
How long does it take to go blind with wet macular degeneration?
How Long Does it Take to Lose Vision with Macular Degeneration? In late stages of AMD, you may have difficulty seeing clearly. On average, it takes about 10 years to move from diagnosis to legal blindness, but there are some forms of macular degeneration that can cause sight loss in just days.
How effective is treatment of wet macular degeneration?
Wet AMD has no cure, but treatment can help slow its progression. Partial recovery of your vision may be possible if you start treatment early enough. Sometimes vision can improve as previously leaked fluid leaves your eye, if you're still receiving treatment that stops new leaking.Mar 17, 2021
Can wet age-related macular degeneration be cured?
There's no cure, but treatment for age-related macular degeneration (AMD) may slow the disease and keep you from having a severe loss of vision. Talk to your doctor about the best way to manage your condition.Feb 28, 2022
What is the latest treatment for wet macular degeneration?
On October 22, 2021, the FDA approved Susvimo™ (ranibizumab injection) 100 mg/mL for intravitreal use via ocular implant for the treatment of people with wet, or neovascular, age-related macular degeneration (AMD) who have previously responded to at least two anti-vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) injections.Oct 22, 2021
Are eye injections worth it?
Eye fillers can work wonders, but they're not a miracle solution. For example, they're not permanent, and they won't address some concerns, such as crow's feet. Talking to a doctor about the results you're hoping for is an important first step. Everyone deserves to feel confident about their looks.Feb 22, 2020
Which is worse dry or wet macular degeneration?
Wet macular degeneration is more serious and is the leading cause of permanent central vision loss. Though the dry type is less serious, it can lead to the wet type if not monitored closely by a doctor.Jan 4, 2021
How many injections do you need for wet macular degeneration?
You may need injections every four to six weeks to maintain the beneficial effect of the medication. In some instances, you may partially recover vision as the blood vessels shrink and the fluid under the retina absorbs, allowing some vision gain.Dec 11, 2020
Do you always go blind with wet macular degeneration?
Only the center of vision is affected with this disease. It is important to realize that people rarely go blind from it. AMD affects the central vision, and with it, the ability to see fine details.
What foods should be avoided with macular degeneration?
Foods to avoid with macular degenerationProcessed foods that contain trans fats.Tropical oils, like palm oil (use vitamin E–rich safflower and corn oil instead)Lard and vegetable shortening, and margarine.High-fat dairy foods (eggs in moderation are a good source of eye-healthy nutrients)Fatty beef, pork and lamb.
How does macular degeneration affect vision?
If you have macular degeneration, the cells in your macula are degrading. This can affect your vision. At first, you may not be aware of any vision loss, but your eye doctor will be able to see changes to your retina. As macular degeneration progresses, you will begin to notice vision loss. Macular degeneration is caused by a combination ...
What is the cause of macular degeneration?
Macular degeneration is caused by a combination of environmental and genetic factors. It’s usually referred to as age-related macular degeneration (AMD) when it’s found in people over 55 years of age. According to the American Macular Degeneration Foundation, about 85 to 90 percent of AMD diagnoses are dry (atrophic) AMD.
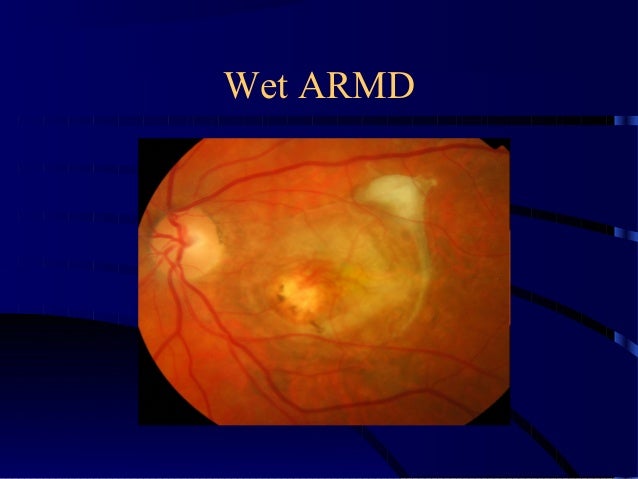
What is wet AMD?
How serious is wet AMD? Wet age-related macular degeneration (AMD) causes rapid and progressive central vision loss due to leaking blood vessels in the eyes. Early treatment can reduce the amount of vision loss you experience.
What is the center of the retina?
At the center of each retina is an area called the macula. Your macula processes your central vision and helps you focus on tasks like driving, seeing fine detail, recognizing faces, and reading this article. If you have macular degeneration, the cells in your macula are degrading. This can affect your vision.
What percentage of AMD is dry?
According to the American Macular Degeneration Foundation, about 85 to 90 percent of AMD diagnoses are dry (atrophic) AMD. Atrophic refers to the macula’s decrease in size. The remaining 10 to 15 percent are wet (exudative) AMD. Exudative means leaking fluid.
What happens when you have dry AMD?
With dry AMD, the photoreceptor and retinal pigmented epithelial (RPE) cells in the macula deteriorate and die. This can progress to wet AMD when cell death causes an abnormal growth of blood vessels in the area. When these vessels leak and bleed, they damage your central vision.
How to protect your vision?
Lifestyle changes. Lifestyle changes can protect your vision. Exercise regularly, maintain a healthy weight for your body size, eat nutritious food like dark, leafy greens, manage your blood pressure and cholesterol, and avoid smoking.
What is wet macular degeneration?
Wet macular degeneration is a form of age-related macular degeneration (AMD). AMD is a progressive eye disease that affects up to 11 million Americans. It’s also one of the most common causes of vision loss in people 60 years of age and older. AMD is a disease that affects the retina—the light-sensing cells lining the back of the eye.
How to reduce the risk of macular degeneration?
This includes: Eating a diet rich in antioxidants by including plenty of fresh fruits and vegetables.
What happens when you have wet AMD?
Once wet AMD develops in one eye, certain factors increase the risk of developing it in the other. Everyone who develops wet AMD started out having dry AMD. Wet AMD occurs when new blood vessels begin growing under the macula. These vessels aren’t normal and can leak blood and fluid.
Who is Sarah Lewis?
Sarah Lewis is a pharmacist and a medical writer with over 25 years of experience in various areas of pharmacy practice. Sarah holds a Bachelor of Science in Pharmacy degree from West Virginia University and a Doctor of Pharmacy degree from Massachusetts College of Pharmacy.
Can AMD cause central vision loss?
Left untreated, wet AMD progresses quickly and can lead to complete central vision loss. Seek prompt medical care if you notice changes in your central vision. If you have dry AMD, contact your doctor right away if you notice changes in your at-home vision testing.
Can laser therapy help with AMD?
In the past, laser treatment was the only way to seal leaky blood vessels and treat wet AMD. However, there were limitations to laser therapy. Not all lesions were eligible for laser treatment, up to half of people continued to have some leakage, and there was a 50% chance of recurrence within two years.
Is AMD dry or wet?
There are two types of AMD—dry and wet. In wet macular degeneration vs. dry, dry AMD is the most common form. It accounts for about 80 to 90% of cases. Wet AMD is less common, but more severe than the dry type. It causes 90% of severe vision loss in people with AMD. Everyone who gets wet AMD had dry AMD at one point.
What is the best treatment for wet AMD?
Learn more about AMD. There are 2 treatment options that can slow down or stop vision loss from wet AMD: Anti-VEGF injections. Photodynamic therapy (PDT)
What is wet AMD?
Wet AMD (also called advanced neovascular AMD) is a serious type of late AMD. It happens when a protein called vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) makes abnormal blood vessels grow in the wrong place in the back of your eye. The good news is that there are effective treatments for wet AMD.
How to treat a swollen eye?
When you get this treatment, your doctor will: 1 Give a shot of verteporfin in your arm 2 Put numbing medicine in your eye 3 Place a special contact lens on your eye to help guide the laser 4 Shine the laser onto the extra blood vessels in the back of your eye
How to stop AMD?
Put numbing medicine in your eye. Place a special contact lens on your eye to help guide the laser. Shine the laser onto the extra blood vessels in the back of your eye. Some people will need to get PDT more than once. Talk to your doctor to find out if you will need more treatments to help stop vision loss from AMD.
How does PDT work?
PDT works by using a light-sensitive medicine called verteporfin that “turns on” when hit by a specific type of laser (sometimes called a cold laser). Your doctor will shine the laser on a very small area in the back of your eye, causing the verteporfin to break down the blood vessels that are causing your vision loss.
How to treat wet macular degeneration?
This treatment is appropriate for people with wet macular degeneration, according to Mayo Clinic. Doctors inject a drug into an arm vein, and then shine a laser on abnormal eye blood vessels. When the drug enters these blood vessels, it is activated by the laser, and the blood vessel is closed.
What is the most common form of macular degeneration?
The dry form is the most common, according to the American Macular Degeneration Foundation, as it represents about 90 percent of the cases of macular degeneration. This form of macular degeneration involves yellow deposits (known as drusen) sitting beneath the macula, causing thinning and dying of that vital tissue.
Why do people lose their vision?
This damage is caused by abnormal blood vessels growing beneath the macula. When those blood vessels leak blood, rapid destruction of the macula takes hold.
What is the retina?
The retina perceives images that move through the eye, and the retina transforms those images into electrical signals that can be processed by the brain. At the very center of the retina is the macula, and it's responsible for our ability to see things at the center of our vision.
How does the lens work?
The lens of the eye works closely with the retina. The lens focuses the light that enters the eye, making sure that the light hits the retina in just the right place. Some surgeons are experimenting with lens therapies for macular degeneration, thinking that making the lens work better might make the damage easier to move past.
Does macular degeneration surgery help?
More retinal cells are exposed to the light moving through the eye, which allows undamaged cells to take over for their damaged counterparts. This surgery is not designed to halt the progression of macular degeneration, but it can help to make life with the disorder better.
What is the macula made of?
The macula is made up of sensitive tissues that rely on a mix of nutrients to stay healthy. An optimal diet can help to provide those cells with the nutrition they need, but many people simply don't eat a diet that is rich in the right types of ingredients to help the eyes stay healthy . Vitamin supplements may help to fill the gap.
What is the treatment for macular degeneration?
The current treatment is regular injections of anti-VEGF medication into each affected eye. Research continues to find treatments that are easier to take than regular eye injections. Prior to the availability of current treatments for wet macular degeneration, having this condition meant you were certain to experience significant vision loss.
What happens if you have wet AMD?
Wet AMD results in loss of central vision if left untreated. Fortunately, there are treatments available to help slow and even prevent vision loss. If you have wet AMD, vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) triggers the growth of abnormal blood vessels under your retina.
Why is VEGF important?
In some ways, VEGF is important. It triggers the growth of new blood vessels that help to heal wounds. However, in the retina of your eyes, too much VEGF can cause wet AMD. Modern treatment breakthroughs for wet AMD are aimed at reducing this growth of abnormal blood vessels.
What is a PDS eye?
The PDS is a small, surgically implanted eye reservoir that holds medication for a controlled and continuous release into your eye. A doctor refills the device using a specialized syringe. A PDS can hold several months’ worth of medication, which means fewer trips to the doctor’s office.
How often should I get anti-VEGF injections?
However, this treatment requires regular injections every 4 to 8 weeks, which is a difficult schedule to keep for some people.
Is gene therapy still available?
This is done in one treatment, either as a surgical procedure under the retina or as an injection into the eye. As of 2021, gene therapy is still in clinical trials but may be available as a treatment option in the next several years.
What is the goal of gene therapy?
The goal of gene therapy is to enable your eyes to block the action of VEGF in your eyes and reduce the growth of abnormal blood vessels. This eliminates the need for repeated injections or implants.
What is the treatment for wet AMD?
Treatments for Wet AMD: Anti-VEGF Therapy . VEGF is an acronym for vascular endothelial growth factor. Currently, the most common and effective clinical treatment for wet Age-related Macular Degeneration is anti-VEGF therapy – which is periodic intravitreal (into the eye) injection of a chemical called an “anti-VEGF.”.
What are the drugs that inhibit VEGF?
Chemically synthesized short strands of RNA (nucleic acid) called “aptamers” prevent the binding of VEGF to its receptor. The various forms of anti-VEGF injections include ranibizumab (Lucentis, made by Genentech/Novartis), be vacizumab (off label Avastin from Genentech), and the recently Food and Drug Administration-approved aflibercept ( Eylea /VEGF Trap-Eye from Regeneron/Bayer). Each of these chemicals works in a different way to inhibit blood vessel growth.
What are the phases of macular degeneration?
The American Macular Degeneration Foundation recognizes three phases of macular degeneration: early, intermediate, and late. Those phases are determined by the symptoms doctors can see as well as the symptoms you might report to a doctor. What you should do at each stage of the disorder varies.
What is the cause of age related macular degeneration?
Age-related macular degeneration (AMD) is caused by changes beneath the sensitive tissues that communicate with your optic nerve and allow you to see. In the dry form of the disease, which is the most common form, the damage begins with accumulations of yellow deposits below the retina, known as drusen.
What is intermediate AMD?
Intermediate AMD: What It Is and What to Do. The organization Prevent Blindness suggests that people in the intermediate stage of AMD have many drusen, and while some may not have symptoms, others may begin to see holes or black spots in the center of the visual field.
How long does it take to get blind?
The American Optometric Association reports that most people move through the process of diagnosis to legal blindness in about 10 years, but this is very much an estimate. Taking care of your health, using vitamins, and following the advice of your doctor may all be vital in helping you to slow this progression.
Can AMD cause fuzziness?
In the late stages of AMD, you may have many drusen and your vision may be significantly impaired. Straight lines may look wavy, and you may have a large spot of fuzziness in the center of your visual field. You may be unable to read expressions on the faces of those you're talking to, and you may struggle to read or work on a computer.
How long does it take to lose sight?
According to The American Journal of Managed Care, some people lose their sight within days of experiencing symptoms. This is why it's so vital for you to work with a doctor you can trust and explain your symptoms as soon as they appear.
Is blindness reversible?
As the Foundation Fighting Blindness puts it, your vision may be stable between visits with your doctor, but that does not mean that the condition is reversing. That isn't part of the condition, but it can mean that you are doing a good job of keeping rapid deterioration from taking hold.
Diagnosis
- Your doctor will review your medical and family history and conduct a complete eye exam. To confirm a diagnosis of macular degeneration, he or she may do several other tests, including: 1. Examination of the back of your eye.Your eye doctor will put drops in your eyes to dilate them a…
Treatment
- Treatments are available that may help slow disease progression, preserve existing vision and, if started early enough, recover some lost vision.
Clinical Trials
- Explore Mayo Clinic studiestesting new treatments, interventions and tests as a means to prevent, detect, treat or manage this condition.
Coping and Support
- Vision loss from macular degeneration can affect your ability to do things such as read, recognize faces and drive. These tips may help you cope with your changing vision: 1. Ask your eye doctor to check your eyeglass prescription.If you wear contacts or glasses, be sure your prescription is up to date. If new glasses don't help, ask for a referral to a low vision specialist. 2. Use magnifiers. …
Preparing For Your Appointment
- To check for macular degeneration, a dilated eye exam is usually necessary. Make an appointment with a doctor who specializes in eye care — an optometrist or an ophthalmologist. He or she can perform a complete eye exam.