
What are the primary stages of sewage treatment?
Primary treatment of wastewater involves sedimentation of solid waste within the water. This is done after filtering out larger contaminants within the water. Wastewater is passed through several tanks and filters that separate water from contaminants.
What does a primary sewage treatment involve?
Primary treatment removes material that will either float or readily settle out by gravity. It includes the physical processes of screening, comminution, grit removal, and sedimentation. Screens are made of long, closely spaced, narrow metal bars. They block floating debris such as wood, rags, and other bulky objects that could clog pipes or pumps.
What are the main steps in sewage treatment?
Apr 06, 2022 · Primary wastewater treatment is a process to remove settleable and floating solids before the wastewater is discharged to surface water. The immediate treatment removes about 30 to 50 percent of the Biological Oxygen Demand (BOD) and 30 to 60 percent of suspended solids.
What is removed during primary wastewater treatment?
Primary treatment of sewage basically involves the physical removal of large and small particles, through filtration and sedimentation. This is done in many stages. Initially, floating debris is removed by sequential filtration and then the grit i.e. soil and small pebbles, is removed by sedimentation. All the solids that settle down, form the primary sludge and the supernatant …
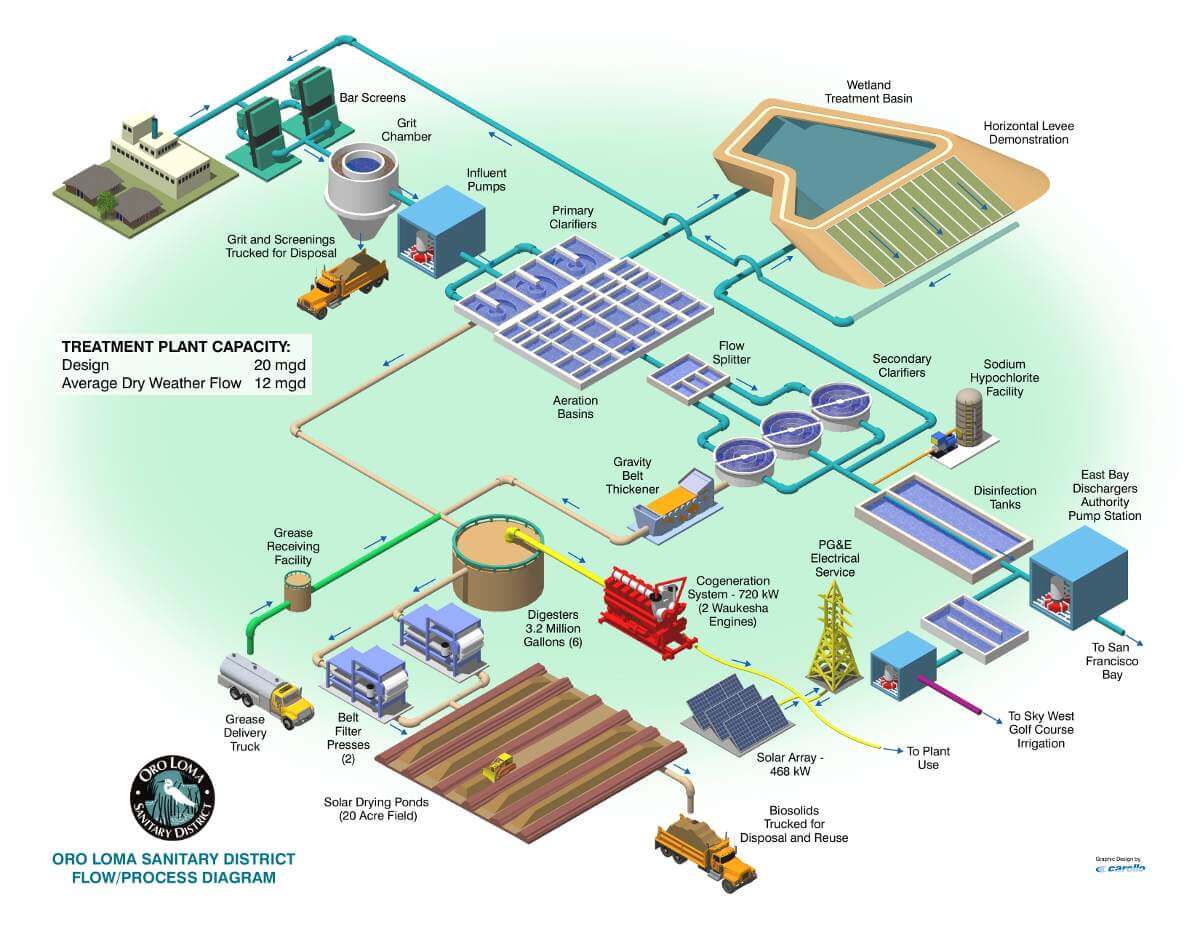
What is primary and secondary treatment for sewage?
In the primary stage, solids are allowed to settle and removed from wastewater. The secondary stage uses biological processes to further purify wastewater. Sometimes, these stages are combined into one operation.
What is the first process in the primary treatment of sewage?
Treatment StepsStep 1: Screening and Pumping. ... Step 2: Grit Removal. ... Step 3: Primary Settling. ... Step 4: Aeration / Activated Sludge. ... Step 5: Secondary Settling. ... Step 8: Oxygen Uptake. ... Sludge Treatment.
What is sewage treatment process?
Sewage Treatment refers to the process of removing contaminants, micro-organisms and other types of pollutants from wastewater. Wastewater, or raw sewage, is water that drains from toilets, sinks, showers, baths, dishwashers, washing machines and liquid industrial waste.
What is the secondary treatment of sewage?
Secondary treatment is the removal of biodegradable organic matter (in solution or suspension) from sewage or similar kinds of wastewater. The aim is to achieve a certain degree of effluent quality in a sewage treatment plant suitable for the intended disposal or reuse option.
What is primary treatment and secondary treatment?
Differences between primary and secondary wastewater treatmentPrimary Wastewater TreatmentSecondary Wastewater TreatmentIn this method, the waste is processed through a physical procedure with equipment and filtration.The wastewater is purified through biological processes using microorganisms.3 more rows
What is the primary sludge?
Primary sludge is generated from chemical precipitation, sedimentation, and other primary processes, whereas secondary sludge is the activated waste biomass resulting from biological treatments. Some sewage plants also receive septage or septic tank solids from household on-site wastewater treatment systems.
What are the 3 types of sewage treatment?
There are three main stages of the wastewater treatment process, aptly known as primary, secondary and tertiary water treatment. In some applications, more advanced treatment is required, known as quaternary water treatment.Dec 6, 2018
How is primary effluent treated in a sewage treatment plant before it can safely be released into rivers or streams?
Primary treatment: It involves the physical removal of particles from sewage through filtration and sedimentation. Floating debris is removed by filtration and grit is removed by sedimentation. Thus, all solids which settle from the primary sludge and the supernatant forms the effluent.
What is sewage treatment answer?
Answer: Treatment of wastewater involves physical, chemical, and biological processes, which remove physical, chemical and biological matter that contaminates the wastewater.
Why primary sewage treatment plant is also called physical treatment?
Primary treatment basically involves physical removal of particles large and small from the sewage through the filtration and sedimentation. These are removed in stages initially floating debris is removed by sequential filtration. Was this answer helpful?
Why primary sewage treatment plant is also called physical treatment and secondary as biological treatment?
No microbes are used. The sediment of primary treatment, called primary sludge, is treated by aerobic microbes and then by anaerobic microbes to reduce its organic components during secondary treatment. A secondary treatment involves microbes, thus it is also called biological treatment.Mar 12, 2022
What is the main difference between primary and secondary clarifiers?
A typical primary clarifier removes 60 percent of suspended solids and 30 to 40 percent of Biological Oxygen Demand (BOD). Secondary clarification follows the biological treatment process with the main goal of returning activated sludge.
Screening – Primary treatment for waste water
The first process in Primary Treatment for Wastewater is screening. I will show you the screening process and different types of screens used in primary wastewater treatment.
Flow Equalisation – Primary treatment for waste water
Under uniform flow rates, clarifiers and mechanised secondary treatment are more efficient.
Sedimentation – Primary treatment for wastewater
The wastewater, then moves to sedimentation ponds, settling tanks, or clarifiers after the removal of settled grit. The sedimentation process removes the settleable solids by gravitational settling under quiescent conditions.
Flocculation
Flocculation is a water treatment process to remove small suspended solids which don’t settle in the sedimentation tank. In this process solids form larger clusters, or flocs on the addition of a flocculent like aluminium sulphate.
Scum Removal
Lighter materials rise to the surface as sludge settles to the bottom of the sedimentation tanks. The constituents of ‘scum’ are grease, oils, plastics, and soap. Scum is skimmed off the surface of the wastewater by slow-moving rakes. Scum is thickened before being poured into the digesters with the sludge.
What is a primary clarifier?
It is also known as a primary clarifier or primary setting tank. The purpose of this unit is to remove the settleable solids present in the sewage. It is a rectangular tank constructed with brick masonry.
What is a grit chamber?
The grit chamber is an enlarged chamber or a long basin. They may be placed either before or after the screens. The function of the grit chamber is to remove grit, sand and other inorganic matter from sewage. Grit chambers are that any can be stopped for the purpose of cleaning.
What is the function of a screen?
The function of the screen is to remove all the floating matter of comparatively large size. Screens are located just before the grit chamber. The screen may be constructed of M.S bars or rods, gratings, wire meshes or perforated plates.

Screening – Primary Treatment For Waste Water
Flow Equalisation – Primary Treatment For Waste Water
- Under uniform flow rates, clarifiers and mechanised secondary treatment are more efficient.
- Equalization basins store diurnal or wet-weather flow peaks temporarily and make the water flow rate uniform.
- Basins serve as a temporary holding area for the incoming wastewater during temporary plant shut down and maintenance.
- Under uniform flow rates, clarifiers and mechanised secondary treatment are more efficient.
- Equalization basins store diurnal or wet-weather flow peaks temporarily and make the water flow rate uniform.
- Basins serve as a temporary holding area for the incoming wastewater during temporary plant shut down and maintenance.
- It acts as a means of diluting and distributing hazardous or high-strength waste into batches.
Sedimentation – Primary Treatment For Wastewater
- The wastewater, then moves to sedimentation ponds, settling tanks, or clarifiers after the removal of settled grit. The sedimentation process removes the settleable solids by gravitational settling under quiescent conditions. On proper adjustment of water flow in the sedimentation tank, the suspended particles begin to fall to the bottom and form a solid mass. Raw primary biosolids, al…
Flocculation
- Flocculation is a water treatment process to remove small suspended solids which don’t settle in the sedimentation tank. In this process solids form larger clusters, or flocs on the addition of a flocculent like aluminium sulphate. The coagulant molecules have a positive charge. Hence, they can neutralize the negatively charged solid particles that are suspended in the water. Neutralizat…
Scum Removal
- Lighter materials rise to the surface as sludge settles to the bottom of the sedimentation tanks. The constituents of ‘scum’ are grease, oils, plastics, and soap. Scum is skimmed off the surface of the wastewater by slow-moving rakes. Scum is thickened before being poured into the digesters with the sludge. Primary treatment removes about 60% of the total suspended solids and nearly …