
What is normalizing treatment of a metal?
What Is The Purpose Of The Normalizing Heat Treatment For Steel The normalizing heat treatment helps remove impurities and improves toughness and ductility. Normalized steel has greater strength and hardness than annealed steel, and the process is more economical due to cooling directly with air.
What is steel normalizing and how does it work?
Apr 21, 2022 · What is normalizing Normalizing is a heat treatment that improves the toughness of steel. After heating the steel components to 30~50°C above the Ac3 temperature, hold them for a period of time and then release them for air cooling. 1. Character a. Cooling faster than annealing but slower than quenching. b.
What is the objective of normalizing heat treatment?
Oct 29, 2014 · Normalizing begins by heating the as-rolled plate up to 800-900°C, depending on chemical analysis, and holding the steel at this temperature for a set time ahead of being cooled in still air. The process refines the grain size, improves the mechanical properties and relieves internal stresses. Can all Grades of Steel be Normalized?
What are the different ways of heat treatment for metals?
Jan 24, 2019 · Normalizing is a heat treatment process that is used to make a metal more ductile and tough after it has been subjected to thermal or mechanical hardening processes. Normalizing involves heating a material to an elevated temperature and then allowing it to cool back to room temperature by exposing it to room temperature air after it is heated.

What is the purpose of normalizing steel?
Normalizing involves heating the steel to an elevated temperature, followed by slow cooling to room temperature. The heating and slow cooling changes the microstructure of the steel. This reduces the hardness of the steel and will increases its ductility.
What is the purpose of normalizing?
Purpose of Normalizing To remove structural irregularities or impurities and defects from the metal. To improve ductility that has been lost in some metal processing. To reduce the hardness that has been increased by mechanical or thermal hardening processes.May 2, 2021
What is the purpose of heat treatment of steel?
Heat treatment is a controlled process used to alter the microstructure of metals and alloys such as steel and aluminium to impart properties which benefit the working life of a component, for example increased surface hardness, temperature resistance, ductility and strength.
What is the purpose of normalizing heat treatment?
Normalizing heat treatment helps to remove impurities and improve ductility and toughness. During the normalizing process, material is heated to between 750-980 °C (1320-1796 °F).
What is normalized heat treatment?
Normalizing is a heat treatment process which is used to make metal, such as steel, more ductile and tough. Thermal and mechanical hardening processes decrease ductility and increase hardness of steel parts. Therefore, normalizing can reform the microstructure into more ductile structures.
What is steel normalizing?
Steel normalizing is a kind of heat treatment, so understanding heat treatment is the first step in understanding steel normalizing. From there, it isn't hard to understand what steel normalizing is, and why it's a common part of the steel industry.
How does normalization work?
The Basics of Normalization. Normalization removes impurities in steel and improves its strength and hardness. This happens by changing the size of the grain, making it more uniform throughout the piece of steel. The steel is first heated up to a specific temperature, then cooled by air.
What temperature does steel need to be heated?
Depending on the type of steel, normalizing temperatures usually range from 810 degrees Celsius to 930 degrees Celsius. The thickness of the metal determines how long a piece of metal is held at the "soaking temperature"—the temperature that transforms the microstructure.
What is carburizing steel?
Carburizing steel: Carburizing heat treatment is the introduction of carbon into the surface of the steel. Carburizing occurs when the steel is heated above the critical temperature in a carburizing furnace that contains more carbon than the steel contains.
What temperature does decarburization occur?
Decarburization occurs when the steel is heated above the critical temperature in an atmosphere that contains less carbon than the steel contains. Deep freezing steel: Deep freezing is cooling steel to approximately -100 degrees Fahrenheit, or lower, to complete the transformation of austenite to martensite. Cite this Article.
Why do we heat treat metals?
Metals are typically treated to improve their strength, hardness, toughness, ductility, and corrosion resistance. The different ways in which metals can undergo heat treatment include annealing, tempering, and normalizing.
What is heat treatment?
Heat treatment is a process in which metals are heated and cooled to change their structure. The changes to the metals' chemical and physical properties differ based on the temperatures that they are heated to and how much they're cooled down afterward. Heat treatment is used for a wide variety of metals.
What is Normalizing?
Giving the steel a uniform and fine-grained structure is the intended purpose of the normalization process. Normalizing is used to confirm a predictable microstructure and guarantee of the material’s mechanical properties.
What does the Process of Normalizing Steel Consist of?
Once the steel is cooled in its “As-Rolled” state the material may require further heat treatment to achieve the desired mechanical properties.
Can all Grades of Steel be Normalized?
In theory all grades of steel can undergo normalizing. However, some grades of steel must be normalized in the scope of the material specification, whilst other material specifications allow normalizing to be at the discretion of the manufacturer or the purchaser.
Will Normalizing Steel have an Impact on the Cost?
Normalizing is an additional process and as such will have an impact on the cost of steel. Actual cost would have to be confirmed with the manufacturer at the time of enquiry.
About Masteel UK Ltd
Masteel UK Ltd are a global steel supply and stockholding company, supplying the engineering, power generation, petrochemical, oil & gas and nuclear industries.
Why is heat treatment important?
It is important that the material used for any project possesses the correct mechanical properties for the specific application . Heat Treatment processes are often used to alter the mechanical properties of a metal, with one of the more common heat treatment processes being Normalizing.
What is normalizing metal?
What Is Normalizing? Normalizing is a heat treatment process that is used to make a metal more ductile and tough after it has been subjected to thermal or mechanical hardening processes. Normalizing involves heating a material to an elevated temperature and then allowing it to cool back to room temperature by exposing it to room temperature air ...
Why is normalizing important?
This is important because it makes the metal more formable, more machinable, and reduces residual stresses in the material that could lead to unexpected failure.
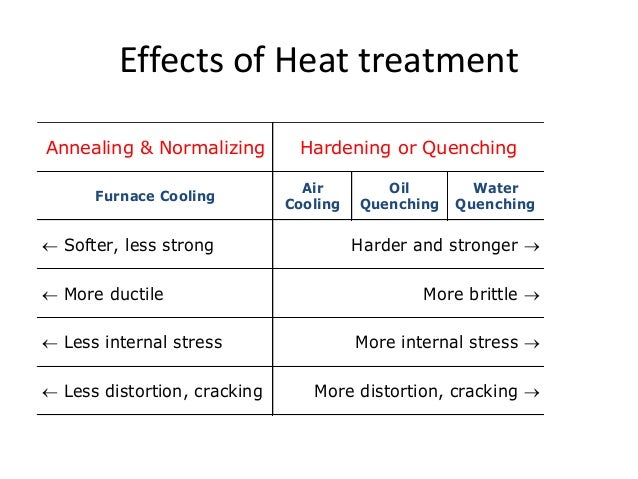
What is the difference between annealing and normalizing?
The main difference between annealing and normalizing is that annealing allows the material to cool at a controlled rate in a furnace. Normalizing allows the material to cool by placing it in a room temperature environment and exposing it to the air in that environment. This difference means normalizing has a faster cooler rate than annealing.
What are the stages of normalizing?
There are three main stages to a normalizing process. Recovery stage. Recrystallization stage. Grain growth stage. Recovery Stage. During the recovery stage, a furnace or other type of heating device is used to raise the material to a temperature where its internal stresses are relieved. Recrystallization Stage.
What is metal supermarket?
Metal Supermarkets is the world’s largest small-quantity metal supplier with over 90 brick-and-mortar stores across the US, Canada, and United Kingdom. We are metal experts and have been providing quality customer service and products since 1985.
How to normalize steel?
Steel normalizing is a heat treatment process performed after rolling, welding, or forging processes to refine the distorted grains in the microstructure. The normalizing process of steel involves the following steps: 1 Steel is heated to about 40-50 0 C (Refer to Fig. 1) above the upper critical temperature (A 3 or A cm ). 2 The alloy is then held at that temperature for around 10-20 minutes. 3 Cooling it in still or slightly agitated air to bring back to room temperature.
What is the purpose of ductility?
To improve ductility that has been lost in some metal processing. To reduce the hardness that has been increased by mechanical or thermal hardening processes. To increase the toughness of the metal. To relieve internal stresses.
What is steel normalizing?
Steel normalizing is a heat treatment process performed after rolling, welding, or forging processes to refine the distorted grains in the microstructure. The normalizing process of steel involves the following steps:
What is the carbon content of low carbon steel?
Low carbon steel contains carbon contain of 0.15% to 0.45%. Heat treatment on low carbon steel is to increase ductility, to improve toughness, strength, hardness and tensile strength and to relive stress developed in the material. It is neither externally brittle nor ductile due to its lower carbon content. It has lesser tensile strength and ...
How does heat treatment work?
The process that heat treatment is carried out first by heating the material and then cooling it in water, oil and brine water. The use of heat treatment is to soften or harden the material, to modify the size of the grain, to modify the structure of the material and relive the stress setup in the material. Read More Info Regarding This Post : ...
What is normalizing ferrous?
Normalizing is technique used to provide uniformity in grain size and composition throughout alloy. The term is frequently used for ferrous alloys that have been austenitized and then cooled in open air.
What is the process of absorbing carbon?
Carburizing is the heat treatment process in which iron or steel absorbs carbon liberated when metal is heated in the presence of a carbon bearing material, such as charcoal or carbon monoxide, with the intent of making the material harder.
Normalizing Heat Treatment & Process
Carbon Steel Normalizing
- Carbon steel contains carbon in the range of 0.12 to 2%. As the percentage of carbon content increases, the steel becomes harder, tougher and less ductile. Low carbon steels usually do not need normalizing. However, they can be normalized on the requirement. In normalizing heat treatment of carbon steel, it is heated to a temperature of 55 °C (131 °F) above the austenitic te…
Microstructure in Normalizing
- The thickness of carbon steel can have a significant effect on the cooling rate and thus the resulting microstructure. The thicker pieces cool down slower and become more ductile after normalizing than thinner pieces. After normalizing the portions of steel containing 0.80% of carbon are pearlite while the areas having low carbon are ferrites. The redistribution of carbon at…
Normalizing Equipment
- The equipment in use for normalizing comes in both batch and continuous operations. Bell furnace offers an economical method of heat treatment and different bell lifting mechanisms. Continuous furnaces heat treats the metal in the continuous fashion. The conveyor runs at constant speed, and the product is carried to desired conditions after heat treatment.
Application of Normalizing
- The low cost of the normalizing process makes it one of the most extensively used industrial process when compared to annealing. The furnace is available for the next batch as soon as heating and holding periods are over. Normalizing is used to: 1. Improve the grain size refinement and machinability of cast structures of castings 2. Recover the original mechanical properties o…
What Is Heat Treatment?
The Basics of Normalization
- Normalization removes impurities in steel and improves its strength and hardness. This happens by changing the size of the grain, making it more uniform throughout the piece of steel. The steel is first heated up to a specific temperature, then cooled by air. Depending on the type of steel, normalizing temperatures usually range from810 degrees Celsius to 930 degrees Celsius. The t…
Benefits of Normalization
- The normalization form of heat treatment is less expensive than annealing. Annealing is a heat treatmentprocess that brings metal closer to a state of equilibrium. In this state, the metal becomes softer and easier to work with. Annealing—which the American Foundry Society refers to as "extreme over-aging"—requires slow-cooking metal to allow its microstructure to transform. I…
Preventing Structural Irregularities
- While normalization may have advantages over annealing, iron generally benefits from any kind of heat treatment. This is doubly true when the casting shape in question is complicated. Iron castings in complex shapes (which can be found in industrial settings like mines, oilfields, and heavy machinery) are vulnerable to structural problems after they cool. These structural irregula…
Metals That Don't Require Normalizing
- Not all metals require the normalization thermal process. For example, it's rare for low-carbon steels to require normalization. That being said, if such steels are normalized, no harm will come to the material. Also, when iron castings have a consistent thickness and equal section sizes, they are generally put through the annealing process, rather than the normalization process.
Other Heat Treatment Processes
- Carburizing steel: Carburizing heat treatment is the introduction of carbon into the surface of the steel. Carburizing occurs when the steel is heated above the critical temperature in a carburizing furnace that contains more carbon than the steel contains. Decarburization: Decarburization is the removal of carbon from the surface of the steel. Decarburization occurs when the steel is heate…