
Is melanoma in situ the most curable stage?
Treatment: Stage 0 melanoma is removed surgically, with minimal but clear margins. This is sometimes called an excision. Wide local excision, a minor surgery, usually cures local melanoma. Learn more about melanoma treatments here. Prognosis: Stage 0 melanoma, or melanoma in situ, is highly curable.
Is DCIS really cancer?
DCIS is considered a pre-cancer because sometimes it can become an invasive cancer. This means that over time, DCIS may spread out of the ducts into nearby tissue, and could metastasize. Currently, there’s no good way to predict which will become invasive cancer and which won’t. Therefore, almost all women with DCIS will be treated.
Why is DCIS not cancer?
DCIS is stage 0: It has not spread outside a breast duct (where virtually all breast cancer begins) into the surrounding breast tissue. For this reason, DCIS is often referred to as a precancer. If left untreated, some DCIS lesions go on to become invasive cancers, while others remain a harmless precancer and never leave the duct.
How long can you live with metastatic squamous cell carcinoma?
Once squamous cell carcinoma has spread beyond the skin, though, less than half of people live five years, even with aggressive treatment. There are many ways to treat squamous cell carcinoma that has not spread.
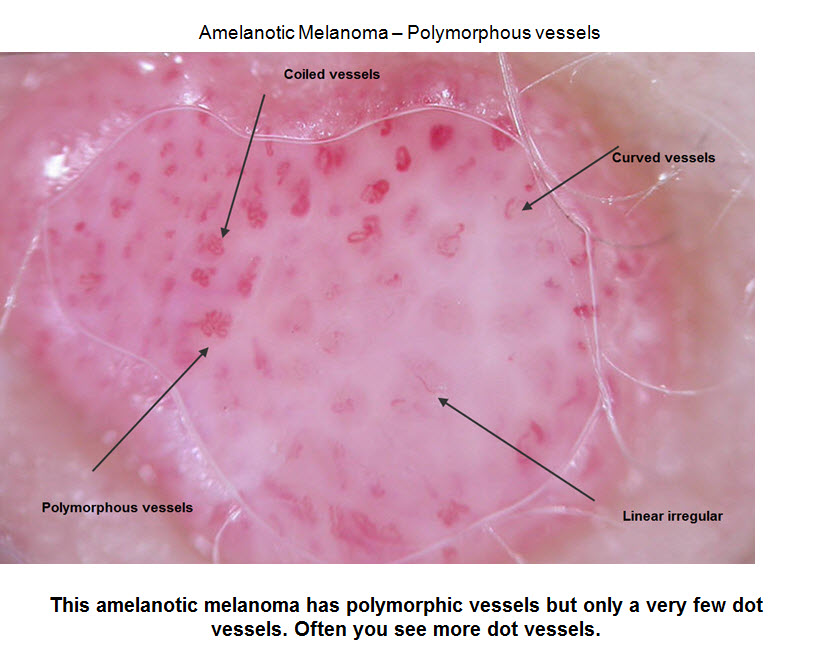
What is the treatment for carcinoma in situ?
TREATMENT APPROACH Patients with DCIS undergo local treatment with breast-conserving therapy (BCT) or mastectomy. BCT consists of lumpectomy (also called breast-conserving surgery, wide excision, or partial mastectomy) followed in most cases by adjuvant radiation.
Is carcinoma in situ curable?
About 1 in 5 new breast cancers will be ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS). Nearly all women with this early stage of breast cancer can be cured. DCIS is also called intraductal carcinoma or stage 0 breast cancer. DCIS is a non-invasive or pre-invasive breast cancer.
Is carcinoma in situ considered cancer?
In general, carcinoma in situ is the earliest form of cancer, and is considered stage 0. An example of carcinoma in situ is ductal carcinoma in situ, or DCIS, which is considered an early form of breast cancer and occurs when abnormal cells form a breast's milk duct.
What stage of cancer is carcinoma in situ?
Also called stage 0 disease. Carcinoma in situ (CIS) is a group of abnormal cells that are found only in the place where they first formed in the body (see left panel). These abnormal cells may become cancer and spread to nearby normal tissue (see right panel).
Can AIS go away?
The good news is that AIS is very treatable. The goal of treatment is to remove the abnormal cells before they turn into cancerous cells. This is done by surgically removing the cells or tumor. This type of surgery can often be done by laparoscopy.
Is chemotherapy needed for DCIS?
Chemotherapy. Chemotherapy is not needed for DCIS since the disease is noninvasive. Hormonal (endocrine) therapy. Hormonal (endocrine) therapy may be appropriate for those whose ductal carcinoma in situ is hormone receptor positive.
Do I need a mastectomy for DCIS?
Most women with DCIS or breast cancer can choose to have breast-sparing surgery, usually followed by radiation therapy. Most women with DCIS or breast cancer can choose to have a mastectomy. You have small breasts and a large area of DCIS or cancer. You have DCIS or cancer in more than one part of your breast.
What is the treatment for DCIS stage 0?
Surgery is the main treatment for DCIS. Most women are offered breast-conserving surgery. If there are several areas of DCIS in the breast, doctors may do a mastectomy to make sure that all of the cancer is removed.
What is difference between cancer and carcinoma?
Carcinoma is a type of cancer that starts in cells that make up the skin or the tissue lining organs, such as the liver or kidneys. Like other types of cancer, carcinomas are abnormal cells that divide without control. They are able to spread to other parts of the body, but don't always.
Is radiation necessary after lumpectomy for DCIS?
A study has found that for women diagnosed with DCIS considered to have a low risk of recurrence treated with lumpectomy without radiation, the risk of DCIS recurrence or developing invasive disease in the same breast increased through 12 years of follow-up and didn't level off.
How long can you wait for DCIS surgery?
In women with a clinical diagnosis of DCIS, greater delay to surgery is associated with lower OS. Although most women with DCIS undergo surgical extirpation within 2 months of diagnosis, longer time to surgery is associated with greater risk of finding invasion and should be limited.
How long does it take DCIS to become invasive?
It assumes that all breast carcinomas begin as DCIS and take 9 years to go from a single cell to an invasive lesion for the slowest growing lesions, 6 years for intermediate growing DCIS lesions, and 3 years for fast-growing DCIS lesions.
What are the factors that determine the treatment for carcinoma in situ?
Treatments for carcinoma in situ will depend on factors, such as: the location of the precancerous cells. the size and location of any benign tumor. individual risk factors, for example, a personal or family history of cancer. the age of the person. other health conditions. personal preferences.
What type of surgery is used to treat carcinoma in situ?
There are a number of surgical options available to treat carcinoma in situ. A doctor may recommend different types of surgery, such as:- open surgery, such as a mastectomy for breast cancer or a preventive hysterectomy for cervical cancer. laser surgery.
What is lobular carcinoma in situ?
Ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) and lobular carcinoma in situ (LCIS) happen when changes occur in breast cells. These conditions are not cancer. The cells are noninvasive, and they may not spread. However, precancerous cells may become invasive at a later date, so it is best to remove them.
What is the name of the cancer that is small, finger shaped?
The bladder. Papillary urothelial carcinoma is a type of bladder cancer that involves small, finger shaped growths. These often remain in situ, which means they do not spread to other areas. However, around 10–15% become invasive, or cancerous.
What is cancer in situ?
Carcinoma in situ refers to cancer in which abnormal cells have not spread beyond where they first formed. The words “in situ” mean “in its original place.”. These in situ cells are not malignant, or cancerous. However, they can sometime become cancerous and spread to other nearby locations. Doctors may also talk about precancerous cells.
How do you know if you have carcinoma in situ?
If a person has carcinoma in situ, they may not notice any symptoms, unless the changes affect the skin, the mouth, or other visible parts of the body. Skin: There may be changes in the color or texture of the skin and possibly the nails.
Where does squamous cell carcinoma in situ occur?
Squamous cell carcinoma in situ refers to changes in skin cells that could become cancerous. The changes are on the surface layer of the skin only. The cells most commonly appear where the skin has exposure to the sun, such as the face, ears, and neck.
What is the treatment for DCIS?
In most people, treatment options for DCIS include: Breast-conserving surgery (lumpectomy) and radiation therapy. Breast-removing surgery (mastectomy) In some cases, treatment options may include: Lumpectomy only.
What is DCIS on a mammogram?
DCIS is most often discovered during a mammogram used to screen for breast cancer. If your mammogram shows suspicious areas such as bright white specks (microcalcifications) that are in a cluster and have irregular shapes or sizes, your radiologist likely will recommend additional breast imaging. You may have a diagnostic mammogram, which takes ...
What is radiation therapy after lumpectomy?
Radiation therapy after lumpectomy reduces the chance that DCIS will come back (recur) or that it will progress to invasive cancer.
What is a calcification on a mammogram?
Calcifications are small calcium deposits in the breast that show up as white spots on a mammogram. Large, round or well-defined calcifications (shown left) are more likely to be noncancerous (benign). Tight clusters of tiny, irregularly shaped calcifications (shown right) may indicate cancer.
What is clinical trial?
Clinical trials are studying new strategies for managing DCIS, such as close monitoring rather than surgery after diagnosis. Whether you're eligible to participate in a clinical trial depends on your specific situation. Talk with your doctor about your options.
Can alternative medicine cure DCIS?
Alternative medicine. No alternative medicine treatments have been found to cure DCIS or to reduce the risk of being diagnosed with an invasive breast cancer. Instead, complementary and alternative medicine treatments may help you cope with your diagnosis and the side effects of your treatment, such as distress.
Can you have a mastectomy with DCIS?
Most women with DCIS are candidates for lumpectomy. However, mastectomy may be recommended if: You have a large area of DCIS.
How to reduce risk of breast cancer?
If you're worried about your risk of breast cancer, take steps to reduce your risk, such as: Exercise most days of the week. Aim for at least 30 minutes of exercise on most days of the week. If you haven't been active lately, ask your doctor whether it's OK, and start slowly. Maintain a healthy weight.
What is the best medicine for breast cancer?
Tamoxifen is one SERM approved for reducing the risk of breast cancer in premenopausal women and postmenopausal women. Raloxifene (Evista) is approved for postmenopausal women to reduce the risk of breast cancer and also to prevent and treat osteoporosis. Medications that stop the body from making estrogen after menopause.
What type of cancer is PLCIS?
For instance, surgery is often recommended for a specific type of LCIS called pleomorphic lobular carcinoma in situ (PLCIS). This type of LCIS is thought to carry a greater risk of breast cancer than is the more common classical type.
What type of biopsy is used for breast cancer?
Types of breast biopsy that may be used include: Core needle biopsy. A radiologist or surgeon uses a thin, hollow needle to remove several tiny tissue samples. Imaging techniques, such as ultrasound or MRI, are often used to help guide the needle used in a core needle biopsy. Surgical biopsy.
What to do if you have a lump in your breast?
If you have already had a breast abnormality evaluated by one doctor and are making an appointment for a second opinion, bring your original diagnostic images and biopsy results to your new appointment.
What to do if you have LCIS?
If you have LCIS, you might consider participating in a clinical trial exploring an emerging therapy for preventing breast cancer. Ask your doctor whether you might be a candidate for current clinical trials.
What is the procedure to remove LCIS?
Surgical biopsy. A surgeon may perform an operation to remove the suspicious cells for examination. The tissue removed during your biopsy is sent to a laboratory where doctors that specialize in analyzing blood and body tissues (pathologists) closely examine the cells to determine if you have LCIS.

Diagnosis
Treatment
- Treatment of DCIS has a high likelihood of success, in most instances removing the tumor and preventing any recurrence. In most people, treatment options for DCIS include: 1. Breast-conserving surgery (lumpectomy) and radiation therapy 2. Breast-removing surgery (mastectomy) In some cases, treatment options may include: 1. Lumpectomy only 2. Lumpec...
Clinical Trials
- Explore Mayo Clinic studiestesting new treatments, interventions and tests as a means to prevent, detect, treat or manage this condition.
Alternative Medicine
- No alternative medicine treatments have been found to cure DCIS or to reduce the risk of being diagnosed with an invasive breast cancer. Instead, complementary and alternative medicine treatments may help you cope with your diagnosis and the side effects of your treatment, such as distress. If you're distressed, you may have difficulty sleeping and find yourself constantly thinki…
Coping and Support
- A diagnosis of DCIS can be overwhelming and frightening. To better cope with your diagnosis, it may be helpful to: 1. Learn enough about DCIS to make decisions about your care. Ask your doctor questions about your diagnosis and your pathology results. Use this information to research your treatment options. Look to reputable sources of information, such as the Nationa…
Preparing For Your Appointment
- Make an appointment with your doctor if you notice a lump or any other unusual changes in your breasts. If you have already had a breast abnormality evaluated by one doctor and are making an appointment for a second opinion, bring your original diagnostic mammogram images and biopsy results to your new appointment. These should include your mammography images, ultrasound …
Diagnosis
- Lobular carcinoma in situ (LCIS) may be present in one or both breasts, but it usually isn't visible on a mammogram. The condition is most often diagnosed as an incidental finding when you have a biopsy done to evaluate some other area of concern in your breast. Types of breast biopsy that may be used include: 1. Core needle biopsy.A radiologist or surgeon uses a thin, hollow needle t…
Treatment
- A number of factors, including your personal preferences, come into play when you decide whether to undergo treatment for lobular carcinoma in situ (LCIS). There are three main approaches to treatment: 1. Careful observation 2. Taking a medication to reduce cancer risk (preventive therapy) 3. Surgery
Clinical Trials
- Explore Mayo Clinic studiestesting new treatments, interventions and tests as a means to prevent, detect, treat or manage this condition.
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
- If you're worried about your risk of breast cancer, take steps to reduce your risk, such as: 1. Exercise most days of the week.Aim for at least 30 minutes of exercise on most days of the week. If you haven't been active lately, ask your doctor whether it's OK, and start slowly. 2. Maintain a healthy weight. If your current weight is healthy, work to maintain that weight. If you need to los…
Coping and Support
- Although LCISis not cancer, it can make you worry about your increased risk of a future breast cancer. Coping with your diagnosis means finding a long-term way to manage your fear and uncertainty. These suggestions may help you cope with a diagnosis of LCIS: 1. Learn enough about LCIS to make decisions about your care. Ask your doctor questions about your diagnosis …
Preparing For Your Appointment
- Make an appointment with your doctor if you notice a lump or any other unusual change in your breasts. If you have already had a breast abnormality evaluated by one doctor and are making an appointment for a second opinion, bring your original diagnostic images and biopsy results to your new appointment. These should include your mammography images, ultrasound CD and gl…