What is an example of level of treatment?
Level of Treatment Example. The company would then break the total population into three equal sets. One set would be given a 10 mg pill, the second set would be given a 30 mg pill, and the third set would be given a 60 mg pill. In this fictional scenario, each drug strength is considered a level of treatment.
What is the significance level of an effect?
Significance level. By Jim Frost. The significance level, also denoted as alpha or α, is a measure of the strength of the evidence that must be present in your sample before you will reject the null hypothesis and conclude that the effect is statistically significant.
What is the significance level of a study?
Significance level. The significance level, also denoted as alpha or α, is a measure of the strength of the evidence that must be present in your sample before you will reject the null hypothesis and conclude that the effect is statistically significant.
What is an example of a factor level?
Example of factor levels Factor Additive Temperature Level A Low (100C) Level B Medium (150C) Level High (200C)
What is the factor in the study what are the levels of the factor?
In an experiment, the factor (also called an independent variable) is an explanatory variable manipulated by the experimenter. Each factor has two or more levels (i.e., different values of the factor). Combinations of factor levels are called treatments.
What is the difference between the factors and treatments of an experiment?
Factor – A variable under the control of the experimenter. Factors are explanatory variables. A factor has 2 or more levels. Treatment - The combination of experimental conditions applied to an experimental unit.
What is the difference between factor and level in an experiment?
A factor of an experiment is a controlled independent variable; a variable whose levels are set by the experimenter. A factor is a general type or category of treatments. Different treatments constitute different levels of a factor.
What are factors and levels?
What are factors and factor levels? Use factors during an experiment in order to determine their effect on the response variable. Factors can only assume a limited number of possible values, known as factor levels.
How do you identify factors and treatments?
0:004:33factors, levels, treatments - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipLet's talk about factors treatments. And levels. So first let's talk about a factor. So a factor isMoreLet's talk about factors treatments. And levels. So first let's talk about a factor. So a factor is an explanatory variable. For example of fertilizers. So it's the thing when you're doing an
What is the factor with levels and the response variable?
Factors are the variables that experimenters control during an experiment in order to determine their effect on the response variable. A factor can take on only a small number of values, which are known as factor levels.
Are levels the same as treatments?
Levels: values of a factor. Treatment: a particular combination of values for the factors. Experimental units: smallest unit to which a treatment is applied.
What is a treatment in a study?
In an experiment, the factor (also called an independent variable) is an explanatory variable manipulated by the experimenter. Each factor has two or more levels, i.e., different values of the factor. Combinations of factor levels are called treatments.
What does treatment mean in research?
The treatment is any independent variable manipulated by the experimenters, and its exact form depends on the type of research being performed. In a medical trial, it might be a new drug or therapy. In public policy studies, it could be a new social policy that some receive and not others.
What does treatment mean in statistics?
The term “statistical treatment” is a catch all term which means to apply any statistical method to your data. Treatments are divided into two groups: descriptive statistics, which summarize your data as a graph or summary statistic and inferential statistics, which make predictions and test hypotheses about your data.
What is the example of factor?
factor, in mathematics, a number or algebraic expression that divides another number or expression evenly—i.e., with no remainder. For example, 3 and 6 are factors of 12 because 12 ÷ 3 = 4 exactly and 12 ÷ 6 = 2 exactly. The other factors of 12 are 1, 2, 4, and 12.
What is this factor?
A factor is a number that divides another number, leaving no remainder. In other words, if multiplying two whole numbers gives us a product, then the numbers we are multiplying are factors of the product because they are divisible by the product. There are two methods of finding factors: multiplication and division.
1. What is the Importance of a Significant Level of Statistics?
The significant level statistics are usually represented by alpha or α, and is a measure of the potency of the verification which must be at hand i...
2. What is the Confidence Level?
Confidence level refers to the prospect of a factor that lies within a particular range of values, and which is denoted as c. Here, the confidence...
3. Mention some important points of the Level of Significance.
The level of significance is expressed by the Greek symbol α (alpha), and the level of significance can be defined as the values or the observation...
4. Explain Level of Significance?
The level of significance can be defined as the fixed probability of the wrong elimination of the null hypothesis, which is, in fact, true. The lev...
5. Where can I get study material on the P-value significance level?
Math is a subject of utmost importance. The online portal, Vedantu.com offers important questions along with answers and other very helpful study m...
What are factor levels? What are some examples?
Example of factor levels. For example, you are studying factors that could affect plastic strength during the manufacturing process. You decide to include Additive and Temperature in your experiment. The additive is a categorical variable.
Why do we use factors in an experiment?
Use factors during an experiment in order to determine their effect on the response variable. Factors can only assume a limited number of possible values, known as factor levels. Factors can be a categorical variable or based on a continuous variable but only use a few controlled values in the experiment.
What is the significance level?
The level of significance is the measurement of the statistical significance. It defines whether the null hypothesis is assumed to be accepted or rejected. It is expected to identify if the result is statistically significant for the null hypothesis to be false or rejected.
What does significance mean in statistics?
In Statistics, “significance” means “not by chance” or “probably true”. We can say that if a statistician declares that some result is “highly significant”, then he indicates by stating that it might be very probably true. It does not mean that the result is highly significant, but it suggests that it is highly probable.
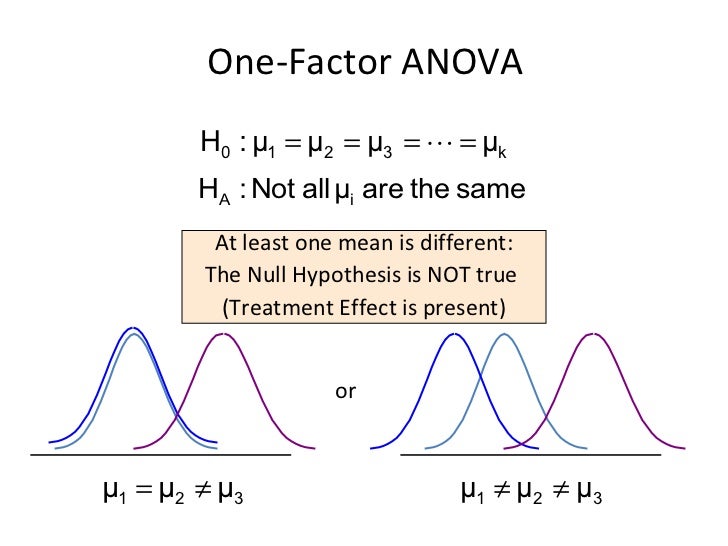
What is the level of significance of a null hypothesis?
The level of significance is defined as the fixed probability of wrong elimination of null hypothesis when in fact, it is true . The level of significance is stated to be the probability of type I error and is preset by the researcher with the outcomes of error. The level of significance is the measurement of the statistical significance. It defines whether the null hypothesis is assumed to be accepted or rejected. It is expected to identify if the result is statistically significant for the null hypothesis to be false or rejected.
What is statistical significance?
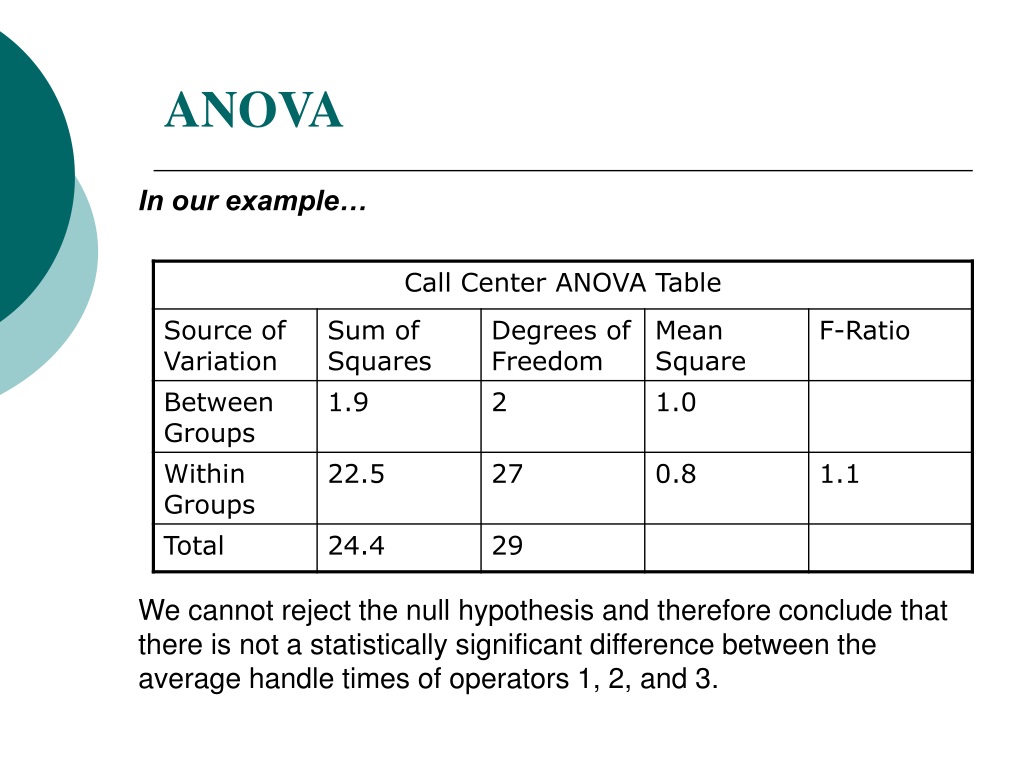
Statistics is a branch of Mathematics. It deals with gathering, presenting, analyzing, organizing and interpreting the data, which is usually numerical. It is applied to many industrial, scientific, social and economic areas. While a researcher performs research, a hypothesis has to be set, which is known as the null hypothesis. This hypothesis is required to be tested via pre-defined statistical examinations. This process is termed as statistical hypothesis testing. The level of significance or Statistical significance is an important terminology that is quite commonly used in Statistics. In this article, we are going to discuss the level of significance in detail.
What is the process of testing a hypothesis?
This hypothesis is required to be tested via pre-defined statistical examinations. This process is termed as statistical hypothesis testing. The level of significance or Statistical significance is an important terminology ...
Is a p-value less than 0.05 significant?
The p-value is said to be more significant if it is as low as possible. Also, the result would be highly significant if the p-value is very less. But, most generally, p-values smaller than 0.05 are known as significant, since getting a p-value less than 0.05 is quite a less practice.

What Is Statistical significance?
Level of Significance Definition
- Thelevel of significanceis defined as the fixed probability of wrong elimination of null hypothesis when in fact, it is true. The level of significance is stated to be the probability of type I error and is preset by the researcher with the outcomes of error. The level of significance is the measurement of the statistical significance. It defines w...
Level of Significance Symbol
- The level of significance is denoted by the Greek symbol α(alpha). Therefore, the level of significance is defined as follows: Significance Level = p (type I error) = α The values or the observations are less likely when they are farther than the mean. The results are written as “significant at x%”. Example: The value significant at 5% refers to p-valueis less than 0.05 or p < …
How to Find The Level of significance?
- To measure the level of statistical significance of the result, the investigator first needs to calculate the p-value. It defines the probability of identifying an effect which provides that the null hypothesis is true. When the p-value is less than the level of significance (α), the null hypothesis is rejected. If the p-value so observed is not less than the significance level α, then theoretically nul…