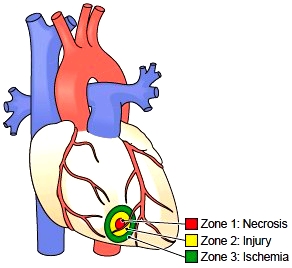
Medication
Pharmacotherapy or surgical treatment (eg, operable coronary artery disease [CAD]) may be appropriate in some cases, whereas radiofrequency ablation is effective in a variety of disorders. ... External electrical defibrillation remains the most successful treatment for ventricular fibrillation (VF).
Procedures
If the patient remains in ventricular fibrillation, pharmacological treatment should begin. Epinephrine is the first drug given and may be repeated every 3 to 5 minutes. If epinephrine is not effective, the next medication in the algorithm is amiodarone 300 mg.
Nutrition
A heart monitor that will read the electrical impulses that make your heart beat will show that your heart is beating erratically or not at all. Pulse check. In ventricular fibrillation, there will be no pulse. To find out what caused your ventricular fibrillation, you'll have additional tests, which can include: Electrocardiogram (ECG).
What is the most effective treatment for ventricular fibrillation?
Defibrillation success rates decrease about 5%-10% for each minute after the onset of VF. In strictly monitored settings where defibrillation was performed most promptly, success rates of 85% have been reported.
What is the first drug given for ventricular fibrillation?
What tests are done to diagnose ventricular fibrillation?
What is the success rate of defibrillation for ventricular fibrillation (VF)?
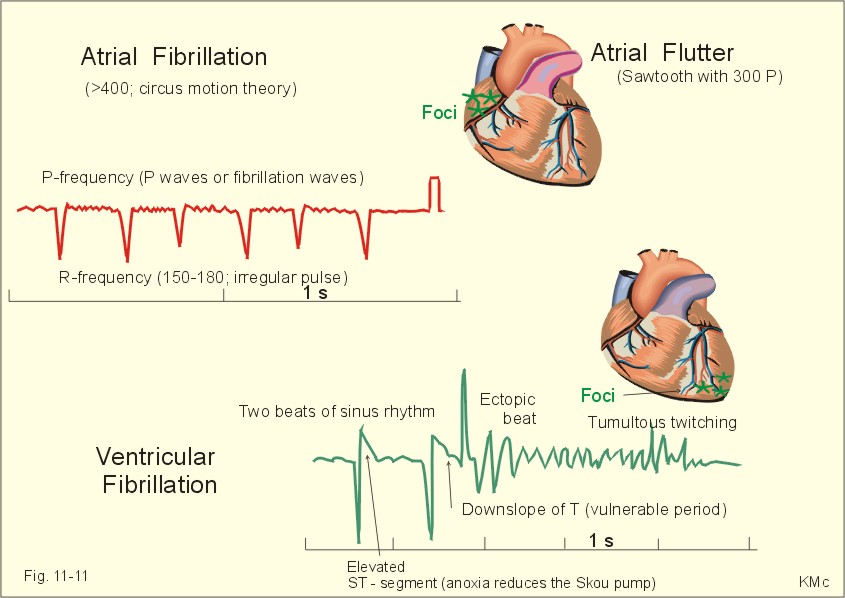
What is the first treatment for ventricular fibrillation?
Epinephrine is the first drug given and may be repeated every 3 to 5 minutes. If epinephrine is not effective, the next medication in the algorithm is amiodarone 300 mg. Defibrillation and medication are given in an alternating fashion between cycles of 2 minutes of high-quality CPR.
What is the drug of choice for ventricular arrhythmias?
Amiodarone (Cordarone, Pacerone, Nexterone) Amiodarone is the drug of choice for the treatment of hemodynamically unstable VT that is refractory to other antiarrhythmic agents. Prehospital studies currently suggest that amiodarone is safe and efficacious for use in out-of-hospital cardiac arrest.
What is the treatment of choice for ventricular tachycardia?
If you have ventricular tachycardia, you may be given medications called anti-arrhythmics by mouth or IV to slow the fast heart rate. Other heart medications, such as calcium channel blockers and beta blockers, may be prescribed with anti-arrhythmic drugs.
What is the initial treatment response for a patient in either pulseless ventricular tachycardia or ventricular fibrillation?
Ventricular Fibrillation/Pulseless Ventricular Tachycardia. The most critical interventions during the first minutes of VF or pulseless VT are immediate bystander CPR (Box 1) with minimal interruption in chest compressions and defibrillation as soon as it can be accomplished (Class I).
Which of the following drugs is used in ventricular fibrillation?
In acute ventricular fibrillation (VF), drugs (eg, vasopressin, epinephrine, amiodarone) are used after three defibrillation attempts are performed to restore normal rhythm.
Which drug is used to treat atrial and ventricular tachycardia or fibrillation?
Procainamide is a medication used to manage and treat ventricular arrhythmias, supraventricular arrhythmias, atrial flutter, atrial fibrillation, AV nodal re-entrant tachycardia, and Wolf-Parkinson-White syndrome. It is a Class 1A antiarrhythmic agent.
Is amiodarone used for ventricular tachycardia?
Amiodarone is used to manage virtually all forms of supraventricular and ventricular tachycardia and has therefore become one of the most frequently used antiarrhythmic drugs in clinical practice.
Can beta blockers treat ventricular tachycardia?
Furthermore, beta-blockers have been advocated for use in patients with ventricular fibrillation (VF) and ventricular tachycardia (VT), in whom these agents appear to reduce the incidence of recurrent ventricular tachyarrhythmias 6, 7.
What is the gold standard treatment for pulseless ventricular tachycardia and ventricular fibrillation?
Treatment / Management Medical treatment of pulseless VT usually is carried out along with defibrillation and includes intravenous vasopressors and antiarrhythmic drugs. 1 mg of epinephrine IV should be given every 3 to 5 minutes. Epinephrine can be replaced by vasopressin given 40 units IV once.
What two treatments may save a patient with ventricular fibrillation?
TreatmentCardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR). CPR mimics the pumping motion of the heart and keeps blood flowing through the body. First call 911 or your local emergency number. ... Defibrillation. This treatment is also called cardioversion.
Why is epinephrine used in ventricular fibrillation?
Clinical studies suggest that epinephrine facilitates ventricular fibrillation (VF) although mechanisms remain unclear. We tested the hypothesis that epinephrine increases the probability of inducing VF and stabilizes VF in association with shortening of fibrillation action potential duration.
Why is VF and VT shockable?
Shockable rhythms are rhythms that are caused by an aberration in the electrical conduction system of the heart....CAUSESTREATMENTTension pneumothoraxneedle decompression with eventual chest tubeThrombosis (myocardial infarction or pulmonary embolus)treat per causeTraumasurgical evaluation2 more rows•Jul 12, 2019
What is VF in cardiac arrest?
Ventricular fibrillation (VF or V-fib) is the most common initial heart rhythm in patients with out-of-hospital cardiac arrest (OHCA), and the most salvageable one . 5 In VF, the etiology of arrest is often attributed to either acute ischemia or non-ischemic arrhythmia. 8
How many joules should a defibrillator be?
If the defibrillator is biphasic, the manufacturer recommended joules should be selected (usually 120 to 200 joules). If the amount is unknown, use the maximum available and subsequent doses should be equivalent, and possibly higher. 1.
What is the most important intervention for cardiac arrest?
Irrespective of the cause of cardiac arrest, the most important interventions are early recognition and calling for help—including appropriate management of the deteriorating patient—early defibrillation, high-quality cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) with minimal interruption of chest compressions, and treatment of reversible causes. 6
What are the causes of VF?
The easiest way to remember the most common causes of VF are to review the reversible “Hs and Ts” in cardiac arrest. The Hs include hypoxia, hypovolemia, hypothermia, hyper/hypokalemia, and hydrogen ions (acidosis). The Ts are tension pneumothorax, cardiac tamponade, toxins, and thrombosis (pulmonary or coronary).
What is the most important algorithm for resuscitation?
Ventricular fibrillation falls under the ACLS Adult Cardiac Arrest Algorithm and is the most important algorithm to know for adult resuscitation. 1 Ventricular fibrillation treatment starts with early and effective CPR with the application of oxygen and monitor/defibrillator placement. Keeping the brain, heart, ...
What is VF treatment?
Acute ventricular fibrillation (VF) is treated according to Advanced Cardiac Life Support (ACLS) protocols. [ 81, 82] ) Interest in improving rates of public cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) training—with a special emphasis on the use of early defibrillation with automated external defibrillators (AEDs) by public service personnel (eg, police, fire, airline)—is widespread. [ 2] These measures can help to achieve the greatest public health benefits in the fight against sudden death.
What is the goal of a paddle defibrillator?
The goal is to use the minimum amount of energy required to overcome the threshold of defibrillation. Excessive energy can cause myocardial injury and arrhythmias. Larger paddles result in lower impedance, which allows the use of lower-energy shocks.
What is a VT/VF?
Consultations. A cardiologist must be involved in the care of patients who have had a ventricular tachycardia/ventricular fibrillation (VT/VF) cardiac arrest or who have symptoms of ischemic heart disease, valvular disorders, or presentations with complex arrhythmias.
Is radiofrequency ablation effective?
Pharmacotherapy or surgical treatment (eg, operable coronary artery disease [CAD]) may be appropriate in some cases, whereas radiofrequency ablation is effective in a variety of disorders.
Is precordial thump appropriate for VF?
Although the precordial thump is less appropriate for VF than for VT, it is actually not appropriate in both.
Ethan Deckert, MD, examines treatment options for refractory ventricular fibrillation
Tones ring out and dispatch announces a 9-Echo call in your district: an approximately 35-year-old male was found lying on the sidewalk, with bystanders currently receiving instructions to start CPR. You arrive on scene to find a sweaty 35-year-old male in running clothes, unresponsive and pulseless.
In Summary
Magnesium sulfate lacks substantial supporting evidence for its use in shock-refractory Vfib/Vtach and is not recommended for routine use at this time.
Diagnosis
Clinical Trials
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
Coping and Support