But those risks also exist without treatment: If a patient in his 70s declines treatment, life expectancy is three to four months, with a risk of infections and other complications. Life expectancy with treatment is longer. Older adults diagnosed with leukemia should partner with oncologists who focuses on the disease.
How long can you live with chronic myeloid leukemia?
Aug 07, 2020 · Today, the average five-year survival rate for all types of leukemia is 65.8%. That means about 69 of every 100 people with leukemia are likely to live at least five years after diagnosis. Many people will live much longer than five years. Your Opinion Matters! In order to improve our content, we want to hear from you.
How long does a person with leukemia live?
Sep 06, 2018 · While there is currently no cure for leukemia, it is possible to treat the cancer to prevent it coming back. Treatment success depends on a range of factors. Treatment can include: chemotherapy...
What is the success rate of leukemia?
Aug 18, 2021 · The 5-year relative survival rate for all types of leukemia is 65 percent, according to the National Cancer Institute (NCI) . Not considering age, …
What are the odds of leukemia?
Jun 30, 2020 · The prognosis for adults is not as good. Only 25 to 35 percent of adults live 5 years or longer. Acute myeloid leukemia (AML): With proper treatment, most people with this cancer can expect to go into remission. About 80 percent who go …

Is leukemia fatal without treatment?
Leukemia isn't curable, but it can be managed with a number of treatments. Learn about what side effects to expect, why they happen, and more. There's no way to prevent leukemia, but there are certain things you can do to avoid some risk factors.Aug 18, 2021
What happens if leukemia is not treated?
If this disease is left untreated, a person with leukemia becomes increasingly susceptible to fatigue, excessive bleeding and infections until, finally, the body becomes virtually defenseless, making every minor injury or infection very serious. Leukemia may be fatal.Mar 30, 2019
Can you have leukemia and not have treatment?
As CLL progresses slowly and often has no symptoms at first, you may not need to be treated immediately. If it's caught early on, you'll have regular check-ups over the following months or years to see if it's getting any worse.
Can leukemia go into remission without treatment?
Without treatment, acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is almost always fatal. Spontaneous remission of AML is a rare phenomenon and usually with a short duration. The exact mechanisms are unknown. However, its association with infection and blood transfusions has been described.
Which type of leukemia is most fatal?
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is the most fatal type of leukemia. The five-year survival rate (how many people will be alive five years after diagnosis) for AML is 29.5%. Leukemia is a cancer that usually affects white blood cells, though it can start in other types of blood cells.Feb 23, 2022
What causes death in leukemia patients?
Studies show that for leukemia patients, infections were the most common cause of death, most often bacterial infections but also fungal infections or a combination of the two. Bleeding was also a fairly common cause of death, often in the brain, lungs or digestive tract.Aug 17, 2018
How do you know if your leukemia is getting worse?
If you start having symptoms of CLL progression, such as unexplained weight loss, fever, night sweats, swollen lymph nodes, and significant fatigue, schedule an appointment with your oncologist or hematologist right away.Feb 6, 2020
What is the survival rate for leukemia?
Latest figures show that the 5-year survival rate for all subtypes of leukemia is 61.4 percent . A 5-year survival rate looks at how many people are still alive 5 years after their diagnosis. Leukemia is most common in people aged over 55, with the median age of diagnosis being 66.
What are the 5 stages of leukemia?
What are the stages of CLL?Stage 0. The blood has too many white blood cells called lymphocytes. This is called lymphocytosis. ... Stage I. The blood has too many lymphocytes. ... Stage II. The blood has too many lymphocytes. ... Stage III. The blood has too many lymphocytes. ... Stage IV. The blood has too many lymphocytes.
What is the end stages of acute myeloid leukemia?
The majority of AML patients are in a hospital setting at the time of death. Important factors for the location of death include age at diagnosis, disease status, social support and prior induction chemotherapy. Symptoms at the end of life included pain, delirium and bleeding.Dec 3, 2015
What happens when chemo doesn't work for leukemia?
If chemotherapy does not work, a possible alternative treatment option is a bone marrow or stem cell transplant. Before transplantation can take place, the person receiving the transplant will need intensive high-dose chemotherapy, and possibly radiotherapy, to destroy the cells in their bone marrow.
Can leukemia be cured without chemo?
As with other types of cancer, there's currently no cure for leukemia. People with leukemia sometimes experience remission, a state after diagnosis and treatment in which the cancer is no longer detected in the body.May 3, 2021
How long do people live with leukemia?
Leukemia survival rates are higher for people under the age of 55. . A 5-year survival rate looks at how many people are still alive 5 years after their diagnosis. Leukemia is most common in people aged over 55, with the median age of diagnosis being 66.
What are the factors that affect the survival rate of a person with leukemia?
Factors include: age. time of diagnosis. progression and spread of the cancer. type of leukemia. a family history of blood conditions and leukemia. the extent of bone damage.
What is the difference between leukemia and leukemia?
There are many different types of leukemia. Which type a person develops depends on which white blood cells are affected, as well as some other factors. Leukemia can prevent white blood cells from fighting infections and cause them to multiply uncontrollably.
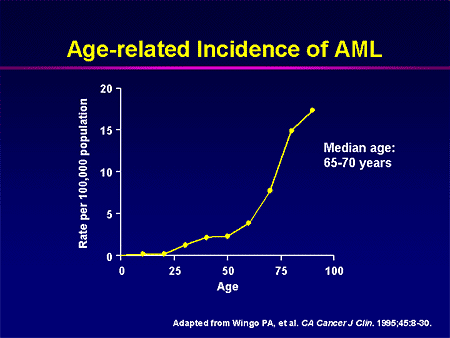
What is the most common age for leukemia?
Leukemia is most common in people aged over 55, with the median age of diagnosis being 66. It is also one of the most common cancers for people under age 20. The survival rate is higher for younger people. According to the National Cancer Institute. Trusted Source.
Can leukemia cause overcrowding?
This overgrowth can cause overcrowding of the healthy blood cells, leading to severe problems throughout the body. Leukemia can either be: Acute, which is when the majority of affected white blood cells cannot function normally, causing rapid degeneration.
Is it normal to feel a mixture of emotions after a cancer diagnosis?
Receiving a leukemia diagnosis is life-changing and challenging for both an individual and their loved ones. It is common to feel a mixture of emotions after a cancer diagnosis, but everybody reacts differently in these situations.
Is there a cure for leukemia?
While there is currently no cure for leukemia, it is possible to treat the cancer to prevent it coming back. Treatment success depends on a range of factors. Treatment can include: chemotherapy. radiation therapy. stem cell transplant. antibiotics. Treatment can last several months or even years depending on the type and severity of the condition.
How long do children live with leukemia?
More than four out of five children live at least 5 years. The prognosis for adults is not as good.
How old is the average person with leukemia?
In adults, leukemia is most common in people older than 55 years, with the average age of diagnosis being 66 years. It is also one of the most common cancers in children and adults younger than 20 years. The survival rate is higher for younger people. According to the National Cancer Institute, the percentage of deaths by age group is as follows: ...
What are the different types of leukemia?
There are four common types of leukemia which include: Acute lymphocytic leukemia (ALL): In this type of leukemia, immature lymphoid cells grow rapidly in the blood. It is the most common type of leukemia in children and rarely affects adults. Acute myeloid leukemia (AML):
What is asparlas mknl?
Asparlas (calaspargase pegol - mknl) Asparlas (calaspargase pegol - mknl) is an asparagine specific enzyme indicated as a component of a multi-agent chemotherapeutic regimen for the treatment of acute lymphoblastic leukemia in pediatric and young adult patients age 1 month to 21 years.
What is Onureg used for?
Onureg is a prescription medicine used for continued treatment of adults with acute myeloid leukemia (AML) who had a first complete remission (CR) following intensive induction chemotherapy with or without recovery of your blood cell counts , and who are not able to complete intensive curative therapy.
What is the disease of the bone marrow?
Leukemia is a cancer of the white blood cells of the bone marrow. Patients with leukemia have an over-production of a particular blood cell type in the body, the white blood cells (cells that fight infection, and provide immunity).
What is the name of the cancer that affects the white blood cells?
Leukemia is a group of cancers of the blood affecting the white blood cells. White blood cells are the infection-fighting cells of the body. In leukemia , white blood cell production becomes abnormal in the bone marrow. The abnormal white blood cells divide uncontrollably and eventually outnumber the healthy white blood cells.
What tests can you do for leukemia?
If this happens, or if you have signs or symptoms that suggest leukemia, you may undergo the following diagnostic exams: Physical exam. Your doctor will look for physical signs of leukemia, such as pale skin from anemia, swelling of your lymph nodes, and enlargement of your liver and spleen. Blood tests. By looking at a sample of your blood, your ...
Why is leukemia confusing?
The term "leukemia" can be confusing because it refers to a group of cancers that aren't all that similar except for the fact that they affect the bone marrow and blood.
How to remove bone marrow from hip?
Bone marrow test. Your doctor may recommend a procedure to remove a sample of bone marrow from your hipbone. The bone marrow is removed using a long, thin needle. The sample is sent to a laboratory to look for leukemia cells.
What is the treatment for bone marrow transplant?
Radiation therapy may be used to prepare for a bone marrow transplant. Bone marrow transplant. A bone marrow transplant, also called a stem cell transplant, helps reestablish healthy stem cells by replacing unhealthy bone marrow with leukemia-free stem cells that will regenerate healthy bone marrow.
Where is bone marrow aspiration done?
In a bone marrow aspiration, a doctor or nurse uses a thin needle to remove a small amount of liquid bone marrow, usually from a spot in the back of your hipbone (pelvis). A bone marrow biopsy is often done at the same time. This second procedure removes a small piece of bone tissue and the enclosed marrow.
What does a blood test show?
A blood test may also show the presence of leukemia cells, though not all types of leukemia cause the leukemia cells to circulate in the blood.
How does immunotherapy work?
Immunotherapy works by interfering with that process. Engineering immune cells to fight leukemia.
How to tell if you have leukemia?
Other common symptoms from leukemia are low blood counts and fatigue. Medicines or blood transfusions may be needed to help correct these problems. Nausea and loss of appetite can be treated with medicines and high-calorie food supplements. Infections that occur may be treated with antibiotics.
What is supportive care for leukemia?
Supportive treatment for leukemia that won't go away. If further treatment or a clinical trial is not an option, the focus of treatment may shift to controlling symptoms caused by the leukemia, rather than trying to cure it. This is called palliative treatment or supportive care.
What is the treatment for AML?
For AML with a mutation in the IDH1 or IDH2 gene. If the leukemia cells have an IDH1 or IDH2 gene mutation, one option if the leukemia doesn’t go away or if it comes back later might be treatment with a targeted drug called an IDH inhibitor, such as ivosidenib (Tibsovo) for AML with an IDH1 mutation, or enasidenib ...
What to do if AML doesn't go away?
If AML doesn’t go away completely with induction treatment, sometimes a second, similar course of chemotherapy (chemo), often called reinduction, can be tried. If this isn't helpful, treatment with other chemo drugs or more intensive doses of chemo may be tried, if the person can tolerate them. A stem cell transplant may be an option ...
How long does it take for AML to come back?
Clinical trials of new treatment approaches might also be an option. If AML comes back sooner than 12 months, most doctors will advise a stem cell transplant for younger patients, if possible. Taking part in a clinical trial is another option.
How long does it take for ATRA to relapse?
For patients whose initial treatment was with the non-chemo drugs all-trans retinoic acid (ATRA) and arsenic trioxide (ATO) and who relapse early (usually within about 6 months), treatment will most likely be with some of the same chemo drugs used to treat other types of AML.
Where does AML recur?
AML most often recurs in the bone marrow and blood. The brain or cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is rarely the first place where it recurs, but if this happens, ...
What age do you have to be to get leukemia?
According to the National Cancer Institute, leukemia is most frequently diagnosed among people between the ages of 65 and 74 years. The median age at diagnosis is 66. There are treatment options for patients of all ages, include chemotherapy and blood transfusions. Advertising Policy.
How long does a person live in his 70s without treatment?
But those risks also exist without treatment: If a patient in his 70s declines treatment, life expectancy is three to four months, with a risk of infections and other complications. Life expectancy with treatment is longer. Advertising Policy.
How much chance of cancer disappears in 60s?
A person in his 60s who undergoes intensive chemotherapy has a 55 to 60% chance of going into remission. This means that all signs and symptoms of cancer disappear, although the cancer may still be in the body. There are risks with undergoing treatment, however, including infections and death.
Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia Survival Rate
The survival rate for CLL is better than for many other types of cancer. Data compiled by the National Cancer Institute (NCI) from 2011 to 2017 indicate that the five-year relative survival rate for CLL is 87.2%. 4 NCI data for that same time frame show a decline in the new case rate and death rate for CLL.
Factors That Influence Outlook
No two people are alike. Your CLL prognosis will vary from that of other people with this condition. Age, overall health, and response to treatment can all have an impact on your outlook and what you can expect.
Is a Cure for CLL in Sight?
There is currently no cure on the horizon for CLL. Research is ongoing and continues to prolong survival and improve the quality of life for people with this condition.
Coping and Support for Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia
Receiving a diagnosis of CLL can be scary and upsetting. People with early-stage disease who are watching and waiting may find it stressful to not pursue treatment. 17
Summary
CLL is a slow-growing cancer. It is possible to have this condition for many years before you start to show symptoms. The prognosis for CLL is much higher than for many other types of cancer. However, there is currently no cure for this disease. CLL has a five-year survival rate of around 83%, although it drops under 70% in those over 75.
A Word From Verywell
Finding out that you or a loved one has CLL may take your breath away. It can be overwhelming to learn you have an incurable condition. It may sound cliché, but incurable and untreatable are not the same thing.
What happens if you have a preleukemic gene?
If the person later develops AML, these same gene changes are then seen in their cancer cells. This makes researchers believe that some of these gene mutations are preleukemic, causing the stem cells to produce cancerous blood cells.
What is preleukemia in medical terms?
Article written by. Maureen McNulty. “Preleukemia” was a term doctors previously used for myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS). Some people with MDS go on to develop acute myeloid leukemia (AML), so doctors sometimes used to view MDS as the first stage of AML. Doctors have found that other conditions and gene changes — including clonal hematopoiesis ...
What are the symptoms of MDS?
Myelodysplastic syndrome can lead to different symptoms depending on which type of blood cell is affected. People with MDS may experience: 1 Anemia — Low numbers of red blood cells, which can cause tiredness, loss of appetite, breathing problems, pale skin, and a rapid heartbeat 2 Neutropenia — Low levels of white blood cells, which can lead to fevers and frequent infections 3 Thrombocytopenia — Low platelet count, which often causes bruising, bleeding problems, and petechiae (tiny purple, red, or brown spots on skin, which may be more difficult to see on darker skin)
Why don't doctors call MDS preleukemia?
Doctors also don’t call MDS preleukemia because the cancer cells from the conditions often act differently from each other. Additionally, cells from these two diseases tend to have different gene changes. Experts now often view MDS as a separate type of cancer rather than just the first phase of AML.
What are the symptoms of myelodysplastic syndrome?
People with MDS may experience: Anemia — Low numbers of red blood cells, which can cause tiredness, loss of appetite, breathing problems, pale skin, and a rapid heartbeat. Neutropenia — Low levels of white blood cells, ...
What is a chip cell?
CHIP occurs when immature stem or progenitor cells develop one or more gene mutations that are sometimes found in cancer. The cells then make mature blood cells that also contain this mutation. None of these cells are cancerous, but they may potentially become cancerous in the future.
What causes a mutation in a gene?
Certain risk factors known to cause gene mutations have been linked to higher risks of developing different types of cancer. MDS occurs when abnormal stem cells make defective blood cells. People with MDS experience low blood cell counts and have at least one blood cell type that looks abnormal and acts abnormally.

What Is AML?
What Influences Aml Survival Rate?
- AML isn’t staged like other cancers since it doesn’t form solid tumors. It’s often widespread in the bone marrow and the blood when it’s first discovered and has sometimes spread to other organs as well. Instead, the subtype of AML plays a role in the survival rate and prognosis, as well as their age, general health, and results from other tests. Doctors will typically label AML as one of thes…
Coping and Support
- There are places to turn when it comes to coping with a disease with a low survival rate: 1. Ask your care team for resources and support. 2. Tell your family how you’re feeling. 3. Join support groups for AML patients. 4. Find ways to relieve stress or take your mind off of your prognosis. 5. Make lists of questions for your doctors in advance. Bring someone with you to appointments t…
Summary
- The prognosis for acute myeloid leukemia varies depending on age, subtype, and response to treatment. The best survival is in patients under age 20, with a five-year survival rate of 68%. For people 20 and older, the five-year survival rate is 26%. Older AML patients are more likely to have chromosomal abnormalities in their cancer cells that indic...
A Word from Verywell
- Facing a diagnosis of AML can be difficult. While the overall survival rate is poor for AML patients, understanding how your specific characteristics may impact your specific prognosis may help you understand what to expect. Ask your healthcare providers and care team for help understanding your prognosis, and make sure you lean on them for support if you’re having trouble processing …