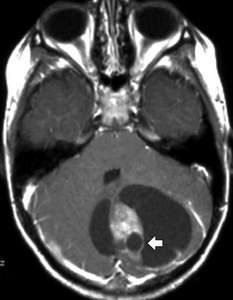
Is there a cure for non hematological cancer?
Keytruda (pembrolizumab) is indicated for the treatment of adult and pediatric patients with unresectable or metastatic solid tumors that have been identified as having a …
What are the two types of solid tumors?
in the same primary site: Use the 2018 Solid Tumor Rules •A melanoma diagnosed before 1/1/2021 and a subsequent melanoma diagnosed 1/1/2021 or later: Use the 2021 Cutaneous Melanoma Rules 7. Use the Solid Tumor Rules in the following order: A. For multiple tumors, you must decide whether they are a single or multiple primaries: i.
How has the treatment of cancer evolved over time?
Jan 01, 2018 · The Solid Tumor Cutaneous Melanoma Rules and General Instructions replace the 2007 Multiple Primary & Histology (MP/H) Rules beginning 1/1/2021. Revision status for remaining 2007 Multiple Primary and Histology rules: We are currently working on revisions to the Other Sites MP/H module. Release date has not yet been determined.
What kind of cancer can be treated with radiation?
Aug 21, 2019 · A biopsy is necessary to determine the type of lump. The doctor will take a small sample of tissue and send it to a laboratory where technicians will examine it under a microscope. The doctor may...
How are solid tumors treated?
Surgery for Solid Tumors.Surgery is a primary treatment for solid tumors. Every year, St. ... Radiation for Solid Tumors.Radiation treatment (RT) is used to destroy tumor cells to help control your child's cancer. ... Chemotherapy for Solid Tumors.Chemotherapy is treatment with medicines that kill cancer cells.
What is the first line of treatment for most solid tumors?
Chemotherapy with or without Retroperitoneal Lymph Node Dissection. The standard first-line chemotherapy for all patients is bleomycin, etoposide, and cisplatin (BEP) using a 5-day schedule.
Which anticancer is used for solid tumor?
Keytruda (pembrolizumab) is indicated for the treatment of adult and pediatric patients with unresectable or metastatic solid tumors that have been identified as having a biomarker referred to as microsatellite instability-high (MSI-H) or mismatch repair deficient (dMMR).May 23, 2017
What type of treatment is capable of removing a solid tumor from the body?
Treatment for most solid tumors starts with surgery. Your child's team will decide what the best treatment is after surgery. It may be chemotherapy, radiation therapy or both.
What does 1st line treatment mean?
The first treatment given for a disease. It is often part of a standard set of treatments, such as surgery followed by chemotherapy and radiation. When used by itself, first-line therapy is the one accepted as the best treatment.
What is first-line treatment?
First-line treatment or therapy simply refers to the initial, or first treatment recommended for a disease or illness. This may also be referred to as primary treatment, initial treatment, or induction therapy. With many conditions, including cancer, there are many possible treatments that could be effective.Mar 30, 2021
What are solid tumors?
An abnormal mass of tissue that usually does not contain cysts or liquid areas. Solid tumors may be benign (not cancer), or malignant (cancer). Different types of solid tumors are named for the type of cells that form them. Examples of solid tumors are sarcomas, carcinomas, and lymphomas.
What is chemotherapy drug?
Chemotherapy is a drug treatment that uses powerful chemicals to kill fast-growing cells in your body. Chemotherapy is most often used to treat cancer, since cancer cells grow and multiply much more quickly than most cells in the body.Mar 22, 2022
How is benign treated?
Treatment of Benign Tumors Surgery is a common type of treatment for benign tumors. The goal is to remove the tumor without damaging surrounding tissues. Other types of treatment may include medication or radiation.Jul 25, 2021
What are immunotherapy treatments?
Immunotherapy is treatment that uses certain parts of a person's immune system to fight diseases such as cancer. This can be done in a couple of ways: Stimulating, or boosting, the natural defenses of your immune system so it works harder or smarter to find and attack cancer cells.Dec 27, 2019
How do surgeons remove tumors?
The surgeon usually does this by cutting into your body and removing the cancer along with some surrounding healthy tissue to ensure that all of the cancer is removed. Your surgeon may also remove some lymph nodes in the area to determine whether the cancer has spread.
Which medicine is best for tumor?
Drugs Approved to Treat Solid Tumors Anywhere in the BodyDostarlimab-gxly.Entrectinib.Jemperli (Dostarlimab-gxly)Keytruda (Pembrolizumab)Larotrectinib Sulfate.Pembrolizumab.Rozlytrek (Entrectinib)Vitrakvi (Larotrectinib Sulfate)Aug 26, 2021
How long does it take for the FDA to approve a drug?
The FDA granted this application Priority Review designation, under which the FDA’s goal is to take action on an application within six months where the agency determines that the drug, if approved, would significantly improve the safety or effectiveness of treating, diagnosing or preventing a serious condition.
How does Keytruda work?
Keytruda works by targeting the cellular pathway known as PD-1/PD-L1 (proteins found on the body’s immune cells and some cancer cells). By blocking this pathway, Keytruda may help the body’s immune system fight the cancer cells. The FDA previously approved Keytruda for the treatment of certain patients with metastatic melanoma, ...
What is MSI H?
MSI-H and dMMR tumors contain abnormalities that affect the proper repair of DNA inside the cell. Tumors with these biomarkers are most commonly found in colorectal, endometrial and gastrointestinal cancers, but also less commonly appear in cancers arising in the breast, prostate, bladder, thyroid gland and other places.
Who approved Keytruda?
The FDA granted accelerated approval of Keytruda to Merck & Co. The FDA, an agency within the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, protects the public health by assuring the safety, effectiveness, and security of human and veterinary drugs, vaccines and other biological products for human use, and medical devices.
How long does Keytruda last?
For 78 percent of those patients, the response lasted for six months or more. Common side effects of Keytruda include fatigue, itchy skin (pruritus), diarrhea, decreased appetite, rash, fever (pyrexia), cough, difficulty breathing (dyspnea), ...
Is Keytruda approved for melanoma?
The FDA previously approved Keytruda for the treatment of certain patients with metastatic melanoma, metastatic non-small cell lung cancer, recurrent or metastatic head and neck cancer, refractory classical Hodgkin lymphoma, and urothelial carcinoma. Keytruda was approved for this new indication using the Accelerated Approval pathway, ...
Does Keytruda cause hepatitis?
Keytruda can cause serious conditions known as immune-mediated side effects, including inflammation of healthy organs such as the lungs (pneumonitis), colon (colitis), liver (hepatitis), endocrine glands (endocrinopathies) and kidneys (nephritis).
What is a large cell carcinoma?
Large cell carcinoma lacks the features of small cell carcinoma, adenocarcinoma, or squamous carcinoma.
What is the code for adenocarcinoma?
Diagnosis for a single tumor is adenocarcinoma 8140 with the majority or predominant part of tumor being enteric- type adenocarcinoma 8144. Code the subtype/variant: enteric-type adenocarcinoma 8144. Example 2:
2021 Cutaneous Melanoma Rules
Use the 2021 Solid Tumor Cutaneous Melanoma rules to determine the number of primaries to abstract and the histology to code for cases diagnosed 1/1/2021 forward. The Solid Tumor Cutaneous Melanoma coding rules and the 2018 General Instructions replace the 2007 Multiple Primary & Histology (MP/H) Rules beginning 1/1/2021.
Revision History
The change log contains updates made in December 2020. Please see the Revision Archive for earlier changes.
Histology Coding Clarifications
On occasion, data collection requirements of AJCC and NCI SEER have resulted in conflicting cancer coding instructions for cancer registrars. For more information and specific instructions about reviewing cases already coded, please visit the Histology Coding Clarifications page.
How is cancer treated?
Cancer can be treated by surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, hormonal therapy, targeted therapy (including immuno therapy such as monoclonal antibody therapy) and synthetic lethality, most commonly as a series of separate treatments (e.g. chemotherapy before surgery). The choice of therapy depends upon the location and grade ...
What is the treatment for brain cancer?
External beam radiation is commonly used for brain cancer. The area radiated typically includes the tumor and an area surrounding the tumor. For metastatic brain tumors, radiation is sometimes given to the entire brain. Radiation therapy uses special equipment to send high doses of radiation to the cancer cells.
How do you treat colon cancer?
There are five different stages of colon cancer, and these five stages all have treatment: 1 Stage 0, is where the patient is required to undergo surgery to remove the polyp (American Cancer Society ). 2 Stage 1, depending on the location of the cancer in the colon and lymph nodes, the patient undergoes surgery just like Stage 0. 3 Stage 2 patients undergoes removing nearby lymph nodes, but depending on what the doctor says, the patent might have to undergo chemotherapy after surgery (if the cancer is at higher risk of coming back). 4 Stage 3, is where the cancer has spread all throughout the lymph nodes but not yet to other organs or body parts. When getting to this stage, Surgery is conducted on the colon and lymph nodes, then the doctor orders Chemotherapy (FOLFOX or CapeOx) to treat the colon cancer in the location needed (American Cancer Society ). The last a patient can get is Stage 4. 5 Stage 4 patients only undergo surgery if it is for the prevention of the cancer, along with pain relief. If the pain continues with these two options, the doctor might recommended radiation therapy. The main treatment strategy is chemotherapy due to how aggressive the cancer becomes in this stage, not only to the colon but to the lymph nodes.
Why is there a higher incidence of concurrent cancer during pregnancy?
The incidence of concurrent cancer during pregnancy has risen due to the increasing age of pregnant mothers and due to the incidental discovery of maternal tumors during prenatal ultrasound examina tions.
Which gene is lethal for DNA repair?
Mutations in DNA repair genes BRCA1 or BRCA2 (active in homologous recombinational repair) are synthetically lethal with inhibition of DNA repair gene PARP1 (active in the base excision repair and in the microhomology-mediated end joining pathways of DNA repair).
What is targeted therapy?
Small molecule targeted therapy drugs are generally inhibitors of enzymatic domains on mutated, over expressed, or otherwise critical proteins within the cancer cell. Prominent examples are the tyrosine kinase inhibitors imatinib (Gleevec/Glivec) and gefitinib (Iressa).
How does genome sequencing help cancer patients?
Cancer genome sequencing helps in determining which cancer the patient exactly has for determining the best therapy for the cancer.
What is a tumor?
Outlook. A tumor is a mass or lump of tissue that may resemble swelling. Not all tumors are cancerous, but it is a good idea to see a doctor if one appears. The National Cancer Institute define a tumor as “an abnormal mass of tissue that results when cells divide more than they should or do not die when they should.”.
Where do malignant tumors originate?
Different types of malignant tumor originate in different types of cell. Examples include: Carcinoma: These tumors form from epithelial cells, which are present in the skin and the tissue that covers or lines the body’s organs. Carcinomas can occur in the stomach, prostate, pancreas, lung, liver, colon, or breast.
What causes fibroids in the uterus?
Uterine fibroids are common and can cause: 1 vaginal bleeding 2 pelvic pain or discomfort 3 urinary incontinence
Where do adenomas develop?
Adenomas develop in glandular epithelial tissue, which is the thin membrane that covers glands, organs, and other structures in the body. Examples include: polyps in the colon. fibroadenomas, a common form of benign breast tumor. hepatic adenomas, which occur on the liver. Adenomas do not start as cancer.
What happens when you have cancer?
When a person has cancer, new cells form when the body does not need them. If there are too many new cells, a group of cells, or tumor, can develop. Although some tumors are benign and consist of noncancerous cells, others are malignant. Malignant tumors are cancerous, and the cells can spread to other parts of the body.
Is a malignant tumor a benign tumor?
Malignant: Malignant tumors are cancerous. The cells can grow and spread to other parts of the body. It is not always clear how a tumor will act in the future. Some benign tumors can become premalignant and then malignant. For this reason, it is best to monitor any growth.
Where do sarcomas originate?
They originate in the cells outside the bone marrow. Most sarcomas are malignant. Germ cell tumor: These tumors develop in the cells that produce sperm and eggs. They usually occur in the ovaries or testicles, but they may also appear in the brain, abdomen, or chest.
How to get rid of cancer cells?
tell blood vessels to grow toward tumors. These blood vessels supply tumors with oxygen and nutrients and remove waste products from tumors. hide from the immune system. The immune system normally eliminates damaged or abnormal cells. trick the immune system into helping cancer cells stay alive and grow.
What is the microenvironment of a tumor?
Within a tumor, cancer cells are surrounded by a variety of immune cells, fibroblasts, molecules, and blood vessels— what’s known as the tumor microenvironment. Cancer cells can change the microenvironment, which in turn can affect how cancer grows and spreads.
What are some examples of cancer?
Not every change in the body’s tissues is cancer. Some tissue changes may develop into cancer if they are not treated, however. Here are some examples of tissue changes that are not cancer but, in some cases, are monitored because they could become cancer: 1 Hyperplasia occurs when cells within a tissue multiply faster than normal and extra cells build up. However, the cells and the way the tissue is organized still look normal under a microscope. Hyperplasia can be caused by several factors or conditions, including chronic irritation. 2 Dysplasia is a more advanced condition than hyperplasia. In dysplasia, there is also a buildup of extra cells. But the cells look abnormal and there are changes in how the tissue is organized. In general, the more abnormal the cells and tissue look, the greater the chance that cancer will form. Some types of dysplasia may need to be monitored or treated, but others do not. An example of dysplasia is an abnormal mole (called a dysplastic nevus) that forms on the skin. A dysplastic nevus can turn into melanoma, although most do not. 3 Carcinoma in situ is an even more advanced condition. Although it is sometimes called stage 0 cancer, it is not cancer because the abnormal cells do not invade nearby tissue the way that cancer cells do. But because some carcinomas in situ may become cancer, they are usually treated.
Why is cancer a genetic disease?
Genetic changes that cause cancer can happen because: of errors that occur as cells divide.
What is cancer in the body?
The Definition of Cancer. Cancer is a disease in which some of the body’s cells grow uncontrollably and spread to other parts of the body. Cancer can start almost anywhere in the human body, which is made up of trillions of cells. Normally, human cells grow and multiply (through a process called cell division) to form new cells as ...
Where do cancer cells travel?
Cancer cells can break away from the original tumor and travel through the blood or lymph system to distant locations in the body, where they exit the vessels to form additional tumors. This is called metastasis.
What is cancer caused by?
Cancer is a disease caused when cells divide uncontrollably and spread into surrounding tissues. Cancer is caused by changes to DNA. Most cancer-causing DNA changes occur in sections of DNA called genes. These changes are also called genetic changes.
What is it called when cancer spreads to another part of the body?
With time, the cancer cell can grow and form a new tumor that may not be near the primary site. When cancer spreads to another part of the body, it is called metastatic cancer .
What type of cancer starts in the lymph nodes?
Lymphomas. Cancers that start in cells of the lymph nodes and lymphatic system. They may cause tumors in lymph tissue. Brain cancers, nerve cancers, melanomas, and certain testicular and ovarian cancers are other types of cancer categories. They start in different kinds of cells in the body.
Why do cells divide?
Normal, healthy cells divide to replace those lost or damaged and then stop dividing. Cells normally divide and increase in number in a process called mitosis. Cancer is a condition where cells multiply. But this multiplying is continuous and not normal. The cells divide and grow out of control. They may grow into nearby tissue or spread ...
How does cancer spread?
The cancer may spread by directly entering nearby tissues. The cancer may spread throughout the body. This is called systemic spread. The cancer cell may get into and travel through the: Blood system. Arteries and veins take blood to and from all areas of the body.
Where does cancer start?
Cancers start in a single cell that has been damaged (mutated). That cell is the source of the primary cancer. The cancer is always named for the primary site where the original or first tumor started, such as skin, colon, or breast.
Is liver cancer a cancer?
It is not called liver cancer. Lung cancers are those that started from a lung cell. If the cancer spreads to the brain, it's called metastatic lung cancer, not brain cancer. When cancer spreads to the nearby lymph nodes, those nodes are said to contain metastatic cancer.
Can cancer spread to distant parts of the body?
They may grow into nearby tissue or spread to distant parts of the body. Over time, the mass of cancer cells can get big enough to make lumps (also called masses or tumors) that can be felt or seen. But, not all tumors are cancer. Tumors can be benign or malignant:
What is the treatment for metastatic lung cancer?
Chemotherapy is often the first course of treatment for cancer metastatic to the lung. Other treatment options may be used, depending on the primary cancer. Options may include targeted therapies, immunotherapy, or a combination of treatments. Palliative therapy may be used to reduce pain or help manage other symptoms.
What is secondary lung cancer?
Secondary lung cancer, on the other hand, is cancer that has spread to a lung from another part of the body. A second primary lung cancer is a new lung cancer that develops in the lungs unrelated to the original cancer.
Is lung cancer a secondary tumor?
In the same way that a brain tumor that originates from a primary lung tumor is deemed secondary brain cancer, a tumor in the lungs that has metastasized from cancer elsewhere in the body is called secondary lung cancer. Cancer that originates in the breast and spreads to the lungs, for instance, falls into this category.
What is the most common site of lung cancer?
Lung cancer in the brain is considered secondary brain cancer. The most common sites for lung cancer metastases are: 4. Lymph nodes . Liver.
Is secondary lung cancer the same as primary lung cancer?
It will be referred to as a lung metastasis from primary lung cancer. On your lab report, it might say something like “primary lung cancer metastatic to another region in the lungs.”. Symptoms of secondary lung cancer are the same as the symptoms of primary lung cancer. How Cancer Spreads to Your Lungs and What It Means.
Is lung cancer a metastasis?
If the recurrent cancer is the same type of cancer (lung cancer cells with the same mutation), the new appearance will be considered a metastasis from the primary lung cancer, not a new primary or second primary cancer.
Can doctors determine the origin of lung cancer?
Doctors can’t always determine the origin of a lung cancer tumor. Tests may not be able to confirm if the cancer started in the lung or another part of the body. 11 In this instance, the tumor is known as " cancer of unknown primary " or “metastatic cancer to the lungs of unknown origin.".
What are the symptoms of schwannoma?
Facial paralysis. Trouble swallowing. Trouble moving the eye. Numbness or tingling. Muscle weakness. Imaging: If you have symptoms of schwannoma, your doctor will use scans such as CT and MRI to see where the tumor is in the body and how big it is.
How to tell if you have a schwannoma?
Some people with schwannoma have symptoms, but others don’t. Symptoms may differ depending on where the tumor is in the body. Symptoms can include: 1 Hearing loss or ringing in the ears 2 Dizziness and balance problems 3 Pain 4 Facial paralysis 5 Trouble swallowing 6 Trouble moving the eye 7 Numbness or tingling 8 Muscle weakness
Is schwannoma a rare disease?
Schwannoma is not common. It is a rare disease, which means it affects fewer than 200,000 people. Schwannoma is the most common type of peripheral nerve tumors in adults. Schwannoma can occur in people of all ages.
Overview
Types of treatments
The treatment of cancer has undergone evolutionary changes as understanding of the underlying biological processes has increased. Tumor removal surgeries have been documented in ancient Egypt, hormone therapy and radiation therapy were developed in the late 19th century. Chemotherapy, immunotherapy and newer targeted therapies are products of the 20th century. As new information about the biology of cancer emerges, treatments will be developed and modifie…
Symptom control and palliative care
Although the control of the symptoms of cancer is not typically thought of as a treatment directed at the cancer, it is an important determinant of the quality of life of cancer patients, and plays an important role in the decision whether the patient is able to undergo other treatments. Although doctors generally have the therapeutic skills to reduce pain, chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting, diarrhea, hemorrhage and other common problems in cancer patients, the multidiscipli…
Research
Clinical trials, also called research studies, test new treatments in people with cancer. The goal of this research is to find better ways to treat cancer and help cancer patients. Clinical trials test many types of treatment such as new drugs, new approaches to surgery or radiation therapy, new combinations of treatments, or new methods such as gene therapy.
A clinical trial is one of the final stages of a long and careful cancer research process. The searc…
Complementary and alternative
Complementary and alternative medicine (CAM) treatments are the diverse group of medical and health care systems, practices, and products that are not part of conventional medicine and have not been shown to be effective. "Complementary medicine" refers to methods and substances used along with conventional medicine, while "alternative medicine" refers to compounds used instead of conventional medicine. CAM use is common among people with cancer; a 2000 stud…
Special circumstances
The incidence of concurrent cancer during pregnancy has risen due to the increasing age of pregnant mothers and due to the incidental discovery of maternal tumors during prenatal ultrasound examinations.
Cancer treatment needs to be selected to do least harm to both the woman and her embryo/fetus. In some cases a therapeutic abortion may be recommended.
Racial and social disparities
Cancer is a significant issue that is affecting the world. Specifically in the U.S, it is expected for there to be 1,735,350 new cases of cancer, and 609,640 deaths by the end of 2018. Adequate treatment can prevent many cancer deaths but there are racial and social disparities in treatments which has a significant factor in high death rates. Minorities are more likely to suffer from inadequate treatment while white patients are more likely to receive efficient treatments in a tim…
See also
• American Cancer Society
• Cancer and nausea
• Cancer prevention
• Experimental cancer treatment
• Global Task Force on Expanded Access to Cancer Care and Control in Developing Countries