
Treatment
- Medications. Medications are the cornerstone of schizophrenia treatment, and antipsychotic medications are the most commonly prescribed drugs.
- Second-generation antipsychotics. ...
- First-generation antipsychotics. ...
- Long-acting injectable antipsychotics. ...
- Psychosocial interventions. ...
- Hospitalization. ...
- Electroconvulsive therapy. ...
What is the first line treatment for schizophrenia?
- Conventional antipsychotics and traditional services. Kane & Lieberman, 1987 ). ...
- New treatments: atypical antipsychotics and psychosocial interventions. ...
- Atypicals first-line drug. ...
- Barriers to progress. ...
- Using atypicals properly. ...
What is the most effective medicine for schizophrenia?
The most effective treatment for schizophrenia is a multidisciplinary approach including: 7
- Medication
- Psychological treatment
- Social support
Which therapies may treat schizophrenia?
The therapies most studied for schizophrenia include:
- Skills training
- Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) – a type of psychotherapy focused on building skills and changing behaviors
- Cognitive remediation – uses brain exercises to improve the cognitive impairment typical in schizophrenia
- Social cognition training – focuses on creating an understanding of social relationships and interactions
Are there any natural remedies for schizophrenia?
The following herbs can help in the treatment of schizophrenia:
- Ginkgo Biloba While some reviews of studies on ginkgo biloba are inconclusive, some studies indicate that the herb improves symptoms of schizophrenia. ...
- Asian Ginseng Asian Ginseng has natural antioxidant properties. It protects the neurons in the brain from damage and is therefore useful in the treatment of many mental problems notably ...
- St. ...
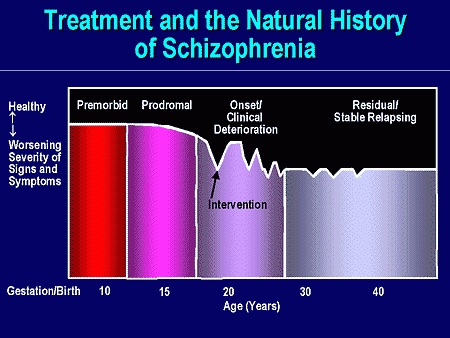
What is the most effect treatment for schizophrenia and most other psychotic disorders?
The best treatment for schizophrenia is a combination of medication, psychological therapy, and community support. People with schizophrenia experience more positive outcomes if they have: Medication and psychological treatment together. Medications to manage depression or anxiety, if needed.
What is the best treatment for psychotic disorders?
Antipsychotic medicines are usually recommended as the first treatment for psychosis. They work by blocking the effect of dopamine, a chemical that transmits messages in the brain. However, they're not suitable or effective for everyone, as side effects can affect people differently.
What types of treatment are used for schizophrenia?
Types of Antipsychotic MedicationsChlorpromazine (Thorazine)Fluphenazine (Prolixin)Haloperidol (Haldol)Perphenazine (Trilafon)Thioridazine (Mellaril)Thiothixene (Navane)Trifluoperazine (Stelazine)
What is first-line treatment for schizophrenia?
Antipsychotic medications are the first-line medication treatment for schizophrenia. They have been shown in clinical trials to be effective in treating symptoms and behaviors associated with the disorder. However, antipsychotic medications have significant side effects.
Which therapy seems to be the most effective treatment for schizophrenia?
A Combination is the Best Treatment for Schizophrenia A combination of approaches, including medications, psychotherapy, social support and family education, vocational and housing support, treatment for co-occurring issues, and sometimes electroconvulsive therapy, is most effective for most patients.
Which of the following has been most effective in the treatment of schizophrenia?
Medications. Medications are the cornerstone of schizophrenia treatment, and antipsychotic medications are the most commonly prescribed drugs. They're thought to control symptoms by affecting the brain neurotransmitter dopamine.
What is the most common medication for schizophrenia?
The most commonly prescribed types of medications for schizophrenia are antipsychotics, and there are two classifications of antipsychotics, typical and atypical....Atypical AntipsychoticsRisperdal (risperidone)Rexulti (brexpiprazole)Saphris (asenapine)Seroquel (quetiapine)Vraylar (cariprazine)Zyprexa (olanzapine)More items...•
What is schizophrenia spectrum?
Schizophrenia is a complicated illness that is often misunderstood. It is a chronic illness that can be debilitating since people with schizophreni...
What are the 5 types of schizophrenia?
The five types of schizophrenia are catatonic schizophrenia, disorganized schizophrenia/hebephrenic schizophrenia, paranoid schizophrenia, residual...
What are the 3 schizophrenia spectrum disorders?
The three schizophrenia spectrum disorders are schizoaffective disorder, schizophreniform disorder, and schizotypal personality disorder.
How to treat schizophrenia?
Schizophrenia requires lifelong treatment, even when symptoms have subsided. Treatment with medications and psychosocial therapy can help manage the condition. In some cases, hospitalization may be needed. A psychiatrist experienced in treating schizophrenia usually guides treatment.
What is the best way to help people with schizophrenia?
Most individuals with schizophrenia require some form of daily living support. Many communities have programs to help people with schizophrenia with jobs, housing, self-help groups and crisis situations. A case manager or someone on the treatment team can help find resources.
Why are people with schizophrenia reluctant to take medication?
Because medications for schizophrenia can cause serious side effects, people with schizophrenia may be reluctant to take them. Willingness to cooperate with treatment may affect drug choice. For example, someone who is resistant to taking medication consistently may need to be given injections instead of taking a pill.
What is the diagnosis of schizophrenia?
Diagnosis of schizophrenia involves ruling out other mental health disorders and determining that symptoms are not due to substance abuse, medication or a medical condition. Determining a diagnosis of schizophrenia may include:
How often do you give antipsychotics?
Some antipsychotics may be given as an intramuscular or subcutaneous injection. They are usually given every two to four weeks, depending on the medication. Ask your doctor about more information on injectable medications. This may be an option if someone has a preference for fewer pills and may help with adherence.
How to help someone with schizophrenia?
Avoid alcohol and drug use. Using alcohol, nicotine or recreational drugs can make it difficult to treat schizophrenia.
What is the treatment team for schizophrenia?
The treatment team also may include a psychologist, social worker, psychiatric nurse and possibly a case manager to coordinate care. The full-team approach may be available in clinics with expertise in schizophrenia treatment.
What was the first antipsychotic for schizophrenia?
Among the first antipsychotic medications used for the treatment of schizophrenia was Thorazine. Developed as a derivative of antihistamines, Thorazine was the first line of treatment that produced a calming effect on even the most severely agitated patients and allowed for the organization of thoughts. Despite their effectiveness in managing psychotic symptoms, conventional antipsychotics (such as Thorazine and Chlorpromazine) also produced significant side effects similar to that of neurological disorders. Therefore, psychotic symptoms were replaced with muscle tremors, involuntary movements, and muscle rigidity. Additionally, these conventional antipsychotics also produced tardive dyskinesia in patients, which included involuntary movements isolated to the tongue, mouth, and face (Tenback et al., 2006). While only 10% of patients reported the development of tardive dyskinesia, this percentage increased the longer patients were on the medication, as well as the higher the dose (Achalia, Chaturvedi, Desai, Rao, & Prakash, 2014). In efforts to avoid these symptoms, clinicians have been cognizant of not exceeding the clinically effective dose of conventional antipsychotic medications. If the management of psychotic symptoms cannot be resolved at this level, alternative medications are often added to produce a synergistic effect (Roh et al., 2014).
When does schizophrenia occur?
Schizophrenia typically occurs between late teens and mid-30s, with the onset of the disorder slightly earlier for males than females (APA, 2013).
What is a schizoaffective disorder?
Schizoaffective disorder is characterized by the psychotic symptoms included in schizophrenia and a concurrent uninterrupted period of a major mood episode— either a depressive or manic episode. It should be noted that because the loss of interest in pleasurable activities is a common symptom of schizophrenia, to meet the criteria for a depressive episode within schizoaffective disorder, the individual must present with a pervasive depressed mood (APA, 2013). While schizophrenia and schizophreniform disorder do not have a significant mood component, schizoaffective disorder requires the presence of a depressive or manic episode for the majority, if not the total duration of the disorder. While psychotic symptoms are sometimes present in depressive episodes, they often remit once the depressive episode is resolved. For individuals with schizoaffective disorder, psychotic symptoms should continue for at least two weeks in the absence of a major mood disorder (APA, 2013). This is the key distinguishing feature between schizoaffective disorder and major depressive disorder with psychotic features.
What are the symptoms of schizophrenia?
These schizophrenia spectrum disorders are defined by one of the following main symptoms: delusions, hallucinations, disorganized thinking (speech), disorganized or abnormal motor behavior, and negative symptoms. Individuals diagnosed with a schizophrenia spectrum disorder experience psychosis, which is defined as a loss of contact with reality. Psychosis episodes make it difficult for individuals to perceive and respond to environmental stimuli, causing a significant disturbance in everyday functioning. While there are a vast number of symptoms displayed in schizophrenia spectrum disorders, presentation of symptoms varies greatly among individuals, as there are rarely two cases similar in presentation, triggers, course, or responsiveness to treatment (APA, 2013).
How long does schizophrenia last?
Schizophreniform disorder is considered an “intermediate” disorder between schizophrenia and brief psychotic disorder as the symptoms are present for at least one month but not longer than six months . As you may recall, schizophrenia symptoms must be present for at least six months; A brief psychotic disorder is diagnosed when symptoms are present for less than one month. Approximately two-thirds of individuals who are initially diagnosed with schizophreniform disorder will have symptoms that last longer than six months, at which time their diagnosis is changed to schizophrenia (APA, 2013).
How long do schizoaffective symptoms last?
For individuals with schizoaffective disorder, psychotic symptoms should continue for at least two weeks in the absence of a major mood disorder (APA, 2013). This is the key distinguishing feature between schizoaffective disorder and major depressive disorder with psychotic features. 12.1.5. Delusional Disorder.
How many people are diagnosed with schizophrenia?
Less than 1% of the general population is diagnosed with schizophrenia and 20% of these people fully recovery from the disorder. Both genders have an equal risk of developing schizophrenia while men typically display more negative symptoms while women present with more mood-related symptoms.
What are the symptoms of schizophrenia?
Individuals with schizophrenia spectrum and other psychotic disorders lose contact with reality and experience a range of extreme symptoms that may include hallucinations, delusions, disorganized thinking (speech), and/or grossly disorganized or abnormal behavior (including catatonia).
When does schizophrenia start?
Schizophrenia often first appears in men in their late teens or early twenties. Onset in women is typically twenties or early thirties. Schizophrenia has a strong genetic component and may run in families, but can be effectively treated with medication and therapy.
What is a substance induced psychotic disorder?
Substance-induced psychotic disorder. Characterized by hallucinations and/or delusions due to the direct effects of a substance, or withdrawal from a substance.
What are the different types of delusions?
There are several different types of delusional disorder, including: grandiose, jealous, persecutory, somatic, erotomatic, and mixed. If an individual's delusions does not fall into one of these categories, or cannot be clearly defined, the disorder is classified as unspecified delusional disorder.
What is it called when you have one or more delusions?
Delusional disorder. An individual displays one or more delusions for at least a month. This is different from schizophrenia, as functioning is generally not impaired and behavior (other than the delusion) doesn't appear "odd".
How to manage schizophrenia?
Schizophrenia is a serious mental illness that affects your thinking, emotions, relationships, and decision making. And because there’s no cure, getting the proper treatment early is the best way to improve chances of managing the illness.#N#Schizophrenia treatment will center on managing your symptoms. You may need to stay on medication for a long time, possibly even for life. Psychotherapy, a kind of talk therapy, will likely also be a big part of the plan to help you understand and manage your symptoms. The right treatments, along with practical and emotional support from your loved ones, will go a long ways to help you navigate your life.
How to help a friend with schizophrenia?
Family education. Your knowledge of psychosis and schizophrenia can help a friend or family member who has it. Research shows that people with schizophrenia who have a strong support system do better than those without the encouragement of friends and family. Self-help groups.
What are the side effects of atypical antipsychotics?
Side effects. Different atypical antipsychotics may cause different side effects. Your doctor will help you pick a drug that works best for you with the minimum amount of adverse effects. Some common issues may include: 1 Weight gain 2 Higher blood sugar and cholesterol levels 3 Low blood pressure 4 Drowsiness 5 Type 2 diabetes 6 Constipation 7 Blurry vision 8 Dry mouth
What is active community treatment?
Assertive community treatment (ACT). This offers highly personalized services to help people with schizophrenia meet life’s daily challenges, like taking medications. ACT professionals also help them handle problems proactively and work to prevent crises. Social recovery therapy.
What is the aim of a family therapy program for schizophrenia?
The aim is to change the direction and prognosis for the disease by catching it in its earliest stages. Research shows that people with schizophrenia who get early and intensive treatment have the best long-term results.
How often do you need to take antipsychotics?
If you have trouble taking pills every day, you can get shots for several second-generation antipsychotics. These long-acting drugs require injections every couple of weeks to every 3 months.
What is cognitive behaioral therapy?
This type of therapy is also called cognitive remediation. It teaches people how to better recognize social cues, or triggers, and improve their attention, memory, and ability to organize their thoughts.
What is the treatment for psychotic disorders?
Most psychotic disorders are treated with a combination of medications and psychotherapy, which is a type of counseling. Medication: The main type of drug that doctors prescribe to treat psychotic disorders are “antipsychotics.”.
What type of therapy is used for a person with a psychotic disorder?
Psychotherapy: There are different types of counseling -- including individual, group, and family therapy – that can help someone who has a psychotic disorder. Most people with psychotic disorders are treated as outpatients, meaning they don’t live in institutions.
How long do psychotic disorders last?
There are different types of psychotic disorders, including: Schizophrenia: People with this illness have changes in behavior and other symptoms -- such as delusions and hallucinations -- that last longer than 6 months. It usually affects them at work or school, as well as their relationships.
What is a psychotic disorder?
Psychotic disorders are a group of serious illnesses that affect the mind. They make it hard for someone to think clearly, make good judgments, respond emotionally, communicate effectively, understand reality, and behave appropriately. When symptoms are severe, people with psychotic disorders have trouble staying in touch with reality ...
What are the symptoms of schizophrenia?
Schizoaffective disorder: People have symptoms of both schizophrenia and a mood disorder, such as depression or bipolar disorder. Learn more about the symptoms of schizoaffective disorder.
Why do doctors prescribe newer antipsychotics?
Doctors usually first prescribe the newer ones because they have fewer and more tolerable side effects than older antipsychotics.
How to diagnose a psychotic disorder?
To diagnose a psychotic disorder, doctors will take a medical and psychiatric history and possibly perform a brief physical exam. The person may get blood tests and sometimes brain imaging (such as MRI scans) to rule out physical illness or drug use like cocaine or LSD.
How to help people with schizophrenia?
Cognitive behavioral therapy, behavioral skills training, supported employment, and cognitive remediation interventions may help address the negative and cognitive symptoms of schizophrenia. A combination of these therapies and antipsychotic medication is common. Psychosocial treatments can be helpful for teaching and improving coping skills to address the everyday challenges of schizophrenia. They can help people pursue their life goals, such as attending school, working, or forming relationships. Individuals who participate in regular psychosocial treatment are less likely to relapse or be hospitalized. For more information on psychosocial treatments, see the Psychotherapies webpage on the NIMH website.
What is schizophrenia mental illness?
Overview. Schizophrenia is a serious mental illness that affects how a person thinks, feels, and behaves. People with schizophrenia may seem like they have lost touch with reality, which causes significant distress for the individual, their family members, and friends. If left untreated, the symptoms of schizophrenia can be persistent and disabling.
What are the symptoms of schizophrenia?
The symptoms of schizophrenia generally fall into the following three categories: Psychotic symptoms include altered perceptions (e.g., changes in vision, hearing, smell, touch, and taste), abnormal thinking, and odd behaviors.
How does psychosocial therapy help?
They can help people pursue their life goals, such as attending school, working, or forming relationships. Individuals who participate in regular psychosocial treatment are less likely to relapse or be hospitalized. For more information on psychosocial treatments, see the Psychotherapies webpage on the NIMH website.
What is CSC in psych?
Coordinated specialty care (CSC) is a general term used to describe recovery-oriented treatment programs for people with first episode psychosis, an early stage of schizophrenia. A team of health professionals and specialists deliver CSC, which includes psychotherapy, medication management, case management, employment and education support, and family education and support. The person with early psychosis and the team work together to make treatment decisions, involving family members as much as possible. Compared to typical care for early psychosis, CSC is more effective at reducing symptoms, improving quality of life, and increasing involvement in work or school. Check here for more information about CSC programs.
How does CSC help with early psychosis?
Compared to typical care for early psychosis, CSC is more effective at reducing symptoms, improving quality of life, and increasing involvement in work or school.
What does it mean when you are psychotic?
People with psychotic symptoms may lose a shared sense of reality and experience themselves and the world in a distorted way. Specifically, individuals typically experience: Hallucinations, such as hearing voices or seeing things that aren’t there.
What Are Psychotic Disorders?
Psychotic disorders are relatively rare and can be severe. It’s challenging to know what to do when you or someone you love is experiencing a psychotic disorder. This comprehensive guide to psychotic disorders will teach you about diagnosing and treating these serious mental health conditions.
Types of Psychotic Disorders
There is a wide range of psychotic disorders, each with its own features, symptoms, and diagnostic criteria. The following sections will explore eight main types of psychotic disorders.
Psychotic Disorders Causes and Risk Factors
The following sections will explore the three leading causes of psychotic disorders and the risk factors associated with psychotic disorders.
Diagnosis and Symptoms of Psychotic Disorders
Early diagnosis and treatment of psychotic disorder symptoms are time-sensitive. Delays in care can be life-changing and significantly alter the person’s likelihood of recovery. If you or someone you know struggles with psychosis, continue reading to learn about the symptoms and diagnosis process.
Psychotic Disorders Treatment
Psychotherapy and medications for psychotic disorders are the two primary treatments to help individuals recover. The following sections will provide additional information about therapy for psychotic disorders and medication.
