Given restricted stock is routinely granted as a form of employee compensation, you will usually see it reported on your W-2. Typically, employees withhold taxes on behalf of their employees, which will go against what you owe when doing your taxes.
What is the tax treatment for the employer when granted restricted stock?
Employees are taxed at ordinary rates on the full market value of the shares on the date the restricted stock vests. What is the tax treatment for the employer when restricted stock is granted to employees? The deduction equals the ordinary income recognized by the employee and the timing is based on whether or not Sec. 83(b) is elected.
What do you need to know about restricted stock awards?
Restricted stock awards and taxes: What employees and employers should know. The employee adjusts his or her original basis in the stock by the income amount. The employer may claim a deduction on the date the restriction lapses for the amount included in the employee’s income.
What is the difference between restricted stock&stock options?
Stock options can pay off if the stock price rises, but if it's steady or drops, they lose their value. Restricted stocks are free to the employees, so long as they stay at the company for the vesting period. Even if the share price drops, the value of the stock can be collected free of charge by an employee.
How are restricted stock and RSUs taxed?
Restricted stock and RSUs are taxed differently than other kinds of stock options, such as statutory or non-statutory employee stock purchase plans (ESPPs). Those plans generally have tax consequences at the date of exercise or sale, whereas restricted stock usually becomes taxable upon the completion of the vesting schedule.

What is the tax treatment for the employer when restricted stock is granted to employees multiple choice question?
The market value of the stock is taxed at the lower capital gains rate on the grant date. What is the tax treatment for the employer when restricted stock is granted to employees? The deduction equals the ordinary income recognized by the employee and the timing is based on whether or not Sec.
How is restricted stock treated for purposes of taxes?
Taxation. With RSUs, you are taxed when the shares are delivered, which is almost always at vesting. Your taxable income is the market value of the shares at vesting. You have compensation income subject to federal and employment tax (Social Security and Medicare) and any state and local tax.
What is the tax treatment of incentive stock options for employers?
Your employer is not required to withhold income tax when you exercise an Incentive Stock Option since there is no tax due (under the regular tax system) until you sell the stock.
Do employees have to pay for restricted stock?
Both are a type of employee equity compensation, but RSUs are given to the employee free of charge and only have financial value once vested. Stock options give the employee the right to buy company stock at a set price called the strike price; they are only valuable when the market price is higher than the set price.
When an employer compensates an employee with restricted stock when is the compensation taxable?
Upon vesting, the value of the restricted stock is taxed as compensation to the employee, and is subject to income tax withholding and applicable payroll taxes. The employer receives a corresponding deduction in its tax year which includes Dec. 31 of the year in which the employee recognizes the income.
How are RSUs taxed private company?
Payment of RSU Taxes Federal income tax: 22% (37% once your supplemental wages exceed $1,000,000) California income tax: 10.23%
Are incentive stock options tax deductible?
The value of incentive stock options is included in minimum taxable income for the alternative minimum tax in the year of exercise; consequently, some taxpayers are liable for taxes on “phantom” gains from the exercise of incentive stock options.
How is RSU tax calculated?
To summarize:RSU tax at vesting date is: The # of shares vesting x price of shares = Income taxed in the current year.If held beyond the vesting date, the RSU tax when shares are sold is: (Sales price – price at vesting) x # of shares = Capital gain (or loss)
What is the typical tax treatment of stock options in an acquisition?
If you've got stock options available that you haven't exercised yet, the sale of those in an all-cash acquisition will be counted and taxed as ordinary income.
How are RSUs reported on W-2?
The value of RSUs is typically recorded in Box 14 of the W-2, which is labeled "Other." Box 14 doesn't have a standard list of codes, thus allowing employers to enter any description they like. You might see the value of your vested stock followed by "RSU."
How do I avoid paying taxes on RSU?
The first way to avoid taxes on RSUs is to put additional money into your 401(k). The maximum contribution you can make for 2021 is $19,500 if you're under age 50. If you're over age 50, you can contribute an additional $6,000.
Do you pay capital gains tax on RSU?
You will also pay capital gains tax when you sell your RSU shares. After vesting, your RSU shares become yours. If you decide to sell your RSU shares, and the selling price is higher than the fair market value of your stocks, you will be liable for capital gains tax.
What is restricted stock?
Restricted stock is, by definition, a stock that has been granted to an executive that is nontransferable and subject to forfeiture under certain conditions, such as termination of employment or failure to meet either corporate or personal performance benchmarks.
What are the advantages of stock compensation?
This type of compensation has two advantages: It reduces the amount of cash that employers must dole out, and also serves as an incentive for employee productivity. There are many types of stock compensation, and each has its own set of rules and regulations.
What is Section 83 B?
Section 83 (b) Election. Shareholders of restricted stock are allowed to report the fair market value of their shares as ordinary income on the date that they are granted, instead of when they become vested if they so desire. 2 The capital gains treatment still applies, but it begins at the time of grant.
What is the rule for insider trading?
Although there are some exceptions, most-restricted stock is granted to executives who are considered to have "insider" knowledge of a corporation, thus making it subject to the insider trading regulations under SEC Rule 144. 1 Failure to adhere to these regulations can also result in forfeiture.
How much does Sam have to report in vesting?
Sam will have to report a whopping $900,000 of the stock balance as ordinary income in the year of vesting, while Alex reports nothing unless the shares are sold, which would then be eligible for capital gains treatment.
Can you deliver stock until vesting and forfeiture requirements have been satisfied?
Therefore, the shares of stock cannot be delivered until vesting and forfeiture requirements have been satisfied and release is granted. Some RSU plans allow the employee to decide within certain limits exactly when to receive the shares, which can assist in tax planning.
Is there a forfeiture risk in Section 83 B?
Unfortunately, there is a substantial risk of forfeiture associated with the Section 83 (b) election that goes above and beyond the standard forfeiture risks inherent in all restricted stock plans.
Why do employers issue restricted stock units?
Some employers choose to issue restricted stock units (RSUs) to employees rather than restricted stock, because employees cannot make a Sec. 83 (b) election in connection with restricted stock units. RSUs are unfunded promises to pay cash or stock to the employee based on a vesting schedule. One RSU is typically equal in value to one share ...
Why are restricted stock awards used?
One of the reasons for the shift to restricted stock is the reduced charge against income provided by restricted stock awards as compared to stock option grants. Restricted stock is also less dilutive to the company’s stock than options, because value to the employee can be achieved with fewer shares.
What is an RSU in a company?
RSUs are unfunded promises to pay cash or stock to the employee based on a vesting schedule. One RSU is typically equal in value to one share of company stock. The company does not deliver the cash or shares of stock until the vesting and forfeiture requirements have been satisfied.
Why is the Sec 83 B election invalid?
83 (b) election was invalid because the company held the shares in escrow and they were not legally transferred to him.
Why is restricted stock less dilutive than options?
Restricted stock is also less dilutive to the company’s stock than options, because value to the employee can be achieved with fewer shares. Executive compensation practices came under increased congressional scrutiny when abuses at corporations such as Enron became public.
What is a capital loss deduction?
1.83-2 (a) does permit a capital loss deduction for the excess paid for forfeited stock above any amount realized upon the forfeiture, including any amount of the purchase price restored by the employer to the employee. Regs. Sec. 1.83-2 (a) also warns that a sale or other disposition of the property ...
Do CPAs have to be familiar with restricted stock awards?
With the increased popularity of restricted stock, CPA tax practitioners must be familiar with the rules governing taxation of restricted stock awards when advising clients who have been or may be offered restricted stock awards, as well as when advising corporations that make the awards.
What is restricted stock?
Restricted stock awards are similar to stock options; employers use both to compensate employees by offering them shares of stock in the company. Restricted stock will go through different periods of “vesting” and will trigger different tax treatment along the way, including both ordinary income tax and capital gains taxes. Investors can collect dividends on restricted stocks. The dividends are also subject to different tax treatment that depends upon the length of time the stock has been owned.
How long does it take to pay taxes on restricted stock?
Owners of restricted stock awards can choose to be taxed under Section 83 (b), which lets them pay taxes within 30 days of receiving the award grant. By paying the taxes at the front end, employees can reap a benefit if the shares rise, as they won’t have to pay higher taxes later.
How do restricted stock awards work?
With restricted stock awards, employees owe income taxes on them immediately upon reaching the vesting period. Restricted stock awards are treated like income on which ordinary taxes are owed, depending upon the investor’s tax bracket. Taxes are owed on the value of the stock when they vest, not when the stocks are granted to the employee.
Do restricted stock awards owe income tax?
With restricted stock awards, employees owe income taxes on them immediately upon reaching the vesting period. Restricted stock awards are treated like income on which ordinary taxes are owed, depending upon the investor’s tax bracket. Taxes are owed on the value of the stock when they vest, not when the stocks are granted to the employee.
Do restricted stock options pay off?
Stock options can pay off if the stock price rises, but if it's steady or drops, they lose their value. Restricted stocks are free to the employees, so long as they stay at the company for the vesting period. Even if the share price drops, the value of the stock can be collected free of charge by an employee. ...
Can an employee collect stock options free of charge?
Even if the share price drops, the value of the stock can be collected free of charge by an employee. As a result, employers usually give fewer shares of restricted stock than they allow for stock options.
Can you collect dividends on restricted stocks?
Investors can collect dividends on restricted stocks. The dividends are also subject to different tax treatment that depends upon the length of time the stock has been owned.
What is restricted stock unit?
Restricted stock units (RSUs) are a way your employer can grant you company shares. RSUs are nearly always worth something, even if the stock price drops dramatically. RSUs must vest before you can receive the underlying shares. Job termination usually stops vesting.
Why is a grant restricted?
The grant is "restricted" because it is subject to a vesting schedule, which can be based on length of employment or on performance goals, and because it is governed by other limits on transfers or sales that your company can impose. You typically receive the shares after the vesting date.
How are RSUs taxed?
With RSUs, you are taxed when the shares are delivered, which is almost always at vesting. Your taxable income is the market value of the shares at vesting. You have compensation income subject to federal and employment tax (Social Security and Medicare) and any state and local tax. That income is subject to mandatory supplemental wage withholding. Withholding taxes, which for U.S. employees appear on Form W-2 along with the income, include the following: 1 federal income tax at the flat supplemental wage rate, unless your company uses your W-4 rate 2 Social Security (up to the yearly maximum) and Medicare 3 state and local taxes, when applicable
What is taxable income?
Your taxable income is the market value of the shares at vesting. You have compensation income subject to federal and employment tax (Social Security and Medicare) and any state and local tax. That income is subject to mandatory supplemental wage withholding. Withholding taxes, which for U.S.
What taxes are included in W-2?
Withholding taxes, which for U.S. employees appear on Form W-2 along with the income, include the following: federal income tax at the flat supplemental wage rate, unless your company uses your W-4 rate. Social Security (up to the yearly maximum) and Medicare. state and local taxes, when applicable.
How long does a vesting schedule last?
Example: You are granted 5,000 RSUs. Your graded vesting schedule spans four years, and 25% of the grant vests each year.
What is restricted stock?
As the use of 'restricted' entails, any restricted stock has certain restrictions on how the employee and future owner of this stock may use it. Generally speaking, an employee of a company is required to hold onto this restricted stock for a specific time.
What is non qualified stock option?
Non-qualified stock options are one type of stock option that doesn't feature any favorable tax treatment when dealt with under the US Internal Revenue Code. As a result of this, the use of the word, 'non-qualified' applies to the tax treatment of these stocks because it isn't eligible for special tax treatment or any other favorable considerations.
What is incentive stock option?
Incentive stock options, or ISOs, are designed in a way that qualifies these stock options for special tax treatment when placed under the US Internal Revenue Code. In addition to this, these ISOs aren't subjected to Medicare, Social Security, or withholding taxes. Nonetheless, to qualify for these taxation treatments, these stock options are required to meet rigid criteria under the US tax code. In addition to this, the mechanisms making up incentive stock options detail that these can only be granted to employees. Such stock options can't be released to contractors or consultants, which is unlike NQSOs.
Why are stock grants important?
Stock grants are designed with the benefit of being equitable property. Due to this, these stock grants have some intrinsic value. When the stock market is classified as being volatile, stock options are known to become less valuable than a company's employee cost. This makes stock options seemingly worthless. With that being said, stock grants are equipped to constantly remain at some value, as the employees of a business haven't outright purchased these stocks.
What is net after tax cost to employees?
The net after-tax cost to employees is zero and the employer receives a tax deduction for the cost of the benefit. d.The employees are NOT taxed on the benefit until it is used/received and the employer receives a tax deduction for the cost of providing the benefit.
When does an employer have to deduct wages?
When the employer and the employee are related, the employer must deduct wages expense in the same year the employee reports it as gross income. Employers must deduct the compensation the same year that the employees include the amounts in gross income regardless of the accounting method.
Do you have to pay for stock after vesting date?
Employees must use cash to purchase the employer's stock once the vesting date is reached. The employee is not required to pay for the stock but rather is given the shares on the grant date. The employee may sell the stock immediately after the vesting date or retain it, but there is NO required holding period.
Can you exercise options if the strike price is below the strike price?
Employees may choose NOT to exercise their options if the market value of the shares is below the strike price. Employees may exercise their options by paying the strike price to the employer anytime between the vesting and expiration dates.
Is stock market value taxed on grant date?
The market value of the stock is taxed as ordinary income on the grant date, providing a tax advantage if the value increases after that date. d. If employment is terminated before the vesting date, the employee can NOT recoup the tax that was paid on the grant date or receive the stock.
What is restricted stock unit?
Restricted Stock Units (RSUs) ESPPs and stock options can, when exercised, have a diluting effect on a company's stock. One way that a company can prevent this is through a restricted stock unit plan.
What is a non qualified stock option?
Non-qualified stock options (NSOs) may be offered to only a few employees, who pay tax on the difference between the stock price offered in the option and the stock's fair market value.
What is vesting in RSU?
In an RSU plan, a grant made to an employee is valued in terms of company stock, but stock isn't issued at the time of the grant. Only after the employee completes the terms of vesting are shares or a cash equivalent to shares awarded. Vesting usually takes a set time period, but it may also be based on performance targets.
What is an ESPP plan?
Employee Stock Purchase Plans (ESPPs) Employee Stock Purchase Plans are similar to stock options, particularly in the way they are taxed, with holding periods usually applying to non-qualified plans. Some features of a typical ESPP include: • stock may be discounted up to 15% of the fair market price. • stock may be purchased through payroll ...
Is stock option a fringe benefit?
Holding stock or stock options in an employer's business can be a lucrative fringe benefit, one that encourages employee participation in the company's success. Employee stock ownership plans also include some tax breaks for both the company and participating workers, particularly with plans intended to augment other retirement savings programs.
Is stock ownership deductible for employer?
Employers have tax incentives to provide employee stock ownership plans. Employer contributions are deductible, up to 25% of the payroll covered by stock ownership plans. Dividends paid to employee-owned stock are also deductible, as long as the dividends are what the Internal Revenue Service considers reasonable.
What is restricted stock award?
Restricted stock awards. RSAs are shares of company stock that employers transfer to employees, usually at no cost, subject to a vesting schedule. When the stock vests, the fair market value (FMV) of the shares on that date is deductible by the employer and constitutes taxable W - 2 wages to the employee.
What is the taxable event on exercise of NQSO?
If the taxable event occurs on exercise of the NQSO, the employer is entitled to an ordinary compensation deduction equal to the amount of ordinary income recognized by the employee on the spread between the FMV of the stock on the exercise date and the option exercise price.
What is a disqualifying disposition?
Upon a disqualifying disposition, the employer is entitled to a tax deduction equal to the taxable compensation reported on the employee's Form W - 2 (in fact, the deduction is contingent upon reporting the income on Form W - 2 ).
When is Sec 409A avoided?
Application of Sec. 409A is avoided when the exercise price is no less than the stock's FMV on the grant date. Because most compensatory NQSOs do not have a readily ascertainable FMV on the grant date, they are not considered "property" on the date of grant under Sec. 83 and are not eligible for an 83 (b) election.
How long can you defer taxes on equity compensation?
83 (i), enacted as part of the TCJA, allows employees of certain privately held companies to elect to defer the payment of income taxes on certain equity compensation for up to five years. The amount of tax owed by the employee is calculated on the taxable event and compensation amount as described above, with only the remittance of the tax being delayed by the Sec. 83 (i) election. The delayed payment by the employee in turn delays the employer's tax deduction to the year in which the employee's tax is paid. Plans of qualifying employers are not automatically subject to these deferral rules.
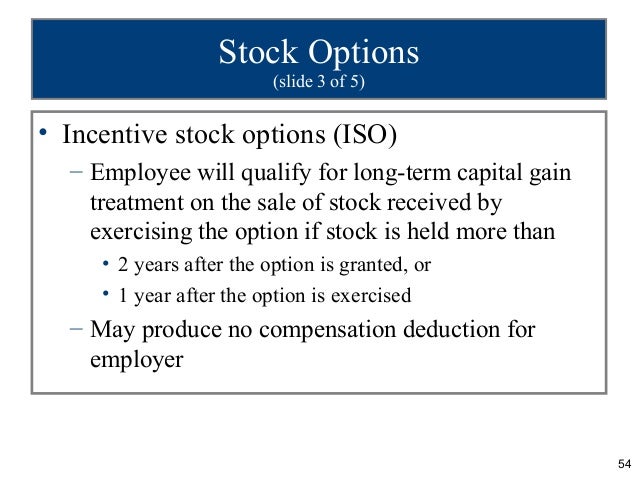
How long do you have to dispose of ISO stock?
The employee must not dispose of the ISO shares sooner than two years after the grant date and one year after the exercise date. If all of the ISO requirements are met, the employer would never get a tax deduction for the ISO stock compensation.
How can employers attract and retain employees?
Employers can attract or retain employees by compensating them with employer stock. There are a few different kinds of compensatory stock - based awards to consider, and each has advantages and disadvantages.
