What are the primary stages of sewage treatment?
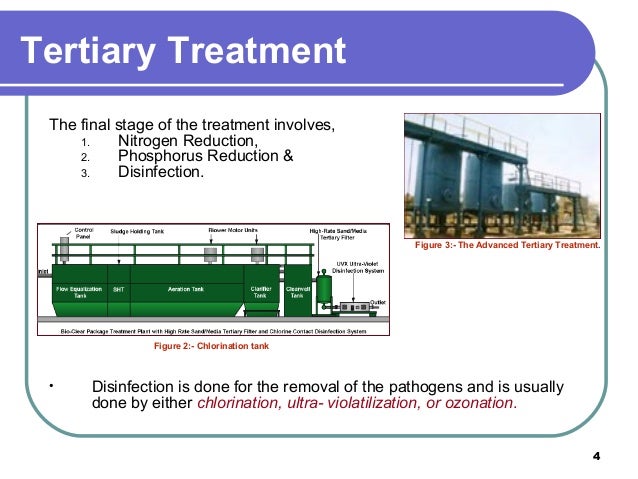
There are four major processes under the tertiary treatment:
- Solids removal
- Biological nitrogen removal
- Biological phosphorus removal
- Disinfection.
What is tertiary wastewater treatment, and how does it work?
- Bag filters: Bag filters are ideal for wastewater treatment plants that need to reduce contaminants to a specific micron rating. ...
- Drum filters: A drum filter consists of a drum with a woven cloth filter around it. ...
- Disc filters: A disc filter consists of a central drum attached to multiple discs with cloth filters. ...
What is primary sewage treatment?
What are the steps involved in wastewater treatment?
- Screening and Pumping.
- Grit Removal.
- Primary Settling.
- Aeration / Activated Sludge.
- Secondary Settling.
- Filtration.
- Disinfection.
- Oxygen Uptake.
What is MBBR wastewater treatment?
- Compact: MBBR is an excellent option for facilities with space constraints, since it typically has a much smaller footprint than other systems. ...
- Simple: Another practical advantage of MBBR is that it is a relatively straightforward process. ...
- Low maintenance: MBBR is also known for being a low-maintenance process. ...

What is a tertiary treatment system?
The tertiary treatment is one or several treatment units added to remove certain pollutants such as phosphorus and nitrogen from the wastewater after the secondary treatment; From: Water Conservation and Wastewater Treatment in BRICS Nations, 2020.
What are 3 methods of tertiary treatment?
The tertiary treatment methods are: 1.Filtration 2.Air/Steam Stripping 3.Biological Processes 4. Adsorption 5.Membrane Separation Processes 6.Ion Exchange Process 7.Precipitation 8.Oxidation and Reduction and 9.
What are the agents of tertiary treatment in sewage treatment?
Several disinfection agents can be used depending on wastewater condition (pH, clarity, etc.) And among them, chlorine, ozone, ultraviolet (UV) light are the most common. These have their advantages and disadvantages. Chlorine is a time-tested effective disinfection agent.
Why is tertiary sewage treatment important?
The purpose of tertiary treatment is to provide a final polishing treatment stage prior to discharge or reuse of the wastewater. Chlorination – A water treatment method that destroys harmful bacteria, parasites, and other organisms.
What is tertiary system?
Tertiary systems carry the same treatment process as a secondary system with an additional filtration or "polishing" process often in the form of UV treatment. This process will further remove the remaining organic matter and bacteria. Tertiary systems are required in very sensitive receiving environments.
What are some types of tertiary treatment?
Tertiary TreatmentWastewater Treatment.Membrane Bioreactors.Activated Sludge.Advanced Oxidation Process.Microalgae.Nitrogen.Reuse.
Which of the following is a tertiary treatment process?
Tertiary water treatment is the final stage of the multi-stage wastewater cleaning process. This third stage of treatment removes inorganic compounds, bacteria, viruses, and parasites. Removing these harmful substances makes the treated water safe to reuse, recycle, or release into the environment.
What is a tertiary septic system?
The tertiary system treats the wastewater to a higher level than a septic tank. The treated effluents are discharged into a much smaller area, and it uses aeration to accelerate the time to break down solids.
What is an advantage of using tertiary treatment?
Tertiary treatment improves the quality of wastewater before it is reused, recycled or discharged to the environment. Industrial wastewater can con...
What are the major objectives of tertiary treatment?
The main purpose of the tertiary treatment is to ensure that the treated water which is to be released on to the environment is biologically accept...
What is sewage treatment?
wastewater treatment, also called sewage treatment, the removal of impurities from wastewater, or sewage, before it reaches aquifers or natural bod...
What is part of the tertiary treatment of wastewater?
Third, the Tertiary Wastewater Treatment process consists of flocculation basins, clarifiers, filters, and chlorine basins or ozone or ultraviolet...
What are some types of tertiary treatment?
Tertiary treatment removes the load of nitrogen and phosphorus present in the water. It includes processes like filtration, ion exchange, activated...
What are 3 methods of tertiary treatment?
Several tertiary treatment processes can be employed depending on the purpose, with some of the most used being the following: membrane separation...
What is meant by tertiary treatment?
Tertiary treatment is the advanced treatment process, following secondary treatment of waste water, that produces high—quality water. Tertiary trea...
What are the 3 stages of sewage treatment?
There are three main stages of the wastewater treatment process, aptly known as primary, secondary and tertiary water treatment.Dec 6, 2018
What is tertiary treatment of sewage water?
Tertiary treatment is the third, and final, stage in a standard wastewater management system. Once effluent has been treated in the primary and sec...
How does tertiary wastewater treatment work?
What Is Tertiary Wastewater Treatment, and How Does It Work? In the wastewater industry, plants often focus on primary and secondary treatments, which do most of the work of preparing wastewater for discharge into the environment. Tertiary treatment is also critical in many situations. It affords the peace of mind of knowing ...
What happens to wastewater after tertiary treatment?
Once the wastewater has undergone tertiary treatment, it is ready for discharge back into the environment. Many municipalities have specific requirements about the discharge of treated water, and tertiary treatment should be sufficient to meet those standards, keep the environment clean, and preserve human health.
What are tertiary filtration components?
Tertiary filtration components can contain a few different materials. Sand and activated carbon filters are common, and filters can also contain fine woven cloth. The filters also come in a few different types, including bag filters, drum filters and disc filters: Bag filters: Bag filters are ideal for wastewater treatment plants ...
Why is chlorine used in wastewater treatment?
Wastewater treatment plants can dump chlorine into the wastewater to kill harmful microorganisms like bacteria and viruses.
What is SSI aeration?
As a full-service wastewater treatment engineering company, SSI has the experience and industry expertise to help you improve your treatment’s efficiency or meet environmental regulatory standards for your discharged wastewater. We offer comprehensive system design and engineering and are happy to assist with lab services , field services, and treatment product selection.
What is wastewater treatment?
Most wastewater treatment systems consist of at least two main treatment processes: primary and secondary treatment, with some additional preliminary methods. Primary treatment, which typically removes 50% to 70% of the suspended solids in wastewater, uses physical processes like filtration and settling to remove grit, debris, oil, ...
What is secondary treatment?
Secondary treatment applies additional biological processes like aeration and activated sludge treatment to break down dissolved and suspended biosolids using good bacteria. Tertiary treatment adds a third, more advanced and rigorous level of treatment.
What is tertiary treatment?
Tertiary treatment includes the removal of the remaining inorganic compounds (phosphate, sulfate, ammonium) and other refractory organic compounds by one or more physical separation methods, such as carbon adsorption, deep-bed filtr ation, and in some cases, membrane-based techniques, such as reverse osmosis or electrodialysis.
When is tertiary treatment necessary?
Usually tertiary treatment of wastewater is only regarded as necessary when the nutrient concentrations in the effluent have to be reduced i.e., if the mill discharges to very sensitive recipients. View chapter Purchase book. Read full chapter.
What is suspended solid removal?
Suspended solids removal in tertiary treatment implies the removal of those materials that have been carried over from a secondary clarification process. It is also employed as a pretreatment method prior to physical chemical treatment processes. Influent suspended solids concentration must be less than about 100 mg/liter or backwashing requirements become excessive. Finely dispensed suspended solids may require the addition of coagulant prior to filtration. Several means for removal of suspended solids have been proposed and tested. These include the use of diatomaceous earth filtration, pressure filtration, chemical clarification, sand filtration with conventional units and multimedia, ultrafiltration, and the moving-bed filter. With the exception of the chemical clarification processes, these methods all involve the physical straining of the finely divided solids that are removed.
What is sand filtration?
Sand filtration is a conventional wastewater treatment process characterized by its simplicity, low energy inputs, and easy maintenance. In this system, chemical reagents are not required, resulting in lower costs in comparison with other methods.
What are the two types of chemical treatments?
There are two different types of chemical treatments, flocculation and precipitation , as they involve different types of purification mechanisms. Flo cculation, is based on an addition of ferric ions, aluminum ions, or/and long-chained polymers to the effluents.
What are the drawbacks of biological treatment?
Although chemical treatment shows good results, the treatment has associated drawbacks such as dewatering and disposal of the generated sludge.
What chemicals are used in lignin treatment?
The chemicals that are used are usually aluminum (Al) salts, ferric (Fe 3+) salts, and lime (CaO). The chemical treatment gives a further reduction of some recalcitrant compounds such as high-molecular degradation products from lignin.
Tertiary Waste Water Treatment Methods
Most methods used in tertiary treatment include physicochemical methods such as coagulation, filtration, adsorption on activated carbon, reverse osmosis, and further disinfection. We also use some biological methods like constructed wetlands and membrane bioreactors for nutrients removal.
Reverse Osmosis -Tertiary Wastewater Treatment
Reverse Osmosis produces demineralized water by forcing water through semipermeable membranes at high pressure. We apply a pressure greater than the osmotic pressure across a membrane separating a concentrated solution and dilute phase in this process. This forces the solvent or water to move towards the dilute phase.
Electrodialysis – Tertiary Wastewater Treatment
Electrodialysis is another popular tertiary wastewater treatment method that employs the removal of the solute from the solution instead of removing the solvent. This process uses selectively permeable membranes and an electric potential difference to separate ions from a solution.
Filtration
The removal of total suspended solids (TSS) by tertiary treatment entails the removal of components that have remained after a secondary clarifying process. Before we proceed with filtration, pretreatment is required. The concentration of suspended particles in the influent must be less than 100 mg/l for effective filtration.
Conclusion
In this blog, we had a short discussion about some of the tertiary wastewater treatment methods like reverse osmosis, electrodialysis, ultrafiltration etc. Depending on the end-use of the wastewater we use a single method or a combination of the above-mentioned ones.
What is tertiary treatment?
What is Tertiary Sewage Treatment? After biochemical degradation of the sewage in the secondary treatment, the clarified effluent is further treated to treat it of the non-biodegradable toxic organic pollutants such as chlorophenols, polychlorinated biphenyls and other synthetic pollutants.
What metals are removed from sewage?
For this purposes activated carbon filters are used. Removal of heavy metals like mercury, lead, chromium and cadmium are also done during tertiary treatment. These metal ions, which are found absorbed in the sewage water are converted into either toxic products or residues.
How is nitrogen removed from wastewater?
Nitrogen is removed by volatiIisation as ammonia. Ammoniacal nitrogen is removed by breakpoint chlorination by adding hypochlorous acid in 1:1 ratio. Disinfection. The final step of tertiary process is disinfection, which is typically carried out by adding chlorine to the wastewater.
What is the process of filtration?
Filtration. In the filtration process, either sand, charcoal or activated carbon are used to filter the wastewater. The water is made to pass through a bed of sand or charcoal, so that the particulate matter in the water adheres to the filter medium and gets removed from the water. Lagooning.
