What is hypoxemia and how is it treated?
Hypoxemia occurs when levels of oxygen in the blood are lower than normal. If blood oxygen levels are too low, your body may not work properly. Blood carries oxygen to the cells throughout your body to keep them healthy.
Is it possible to have hypoxemia without hypoxia?
Symptoms. It's possible to have hypoxemia without hypoxia if your body compensates for your low blood levels of oxygen by boosting the amount of oxygen that actually reaches your tissues (for example, by making your heart beat faster to move oxygen-carrying blood around more quickly). It's also possible to have hypoxia without hypoxemia,...
What is oxygen therapy for hypoxia?
Chapter 5. Oxygen Therapy Hypoxemia or hypoxia is a medical emergency and should be treated promptly. Failure to initiate oxygen therapy can result in serious harm to the patient. The essence of oxygen therapy is to provide oxygen according to target saturation rate, and to monitor the saturation rate to keep it within target range.
What are the steps involved in the treatment of hypoxia?
Steps 1 Complete respiratory assessment for hypoxia. 2 If a patient requires oxygen therapy, choose an oxygen delivery system based on your patient’s... 3 Once oxygen is applied, reassess your patient in 5 minutes to determine the effects on the body. 4 If required, adjust O 2 levels. 5 If hypoxia continues, contact respiratory therapist...

What is the most common cause of hypoxemia?
Lung diseases such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), emphysema, bronchitis, pneumonia, and pulmonary edema (fluid in the lungs) Strong pain medicines and other drugs that hold back breathing. Heart problems. Anemia (a low number of red blood cells, which carry oxygen)
What happens if hypoxemia is left untreated?
Untreated hypoxemia jeopardizes the heart and brain. Cardiac manifestations include arrhythmias, congestive heart failure, and myocardial infarction. Central nervous system manifestations include altered consciousness and seizures. Complications are more common with severe hypoxemia.
How can I increase my blood oxygen level by medicine?
SubstancesBlood Substitutes.Hemoglobins.Recombinant Proteins.Erythropoietin.Darbepoetin alfa.Epoetin Alfa. Oxygen.
Can you live with hypoxemia?
Hypoxemia is a serious condition and can lead to organ damage or even death if left untreated. You should always seek emergency medical care if you have shortness of breath that occurs suddenly and affects your ability to function or breathe properly.
How do you reverse hypoxia?
Reversing hypoxia involves increasing your oxygen intake. A standard method for providing extra oxygen is oxygen therapy. Oxygen therapy is also called supplemental or prescribed oxygen. It consists of using a mechanical device that supplies oxygen to your lungs.
How can I increase my oxygen level quickly?
In the immediate short term:Stand or sit up straight. Rather than lying down, which may put pressure on your lungs and make it harder to breathe.Cough. If you have a cold or the flu, difficulty breathing can decrease oxygen saturation in your blood. ... Go outside. ... Drink lots of water. ... Take slow, deep breaths.
What is the minimum oxygen level for COVID-19 patients?
Some COVID-19 patients may show no symptoms at all. You should start oxygen therapy on any COVID-19 patient with an oxygen saturation below 90 percent, even if they show no physical signs of a low oxygen level. If the patient has any warning signs of low oxygen levels, start oxygen therapy immediately.
What happens when your oxygen level drops to 40?
Blood oxygen level below 40 percent leads to compromise the function of Brain and Heart and Blood oxygen level below 20 percent leads to comma and ultimately, it causes death. Continue low levels of Blood oxygen causes many serious problems like cardiac, respiratory and neurological problems.
How to treat hypoxemia?
Treatment. Since hypoxemia involves low blood oxygen levels, the aim of treatment is to try to raise blood oxygen levels back to normal. Oxygen therapy can be utilized to treat hypoxemia. This may involve using an oxygen mask or a small tube clipped to your nose to receive supplemental oxygen.
How to diagnose hypoxemia?
In order to diagnose hypoxemia, your doctor will perform a physical examination during which they’ll check your heart and lungs. They may also check the color of your skin, fingernails, or lips. There are some additional tests that they can perform to assess your oxygen levels and breathing.
What is hypoxemia in the body?
Your blood carries oxygen to the organs and tissues of your body. Hypoxemia is when you have low levels of oxygen in your blood. Hypoxemia can be caused by a variety of conditions, including asthma, pneumonia, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). It’s a serious medical situation and requires prompt medical attention.
What is it called when you have low oxygen levels?
Hypoxemia is when you have low levels of oxygen in your blood. There are several different types of hypoxemia and many different conditions can cause it. Hypoxemia is a serious condition and can lead to organ damage or even death if left untreated.
Is hypoxia a blood condition?
While hypoxemia refers to low oxygen levels in your blood, hypoxia refers to low levels of oxygen in the tissues of your body. The two can sometimes, but not always, occur together. Generally, the presence of hypoxemia suggests hypoxia. This makes sense because if oxygen levels are low in your blood, the tissues of your body are also probably not ...
Can anemia cause low oxygen levels?
Because of this, a person with anemia may have low levels of oxygen in their blood. Additionally, hypoxemia can be a symptom of another condition such as respiratory failure. Respiratory failure occurs when not enough oxygen passes from your lungs to your blood.
Can COPD cause hypoxemia?
Destruction of the walls of alveoli and surrounding capillaries in COPD can lead to problems with oxygen exchange, which can lead to hypoxemia. Anemia is a condition in which there aren’t enough red blood cells to effectively carry oxygen. Because of this, a person with anemia may have low levels of oxygen in their blood.
What is hypoxemia treatment?
Treatment. Hypoxemia is typically the result of another condition that affects how your body processes oxygen. It's imperative that your physician creates a plan that treats your underlying condition in addition to treating symptoms of hypoxemia.
How to diagnose hypoxemia?
Hypoxemia is diagnosed by measuring the blood oxygen level via a blood test known as arterial blood gases (ABG) or via pulse oximetry, a noninvasive scanning probe that is usually clipped to a finger or earlobe and uses light to measure the amount of oxygen in your blood. 2
What is hypoxemia in COPD?
Though this can happen for a variety of reasons, hypoxemia appears to be relatively common in people with advanced chronic obstructive pulmonary disease ( COPD ). 1 It also may result from other conditions, such as asthma, anemia, sleep apnea, and pneumonia.
What happens if you don't have enough oxygen?
Complications. Hypoxemia often leads to hypoxia, a condition in which you don't have enough oxygen getting to your tissues. While many people confuse the two because of their similar names, they are distinct (hypoxemia only involves low oxygen in the blood itself). 2 Hypoxemia may also result in cyanosis.
What is the medical term for a person who doesn't have enough oxygen?
Sanja Jelic, MD, is board-certified in sleep medicine, critical care medicine, pulmonary disease, and internal medicine. Hypoxemia is a condition that occurs when you don't have enough oxygen in your blood. Though this can happen for a variety of reasons, hypoxemia appears to be relatively common in people with advanced chronic obstructive ...
What are the causes of hypoxemia?
Some of the most common causes of hypoxemia include: 2 . Sleep apnea. Asthma.
What is the normal oxygen level in the arteries?
A normal oxygen level in your arteries is about 80 to 100 mmHg. 7 People with COPD usually have lower levels. If you have a very low level—usually around 60 mmHg—you may need supplemental oxygen. 1 However, providing too much oxygen can be dangerous, too, so your doctor will need to work with you to get the correct balance. ...
How to prevent hypoxia from cyanide?
Cyanide poisoning (Cyanide is a chemical used to make plastics and other products.) Preventing Hypoxia. The best way to prevent hypoxia is to keep your asthma under control, every day. Stick with your asthma treatment plan. Take your medicine to help prevent flares and the need to use your rescue inhaler.
What causes hypoxia in the lungs?
Other things can cause hypoxia include: 1 Lung diseases such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease ( COPD ), emphysema, bronchitis, pneumonia, and pulmonary edema (fluid in the lungs) 2 Strong pain medicines and other drugs that hold back breathing 3 Heart problems 4 Anemia (a low number of red blood cells, which carry oxygen) 5 Cyanide poisoning (Cyanide is a chemical used to make plastics and other products.)
What causes low oxygen levels in the body?
Hypoxemia (low oxygen in your blood) can cause hypoxia (low oxygen in your tissues) when your blood doesn't carry enough oxygen to your tissues to meet your body's needs. The word hypoxia is sometimes used to describe both problems.
How to get oxygen level up?
The most important thing is to get more oxygen into your body. You'll receive it through a small plug in your nose or through a mask that covers your nose and mouth. For many people, this is enough to bring your oxygen level up to normal. An inhaler or asthma medicine by mouth may make breathing easier.
What happens if you don't have enough oxygen?
When your body doesn't have enough oxygen, you could get hypoxemia or hypoxia. These are dangerous conditions. Without oxygen, your brain, liver, and other organs can be damaged just minutes after symptoms start.
How to stop asthma attacks?
Take your medicine to help prevent flares and the need to use your rescue inhaler. Eat right and stay active. Know your asthma triggers, and find ways to avoid them. Work with your doctor to come up with an action plan for asthma attacks, so you know what to do when you have trouble breathing.
Can asthma cause hypoxia?
A severe asthma attack, or flare, can cause hypoxia in adults and kids. During an attack, your airways narrow, making it hard to get air into your lungs. Coughing to clear your lungs uses even more oxygen and can make symptoms worse.
Hypoventilation
Hypoventilation occurs when breathing is insufficient for the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the body. When hypoventilation occurs, there is a high level of carbon dioxide (CO 2) and a low level of oxygen in the blood. As a result, hypoxemia is often present, especially during sleep.
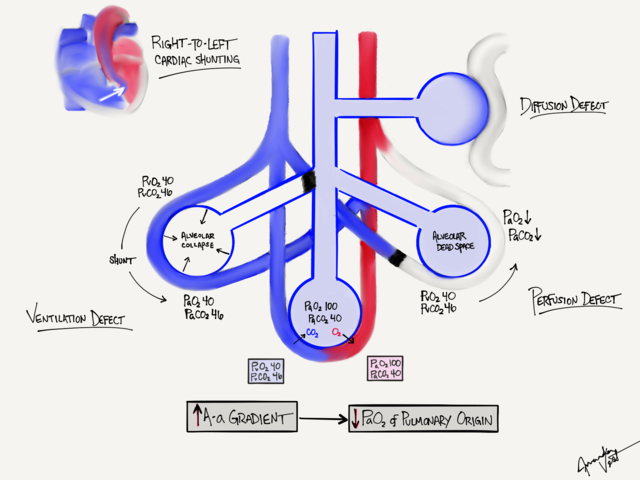
Right-to-left shunt
A shunt refers to when blood from the heart’s right side enters the left side without any exchange of oxygen or CO 2.
Diffusion impairment
Diffusion impairment occurs when there is dysfunction, or limitation, in the oxygen transport between the alveoli and the capillaries. The alveoli are sacs in the lungs where gas exchange takes place and capillaries are the blood vessels that oxygen diffuses into.
Low PaO 2
A low environmental PaO 2 may result in hypoxemia. For example, the partial pressure of oxygen is lower at higher altitudes. This means that a person accustomed to breathing at sea level may experience hypoxemia at higher altitudes, as the amount of oxygen available is lower.
Indacaterol
Indacaterol is a long-acting beta-agonist bronchodilator, prescribed for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) symptoms.
Methylprednisolone
Methylprednisolone is a corticosteroid prescribed for severe allergies, arthritis, asthma, certain blood disorders and skin conditions.
What are some ways to treat hypoxia?
For example, if hypoxia is caused by pneumonia, additional treatment for hypoxia may include antibiotics, increased fluid intake, oral suctioning, position changes, and deep breathing and coughing exercises. If a patient has COPD, check physician order for the amount of required oxygen and the expected saturation level.
How to help a patient with oxygen?
Deep breathing and coughing techniques help patients effectively clear their airway while maintaining their oxygen levels. Teach patients “controlled coughing” by having them take a deep breath in and cough deeply with the mouth slightly open. If they have difficulty coughing, teach the huffing technique. This involves taking a medium breath and then making a sound like “ha” to push the air out fast with the mouth slightly open. This is done three or four times, and then they are instructed to cough. If secretions are thick and tenacious, the patient may be dehydrated and require additional fluids (if medical condition does not contraindicate additional fluids).
What is the best level of oxygen to maintain a sao 2?
SaO 2 should be greater than 92% unless otherwise stated by the physician. The goal is to use the least amount of oxygen to maintain levels between 92% and 98%. Assess need for O 2: check SaO 2 level with a pulse oximetry device. Assess for underlying medical conditions or alternate causes of hypoxia (cardiovascular).
Why do people need oxygen?
The most common reasons for initiating oxygen therapy include acute hypoxemia related to pneumonia, shock, asthma, heart failure, pulmonary embolus, myocardial infarction resulting in hypoxemia, post operative states, pneumonthorax, and abnormalities in the quality and quantity of hemoglobin.
Is oxygen therapy short term or long term?
Oxygen therapy may be short- or long-term depending on the SaO 2 requirements of the patients and underlying diseases processes (Perry et al., 2014). Checklist 41 reviews the steps for applying and titrating oxygen therapy (see Figure 5.2).
Can obstructive sleep apnea cause hypoxemia?
Obstructive sleep apnea. Patients with obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) may be unable to maintain a patent airway. In OSA, nasopharyngeal abnormalities that cause narrowing of the upper airway produce repetitive airway obstruction during sleep, with the potential for periods of apnea and hypoxemia.
Can a CVA cause hypoxia?
Patients with muscle disorders or who have experienced a cerebral vascular accident (CVA) are at risk for aspiration related to ineffective cough reflex, which could lead to hypoxia. Provide oral suction if patient is unable to clear secretions, foreign debris, or mucous from the mouth and pharynx.