
Purpose of Heat Treatment of Steel
- To improve mechanical properties such as tensile strength, hardness, ductility, shock resistance, and resistance to corrosion.
- Improve machinability.
- To relieve the internal stresses of the metal-induced during cold or hot working.
- To change or refine grain size.
- Improve magnetic and electric properties.
- Increase resistance to wear, and corrosion.
How do you heat treat 4130 steel?
Things You'll Need
- Heat treat oven
- Trough of mineral oil
- Protective equipment
Why heat treat steel?
- Nickel makes the austenitic structure more stable, adds ductility and increases high-temperature strength and corrosion resistance.
- Manganese also stabilizes the austenitic structure, and it improves hot working properties.
- Molybdenum increases resistance to corrosion from chlorides.
How to temper steel?
Things you'll need:
- Blowtorch
- Two, six inch 1040 steel rods
- Fire extinguisher
- Safety glasses and gloves
- Cold tap water in a large bucket
What is the heat treatment for high carbon steel?
What you'll need:
- Heat Treating Furnace - I've got another instructable showing you how to build this furnace.
- Source of heat - I'm using a MAPP Gas torch. ...
- Tongs/pliers - something to hold the hot metal with.
- Quenching liquid. ...
- Container for the quench. ...
- Fire extinguisher. ...
Why is steel heat treated?
The purpose of make steel been through heat treatment is to get the desired structure and properties.
Why do we use heat to treat steel?
It is the way of just only heat treats the steel surface, to change its mechanical properties of the surface. In order to just processing its surface without excessive heat being involved in the steel inside. Need to use the heat source with high energy density. It can give more heat energy to steel material per unit area.
How does heat treatment change the chemical composition of steel?
It is to change the chemical composition, structure, properties of steel material surface. It can change the chemical composition of the surface layer of the steel material. It is a big difference between chemical heat treatment and surface heat treatment. The way of chemical heat treatment is to heat the material in a medium (gas, liquid, solid) containing carbon, nitrogen or other alloying elements for a long time. To make the carbon, nitrogen, boron and chromium elements get into its surface layer. After that, also need other heat treatments sometimes, such as quenching and tempering. Carburizing, nitriding are the main methods of chemical heat treatment.
What are the two methods of surface heat treatment?
Make the surface of steel quickly get high temperature. The main methods of surface heat treat are flame quenching and induction heat treatment. The oxyacetylene, ethylene oxide and etc are the most useful heat sources.
What is thermomechanical treatment?
The way of thermomechanical treatment needs pressure processing deformation and heat treatment effectively combining. It will make the steel material get good hardness and toughness. The heat treatment performed in a vacuum atmosphere or in a vacuum is referred to as a vacuum heat treatment. It not only can prevent the alloy steel material ...
What temperature should steel be kept at?
The steel after quenching is kept warm for a long time at a suitable temperature above room temperature and below 650 ° C and then cooled. These four steps will evolve different heat treatment according to the different temperature and the way of cooling.
What is chemical heat treatment?
Chemical Heat Treatment. It is to change the chemical composition, structure, properties of steel material surface. It can change the chemical composition of the surface layer of the steel material. It is a big difference between chemical heat treatment and surface heat treatment. The way of chemical heat treatment is to heat ...
What are the purposes of heat treatment?
The following are the purposes of heat treatment. To improve mechanical properties such as tensile strength, hardness, ductility, shock resistance, and resistance to corrosion. Improve machinability. To relieve the internal stresses of the metal-induced during cold or hot working. To change or refine grain size.
Why is heat treatment done?
The heat treatment is done to improve the machinability. To improve magnetic and electrical properties. To increase resistance to wear, heat and corrosion, ...
What is tempered steel?
It is an operation used to modify the properties of steel hardened by quenching for the purpose of increasing its usefulness. Tempering or draw results in a reduction of brittleness and removal of internal strains caused during hardening. Steel must be tempered after the hardening process.
What is the process of hardening a metal?
Nitriding. Nitriding is the process of the case or surface hardening in which nitrogen gas is employed to obtain hard skin of the metal. In this process, steel is heated in the presence of ammonia environment. Due to this, a nitrogen atom is deposited and makes material hard.
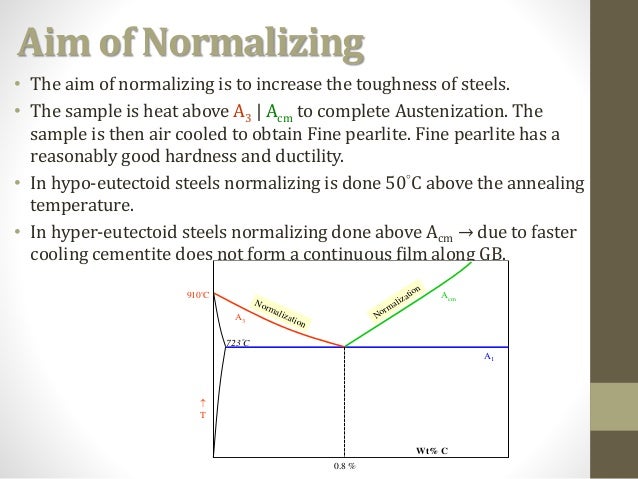
What is the purpose of normalizing steel?
Normalizing. Normalizing: The main aim of normalizing is to remove the internal stresses developed after the cold working process. In this, steel is heated 30 – 50°C above its upper critical temperature and cooling it in the air. It improves mechanical and electrical properties, machinability & tensile strength.
What temperature is a molten salt bath?
The parts to be treated is dipped in a molten cyanide salt bath maintained at a temperature of 950°C. The molten salts used are sodium chloride, sodium carbonate, sodium cyanide and soda ash.
What are the different types of heat treatment?
Types of Heat Treatment. 1. Annealing. Annealing is one of the most important processes of heat treatment. It is one of the most widely used operations in the heat treatment of iron and steel and is defined as the softening process.
Why heat treatment on low carbon steel?
Heat treatment on low carbon steel is to increase ductility, to improve toughness, strength, hardness and tensile strength and to relive stress developed in the material. It is neither externally brittle nor ductile due to its lower carbon content. It has lesser tensile strength and malleable. The increase in carbon content makes ...
How does heat treatment work?
The process that heat treatment is carried out first by heating the material and then cooling it in water, oil and brine water. The use of heat treatment is to soften or harden the material, to modify the size of the grain, to modify the structure of the material and relive the stress setup in the material. Read More Info Regarding This Post : ...
What is casehardening in metals?
Casehardening is a thermo chemical diffusion process in which an alloying element, most commonly carbon or nitrogen, diffuses into the surface of a monolithic metal. The subsequent interstitial solid solution is harder than the base material, which improves wear resistance without sacrificing touchiness.
What is normalizing ferrous?
Normalizing is technique used to provide uniformity in grain size and composition throughout alloy. The term is frequently used for ferrous alloys that have been austenitized and then cooled in open air.
Types of Heat Treating Steel Processes
This is a heat treatment process in which a specific metal – such as aluminum, silver, steel, copper, brass, etc. – is heated steadily until it reaches a particular temperature. This temperature is maintained for a specific period in order to give room for transformation to take place.
Why Heat Treating is Important in Manufacturing Quality Parts
Precision is key when it comes to manufacturing high-quality parts. Heat treating metal dramatically increases its strength, which is why it is one of the most popular choices in the aerospace and automotive industries.
Types of Furnaces for Heat Treating Metal
To successfully heat treat metal, there must be close control over every factor that affects the cooling and heating of the part. This is only possible using the ideal equipment for heat treating metal.
Conclusion
Heat treatment is a crucial part of precision machining processes in order to transform metals efficiently. It also ensures your parts or pieces perform effectively and efficiently as you desire or need them to.
Industries we serve
The processing and refining of Natural Gas into a marketable products, by separating gas into pipeline-quality natural gas and a stream of mixed natural gas liquids and the transportation of natural gas to through a series of reciprocating compressor stations and pipes, and from there to end users.
Why do we heat treat steel?
This is another heat treatment process that helps to increase the resilience of steel. Iron-based alloys are usually hard but often too brittle for certain applications. Tempering helps to alter the hardness, brittleness, and ductility of the metal. This is in a bid to make the machining process easier.
Why use heat treated metal?
Using effectively heat-treated metal parts ensures the effective and cost-effective running of machines. Furthermore, the product will be a lot more efficient, even for the toughest applications. Also, there may be the need for extremely hard metals for some applications.
What are the benefits of heat treatment?
In a nutshell, the benefits of heat treatment of metals include: Increases strength, making the material ductile or more flexible. It introduces wear-resistant properties to the metal. Relieves stresses, making the part easier to machine or weld.
What is hardening metal?
Hardening. Hardening involves the heating of the metal material to a specific temperature. This temperature is the point at which the elements present in the metal goes into solution. The crystal lattice structure of the metal may have defects that present a source for plasticity.
What is the process of making metal harder?
This usually made the metal a lot harder and less brittle. This is a basic process called heat treatment of metals. Modern machining and metalworking processes are now more precise and sophisticated. Many different techniques help shape metals for various purposes.
Why does cooling occur?
Then, cooling occurs to harden the heated material. The process aims towards changing the microstructure of the metal. Also, it helps to bring out desired mechanical, chemical, and physical characteristics. The alteration of these properties benefits the working life of the component involved.
What happens to the microstructure of a metal when it is hot?
While the metal is hot, the microstructure changes . This is the physical structure of the metal. The change in the structure ultimately results in a change in the physical properties of the metal. The ‘soak time’ is the amount of time used to heat the metal.
What is the purpose of annealing steel?
Heat Treatment Steel: Annealing. The purpose of annealing is to do the opposite of hardening. You anneal metals to relieve stress, soften the metal, increase ductility, and improve their grain structures. Without an appropriate preheating stage, welding can lead to a metal with uneven temperatures, even molten areas next to areas ...
Why is steel normalized?
The purpose of normalizing is to remove any internal stresses from heat treatment, machining, forging, forming, welding, or casting. Metal failure can result from uncontrolled stress, so normalizing steel before any hardening can help ensure the success of projects.
What is the difference between tempering and heat treatment?
Tempering consists of the same three stages as heat treatment. The main difference is the temperature of tempering and its effect on hardness, strength, and, of course, ductility. When you temper a steel part, you reduce the hardness that was caused by hardening and you develop certain physical properties. Tempering always follows hardening and, ...
What happens when you add alloys to steel?
When you add alloys to steel to increase its hardness, you also increase the carbon’s ability to harden and strengthen. That means that the carbon content needed to produce the highest level of hardness is lower in alloyed steels versus plain carbon steels.
What happens after you remove a steel part from a furnace?
After you remove a steel part from the tempering furnace, you typically cool it in still air just as you would in the normalizing process . But, as with all of the different heat treatment processes, there are some differences that are beyond the scope of this blog post.
How to harden steel?
To harden most steels, you would use the first two stages of heat treatment (slow temperature heat followed by soaking by a specified time to a uniform temperature), the third stage is different. When you harden metals, you rapidly cool them by plunging them into water, oil, or brine.
Why is steel hard?
The answer may be to temper the steel to reduce that brittleness and remove or relieve the internal stresses.
Why is heat treatment called an arrest?
This temperature is referred to as an "arrest" because at the A temperature the metal experiences a period of hysteresis.
How does steel change carbon?
When steel is heated in an oxidizing environment, the oxygen combines with the iron to form an iron-oxide layer, which protects the steel from decarburization. When the steel turns to austenite, however, the oxygen combines with iron to form a slag, which provides no protection from decarburization. The formation of slag and scale actually increases decarburization, because the iron oxide keeps oxygen in contact with the decarburization zone even after the steel is moved into an oxygen-free environment, such as the coals of a forge. Thus, the carbon atoms begin combining with the surrounding scale and slag to form both carbon monoxide and carbon dioxide, which is released into the air.
How much carbon is in hypoeutectoid steel?
A hypoeutectoid steel contains less than 0.77% carbon. Upon cooling a hypoeutectoid steel from the austenite transformation temperature, small islands of proeutectoid-ferrite will form. These will continue to grow and the carbon will recede until the eutectoid concentration in the rest of the steel is reached.
What happens when an alloy is cooled to an insoluble state?
If the alloy is cooled to an insoluble state, the atoms of the dissolved constituents (solutes) may migrate out of the solution. This type of diffusion, called precipitation, leads to nucleation, where the migrating atoms group together at the grain-boundaries.
Why are nonferrous alloys annealed?
Most non-ferrous alloys that are heat-treatable are also annealed to relieve the hardness of cold working. These may be slowly cooled to allow full precipitation of the constituents and produce a refined microstructure. Ferrous alloys are usually either " full annealed" or " process annealed.".
Why are metals annealed?
Most non-ferrous alloys that are heat-treatable are also annealed to relieve the hardness of cold working.
What is the process of heating something to alter it?
Process of heating something to alter it. Heat treating furnace at 1,800 °F (980 °C) Heat treating (or heat treatment) is a group of industrial, thermal and metalworking processes used to alter the physical, and sometimes chemical, properties of a material. The most common application is metallurgical. Heat treatments are also used in the ...
What is the purpose of austenitic stainless steel heat treatment?
Therefore, the main purpose of austenitic stainless steel heat treatment is not to change the mechanical properties, but to improve corrosion resistance.
What are the classification methods for stainless steel?
There are many classification methods for stainless steel, such as chemical composition, functional characteristics, metallographic structure and heat treatment characteristics. From the perspective of heat treatment, it is more practical to divide it according to the metallographic structure and heat treatment characteristics.
What is the main alloying element in stainless steel?
1. Ferritic stainless steel. The main alloying element is Cr, or to add a small amount of stable ferrite elements, such as Al, Mo, etc., and the structure is ferrite. Strength is not high, which can not use heat treatment methods to adjust the performance, there is a certain plasticity and large brittleness.
Why is stainless steel stronger than stainless steel?
Because it contains ferrite and strengthening elements, after heat treatment, the strength is slightly higher than that of austenitic stainless steel and the plasticity and toughness are better, which is impossible to adjust the performance by heat treatment.
What is the C content of stainless steel?
It has a low C content (generally ≤0.09%), a higher Cr content (generally ≥14% or more), plus Mo, Cu and other elements, which makes it have higher corrosion resistance that is equivalent to Austenitic stainless steel.
What temperature should annealing be used?
In order to eliminateσ phase, brittleness at 475°C and brittleness at high temperature, annealing treatment can be used. It needs to heat and hold at 780~830°C, and then to use air cooling or furnace cooling.
What are the elements that are added to stainless steel?
In addition, alloying elements such as Mo, Cu, Nb, N and W are added, and the C content is controlled very low. Depending on the proportion of alloying elements, some ferrite, some are mainly austenite, constituting two duplex stainless steels that exist simultaneously.

Overall Steel Heat Treatment
- Heat treat the hole steel, then cooling it at the right temperature. It can change the whole mechanical property. It includes annealing, normalizing, quenching, tempering. And the quenching and tempering are closely related. People always used together. Each part of them is indispensable.
Annealing
- Heat the material to make it get the appropriate temperature. According to the size and material of it to choose the right time of heat preservation. Then make it cool slowly. The purpose is to make the material get ready for quenching. Make the material internal structure get equilibrium state. Then it will get great technological properties.
Normalizing
- The steel sample is heated to a suitable temperature and then cooling it in the air. Its influence on the material is the same as annealing. But the resulting tissue is finer. People usually use it to improve the free cutting performance of mild steel. And sometimes use it to do finally heat treatment for the material of lower request.
Quenching
- Heat the steel material to get the right temperature and keep it. Then make it fast cooling in the transmitter substance of water, oil, inorganic salts and etc. After quenching, steel material will become harder. But at the same time, it becomes brittle.
Tempering
- In order to make steel get lower brittleness. The steel after quenching is kept warm for a long time at a suitable temperature above room temperature and below 650 ° C and then cooled. These four steps will evolve different heat treatment according to the different temperature and the way of cooling. In order to get great strength and toughness, need to do the processing of combining q…
Surface Heat Treatment
- It is the way of just only heat treats the steel surface, to change its mechanical properties of the surface. In order to just processing its surface without excessive heat being involved in the steel inside. Need to use the heat source with high energy density. It can give more heat energy to steel material per unit area. Make the surface of steel quickly get high temperature. The main method…
Chemical Heat Treatment
- It is to change the chemical composition, structure, properties of steel material surface. It can change the chemical composition of the surface layer of the steel material. It is a big difference between chemical heat treatment and surface heat treatment. The way of chemical heat treatment is to heat the material in a medium (gas, liquid, solid) containing carbon, nitrogen or ot…
What Is Heat Treatment?
Types of Heat Treatment Processes
Types of Heat Treatment
Purpose of Heat Treatment of Steel
- The following are the purposes of heat treatment. 1. To improve mechanical properties such as tensile strength, hardness, ductility, shock resistance, and resistance to corrosion. 2. Improve machinability. 3. To relieve the internal stresses of the metal-induced during cold or hot working. 4. To change or refine grain size. 5. Improve magnetic and ...
Conclusion