus massage improves infranodal block due to slowing of atrial impulses conducted through the AV node. Exercise or atropine improves AV nodal conduction due to sympathetic stimulation.
Can heart blockage be treated without surgery?
Through angioplasty, our cardiologists are able to treat patients with blocked or clogged coronary arteries quickly without surgery. During the procedure, a cardiologist threads a balloon-tipped catheter to the site of the narrowed or blocked artery and then inflates the balloon to open the vessel.
Is AV block serious?
You might not have symptoms or need treatment. But if you do, a doctor can help you manage your condition. Without the right care, serious AV block can be life threatening.
What causes a 1st degree AV block?
The most common causes of first-degree heart block are AV nodal disease, enhanced vagal tone (for example in athletes), myocarditis, acute myocardial infarction (especially acute inferior MI), electrolyte disturbances and medication.
Does atropine block AV node?
Atropine will have effect if the block is located in the AV node. Note that atropine may aggravate the block if it is located distal to the AV node. Isoprenaline (isoproterenol, 5 micrograms per minute) may also be administered (with caution in case of acute coronary syndromes, as isoprenaline may trigger ventricular tachycardia).
Is Holter ECG necessary?
Holter ECG may be valuable if the diagnosis is uncertain. Otherwise, no further examination is needed beyond the 12-lead ECG. Echocardiography is generally not necessary. Management of AV blocks aims to restore atrioventricular conduction either pharmacologically or by means of artificial pacemakers. Both methods may be used in the acute setting, ...
Can a transcutaneous pacemaker be withdrawn?
Transcutaneous pacemaker is a painful method which mandates sedation but should not be withdrawn if the situation is life-threatening. Any medications causing or aggravating the block must be withdrawn. AV blocks due to reversible causes does not need permanent pacemaker.
Is a second degree heart block rare?
The prognosis for patients with first-degree heart block is excellent. Progression to a second-degree heart block is very rare.
Is a heart block asymptomatic?
While first-degree heart block is usually asymptomatic and an incidental EKG finding, patients should have routine follow-up monitoring to ensure the condition does not progress to worse cardiac conduction issues. Patients can generally lead a normal, symptom-free life absent any progression of the condition.
Is AV block a benign condition?
Although generally believed to be a benign condition, cohort studies have shown that patients with first-degree AV block have a higher incidence of atrial fibrillation, pacemaker placement, and all-cause mortality than patients with normal PR intervals.
Do you need to have a follow up for a heart block?
First-degree heart block usually doesn’t need treatment. Your healthcare provider may ask you to have regular follow-up visits. You may also be asked to take your own pulse and be alert to changes in your heart rate.
Can a heart block be detected?
First-degree heart block often does not have any symptoms. It may be found when your healthcare provider is examining you for some other reason. In more severe cases, people may have an uncomfortable awareness of the heartbeat.
What is the mildest heart block?
First-degree heart block: The electrical impulse still reaches the ventricles, but moves more slowly than normal through the AV node. The impulses are delayed. This is the mildest type of heart block. Second-degree heart block is classified into two categories: Type I and Type II.
What is the name of the block that makes your heart beat?
Heart Block. Heart block, also called AV block, is when the electrical signal that controls your heartbeat is partially or completely blocked. This makes your heart beat slowly or skip beats and your heart can’t pump blood effectively. Symptoms include dizziness, fainting, tiredness and shortness of breath. Pacemaker implantation is ...
What medications slow the heart's electrical impulses?
You take medications that slow the conduction of the heart’s electrical impulses including some heart medications (beta blockers, calcium channel blockers, digoxin), high blood pressure drugs, antiarrhythmics; muscle relaxants and sedatives; antidepressants and antipsychotics; diuretics; lithium.
How long do you need to wear a Holter monitor?
You may need to wear a portable ambulatory monitor device, such as a Holter monitor or an event recorder, for 24 to 48 hours or longer to collect more information about your heart’s electrical activity. If you need to use a monitor, you’ll get detailed information about how to use it.
Can heart block cause lightheadedness?
Type of heart block, its location and severity, and symptoms vary from person to person. If left untreated, severe heart block can cause sudden cardiac arrest (your heart suddenly stops beating), but most commonly can cause either lightheadedness or fainting spells.
Is a heart block a first degree or second degree?
First-degree heart block: May not have any symptoms. May be found during a routine electrocardiogram (ECG) although heart rate and rhythm are usually normal. First-degree block is common in athletes, teenagers, young adults and those with a highly active vagus nerve. Second-degree heart block symptoms:
Can you get heart block if your mother has autoimmune disease?
You may be at increased risk of a heart block if: Your mother has an autoimmune disease, such as lupus. You are of older age. Risk of heart block increases with age. You have other heart conditions including coronary artery disease, heart valve disease. You have birth defects of the heart.
What is AV block?
AV block, or atrioventricular block, is a major cause of significant bradyarrhythmias. To diagnose and manage AV block, it is important to have a basic understanding of the anatomy of the conduction system of the heart.
What causes AV block?
Acquired AV block is most commonly caused by idiopathic fibrosis, acute myocardial infarction, or drug effects. AV block can also be congenital. If AV block is symptomatic, and determined to be permanent, pacing is the only effective long-term therapy. Conduction Terminology.
What is a Mobitz II block?
Mobitz II, or Type II, second degree AV block, can be confused with a nonconducted premature atrial complex. In Mobitz II block, the electrocardiogram (EKG) shows a constant P–R interval, followed by a sudden failure of a P wave to be conducted to the ventricles.
What is the P–R interval of AV block?
First-degree AV block, with a P–R interval greater than 200 ms , is rarely found in young, healthy adults during activity. However, a longer P–R interval, and even Mobitz I (Wenckebach) block can be seen in young, well-conditioned individuals at rest and during sleep. The P–R interval decreases and the Wenckebach block disappears with increased activity, and is considered normal vagal influence on the AV node.
How long can you keep anticoagulant for atrial fibrillation?
Patients on anticoagulants who need temporary or permanent pacemaker placement are at increased risk of bleeding complications. If the procedure is not emergent, and the patient is on warfarin for atrial fibrillation, the drug can be withheld for 3 to 5 days, and restarted postprocedure when the risk of bleeding is acceptable.
What is a slowed conduction?
Slowed conduction, or blocked conduction, can occur anywhere along the path of conduction fibers, and can generally be identified by EKG analysis. Infra-Hisian block is the most important to identify, since it is the cause of most cases of symptomatic complete heart block.
Why is my heart block reversible?
Reversible causes of complete heart block can be due to metabolic abnormalities, drug effects, Lyme disease, or vasovagal episodes. In these cases, the complete heart block resolves once the abnormality has been treated. In true complete heart block, the sinus rate is faster than the ventricular rate.
How does an AV block work?
They team up to pump blood through your body. An electrical signal starts out in a spot called the sinoatrial (SA) node. It's known as your heart's natural pacemaker. The current heads down to a group of cells called the atrioventricular (AV) node.
What happens when you have a heart block?
When you have heart block, the electrical signal from your heart's upper chamber slows down or gets interrupted on its way to the lower chambers. You can get mild AV block as your heart adapts to an intensive exercise routine. It's sometimes called "athlete's heart.".
What is the condition where the heart is blocked?
But sometimes this current gets delayed or stopped. The result: a condition called atrioventricular (AV) block or heart block. Certain health conditions, heart defects, and medicines can cause it.
Why does my heart block after a heart attack?
Extra tissue can thicken, scar, and damage the pathways that send signals from the upper part to the lower part of your heart. Coronary artery disease. This damages your heart's blood vessels. It may cause AV block before or after a heart attack. Some other causes are: Medication.
Where do you put a pacemaker?
Your doctor will put the pacemaker under your skin. They'll most likely place it under your left or right collarbone. It'll connect to your heart with wires that run through your veins. Your doctor may also need to treat the condition that is causing your heart block.
Can AV block be life threatening?
You might not have symptoms or need treatment. But if you do, a doctor can help you manage your condition. Without the right care, serious AV block can be life threatening.
Can blood pressure medications slow your heartbeat?
Certain drugs can slow your heartbeat. This includes blood pressure medicine like beta-blockers and calcium channel blockers. I ncreased vagal tone. This happens when you have more activity in a nerve called the vagus nerve. It's a problem that sometimes shows up if you're very physically fit.