What is the standard measure of energy in radiation treatment? The radiation dose absorbed by a person (that is, the amount of energy deposited in human tissue by radiation) is measured using the conventional unit rad or the SI unit gray (Gy).
What is the unit for measuring radiation?
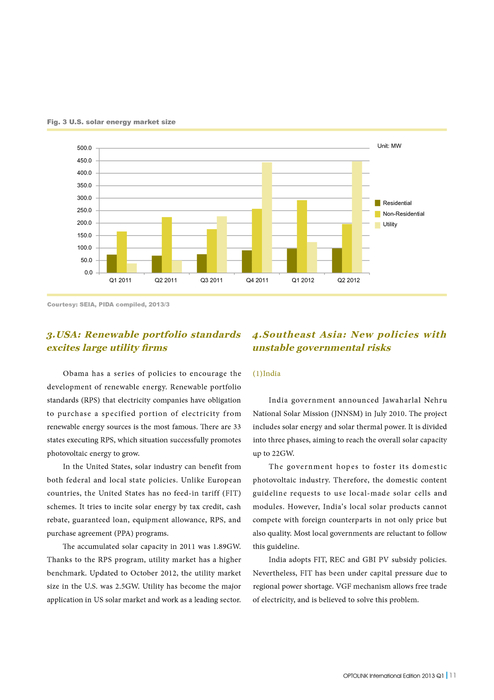
2 rows · Feb 10, 2020 · What is the standard measure of energy in radiation treatment? The radiation dose absorbed by a ...
What is a standard dose of radiation?
May 02, 2011 · Radiation therapy uses high-energy radiation to kill cancer cells by damaging their DNA. What is the word for unit of measurement of energy? A Joule … the standard unit of measure of Energy.
Why is it important to measure radiation therapy dose correctly?
Nov 16, 2015 · This preview shows page 4 - 6 out of 8 pages. What is the standard measure of energy in radiation treatment? Selected Answer: MeV. • Question 13 • 1.8 out of 1.8 points What is the name of the high-frequency sound waves in an imaging process that is used to diagnose patient illness? Selected Answer: ultrasound.
What are the units for exposure and absorbed dose?
For practical purposes, 1 R (exposure) = 1 rad (absorbed dose) = 1 rem or 1000 mrem (dose equivalent). Note that a measure given in Ci tells the radioactivity of a substance, while a measure in rem (or mrem) tells the amount of energy that a radioactive source deposits in living tissue.
What is the name of the high frequency sound waves in an imaging process that is used to diagnose?
Diagnostic ultrasound, also called sonography or diagnostic medical sonography, is an imaging method that uses high-frequency sound waves to produce images of structures within your body. The images can provide valuable information for diagnosing and treating a variety of diseases and conditions.Mar 17, 2020
What is the modifier used to identify the technical component of a radiologic procedure?
TCTC, technical component: This modifier covers the expense of the staff, machinery, equipment, and nonprofessional interpretation elements required to provide a radiological film or image/tracing. Oftentimes, a hospital, ASC, or office will use this modifier when submitting a claim for a radiological service performed.
What radiations occur when the electrons are used in radio therapy?
X-rays and Gamma (γ) rays are the two major forms of electromagnetic radiation used in radiotherapy. X-rays are produced when high speed electrons collide with a material of high atomic number like Tungsten-Molybdenum in the anode of a x-ray tube, while γ rays are produced by intra-nuclear disintegration.
What procedure is one that is performed independently of and not immediately related to another service?
When, however, such a procedure is performed independently of, and is not immediately related to, other services, it may be listed as a "separate procedure." Thus, when a procedure that is ordinarily a component of a larger procedure is performed alone for a specific purpose, it may be reported as a separate procedure.
When do you use modifier 77?
Modifier 77 is used to report a repeat procedure by another physician and is appended to the repeat procedure to: Report the same service provided by another physician. Indicate that a basic procedure or service had to be repeated.Feb 24, 2020
What is a 26 modifier used for?
Generally, Modifier 26 is appended to a procedure code to indicate that the service provided was the reading and interpreting of the results of a diagnostic and/or laboratory service.
How is the radiation in radiotherapy produced?
- In a machine called a 'linear accelerator', particles called 'electrons' are accelerated to high speed towards a metal target. When they hit the target they have to slow down very quickly and this forces them to release energy in the form of radiation.
Which wave is used in radiotherapy?
What is radiation therapy? Radiation therapy uses high-energy radiation to shrink tumors and kill cancer cells (1). X-rays, gamma rays, and charged particles are types of radiation used for cancer treatment.Apr 29, 2014
What are the basic principles of radiation therapy?
Radiation is an effective tool to treat cancer patients and in some cases cure the patient also. The most basic principle is to deliver maximum dose to tumor with minimum dose to surrounding normal structures thus achieving a higher cure rate with acceptable morbidity.
What is being measured while the Sleep testing is being conducted?
Sleep studies are tests that record specific body functions during sleep. Body functions measured during sleep may include heart rate, breathing rate and airflow, brain wave activity, eye movement, blood oxygen level and muscle movement.Oct 29, 2019
What is the largest section in CPT?
For instance, the Surgery section, which is by far the largest, is organized by what part of the human body the surgery would be performed on.
What are the 4 subsections of radiology?
Let's look at the makeup of the Radiology section. These fields and ranges can be informally arranged into four groups. Those groups are: Diagnostic, Ultrasound, Radiation Oncology, and Nuclear Medicine.
What is the unit of radiation absorbed?
The units for absorbed dose are the radiation absorbed dose ( rad) and gray ( Gy ). D ose equivalent (or effective dose) combines the amount of radiation absorbed and the medical effects of that type of radiation. For beta and gamma radiation, the dose equivalent is the same as the absorbed dose. By contrast, the dose equivalent is larger than ...
How many units are there for radioactivity?
There are four different but interrelated units for measuring radioactivity, exposure, absorbed dose, and dose equivalent. These can be remembered by the mnemonic R-E-A-D, as follows, with both common (British, e.g., Ci) and international (metric, e.g., Bq) units in use:
Is the dose equivalent the same as the absorbed dose?
For beta and gamma radiation, the dose equivalent is the same as the absorbed dose. By contrast, the dose equivalent is larger than the absorbed dose for alpha and neutron radiation, because these types of radiation are more damaging to the human body.
What is the unit used to measure the total amount of radiation that the patient is exposed to?
Gray (Gy) is the unit used to measure the total amount of radiation that the patient is exposed to. This can also be recorded as centigray (cGy), which is 0.01 of a single Gy unit.
How long does radiation therapy last?
Standard treatment with radiation therapy lasts for five to eight weeks, depending on the specific type of cancer being treated, and is at the discretion of the oncologist supervising the therapy.
Why is radiation therapy important?
By Yolanda Smith, B.Pharm. Reviewed by Benedette Cuffari, M.Sc. When radiation therapy is used to kill cancerous cells in the body , it is important to measure the dose correctly to avoid unnecessary damage to normal cells in the body. Radiation is not selective to tumor cells and therefore targets any cells that are in the process ...
Why is patient positioning important during radiation treatment?
The exact position of the patient during the radiation treatment is of utmost importance to ensure that the correct dose of radiation is emitted to the intended area of the body. It is common practice for skin to be marked to indicate where the treatment should be focused.
Why do you need a mold for radiation?
Additionally, areas of the body that do not contain tumor cells should be subjected to as little radiation as possible, often necessitating blocks or shields to protect other parts of the body .
Is radiation selective to tumor cells?
Radiation is not selective to tumor cells and therefore targets any cells that are in the process of replication when the therapy is applied. This thereby stresses the importance of administering the correct dose in order to ensure optimal efficiency with minimal side effects. Image Credit: Roman Zaiets / Shutterstock.com.

Standard Dose
Dose Fractioning
- The total radiation dose is usually divided into several fractions. For most patients who require radiation therapy, the total dose is broken up into daily doses of five times a week for a total period of five to eight weeks. Some cancers, however, require treatment more often than once per day. Each fraction will contain a small amount of radiation that gradually accumulates to form th…
Dose Frequency
- Hyperfractionated radiation divides the daily dose into two treatments each day, which means that the patient is subjected to smaller but more frequent doses of radiation over the same period of time. Conversely, hypofractionated radiation breaks the total dose into larger doses, often giving a dose less than once each day.
Treatment Length
- Standard treatment with radiation therapy lasts for five to eight weeks, depending on the specific type of cancer being treated, and is at the discretion of the oncologist supervising the therapy. Accelerated radiation refers to when the total dose is administered over a shorter period of time than usual. This involves more frequent doses, usually more often than once daily, to administer …
Patient Positioning During Treatment
- The exact position of the patient during the radiation treatment is of utmost importance to ensure that the correct dose of radiation is emitted to the intended area of the body. It is common practice for skin to be marked to indicate where the treatment should be focused. The patient should be instructed to remain in the same position without moving for the entire duration of ea…
References
Further Reading