Medication
- The name Bethesda Units (BUs) was adopted at a conference that occurred in Bethesda, MD.
- Alternative Names: factor VIII deficiency; classic hemophilia; bleeding disorder – hemophilia A
- Famous people with hemophilia A:
Therapy
Treatment for hemophilia is extremely expensive. This is a lifetime expense. The average cost is $40,000 to $50,000 a year. Complications from hemophilia can bring further expenses, which may be over $100,000. Clotting factor is also expensive.
Self-care
What Are the Treatments for Hemophilia?
- Monitoring. ...
- Acquiring a blood-borne disease: In the past, people receiving clotting factor from donated blood ran the risk of contracting a blood-borne disease.
- Changes to the immune system: Your immune system may begin to recognize the administered clotting factor as foreign and then destroy it.
Nutrition
Table 2. Acquired hemophilia A Treatment Market Drivers in China Market Table 3. Acquired hemophilia A Treatment Market Restraints in China Market Table 4. Key Players of Acquired hemophilia A Treatment in China Market Table 5. Top Acquired hemophilia A ...
What is the life expectancy for people with hemophilia?
How much does it cost to treat hemophilia?
How do you cure hemophilia?
What is hemophilia and how is it treated?
What is the mainstay of treatment for hemophilia?
Replacement of the congenitally deficient factor VIII or IX through plasma-derived or recombinant concentrates is the mainstay of treatment for hemophilia.
Which gene therapy is best for hemophilia?
Rationale for gene therapy for hemophilia Over the years, hepatic in vivo gene transfer using adeno-associated viral (AAV) vectors has shown the best success in preclinical and clinical studies, with several clinical studies for both hemophilia A and B enrolling patients for phase 3 trials.
Is gene therapy an option for hemophilia?
Gene therapy offers the potential for a cure for patients with hemophilia by establishing continuous endogenous expression of factor VIII or factor IX (FIX) following transfer of a functional gene to replace the hemophilic patient's own defective gene.
Why is gene therapy good for hemophilia?
Gene therapy for hemophilia involves using a modified virus (which does not cause disease) to introduce a copy of the gene that encodes for the clotting factor that's missing in patients. Following treatment with the virus, patients should begin producing their own clotting factor normally.
How to treat bleeding disorders?
Treatment Options for Bleeding Disorders 1 Standard half-life therapies: Standard half-life therapies are used to treat hemophilia A and B, some types of von Willebrand disease, and some rare factor disorders. Dosing can be anywhere from three times a week to every day, depending on the person. 2 Extended half-life (EHL) therapies: EHL contains a molecule that has been modified in some way to delay the breaking down of factor in the body. This results in higher levels of factor in the body lasting for longer, resulting in less frequent infusions. How long the factor is effective in the body depends on the person. Extended half-life therapies are mostly used to treat hemophilia A and B. 3 Bypassing agents are used to treat bleeds in people with hemophilia with inhibitors. These treatments contain other factors that can stimulate the formation of a clot and stop bleeding.
What is EHL therapy?
Extended half-life (EHL) therapies: EHL contains a molecule that has been modified in some way to delay the breaking down of factor in the body. This results in higher levels of factor in the body lasting for longer, resulting in less frequent infusions. How long the factor is effective in the body depends on the person.
What is extended half life therapy?
Extended half-life therapies are mostly used to treat hemophilia A and B. Bypassing agents are used to treat bleeds in people with hemophilia with inhibitors. These treatments contain other factors that can stimulate the formation of a clot and stop bleeding.
Treatment
Hemophilia is associated with various clotting factors. Patients with hemophilia can receive replacement therapy for the specific clotting factor in which they are deficient. Replacement therapy involves infusing clotting factors intravenously. It is effective in combating bleeding episodes, and patients can receive continuous replacement therapy.
Desmopressin
Patients diagnosed with moderate or severe hemophilia A are treated with factor VIII concentrates. Most patients with mild hemophilia A are treated with desmopressin (1-Deamino-8-D-ArgininVasoPressin).
Blood Clotting Intervention
Various studies have been conducted to understand the randomized or quasi-randomized clinical trials involving children and adults with congenital hemophilia A and B. They included patients with varying degrees of severity and ages. Patients with factor VIII or IX inhibitors were excluded from the study.
Treatment Centers and Factor Concentrates
Hemophilia treatment centers are equipped with doctors and nurses who are capable of providing good quality medical care for patients with hemophilia. They provide comprehensive care that can help patients to prevent serious issues related to hemophilia and address major concerns related to a bleeding disorder.
Treatment Products – Emicizumab and DDAVP
Emicizumab replaces the function of factor VIII rather than replacing the deficient factor VIII directly. It is also known as Hemlibra ® or ACE910. It has the potential to reduce bleeding episodes in patients with hemophilia A. It is administered as an injection under the skin and acts as prophylaxis by treating breakthrough bleeds.
How to treat hemophilia?
The preferred treatment for hemophilia is factor replacement therapy. Hemophilia is treated by injecting the missing factor protein into the affected person’s vein. The injection makes the factor immediately available in the bloodstream and the body is able to activate it to continue the clotting cascade and stop the bleeding.
What is a hematologist?
A hematologist can diagnose, provide guidance, and prescribe the factor concentrate and dosage that is needed to treat bleeds prophylactically or on demand. However, hemophilia is a complex disorder that often requires care from other health professionals, like physical therapists, geneticists, and social workers. In order to facilitate comprehensive care for patients with hemophilia, the United States federal government provides funds that support hemophilia treatment centers (HTCs) in cities across the country. HTCs help coordinate care among medical experts to treat all aspects of hemophilia. Please visit www.cdc.gov to find an HTC near you.
How much does hemophilia B weigh?
Actual dosing should be determined by doctor and patient based on that individual’s needs.) For example, a person with severe hemophilia B that weighs 120 pounds, or 54 kilograms, (120 ÷ 2.2) may be given the following doses:
How is hemophilia treated?
Hemophilia is treated with factor concentrates. These factor concentrates are infused via a vein (IV). Hemophilia can be treated in two different methods: on demand only (when bleeding episodes occur) or prophylaxis (receiving factor once, twice, or three times per week to prevent bleeding episodes).
What is hemophilia 2020?
on August 24, 2020. Hemophilia is an inherited bleeding disorder . A person with hemophilia is missing a blood factor needed to clot the blood which results in excessive bleeding.
What is the classification of hemophilia?
Hemophilia can be classified by the particular coagulation factor missing. Hemophilia A results from a deficiency in factor 8. Hemophilia B (also called Christmas disease) results from a deficiency in factor 9. Hemophilia C (also called Rosenthal syndrome) results from a deficiency in factor 11.
What is the bleed rate for hemophilia C?
Hemophilia can also be classified by the amount of coagulation factor found. The less coagulation factor you have, the more likely you are to bleed. Mild: 6–40%.
How do you know if you have hemophilia?
People with hemophilia are sometimes referred to as “free bleeders,” meaning they bleed easily. Depending on the severity, bleeding may occur spontaneously (without injury) or after surgery or trauma. Symptoms include: 1 Prolonged nosebleeds 2 Bleeding from gums 3 Large bruises 4 Prolonged bleeding after surgery or shots, including circumcision 5 Swelling of the large joints (shoulders, elbows, knees, ankles) from bleeding into the joint 6 Pain from bleeding into joint or muscle
What are the symptoms of hemophilia?
Depending on the severity, bleeding may occur spontaneously (without injury) or after surgery or trauma. Symptoms include: Prolonged nosebleeds. Bleeding from gums.
Do men inherit hemophilia?
To understand the inheritance of hemophilia, we need to talk a little about genetics. Males have an X chromosome from their mother and a Y chro mosome from their father. Females inherit an X chromosome from both their father and mother.
What is the ultimate goal of hemophilia treatment?
However, the ultimate therapeutic goal is to eliminate the inhibitor and cure the disease. The treatments used to accomplish these objectives usually depend on ...
What are the adverse effects of hemophilia?
Common adverse effects include cytopenia, alopecia, toxic hepatitis, and severe bacterial infections. [ 20] . In an analysis of 172 patients with acquired hemophilia, about half of the cohort experienced morbidity unrelated to bleeding (usually due to the adverse effects of immunosuppression). [ 14] .
Why is eradicating a hematocrit inhibitor important?
Eradicating the inhibitor is important to restore normal hemostasis and minimize the patient’s risk of bleeding. [ 17] . Patients who achieve complete remission (eradication of the inhibitor) have been shown to have a better overall survival than patients who do not achieve complete remission.
Does hemophilia cause a lower response rate?
The advanced age of patients with acquired hemophilia and the presence of comorbid conditions may preclude the most aggressive treatments and necessitate dose reductions (eg, steroids in patients with diabetes), which may lead to a lower response rate and, thus, a decreased survival rate .
Can hemophilia bleed spontaneously?
Patients with acquired hemophilia A can bleed after negligible or minor trauma, and may even bleed spontaneously. Any physical activity may trigger bleeding in soft tissues. Until inhibitors are eradicated, patients with acquired hemophilia should avoid activities with a significant risk of trauma.
Is immunotherapy better than cyclophosphamide?
Nonetheless, patients who receive immunotherapy typically do better than patients who do not. [ 20] Careful selection and close monitoring of immunosuppressive therapy is critical. Although cyclophosphamide may enhance inhibitor eradication, it is associated with severe adverse effects, especially in elderly persons.
Is RFVIIA used for hemophilia?
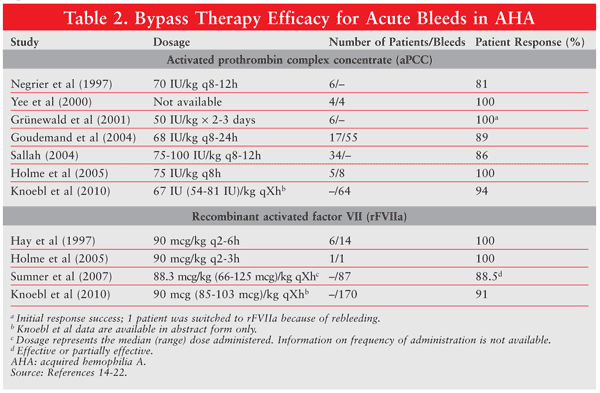
Initially developed for use in patients with con genital hemophilia with alloantibody inhibitors, rFVIIa has been successfully used in patients with acquired hemophilia. It binds to the surface of activated platelets, where it supports thrombin generation and bypasses the need for FVIII. [ 34, 9]
Why is whole blood used?
Since a bag of whole blood only has a small amount of clotting factors, many bags of blood would be needed to stop bleeding. There is a danger of overloading the circulatory system. Whole blood may be used if the person has lost a large amount of blood and needs to replace other blood parts such as red cells.
Why do you use HLA matching?
Using donated platelets that have been HLA matched to the person receiving them is another way to keep antibodies from forming. HLA matching is a way of testing a blood donor’s platelets. It is used to identify a donor whose platelets are most compatible with the blood of the person who will get the platelets.
What is IV in cryo?
The IV is the tubing that the cryo flows through to get into the patient’s blood. People who have to use cryo regularly can talk with their doctors about setting up a known donor pool . This is a group of people at low risk of having a virus who will agree to donate plasma for the patient.
Can you give blood if you have a virus?
The ones whose answers suggest that they might have a virus or other illness are not allowed to give their blood. The blood itself is tested for hepatitis viruses and HIV. These steps keep our blood supply as safe as possible from disease. Also, factor concentrates are now treated to remove or kill viruses.