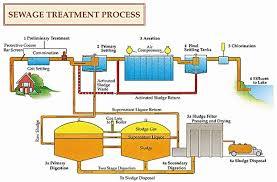
- Step 1: Screening and Pumping. ...
- Step 2: Grit Removal. ...
- Step 3: Primary Settling. ...
- Step 4: Aeration / Activated Sludge. ...
- Step 5: Secondary Settling. ...
- Step 6: Filtration. ...
- Step 7: Disinfection. ...
- Step 8: Oxygen Uptake.
Wastewater collection
What are the rules and regulations around sewage treatment plants?
- Legal Compliance. For starters, you’ll need to make sure your sewage treatment plant is legally compliant – particularly if you’ve moved into a property with an old model.
- Consent to Discharge. ...
- Planning Permission. ...
Primary Sewage Treatment
You’re basically:
- growing the organisms in a suspension and retaining them
- mixing the wastewater with the biomass
- aerating this “mixed liquor” so the bacteria can get to work
- settling out the mixed liquor suspended solids (MLSS)
- sending return activated sludge (RAS) to the reactor basin
- sending waste activated sludge (WAS) to be dewatered and treated accordingly
Sludge Treatment
Maintenance of Sewage Water Treatment Plants:
- Clarifies should not be clogged with solid waste
- There is no biological growth in your aerators
- The growth of the filaments is zero in the aeration tanks
Secondary Sewage Treatment
There are four major processes under the tertiary treatment:
- Solids removal
- Biological nitrogen removal
- Biological phosphorus removal
- Disinfection.
Tertiary Treatment
What work do they do at a sewage treatment plant?
How does a sewage treatment plant actually work?
Why do we need sewage treatment plants?
What are the primary stages of sewage treatment?

What are the 3 stages of sewage treatment plant?
There are three main stages of the wastewater treatment process, aptly known as primary, secondary and tertiary water treatment.
What are the 4 stages of sewage treatment?
4-Step Wastewater Sludge Treatment ProcessStep 1 – Sludge Thickening. The first step in the sewage sludge treatment plan is called thickening. ... Step 2 – Sludge Digestion. After amassing all the solids from the sewage sludge begins the sludge digestion process. ... Step 3 – Dewatering. ... Step 4 – Disposal.
What are the 8 steps of sewage treatment?
The Wastewater Treatment ProcessStage One — Bar Screening. ... Stage Two — Screening. ... Stage Three — Primary Clarifier. ... Stage Four — Aeration. ... Stage Five — Secondary Clarifier. ... Stage Six — Chlorination (Disinfection) ... Stage Seven — Water Analysis & Testing. ... Stage Eight — Effluent Disposal.
What is the first stage in sewage treatment process?
primary sedimentation stageThe first stage in the sewage treatment is the primary sedimentation stage. Sewage including all of the grey and black water from a home flows into a chamber called the primary sedimentation tank and holds waste until it has had enough time for heavy sediment to disperse to the bottom.
What are the four basic principles for water treatment?
4 Steps of Community Water TreatmentCoagulation and Flocculation. ... Sedimentation. ... Filtration. ... Disinfection.
What is the first step in sewage treatment process Mcq?
What is the first step in the sewage treatment process? d) Digestion? Explanation: Thickening is often the first step in a sludge treatment process.
What are the 5 stages of sewage treatment?
Treatment StepsStep 1: Screening and Pumping. ... Step 2: Grit Removal. ... Step 3: Primary Settling. ... Step 4: Aeration / Activated Sludge. ... Step 5: Secondary Settling. ... Step 8: Oxygen Uptake. ... Sludge Treatment.
What is waste treatment process?
Wastewater treatment is a process used to remove contaminants from wastewater and convert it into an effluent that can be returned to the water cycle. Once returned to the water cycle, the effluent creates an acceptable impact on the environment or is reused for various purposes (called water reclamation).
What are the 5 stages of water treatment?
Public water systems often use a series of water treatment steps that include coagulation, flocculation, sedimentation, filtration, and disinfection.
What are the 3 stages of wastewater treatment PDF?
Wastewater is treated in 3 phases: primary (solid removal), secondary (bacterial decomposition), and tertiary (extra filtration).
What is primary treatment of sewage?
Primary treatment of wastewater involves sedimentation of solid waste within the water. This is done after filtering out larger contaminants within the water. Wastewater is passed through several tanks and filters that separate water from contaminants.
What are the different types of sewage treatment plants?
Following are few STP process & System commonly used in India.Activated Sludge Process.Moving Bio Bed Reactor (MBBR)Membrane Bio Reactor (MBR)Electro Coagulation System.Sequential Bio Reactor (SBR)Rotating Bio Reactor (RBC)
What is the first stage sewage treatment process?
Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) studies de- pict that there are 269 sewage treatment plants (STPs) in India, of which only 231 are operation...
What are the four stages in the treatment of sewage?
wastewater treatment, also called sewage treatment, the removal of impurities from wastewater, or sewage, before it reaches aquifers or natural bod...
What are the 5 stages of sewage treatment?
Primary treatment is the first phase of sewage treatment: wastewater is placed in a holding tank and solids settle to the bottom where they are col...
What is sewage treatment plant and how it works?
Primary industrial wastewater treatment plant uses screens, grit chamber, and sedimentation tank to get quality water which is free from waste and...
What are the 3 stages of sewage treatment?
There are three main stages of the wastewater treatment process, aptly known as primary, secondary and tertiary water treatment.Dec 6, 2018
What is the name of the tank where sewage is put into?
At our larger sewage treatment works, we put the wastewater into rectangular tanks called ‘aeration lanes’ , which pump air into the water. This encourages the useful bacteria to break down and eat ...
What is the purpose of screening wastewater?
Screening the wastewater. First, we remove large objects that may block or damage equipment or pollute our rivers. This includes items that should never have been put down the drain in the first place, such as nappies, wet wipes, sanitary items and cotton buds, and sometimes even things like bricks, bottles and rags.
How does a toilet flush work?
1. Taking the wastewater away. Whenever you flush the toilet or empty the sink, the wastewater goes down the drain and into a pipe, which takes it to a larger sewer pipe under the road. The sewer then joins our network of other sewers and takes the wastewater to a sewage treatment works. At the sewage works, we pass the wastewater ...
How to make biogas from sludge?
1. Combined heat and power: We treat the sludge using a process called ‘anaerobic digestion’. This heats the sludge up to high temperatures, encouraging the bacteria inside to break down the waste. This creates biogas that we can then burn to create heat, which in turn creates electricity. 2.
Why is it important to put clean water back into the river?
Putting clean water back into the river is very important, as it helps to keep water flowing and wildlife thriving. The Environment Agency strictly regulates the quality of the cleaned wastewater, and we test it to make sure that it meets their high-quality standards.
How does a sewage plant work?
Basically this consists of oxygenating by bubbling air through or by agitating the surface. By so doing a family of bacteria is propagated which thrives on the oxygen content and digests the sewage to produce an innocuous sludge. In order to exist, the bacteria need a continuing supply of oxygen from the air and sewage wastes. If plant is shut down or bypassed or if the air supply fails, the bacteria die and the plant cannot function correctly until a new bacteria colony is generated. Change of flushing liquid—as when a ship moves from a sea-water environment to fresh water—drastic change of temperature or excess use of lavatory cleaning agents can also affect the bacteria colony. The process of regeneration can take several days depending on the level of harm caused.
Why does sewage smell bad?
The best clue may be that it smells bad. The smell of H2 S may indicate the water has been inoculated with sulfate-reducing bacteria. If these are present in the formation being drilled, the formation may get inoculated and turn sour. If possible, do not use it. If you must use it, have the water tested and get expert advice on how to treat it. In general you may have to use biocides or aerate the water.
How does WWTP work?
WWTP using secondary biological sewage treatment plants has brought enormous benefits to society and the environment. Considering the short hydraulic residence time (few hours), the large reduction in the amount of natural and xenobiotic compounds is remarkable. However, municipal WWTPs are basically designed to remove pathogens and organic and inorganic suspended and flocculated matter, but not pharmaceuticals. Four key factors are critical in predicting the impact of each WWTP: (1) the size of the human population connected to the WWTP, (2) the flow through the works, (3) the type of treatment employed, and (4) the available dilution in the receiving water.
What are the two types of primary sludge?
Two types of primary sludge from sewage treatment plants were used: the first one from a rural area where no heavy metals were included and the second from an urban area where heavy metals exist.
What are the newer treatment technologies?
There are a number of newer treatment technologies that have come into use in recent times that include the MBBR, the FAB, the SBR, and the MBR. Newer technologies are gaining acceptance because of a low footprint and recyclable quality effluent although they are high energy intensive systems.
How should membrane treatment processes be optimized?
However, membrane treatment processes should be optimized by a modification of the membranes (variation of materials and reduction of molecular mass cutoff limits) and/or by modification of the treatment process ( inoculation of special microorganisms).
What are the factors that determine the impact of a WWTP?
Four key factors are critical in predicting the impact of each WWTP: (1) the size of the human population connected to the WWTP, (2) the flow through the works, (3) the type of treatment employed, and (4) the available dilution in the receiving water.
What is the role of sewage treatment plant?
Hence, Sewage treatment plant design and sewage management play a crucial role in the maintenance of human welfare.
What is biological treatment of sewage?
Biological Treatment: Aerobic microorganisms are inoculated into the sewage treatment plant. These microbes utilize the organic components of the sewage and reduce the toxicity. This can be measured by BOD (Biological oxygen demand). After the biological treatment, the sludge is pumped from the treatment plant into a large tank.
How are biogas and microbial fuel cells used?
Biogas is removed from the biogas plant through a separate outlet. Microbial fuel cells are also used to generate electricity from wastewater. Microbial fuel cells utilize the organic matter from the wastewater treatment plant. During digestion, organic matters are converted into the simple molecule and release the carbon dioxide and electrons.
Where are biomasses collected?
Biomasses (Biowastes) are collected at the biogas plant and the slurry is fed. Biomasses are rich in organic matter. Some of the bacteria can grow anaerobically inside the biogas plant. These bacteria can digest the biomasses which are present in the slurry and sewage.
Why is sewage treatment important?
Sewage treatment is necessary to reduce the toxicity of sewage and maintain a safe and healthy environment, as well as promote human welfare.
What happens to organic matter during digestion?
During digestion, organic matters are converted into the simple molecule and release the carbon dioxide and electrons. Those electrons are absorbed by the electrode and used as the source of electricity. To learn more about sewage treatment and energy generation, login to BYJU’S. Test your Knowledge on Sewage Treatment!
How is wastewater treated?
It is done by putting the wastewater into large settlement tanks for the solids to sink to the bottom. The settled solids are called sludge. At the bottom of these circular tanks, large scrappers continuously scrape the floor of the tank and push the sludge towards the center, where it is pumped away for further treatment. The rest of the water is moved to Secondary treatment.
What is the first stage of wastewater treatment?
Screening is the first stage of the wastewater treatment process. Screening removes large objects like diapers, nappies, sanitary items, cotton buds, face wipes, and even broken bottles, bottle tops, plastics, and rags that may block or damage equipment.
Why is air pumped into sludge scraping water?
These are called aeration lanes. Air is pumped into the water to encourage bacteria to break down the tiny bits of sludge that escaped the sludge scraping process.
Where does liquid waste go?
Wastewater (liquid waste) from flushing the toilet, bathing, washing sinks, and general cleaning goes down the drain and into a pipe, which joins a larger sewer pipe under the road. The sewer pipe goes on to connect to a different sewer pipe that leads to the treatment center.
How does a sewage treatment plant filter wastewater?
The wastewater that enters the sewage treatment plant is first filtered through bar screens, a process known as screening. The bar screen separates large trash objects from the wastewater, such as rags, sticks, cans, plastic bags, napkins, sanitary towels, and so on. As a result, screening removes large pieces of trash from the wastewater.
What is wastewater treatment plant?
Wastewater treatment plant is the process of removing contaminants from wastewater and converting it into effluent that can be recycled into the water cycle. Once returned to the water cycle, the effluent has an acceptable environmental impact or is reused for a variety of purposes. A wastewater treatment plant is where the treatment ...
Why is activated sludge returned to the aeration tank?
Some of the activated sludge is returned to the aeration tank to boost the population of aerobic bacteria and accelerate the cleaning of watery waste. The digester tank receives the remaining activated sludge. The water in the second sedimentation tank contains very little organic material and suspended matter.
What is the difference between biogas and sludge?
As a result, wastewater treatment (or sewage treatment) yields two useful products: (i) biogas and (ii) sludge. Biogas is used as a fuel, and sludge is used as manure (or fertiliser).
What is the solid component of sewage?
The majority of the solid organic matter (faeces, for example) settles as sludge on the sloping bottom of the sedimentation tank. As a result, the solid component of sewage is known as sludge .
What is biogas used for?
Biogas is used as a fuel , and sludge is used as manure (or fertiliser). The use of dried sludge as manure restores the nutrients to the soil. b. The wastewater remaining in the first sedimentation tank contains some organic waste in the form of tiny suspended particles as well as soluble organic matter.
What is WWTP in water treatment?
WWTP is an abbreviation for Waste-Water Treatment Plant. A wastewater treatment plant is also referred to as a sewage treatment plant. A modern wastewater treatment plant treats wastewater or sewage through a series of physical, chemical, and biological processes until it becomes fit to be discharged into the environment.