AF Ablation & Rx: Intracardia arrythmia ablation. This procedure is done by an electrophysiologist cardiologist. And if that doesn't work the heart rate can be controlled by medication plus a blood thinner.
What's next If cardioversion doesn't work?
What's next if cardioversion didn't work? Medicine: As a large study showed (the affirm) study, people do fine even with atrial fibrillation as long as the heart rate is controlled with drugs and anticoagulants are given if indicated. AF Ablation & Rx: Intracardia arrythmia ablation. This procedure is done by an electrophysiologist cardiologist.
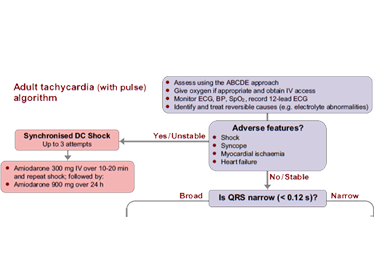
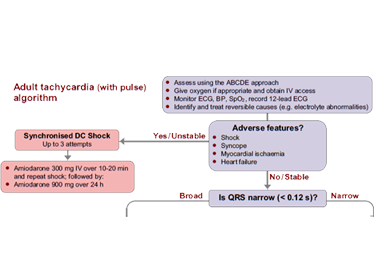
Is cardioversion good for tachycardia?
For most people, cardioversion quickly restores a normal heart rhythm. Cardioversion can correct a heartbeat that's too fast (tachycardia) or irregular (fibrillation). Cardioversion is usually done to treat people who have atrial fibrillation or atrial flutter.
When is cardioversion indicated in the treatment of atrial fibrillation?
This article has been cited byother articles in PMC. Abstract Cardioversion is widely used in patients with atrial fibrillation (AF) and atrial flutter when a rhythm control strategy is pursued.
How can we prevent cardioversion failure after sinus conversion?
First, acute failure of cardioversion can be prevented by pre-treatment with AADs (Table 2).1Next, the influence of AADs on recurrences depends on stage-related arrhythmogenic mechanisms and their subsidence during reversed electrical remodelling induced by persistent sinus rhythm after conversion.

How many times can you have electrical cardioversion?
There is really no limit to the number of cardioversions that people can have but at some point of time, we figure out that either it is a futile strategy or patients tend to get frustrated. But when it is a necessity that our patients who've had 20, 25 cardioversions also.
Can you have a second cardioversion?
Introduction: Repeat cardioversion may be necessary in over 50% of patients with persistent atrial fibrillation (AF), but identifying responders remains challenging.
What happens if AFib can't be controlled?
AFib can lead to blood clots, which will stop the blood flow through that area. This can cause serious issues like a stroke. A left atrial appendage closure will close off your LAA to keep clots from escaping. This will lower your risk of stroke.
What is the success rate of a second cardioversion?
With the second attempt of ECV, 72/94 (76.6%) patients were converted to SR. Patients had a more favorable outcome with the 2nd ECV as compared to initial ECV (76.6% vs 62.67%, p = 0.042). Results of serial electrical cardioversion in atrial fibrillation and follow-up over one year.
Is ablation better than cardioversion?
Conclusion: In patients with AF, there is a small periprocedural stroke risk with ablation in comparison to cardioversion. However, over longer-term follow-up, ablation is associated with a slightly lower rate of stroke.
What percentage of Cardioversions are successful?
The success rate of cardioversion with atrial fibrillation is generally better than 90 percent. Chances of success are lower when the atrial fibrillation has been present for more than several months or when the left atrium is very enlarged. In general, there are two ways that a cardioversion procedure for AF can fail.
Can you get a pacemaker for AFib?
But if you have AFib and your heart is beating too slowly, your doctor may recommend a pacemaker along with other treatment. It sends out electrical pulses that take the place of the mixed-up ones, so your heart beats at the right pace. You also might need a pacemaker if you have AFib and congestive heart failure.
What is the latest treatment for atrial fibrillation?
Newly Approved Treatments A new medicine called edoxaban has been cleared to prevent blood clots and stroke in patients with AFib. Edoxoban is also a NOAC (non-vitamin K oral anticoagulant).
What is the first drug of choice for atrial fibrillation?
Amiodarone as a first-choice drug for restoring sinus rhythm in patients with atrial fibrillation: a randomized, controlled study. Chest.
What are the chances of AFib returning after cardioversion?
Many people who have had successful cardioversion develop atrial fibrillation again. According to studies, this happens within a year in up to 80 out of 100 people. The success rate can be improved somewhat by taking anti-arrhythmic medication over the longer term.
How long do Cardioversions last?
Cardioversion itself takes about 5 minutes. But the whole procedure, including recovery, will probably take 30 to 45 minutes. You may take an anticoagulant medicine before and after cardioversion.
What foods should be avoided with atrial fibrillation?
7 Foods to Avoid When You Have Atrial FibrillationAlcohol. Alcohol tops the list of items to avoid on an atrial fibrillation diet. ... Caffeine. ... Grapefruit. ... Cranberry Juice. ... Asparagus and Leafy Green Vegetables. ... Processed and Salty Foods. ... Gluten.
Failed Cardioversion
all, Feeling very down tonight. Had my first cardioversion today and it failed completely even...
2 Ablations, 1 Cardioversion - what next?
second ablation I went into atrial flutter and had a cardioversion. Since then my medication has...
After unsuccessful Cardioversion yesterday, what's next?
asymptomatic, I'm reluctant to try ablation. I imagine the doc may suggest anti-arrhythmatic drugs...
failed cardioversion
bristol heart hospital yesterday to have a cardioversion-sadly it did,nt work.the nurses told me i...
Why do doctors use cardioversion?
Most often, doctors use cardioversion to treat a fast, irregular heart rhythm called atrial fibrillation. If you have electrical cardioversion, you’ll get medicine to put you to sleep so you don’t feel the shock.
What is cardioversion used for?
Cardioversion also treats other kinds of abnormal heartbeats, including atrial flutter, atrial tachycardia and ventricular tachycardia. Cardioversion or defibrillation is also used in emergency situations for people who suffer sudden life threatening arrhythmias.
How does an IV shock work?
You won’t feel pain during the procedure. Your doctor will deliver an electrical shock through two paddles. One is placed on your chest and the other on your back.
What is abnormal heart rhythm called?
Abnormal heart rhythms are called arrhythmias. Watch an animation of arrhythmias. There are two kinds of cardioversion. Your doctor may give you one or more medicines to bring back your regular heartbeat. This is called pharmacologic (chemical) cardioversion.
How many shocks do you need for a heart attack?
The shock lasts less than a second, and briefly stops (resets) your heart rhythm. Your doctor will check to see if your heartbeat is regular. Some people need only 1 shock .
Can cardioversion cause a stroke?
Cardioversion may knock loose a blood clot in your left atrium. If the clot (embolus) travels to your brain, it can cause a stroke. To avoid this, your doctor may give you medicine (such as warfarin) to make your blood less likely to form blood clots.
What are the risks of cardioversion?
Major risks of cardioversion include: Dislodged blood clots. Some people who have irregular heartbeats have blood clots in their hearts. Electric cardioversion can cause these blood clots to move to other parts of your body.
Why do we do cardioversion?
Cardioversion is usually done to treat people who have atrial fibrillation or atrial flutter. These conditions occur when the electrical signals that normally make your heart beat at a regular rate don't travel properly through ...
How does a cardioversion machine work?
The electrodes connect to a cardioversion machine (de fibrillator) using wires. The machine records your heart rhythm and delivers shocks to your heart to restore a normal heart rhythm. This machine can also correct your heart's rhythm if it beats too slowly after cardioversion.
How is cardioversion done?
Cardioversion is usually done by sending electric shocks to your heart through electrodes placed on your chest. It's also possible to do cardioversion with medications. Cardioversion is usually a scheduled procedure that's performed in a hospital. You should be able to go home the same day as your procedure.
What is cardioversion in medical terms?
Cardioversion is a medical procedure that restores a normal heart rhythm in people with certain types of abnormal heartbeats (arrhythmias). Cardioversion is usually done by sending electric shocks to your heart ...
How long does it take for blood clots to break free?
If your doctor finds blood clots, your cardioversion procedure will be delayed for three to four weeks.
How long before cardioversion can you eat?
However, if your symptoms are severe, you may need to have cardioversion in an emergency setting. You typically can't eat or drink anything for about eight hours before your procedure.
Failed Cardioversion
Feeling very down tonight. Had my first cardioversion today and it failed completely even though...
Failed Cardioversion -what next?
Thursday so now feeling pretty negative about what happens next. Suggestion that might be attempted...
failed cardioversion
can my friends on --healthunlocked tell what others who also failed synus mode ended up having...
After failed cardioversion
6 week check after failed cardioversion- was recommended either chemical cardioversion using...
How to reset heart rate before cardioversion?
Before trying electrical cardioversion, your healthcare provider may try to reset the heart rate in other ways. This might include the Valsalva maneuver. This is a method where you hold your breath and increase the pressure in your belly.
Why is cardioversion important?
Cardioversion upsets the abnormal signaling and lets the heart to reset itself back into a normal rhythm. Cardioversion is usually a scheduled procedure. But sometimes healthcare providers need to do it as an emergency . This is done if symptoms are severe.
How does a cardioversion machine work?
You will receive medicine through a vein in your arm to make you fall asleep. Using the cardioversion machine, a programmed high-energy shock is sent to your heart. This should convert your heart back to a normal rhythm.
How long should I take anti clotting medication?
These are commonly taken for several weeks before and after the procedure. Not everyone needs this medicine, but some people do. You are likely to need anti-clotting medicine if your abnormal rhythm has lasted more than 48 hours or if you have had a blood clot in the past.
What is the name of the condition that causes sudden cardiac death?
This is called an arrhythmia . Arrhythmias can cause problems such as fainting, stroke, heart attack, and even sudden cardiac death. With electrical cardioversion, a high-energy shock is sent to the heart to reset a normal rhythm. It is different from chemical cardioversion, in which medicines are used to try to restore a normal rhythm.
Is electrical cardioversion better than chemical cardioversion?
Electrical cardioversion works better and is used more often than chemical cardioversion. Your healthcare provider may not want you to have cardioversion if you have minor symptoms. It also may not be recommended if you are elderly, if you have had AFib a long time, or if you have other major medical problems.
Why is ViewMedica not allowed?
ViewMedica Error. Your ViewMedica embed is not allowed because the embedding domain (null) does not match your master domain (hopkinsmedicine.org/ortho). Log in to your ViewMedica Account and update your URL to match this location.
How long before cardioversion can you take medicine?
Before the procedure, your doctor may do a type of ultrasound to look for blood clots in your heart. You’ll probably get medicine to take for 3-4 weeks before and after the procedure to help prevent blood clots.
How does electrical cardioversion work?
Electrical cardioversion gives shocks through paddles to regulate your heartbeat. First, you'll get medicine to make you fall asleep. Then, your doctor will put the paddles on your chest, and sometimes your back. These will give you a mild electrical shock to get your heart's rhythm back to normal.
How long does it take for AFIB to work?
Chemical cardioversion: You should know quickly if it works. It usually takes effect within hours, but sometimes it takes days. If it doesn’t work for you, the doctor might suggest electrical cardioversion.
What is the treatment for AFIB?
Cardioversion for AFib. If you have an irregular heartbeat (you might hear it called arrhythmia, atrial fibrillation, or AFib), your doctor will probably suggest a treatment called cardioversion to help you get a normal rhythm back. If your heart beats too fast or unevenly, it can be dangerous. It may not be pumping enough blood to meet your body's ...
How long does it take for your heart to go back to normal?
Once your heart is back in a normal rhythm, your doctor will give you medicine to make sure it stays that way. You'll go back to your doctor in a few weeks for an electrocardiogram (you may hear it called an EKG) to make sure your beat is still regular.
Is cardioversion the same as defibrillation?
Electrical Cardioversion vs. Defibrillation. Defibrillation also uses electric shocks, but it isn’t the same as electric cardioversion. In defibrillation, doctors use high-voltage shocks to treat life-threatening arrhythmias or a heart that has stopped.
What are the factors that bring on the AFIB in the first place?
The factors that brought on the afib in the first place likely are still present: if we don’t address correctable factors we are less likely to maintain the normal sinus rhythm (NSR). Correctable factors include: abnormal thyroid function. abnormal potassium or magnesium. inflammation of adjacent lung or pericardium.
Can AC shock cause ventricular fibrillation?
However, at current levels greater than 50 mA, an AC electrical shock traveling through the chest can, if timed properly, cause the heart to go out of normal rhythm into ventricular fibrillation. We use a “synchronized” electrical cardioversion (termed direct current or DC cardioversion (DCC)) to convert a fibrillating or fluttering atrium back ...
Can AFIB be converted to normal?
There are some medications that we can utilize to convert atrial fibrillation (afib) back to normal (antiarrhythmic drugs), but they are far less effective than the electrical cardioversion, and often can bring out more dangerous heart rhythms.
Can you shock your heart with AFIB?
On the other hand, if you feel fine in afib without any evidence that it is effecting your heart muscle or valves, then it is hard to justify multiple attempts to shock the heart. Any patient that has recurrent symptomatic afib or afib associated with heart failure, should be considered a candidate for an atrial fibrillation ablation.
Does propofol help with cardioversion?
At this level of anesthesia, the patient is breathing on his own but will only respond to painful stimulation. The propofol is short-acting and prevents the patient from feeling the intense pain of the cardioversion (often described as like a mule kicking one in the chest), and from recalling any of the events.
Does AFIB cause shortness of breath?
Some patients feel terrible the moment they go into afib: symptoms of palpitations, chest pain, or shortness of breath predominate and are especially prominent if the heart rate is high. Controlling the high heart rate with beta-blockers or diltiazem will reduce many of these symptoms, but I have a large number of patients who still feel terrible ...
Does cardioversion damage the heart?
certain cardiac valve problems. There is no evidence that the cardioversion per se damages the heart in any way. The major risks of the procedure (again, assuming proper preparation, see below) are related to the anesthesia.
Overview
Why It's Done
Risks
- Complications of electric cardioversion are uncommon. Your doctor can take steps to reduce your risk. Major risks of cardioversion include: 1. Dislodged blood clots. Some people who have irregular heartbeats have blood clots in their hearts. Electric cardioversion can cause these blood clots to move to other parts of your body. This can cause life-threatening complications, such a…
How You Prepare
- Cardioversion procedures are usually scheduled in advance. However, if your symptoms are severe, you may need to have cardioversion in an emergency setting. You typically can't eat or drink anything for about eight hours before your procedure. Your doctor will tell you whether to take any of your regular medications before your procedure. If you do take medications before y…
What You Can Expect
- During the procedure
You'll be given medications through an IV to make you sleep during the procedure so that you won't feel any pain from the shocks. You may receive other medications through the IV to help restore your heart rhythm. A nurse or technician places several large patches called electrodes o… - After the procedure
Electric cardioversion is done on an outpatient basis, meaning you can go home the same day your procedure is done. You'll spend an hour or so in a recovery room being closely monitored for complications. You'll need someone to drive you home, and your ability to make decisions may b…
Results
- For most people, cardioversion can quickly restore a regular heartbeat. It's possible you'll need additional procedures to keep a normal heart rhythm. Your doctor may suggest lifestyle changes to improve your heart health and prevent or treat conditions that can cause arrhythmias, such as high blood pressure. 1. Avoid or limit caffeine and alcohol 2. Eat heart-healthy foods 3. Increase …
Clinical Trials
- Explore Mayo Clinic studiesof tests and procedures to help prevent, detect, treat or manage conditions.