Therapy
Treating carbon monoxide poisoning
- Standard oxygen therapy. Standard oxygen therapy in hospital will be needed if you have been exposed to a high level of carbon monoxide, or you have symptoms that suggest exposure.
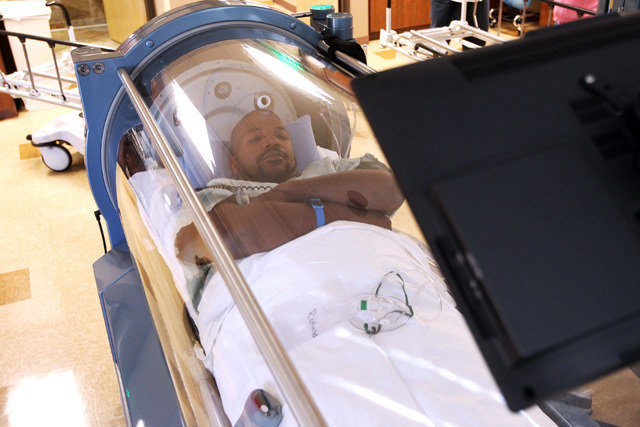
- Hyperbaric oxygen therapy. ...
- Recovery. ...
Self-care
The long term effects of breathing in carbon monoxide can affect:
- memory;
- brain function;
- behaviour;
- cognition.
How do you treat carbon monoxide poisoning?
Carbon monoxide poisoning occurs when carbon monoxide builds up in your bloodstream. When too much carbon monoxide is in the air, your body replaces the oxygen in your red blood cells with carbon monoxide. This can lead to serious tissue damage, or even death. Carbon monoxide is a colorless, odorless, tasteless gas produced by burning gasoline ...
What are the long term effects of carbon monoxide poisoning?
The primary treatment given for Carbon Monoxide Poisoning includes: Removing the source from which the patient got affected to begin with. The patient is then put on 100% oxygen through mask along with supportive measures and close monitoring of the functioning of all the organs, especially the brain (4).
How can you get CO2 poisoning?
How does carbon monoxide poisoning is treated?
What to do if you have carbon monoxide poisoning?
How to get carbon monoxide out of your blood?
How to treat a syphilis?
What is hyperbaric oxygen?
Why is oxygen therapy recommended for pregnant women?
What are the signs of carbon monoxide exposure?
How to treat a headache in the hospital?
See more
About this website

What is the standard protocol for a patient who comes to the hospital with co2 poisoning?
If you or someone you're with develops signs or symptoms of carbon monoxide poisoning — headache, dizziness, nausea, shortness of breath, weakness, confusion — get into fresh air immediately and call 911 or emergency medical help. Hospital staff will need critical information as soon as you arrive.
How do hospitals treat carbon monoxide poisoning?
All patients with symptomatic carbon monoxide poisoning should be treated with 100% oxygen as soon as possible. In severe cases of fire fume intoxication, combined poisoning with CO and cyanides should be considered.
What is the gold standard in treating carbon monoxide poisoning?
The gold standard treatment for severe CO poisoning is hyperbaric oxygen therapy. This markedly raises the arterial oxygen level, and in COPD patients prone to CO2 retention would clearly cause significant elevation of pCO2.
What is the initial treatment for carbon monoxide poisoning?
We recommend initial treatment with 100 percent normobaric oxygen for all suspected victims of CO poisoning, regardless of pulse oximetry or arterial PO2 (Grade 1B).
Which of the following is an appropriate response to carbon monoxide poisoning?
Which of the following is an appropriate response to carbon monoxide (CO) poisoning? Hyperbaric oxygen chamber to increase PO2 and clear CO from the body.
What is the role of the clinical laboratory in the proper diagnosis of carbon monoxide?
Laboratory Studies. The clinical diagnosis of acute carbon monoxide (CO) poisoning should be confirmed by demonstrating an elevated level of carboxyhemoglobin (HbCO). Either arterial or venous blood can be used for testing. Analysis of HbCO requires direct spectrophotometric measurement in specific blood gas analyzers.
Why is a hyperbaric chamber used to treat CO poisoning?
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy is the primary treatment for DCS. It immediately reduces the amount of bubbles in the bloodstream, fills the tissues with oxygen, and reduces dangerous swelling. In most instances, it's critical to get treatment as soon as possible, because the symptoms of DCS can be life-threatening.
What is a hyperbaric chamber used for?
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT) is well known for treating scuba and deep-sea divers affected by the rapid change in pressure around them. But did you know that HBOT is also used to treat a variety of other health problems, including carbon monoxide poisoning and diabetic foot ulcers?
How does the administration of 100 percent oxygen save a patient from carbon monoxide poisoning?
Carbon monoxide has a higher affinity for hemoglobin than oxygen. This means that carbon monoxide will preferentially bind to hemoglobin over oxygen. Administration of 100 percent oxygen is an effective therapy because at that concentration, oxygen will displace the carbon monoxide from the hemoglobin.
How does oxygen help carbon monoxide poisoning?
Treatment Overview The purpose of oxygen therapy for the treatment of carbon monoxide poisoning is to reduce the amount of carbon monoxide in the blood and restore the oxygen level to normal as quickly as possible. For hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT), the affected person lies down on a stretcher.
Why is pulse oximetry normal in carbon monoxide poisoning?
Pulse oximetry is usually normal because the device is unable to distinguish between the color of carboxyhemoglobin and oxyhemoglobin. A specific test for carboxyhemoglobin saturation is needed (using a co-oximeter type of blood gas machine) is required. Delivery of 100% oxygen is the initial treatment of choice.
Epainassist - Useful Information for Better Health
Anti-Bot from Epainassist ...
First Aid Treatment for Carbon Monoxide Poisoning - WebMD
1. Get the Person to Fresh Air. Move the person away from carbon monoxide area. If the person is unconscious, check for injuries before moving. Turn off carbon monoxide source if you can do so safely.
Carbon monoxide poisoning - Symptoms and causes - Mayo Clinic
Causes. Carbon monoxide poisoning is caused by inhaling combustion fumes. When too much carbon monoxide is in the air you're breathing, your body replaces the oxygen in your red blood cells with carbon monoxide.
What are the symptoms of carbon monoxide poisoning?
The symptoms of carbon monoxide (CO) poisoning are nonspecific, ranging from dizziness and headache to unconsciousness and death. A German national guideline on the diagnosis and treatment of this condition is lacking at present.
What study did all patients with CO intoxication do?
Observational study, all patients with CO intoxication
How many patients with CO intoxication have raised cardiac biomarkers?
37% of patients with CO intoxication had raised cardiac biomarkers or ECG changes, in-hospital mortality was 5%,
What is CO in fire?
Carbon monoxide (CO) at low concentrations is an odorless and colorless gas with a molecular weight that is similar to that of air. It develops in incomplete combustion processes of substances containing carbon (e1). In addition to fires, defect gas boilers, or wood pellet storage facilities, the risk of poisoning as a result of smoking hookah has become a focus in recent years (1, e2). Relevant alerting key words and the use of portable CO meters are intended to raise awareness in rescue personnel.
How does carbon monoxide bind to oxygen?
Carbon monoxide diffuses rapidly through the alveolar membrane and binds with an affinity that is 230–300 times that of oxygen, preferably to the iron ion in heme. Conformation changes lead to a leftward shift in the position of the oxyhemoglobin dissociation curve, to reduced oxygen transport capacity, and to reduced oxygen release into the peripheral tissue (2). Within tissue, CO also binds to other heme-containing proteins, such as skeletal and myocardial myoglobin. Since elimination times in tissue and blood differ (e7), tissue injury can also develop with a delay.
Is CO poisoning a risk factor for heart disease?
Patients with pre-existing coronary heart disease are exposed to a greater risk for my ocardial infarction and arrhythmias (e18). A retrospective study including 230 patients with CO poisoning described in 37% of cases raised cardiac biomarkers or changes on the electrocardiogram (13). In the prospective study of the same collective, 32 out of these 85 patients with myocardial involvement died during the median follow-up period of 7.6 years, whereas in the group without myocardial involvement only 22 of 145 patients died (adjusted hazard ratio 2.1; 95% CI [1.2; 3.7]; P=0.009). Age at the time of intoxication was an independent predictor of long-term mortality (AHR 1.2 for every additional five years in age; 95% CI [1.1; 1.3]; P<0.001) (14). Additional retrospective cohort studies showed an association between CO poisoning and the occurrence of severe cardiovascular events (AHR 2.00; 95% CI [1.83; 2.18]; or AHR 1.83; 95% CI [1.43; 2.33]) (15, 16). In case of comorbidities (diabetes mellitus, hypertension, hyperlipoproteinemia), the risk increased by a factor of 14.7 (95% CI [10.9; 19.9]) (16). Table 1shows a summarized overview of the studies.
What tests are needed for carbon monoxide poisoning?
Other testing, such as a fingerstick blood sugar, alcohol and toxicology screen, head CT scan or lumbar puncture may be needed to exclude other causes of altered mental status when the diagnosis of carbon monoxide poisoning is inconclusive.
What is carbon monoxide?
Carbon monoxide (CO) is an odorless, colorless, poisonous gas that can cause sudden illness and death if present in sufficient concentration in the ambient air. When power outages occur during emergencies such as hurricanes or winter storms, the use of alternative sources of fuel or electricity for heating, cooling, ...
How to know if you have CO poisoning?
How to Recognize CO Poisoning: The symptoms and signs of carbon monoxide poisoning are variable and nonspecific. The most common symptoms of CO poisoning are headache, dizziness, weakness, nausea, vomiting, chest pain, and altered mental status.
What is CO poisoning?
The clinical presentation of CO poisoning is the result of its underlying systemic toxicity. Its effects are caused not only by impaired oxygen delivery but also by disrupting oxygen utilization and respiration at the cellular level, particularly in high-oxygen demand organs (i.e., heart and brain).
What is the best test for poisoning?
Chest radiography is recommended for seriously poisoned patients, especially those with loss of consciousness or cardiopulmonary signs and symptoms. Brain computed tomography or MRI is also recommended in these cases; these tests may show signs of cerebral infarction secondary to hypoxia or ischemia.
What is the most common technology used to test for COHGB?
The most common technology available in hospital laboratories for analyzing the blood is the multiple wavelength spectrophotometer , also known as a CO-oximeter. Venous or arterial blood may be used for testing.
Can carbon monoxide be produced by heme?
Note : carbon monoxide can be produced endogenously as a byproduct of heme metabolism. Patients with sickle cell disease can have an elevated COHgb level as a result of hemolytic anemia or hemolysis. An elevated COHgb level of 2% for non-smokers and >9% COHgb level for smokers strongly supports a diagnosis of CO poisoning.
How to treat carbon monoxide poisoning?
The basic treatment for carbon monoxide poisoning is to administer high-flow oxygen by non-rebreather mask—an oxygen mask with a plastic bag hanging off of it—for as long as it takes to replace the carbon monoxide attached to hemoglobin with oxygen. Half-life is a measurement of the time it takes to eliminate half of a substance in the body. The half-life of carbon monoxide without using oxygen is 320 minutes—more than five hours to reduce levels by half. 1 At that rate, it would take about a day for the carbon monoxide to be removed.
How to get carbon monoxide out of your body?
This can be done via one of several methods: continuous airway pressure (CPAP), an oxygen mask with a valve, or administration of oxygen through a reservoir mask at a rate of 15 liters per minute. This helps to force the CO out so it can be replaced with oxygen. 1
How long does it take for carbon monoxide to get out of your system?
Carbon monoxide poisoning is not something you can treat at home. It takes, at a minimum, 100% oxygen concentration for several hours to rid the bloodstream of carbon monoxide. 1
How does light reduce carbon monoxide?
If a process for getting the right color of light, one as close as possible to blood, is developed, it might provide a faster way to reduce carbon monoxide levels .
Does carbon monoxide poisoning cause brain damage?
Providing oxygen to reduce the levels of carbon monoxide in the bloodstream is just one part of carbon monoxide poisoning treatment. The damage done to the brain and heart because of a lack of oxygen in the blood during carbon monoxide poisoning requires treatment as well. Depending on the severity of the poisoning, patients could need support for brain and cardiac function. Some patients will need treatment for brain swelling, which could include medications and admission to the intensive care unit.
Does oxygen therapy help with carbon monoxide?
While there is clear evidence that hyperbaric oxygen therapy clears carbon monoxide from the blood faster, there is little evidence that patients are better off because of it. One meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials found mixed results when looking at the neurological outcomes of carbon monoxide poisoned patients who received hyperbaric oxygen therapy.
Can you treat carbon monoxide in a hyperbaric chamber?
Plus, if multiple patients are affected by carbon monoxide exposure, only one at a time can be treated in the hyperbaric chamber. While there is clear evidence that hyperbaric oxygen therapy clears carbon monoxide from the blood faster, there is little evidence that patients are better off because of it.
What is CO poisoning?
is a life-threatening condition caused by exposure to high levels of CO. CO is a poisonous gas that you cannot see, taste, or smell. Exposure happens when you breathe in CO. CO can build up in your body and replace oxygen in your blood. Your brain, organs, and tissues can be damaged from a lack of oxygen. CO poisoning can be mild or severe. Severe poisoning can cause permanent injury.
How to install a CO detector in your home?
Install a CO detector in every sleeping area in your home. Place it 5 feet above the floor and away from fireplaces or gas-burning equipment. Change the batteries twice each year.
What is carbon monoxide?
Carbon Monoxide is a gas product of incomplete hydrocarbon combustion. It has the capacity to bind with the circulating blood hemoglobin, producing carboxyhemoglobin which reduces the oxygen-carrying capacity of the blood. Its affinity to hemoglobin is 200-300 times than that of the oxygen-hemoglobin. Carbon Monoxide poisoning is ...
How many times does carbon monoxide have affinity to hemoglobin?
Its affinity to hemoglobin is 200-300 times than that of the oxygen-hemoglobin. Carbon Monoxide poisoning is a type of inhalation poisoning through overexposure to carbon monoxide. It may occur at home or in industrial places. It may be in the form of accidental inhalation or intentionally inflicted like that of suicide.
What to do if you have carbon monoxide poisoning?
If you're brought to an emergency room with suspected carbon monoxide poisoning, you may begin treatment immediately. To confirm your diagnosis, the doctor may test a sample of your blood for carbon monoxide.
How to get carbon monoxide out of your blood?
Spending time in a pressurized oxygen chamber. In many cases, hyperbaric oxygen therapy is recommended. This therapy involves breathing pure oxygen in a chamber in which the air pressure is about two to three times higher than normal. This speeds the replacement of carbon monoxide with oxygen in your blood.
How to treat a syphilis?
Once you're at the hospital, treatment may involve: 1 Breathing pure oxygen. In the emergency room, you may breathe pure oxygen through a mask placed over your nose and mouth. This helps oxygen reach your organs and tissues. If you can't breathe on your own, a machine (ventilator) may do the breathing for you. 2 Spending time in a pressurized oxygen chamber. In many cases, hyperbaric oxygen therapy is recommended. This therapy involves breathing pure oxygen in a chamber in which the air pressure is about two to three times higher than normal. This speeds the replacement of carbon monoxide with oxygen in your blood.#N#Hyperbaric oxygen therapy may be used in cases of severe carbon monoxide poisoning. It helps protect heart and brain tissue, which are particularly vulnerable to injury from carbon monoxide poisoning. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy may also be recommended for pregnant women because unborn babies are more susceptible to damage from carbon monoxide poisoning.
What is hyperbaric oxygen?
In an individual (monoplace) hyperbaric oxygen unit, treatment is administered while the affected person rests inside a clear plastic tube. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy can also be provided in a large room. In this case, a lightweight, clear hood is often used to deliver the oxygen.
Why is oxygen therapy recommended for pregnant women?
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy may also be recommended for pregnant women because unborn babies are more susceptible to damage from carbon monoxide poisoning.
What are the signs of carbon monoxide exposure?
Signs or symptoms, and when they started. Any mental impairment, including confusion and memory problems. Any loss of consciousness.
How to treat a headache in the hospital?
These include headache, dizziness, nausea, shortness of breath, weakness and confusion. Once you're at the hospital, treatment may involve: Breathing pure oxygen. In the emergency room, you may breathe pure oxygen through a mask placed over your nose and mouth. This helps oxygen reach your organs and tissues. ...