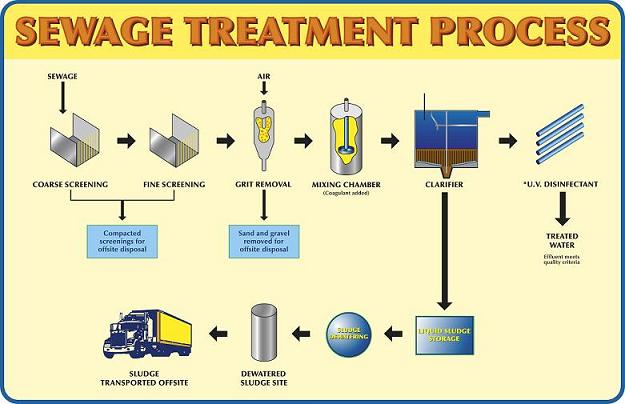
What are the primary stages of sewage treatment?
There are four major processes under the tertiary treatment:
- Solids removal
- Biological nitrogen removal
- Biological phosphorus removal
- Disinfection.
What is tertiary wastewater treatment, and how does it work?
- Bag filters: Bag filters are ideal for wastewater treatment plants that need to reduce contaminants to a specific micron rating. ...
- Drum filters: A drum filter consists of a drum with a woven cloth filter around it. ...
- Disc filters: A disc filter consists of a central drum attached to multiple discs with cloth filters. ...
What is primary sewage treatment?
What are the steps involved in wastewater treatment?
- Screening and Pumping.
- Grit Removal.
- Primary Settling.
- Aeration / Activated Sludge.
- Secondary Settling.
- Filtration.
- Disinfection.
- Oxygen Uptake.
What is MBBR wastewater treatment?
- Compact: MBBR is an excellent option for facilities with space constraints, since it typically has a much smaller footprint than other systems. ...
- Simple: Another practical advantage of MBBR is that it is a relatively straightforward process. ...
- Low maintenance: MBBR is also known for being a low-maintenance process. ...

What is meant by tertiary treatment?
Tertiary treatment is the advanced treatment process, following secondary treatment of waste water, that produces high—quality water. Tertiary treatment includes removal of nutrients such as phosphorus and nitrogen and practically all suspended and organic matter from waste water.
What are 3 methods of tertiary treatment?
The tertiary treatment methods are: 1.Filtration 2.Air/Steam Stripping 3.Biological Processes 4. Adsorption 5.Membrane Separation Processes 6.Ion Exchange Process 7.Precipitation 8.Oxidation and Reduction and 9.
Why is tertiary sewage treatment important?
The purpose of tertiary treatment is to provide a final polishing treatment stage prior to discharge or reuse of the wastewater. Chlorination – A water treatment method that destroys harmful bacteria, parasites, and other organisms.
What is a tertiary septic system?
The tertiary system treats the wastewater to a higher level than a septic tank. The treated effluents are discharged into a much smaller area, and it uses aeration to accelerate the time to break down solids.
What is an advantage of using tertiary treatment?
Tertiary treatment improves the quality of wastewater before it is reused, recycled or discharged to the environment. Industrial wastewater can con...
What are the major objectives of tertiary treatment?
The main purpose of the tertiary treatment is to ensure that the treated water which is to be released on to the environment is biologically accept...
What is sewage treatment?
wastewater treatment, also called sewage treatment, the removal of impurities from wastewater, or sewage, before it reaches aquifers or natural bod...
What is part of the tertiary treatment of wastewater?
Third, the Tertiary Wastewater Treatment process consists of flocculation basins, clarifiers, filters, and chlorine basins or ozone or ultraviolet...
What are some types of tertiary treatment?
Tertiary treatment removes the load of nitrogen and phosphorus present in the water. It includes processes like filtration, ion exchange, activated...
What are 3 methods of tertiary treatment?
Several tertiary treatment processes can be employed depending on the purpose, with some of the most used being the following: membrane separation...
What is meant by tertiary treatment?
Tertiary treatment is the advanced treatment process, following secondary treatment of waste water, that produces high—quality water. Tertiary trea...
What are the 3 stages of sewage treatment?
There are three main stages of the wastewater treatment process, aptly known as primary, secondary and tertiary water treatment.Dec 6, 2018
What is tertiary treatment of sewage water?
Tertiary treatment is the third, and final, stage in a standard wastewater management system. Once effluent has been treated in the primary and sec...
What are the 3 stages of sewage treatment?
There are three main stages of the wastewater treatment process, aptly known as primary, secondary and tertiary water treatment.Dec 6, 2018
What is part of the tertiary treatment of wastewater?
Third, the Tertiary Wastewater Treatment process consists of flocculation basins, clarifiers, filters, and chlorine basins or ozone or ultraviolet...
What is tertiary treatment system?
The tertiary treatment is one or several treatment units added to remove certain pollutants such as phosphorus and nitrogen from the wastewater aft...
What is tertiary treatment of sewage water?
Tertiary treatment is the third, and final, stage in a standard wastewater management system. Once effluent has been treated in the primary and sec...
What Is Tertiary Wastewater Treatment?
What is tertiary treatment in wastewater? To answer this question, let’s look into how treatment plants generally work and how the main stages of wastewater treatment progress.
What happens to wastewater after tertiary treatment?
Once the wastewater has undergone tertiary treatment, it is ready for discharge back into the environment. Many municipalities have specific requirements about the discharge of treated water, and tertiary treatment should be sufficient to meet those standards, keep the environment clean, and preserve human health.
What are tertiary filtration components?
Tertiary filtration components can contain a few different materials. Sand and activated carbon filters are common, and filters can also contain fine woven cloth. The filters also come in a few different types, including bag filters, drum filters and disc filters: Bag filters: Bag filters are ideal for wastewater treatment plants ...
Why is chlorine used in wastewater treatment?
Wastewater treatment plants can dump chlorine into the wastewater to kill harmful microorganisms like bacteria and viruses.
What is a bag filter?
Bag filters: Bag filters are ideal for wastewater treatment plants that need to reduce contaminants to a specific micron rating. They can be made of felt to serve as depth media or made from mesh to serve as surface media. Bag filters and housings come in various shapes and sizes, including single and multi-bag filters and plastic and metal housings, so they are useful across a range of treatment plants and equipment.
How does tertiary treatment work?
Tertiary wastewater treatment often works by using a combination of physical and chemical processes to remove harmful microbiological contaminants from wastewater. The process usually involves filtration followed by additional disinfecting treatment. In some cases, tertiary treatment may also use other specialized treatments like lagoon storage, biological nutrient removal, and nitrogen and phosphorus removal.
What is secondary treatment?
Secondary treatment applies additional biological processes like aeration and activated sludge treatment to break down dissolved and suspended biosolids using good bacteria. Tertiary treatment adds a third, more advanced and rigorous level of treatment.
What is the main tertiary treatment process?
The main tertiary treatment process is then filtration, using either a sand bed or a membrane process, usually microfiltration, possibly followed by ultrafiltration. There may also be too high a content of nitrogen and phosphorus, and this will require additional biological processes, with some more sludge to be separated.
What is tertiary treatment?
Tertiary treatment includes the removal of the remaining inorganic compounds (phosphate, sulfate, ammonium) and other refractory organic compounds by one or more physical separation methods, such as carbon adsorption, deep-bed filtr ation, and in some cases, membrane-based techniques, such as reverse osmosis or electrodialysis.
What is the most used filtration material in wastewater treatment?
Sand, activated carbon, and zeolite are the most employed filtering materials in wastewater tertiary treatment. Sand filtration is a conventional wastewater treatment process characterized by its simplicity, low energy inputs, and easy maintenance. In this system, chemical reagents are not required, resulting in lower costs in comparison with other methods. In addition, the use of sand as wastewater filtering material has shown to be effective as tertiary treatment stage achieving high turbidity removal rates. Its use in combination with activated carbon is an effective alternative to the conventional method [20].
How are dissolved organic compounds separated?
The dissolved organic substances are separated by precipitation and subsequent filtration or clarification. The chemicals that are used are usually aluminum (Al) salts, ferric (Fe 3+) salts, and lime (CaO). The chemical treatment gives a further reduction of some recalcitrant compounds such as high-molecular degradation products from lignin. A chemical floc (precipitation of organic and inorganic matter) is formed, and this floc is then removed by sedimentation or flotation.
What is suspended solid removal?
Suspended solids removal in tertiary treatment implies the removal of those materials that have been carried over from a secondary clarification process. It is also employed as a pretreatment method prior to physical chemical treatment processes. Influent suspended solids concentration must be less than about 100 mg/liter or backwashing requirements become excessive. Finely dispensed suspended solids may require the addition of coagulant prior to filtration. Several means for removal of suspended solids have been proposed and tested. These include the use of diatomaceous earth filtration, pressure filtration, chemical clarification, sand filtration with conventional units and multimedia, ultrafiltration, and the moving-bed filter. With the exception of the chemical clarification processes, these methods all involve the physical straining of the finely divided solids that are removed.
What is chemical precipitation?
Chemical precipitation is a very common and well-known technology, especially for phosphorous removal in municipal wastewater treatment. It involves the addition of metal salts of aluminum, iron, or calcium to alter the physical state of dissolved solids and facilitate their removal by sedimentation.
What is used to reduce solids?
If the solids need to be reduced, sand filters or other clarifiers may be used. The collected materials are then usually bulked with the other sludges on site for further treatment and disposal.
What is tertiary wastewater treatment?
Tertiary treatment ensures that the water is safe for release into water bodies or for irrigation.
What is tertiary treatment?
Tertiary wastewater treatment, also known as advanced wastewater treatment, is the third step of wastewater treatment. After secondary treatment, tertiary treatment of effluent entails several extra procedures to minimise organics, turbidity, nitrogen, phosphorus, metals, and pathogens. Tertiary treatment of wastewater makes it ready for reuse. Some examples of reuse include:
What is sandbed filtration?
The standard method of filtration consists of sandbeds with graded sand placed on a supporting medium with an underdrain to collect the filtered effluent. Solids will build up and eventually block the holes as wastewater containing solids passes through this type of filter. This results in excessive head loss and/or poor effluent quality. As a result, sand filtration demands some provisions for the removal of the accumulated material. Backwashing the sand, or reversing the flow with air scour, helps to keep the sand in suspension while washing away the lighter material.
How does reverse osmosis produce demineralized water?
Reverse Osmosis produces demineralized water by forcing water through semipermeable membranes at high pressure. We apply a pressure greater than the osmotic pressure across a membrane separating a concentrated solution and dilute phase in this process. This forces the solvent or water to move towards the dilute phase.
What is the process of removing solutes from a solution?
Electrodialysis is another popular tertiary wastewater treatment method that employs the removal of the solute from the solution instead of removing the solvent. This process uses selectively permeable membranes and an electric potential difference to separate ions from a solution. The electric power required depends on the number of ions removed from the water.
What are the different types of filtration?
The most common types of filtration include diatomaceous earth filtration, pressure filtration, sand filtration with standard and multimedia units, ultrafiltration, and the moving-bed filter. All these processes involve the physical straining of the finely separated particles.
What is reclaimed water used for?
Reclaimed water finds use in cooling systems, boiler feed, process water, and other industrial applications.
