What causes high ammonia levels in wastewater?
When to List
- Sources and Activities that Suggest Listing Ammonia as a Candidate Cause. ...
- Site Evidence that Suggests Listing Ammonia as a Candidate Cause. ...
- Biological Effects that Suggest Listing Ammonia as a Candidate Cause. ...
- Site Evidence that Supports Excluding Ammonia as a Candidate Cause. ...
Where does ammonia come from in wastewater?
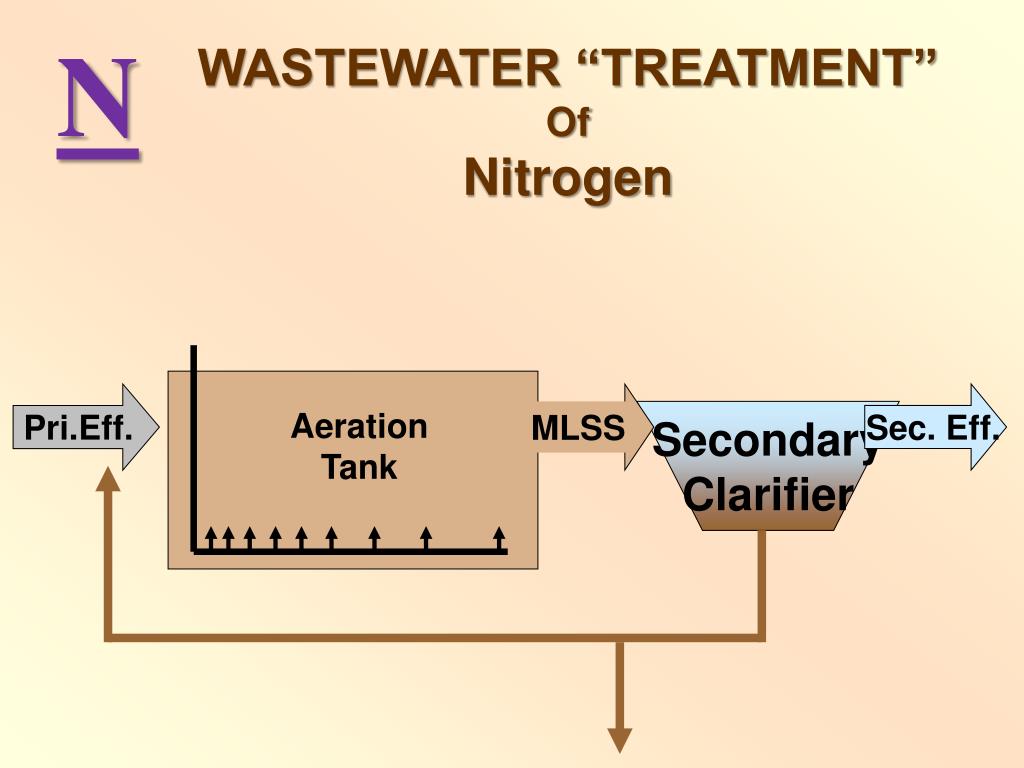
While traveling through sewer pipes, the majority of the nitrogen contained in raw sewage (urea and fecal material) is converted from organic-nitrogen to ammonia through a process called hydrolysis. Biological nitrification is the microbe-mediated process of oxidizing ammonia to remove nitrogenous compounds from wastewaters.
What are the typical ammonia values in wastewater?
achieving excellent nitrogen removal. The monthly average effluent total nitrogen of 4.4 mg/L meets the discharge permit limit of 5.0 mg/L. The monthly average effluent ammonia of 0.8 mg/L meets the discharge permit limit of 2.0 mg/L. There are, however, some days when minor problems occurred. Process adjustments during these
Can ammonia be higher than TKN in wastewater?
When the influent TKN concentration is higher than the ammonia concentration (TKN will always be ≥ ammonia nitrogen), it will be impossible to determine nitrification efficiency because ammonia is being added to the wastewater from the breakdown of organic nitrogen at the same time ammonia is being removed (nitrified) in the bioreactor ...

What is the source of ammonia in wastewater?
Ammonia in wastewater results from the breakdown of proteins and amino acids in organic waste (Pressley et al., 1972). Conventional wastewater treatment does not remove ammonia and the ammonia that enters the plant is discharged to receiving waters with plant effluent.
What are the 3 sources of ammonia?
In the environment, ammonia is part of the nitrogen cycle and is produced in soil from bacterial processes. Ammonia is also produced naturally from decomposition of organic matter, including plants, animals and animal wastes.
What are the primary sources of wastewater?
Wastewater comes from ordinary living processes: bathing, toilet flushing, laundry, dishwashing, etc. It comes from residential and domestic sources. Commercial wastewater comes from non-domestic sources, such as beauty salon, taxidermy, furniture refinishing, musical instrument cleaning, or auto body repair shops.
Why is ammonia removed from wastewater important?
The removal of ammonia from processes or waste effluents is required, due to its toxicity.
What is the source of ammonia?
Where does Ammonia Come From? Ammonia is produced for commercial fertilizers and other industrial applications. Natural sources of ammonia include the decomposition or breakdown of organic waste matter, gas exchange with the atmosphere, forest fires, animal and human waste, and nitrogen fixation processes.
What is ammonia nitrogen in wastewater?
Ammoniacal nitrogen (NH3-N) is a measure for the amount of ammonia, a toxic pollutant often found in landfill leachate and in waste products, such as sewage, liquid manure and other liquid organic waste products.
What is primary wastewater treatment?
Primary treatment removes material that will either float or readily settle out by gravity. It includes the physical processes of screening, comminution, grit removal, and sedimentation.
What are the sources of wastewater treatment?
There are three types of wastewater, or sewage: domestic sewage, industrial sewage, and storm sewage. Domestic sewage carries used water from houses and apartments; it is also called sanitary sewage. Industrial sewage is used water from manufacturing or chemical processes.
What are the two main sources of waste water?
Wastewater comes from water used in the home, in businesses and factories and from rain falling on roofs or the roads and pavements.
What is ammonia in wastewater treatment?
Nitrogen, as ammonia, is a critical nutrient in biological wastewater treatment. It is utilized by bacteria to make proteins, including enzymes needed to break down food or BOD as well as in making energy.
What chemical removes ammonia from water?
Ammonia is difficult to remove from water. It can be removed by cation exchange resin in the hydrogen form, which requires use of acid as a regenerant. Degasification can also be effective.
Where does nitrification occur in wastewater treatment?
In an activated sludge system or other biological treatment system, Nitrification under aerobic conditions. Nitrification is a bio-chemical reaction that occurs inside bacteria.
Why is ammonia used in fertilizer?
Therefore, ammonia is used in fertilizers to provide the nitrogen source required to increase crop yields. Ammonia and ammonia byproducts have a multitude of applications. For example, ammonia is often employed as a refrigerant in cooling systems.
How much ammonia is produced?
Ammonia is currently the second most commonly produced chemical in the world (after sulfuric acid), with around 200 million metric tons (m.t.) produced in 2018. Nearly 85% of all ammonia produced is used for fertilizers (1). Although nitrogen comprises almost 80% of the earth’s atmosphere, because it is inert, it is chemically ...
How does ammonia affect the atmosphere?
In the atmosphere, gaseous ammonia reacts with other pollutants to form tiny particles of ammonium salts that degrade air quality and, by affecting breathing, harm human health (2) . A 2018 study mapped atmospheric ammonia levels with unprecedented precision around the globe (3).
What is the most commonly produced chemical?
Environmental Management. August. 2020. Robert Eden. Ammonia is one of the most commonly produced chemicals globally. Efficiently removing it from wastewater streams could allow it to serve as a source of revenue in many applications. Ammonia is currently the second most commonly produced chemical in the world (after sulfuric acid), ...
What is the use of ammonia in textiles?
When converted back into a gas, it absorbs heat. The textile industry uses ammonia in the dyeing of wool, cotton, and silk, as well as in the production of nylon. Household floor cleaners and detergents commonly use ammonia. Chemical process industries (CPI) facilities use ammonia for pH control and to manage NOx.
Is ammonia a hazardous substance?
In many countries, including the U.S., authorities classify ammonia as an extremely hazardous substance. Facilities that produce, store, or use it in significant quantities must follow strict reporting procedures.
Is ammonia a good source of nitrogen?
Ammonia is also an important ingredient in fermentation processes — it serves as a source of nitrogen to encourage microorganism growth and adjust the pH. Although common in nature and widely used industrially, ammonia can damage human health and ecosystems. In many countries, including the U.S., authorities classify ammonia as an extremely ...
Why is ammonia nitrogen removed from wastewater?
Due to various ecological problems, it is required to remove the ammonia nitrogen from wastewater. Industrial wastewater that was not subjected to any purification was used in this study, while most processes described in the literature were carried out using synthetically prepared solutions.
What are the problems caused by ammonium discharge?
The excessive accumulation of ammonium that is discharged into water can cause serious ecological problems, such as: The accelerated eutrophication of lakes and rivers, the depletion of dissolved oxygen, and toxicity in fish and other aquatic animals in the water body [1].