Is there a natural cure for my CLL?
Mar 15, 2022 · Here are some of the newest treatments for Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL): Calquence (acalabrutinib)4,5. Calquence (acalabrutinib) is a kinase inhibitor indicated for the treatment of adult patients with Chronic Lymphocytic Leukaemia (CLL). Calquence (acalabrutinib) can be used on its own (monotherapy) in patients with CLL who have had previous treatment …
How to treat a previously untreated CLL patient?
May 19, 2021 · Venetoclax, an inhibitor of the anti-apoptotic BCL2 protein and, to a lesser extent, phosphoinositide-3 kinase (PI3K) delta inhibitors, add to the armamentarium of targeted agents for the treatment of CLL. Furthermore, anti-CD20 monoclonal antibodies are used very successfully either alone or in combination with BTK, BCL2 or PI3K inhibitors.
What is the best treatment for CML?
CAR T-cell therapy CAR (chimeric antigen receptor) T-cell therapy is another way of getting your immune system to find and kill CLL cells. The patient's T cells, a type of white blood cell, are removed, reprogrammed, and grown (multiplied) in the lab. They're then given back to the patient so they can destroy CLL cells in the patient's body.
What is the life expectancy for chronic lymphocytic leukemia?
Mar 04, 2022 · Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) treatment can include observation, steroids, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, surgery, or targeted therapy. Learn more about the diagnosis, prognosis, and treatment of newly diagnosed or recurrent CLL in this expert-reviewed summary.

What is the best treatment for CLL in 2021?
Efficacy in older patients — Single-agent ibrutinib is a highly effective treatment for older adults with CLL (algorithm 1). Ibrutinib improves both progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) when compared with single-agent chlorambucil in older patients.Mar 25, 2022
What is the best medicine for CLL?
Typical Treatment of Chronic Lymphocytic LeukemiaIbrutinib (Imbruvica), alone or with rituximab (Rituxan)Acalabrutinib (Calquence), alone or with obinutuzumab (Gazyva)Venetoclax (Venclexta) and obinutuzumab.Venetoclax alone, or with rituximab.Bendamustine and rituximab (or another monoclonal antibody)More items...•Apr 22, 2020
How long can you live with CLL with treatment?
The prognosis of patients with CLL varies widely at diagnosis. Some patients die rapidly, within 2-3 years of diagnosis, because of complications from CLL. Most patients live 5-10 years, with an initial course that is relatively benign but followed by a terminal, progressive, and resistant phase lasting 1-2 years.
Can CLL patients live 20 years?
Most people live for about 10 years, but this varies depending on how CLL behaves. People in stages 0 to II may live for 5 to 20 years without treatment. CLL has a very high incidence rate in people older than 60 years. CLL affects men more than women.Nov 16, 2021
What should be avoided in CLL?
Your CLL treatment may weaken your immune system and raise your chances of getting foodborne illness. These steps can help keep you safe: Cook meat until it's well-done and eggs until the yolks are hard. Avoid raw sprouts, salad bars, and unpasteurized drinks and cheeses.Jan 28, 2021
Does Venclexta cure CLL?
Venetoclax-based treatment is highly potent at eliminating CLL and able to achieve deep remission with fixed-duration therapy.Apr 23, 2020
How do you know if CLL is getting worse?
Extreme tiredness Another symptom of CLL progression is extreme fatigue and shortness of breath while doing your normal day-to-day activities. This is due to fewer healthy red blood cells and more cancer cells accumulating in your body.Feb 6, 2020
At what stage is CLL treated?
Patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (chronic lymphoid leukemia, CLL) do not need drug therapy until they become symptomatic or display evidence of rapid progression of disease, as characterized by the following: Weight loss of more than 10% over 6 months. Extreme fatigue.Feb 8, 2022
Can CLL go into remission?
CLL can be in remission for many years, but there's always a possibility it will come back. This is called a recurrence.
Can you live 30 years with CLL?
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) can rarely be cured. Still, most people live with the disease for many years. Some people with CLL can live for years without treatment, but over time, most will need to be treated.May 10, 2018
Does CLL affect the brain?
The clinical manifestations of CLL involvement of the CNS are heterogeneous and include headache, cranial nerve palsies, cerebellar signs, visual problems, and motor and/or sensory deficits.
Which type of leukemia is most fatal?
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is the most common type of acute leukemia, though it is rare, accounting for only about 1% of all cancers overall. AML is also the most fatal type of leukemia. The five-year survival rate for AML, that is, how many people will be alive 5 years after diagnosis, is 29.5%.Feb 23, 2022
When was venetoclax approved?
The approval of venetoclax as a second-line treatment for all CLL patients, regardless of their del(17p) status, was made in June 2018 by the FDA, while the EMA approved the combination of venetoclax and rituximab in October 2018. Both agencies based their decision on the results of the MURANO trial [26].
What is BTK inhibitor?
With the introduction of the Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitor (BTKi) ibrutinib, which irreversibly inhibits Bruton tyrosine kinase (BTK), an essential enzyme in the B cell receptor (BCR) signaling pathway, the era of targeted agents for CLL patients began [17,18,19] .
What is Venetoclax used for?
Venetoclax, an inhibitor of the anti-apoptotic BCL2 protein and, to a lesser extent, phosphoinositide-3 kinase (PI3K) delta inhibitors, add to the armamentarium of targeted agents for the treatment of CLL.
Is acalabrutinib a BTK?
Recently, acalabrutinib, a second-generation BTKi with higher selectivity for BTK than ibrutinib [20], was approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the European Medicines Agency (EMA) for the treatment of CLL patients.
Is CLL treated with chemotherapy?
Until recently, CLL was treated using chemotherapy in combination with anti-CD20 antibody-based immunotherapy. Depending on age and clinical condition, patients received more or less intensive chemotherapy and were at risk of side effects commonly associated with chemotherapy.
Where is CLL research?
Research on chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) is taking place in many university hospitals, medical centers, and other institutions around the world. Each year, scientists find out more about what causes the disease, how to prevent it, and how to better treat it. Most experts agree that treatment in a clinical trial should be considered ...
What is the T cell therapy?
CAR (chimeric antigen receptor) T-cell therapy is another way of getting your immune system to find and kill CLL cells. The patient's T cells, a type of white blood cell, are removed, reprogrammed, and grown (multiplied) in the lab.
What is BCL2 inhibitor therapy?
BCL2 inhibitor therapy: This treatment blocks a protein called BCL2 which is found on some leukemia cells. This may kill leukemia cells and make them more sensitive to other anticancer drugs. Venetoclax is a type of BCL2 therapy used to treat symptomatic or progressive, recurrent, or refractory CLL.
Why do we do clinical trials?
Clinical trials are done to find out if new cancer treatments are safe and effective or better than the standard treatment.
What is the disease that causes swollen lymph nodes?
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia is a type of cancer in which the bone marrow makes too many lymphocytes (a type of white blood cell). Leukemia may affect red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. Signs and symptoms of chronic lymphocytic leukemia include swollen lymph nodes and feeling tired. Tests that examine the blood are used ...
Can leukemia cause infection?
These leukemia cells are not able to fight infection very well. Also, as the number of leukemia cells increases in the blood and bone marrow, there is less room for healthy white blood cells, red blood cells, and platelets. This may lead to infection, anemia, and easy bleeding. This summary is about chronic lymphocytic leukemia.
What is the name of the cancer in which the bone marrow makes too many lymphocytes?
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia is a type of cancer in which the bone marrow makes too many lymphocytes (a type of white blood cell). Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (also called CLL) is a cancer of the blood and bone marrow that usually gets worse slowly. CLL is one of the most common types of leukemia in adults.
Can lymphocytic leukemia cause tiredness?
Signs and symptoms of chronic lymphocytic leukemia include swollen lymph nodes and feeling tired. In the beginning, CLL does not cause any signs or symptoms and may be found during a routine blood test. Later, signs and symptoms may occur.
What is the process used to find out how far the cancer has spread?
Staging is the process used to find out how far the cancer has spread. In chronic lymphocytic leukemia ( CLL ), the leukemia cells may spread from the blood and bone marrow to other parts of the body, such as the lymph nodes, liver, and spleen.
What is Venus I?
Yeah, so that was a very interesting trial presented, which is called a VenUS I trial. That's just the name of the trial. But what the investigators did was the patients with CLL who had prior therapy for their CLL. So let's suppose they had chemotherapy with bendamustine (Bendeka) or FCR or chlorambucil (Leukeran) or some other therapy for their CLL, and then their disease progressed. So the investigators gave them venetoclax just by itself. They did not give them with an antibody. For example, normally at least in the United States these days, you would combine it with rituximab (Rituxan) in the relapse refractory setting. But the investigators in this trial just gave venetolax by itself and what they found was at the two-year mark, approximately 80% of the patients are still in remission, what is called progression free. So, that looks pretty good. One of the other markers we try to follow in the clinical trial setting specifically is what is called MRD, meaning that whether the patients had disease by a very sensitive assay, generally, it's a detection of one cancer cell in 10,000 normal cells.
Can venetoclax be used without antibody?
All right. So BTK inhibitors, continuing therapy, venetoclax may be not with or without an antibody in that scenario of research. All right. Now, one last thing I want to ask you about is combinations in the data from the EHA about combining drugs, just like we've had FCR or BR.
Does ibrutinib cause headaches?
It did have some of the side effects, which we see with ibrutinib as well, such as atrial fibrillation. It also has an unusual or peculiar side effect of headache.
Is venetoclax monoclonal antibody?
I think this would be BCL-2, you have venetoclax (Venclexta). And so venetoclax has been approved with a monoclonal antibody either I think rituximab (Rituxan) also with obinituzimab (Gazyva), so you get an infusion for a while and then you continue, or you take the pills for a while, hopefully where you can stop after two years. But I understand there was data presented on using venetoclax by itself. So how does that look?
Is BTK inhibitor FDA approved?
As many of our CLL patients would know, there are several BTK inhibitors now in clinical trials and actually FDA approved. The first one in the market was ibrutinib and then more recently acalabrutinib was approved by the FDA.
When was Venetoclax approved?
It was initially approved in April 2016 for the treatment of patients with del(17p) CLL who had received at least 1 prior line of therapy [48].
Is zanubrutinib a BTK inhibitor?
One of the irreversible BTK inhibitors, zanubrutinib, received accelerated approval in the USA (November 2019) for the treatment of adult patients with mantle cell lymphoma who had received at least 1 previous therapy [73].
What is the treatment for CLL?
One of the most promising future treatment options for CLL is CAR T-cell therapy. CAR T, which stands for chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy, uses a person’s own immune system cells to fight cancer. The procedure involves extracting and altering a person’s immune cells to better recognize and destroy cancer cells.
What drugs are used for CLL?
Examples of targeted drugs for CLL include: 1 ibrutinib (Imbruvica): targets the enzyme known as Bruton’s tyrosine kinase, or BTK, which is crucial for CLL cell survival 2 venetoclax (Venclexta): targets the BCL2 protein, a protein seen in CLL 3 idelalisib (Zydelig): blocks the kinase protein known as PI3K and is used for relapsed CLL 4 duvelisib (Copiktra): also targets PI3K, but is typically used only after other treatments fail 5 acalabrutinib (Calquence): another BTK inhibitor approved in late 2019 for CLL 6 venetoclax (Venclexta) in combination with obinutuzumab (Gazyva)
What is CLL in medical terms?
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) is a slow-growing cancer of the immune system. Because it’s slow-growing, many people with CLL won’t need to start treatment for many years after their diagnosis.
Why are CLL drugs called targeted therapies?
These drugs are called targeted therapies because they’re directed at specific proteins that help CLL cells grow.
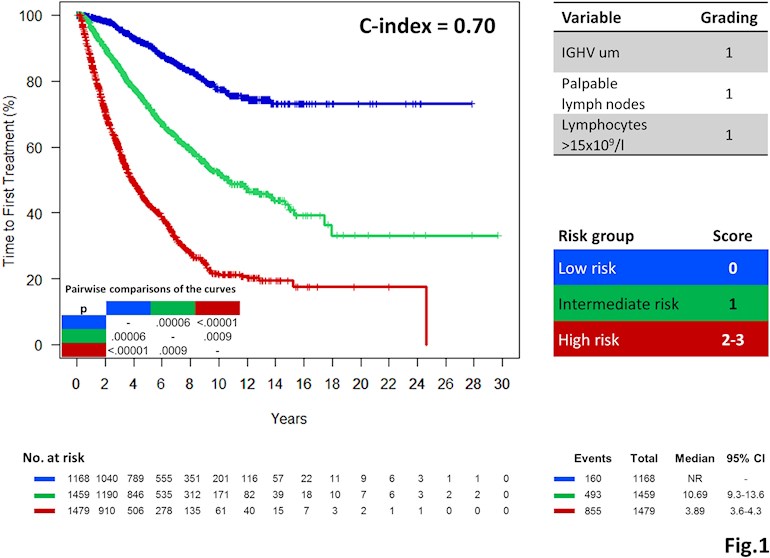
What is low risk CLL?
Treatments for low-risk CLL. Doctors typically stage CLL using a system called the Rai system. Low-risk CLL describes people who fall in “stage 0” under the Rai system. In stage 0, the lymph nodes, spleen, and liver aren’t enlarged. Red blood cell and platelet counts are also near normal. If you have low-risk CLL, ...
How many clinical trials are there for CLL?
These new treatments may work better for you than the ones currently available. There are currently hundreds of clinical trials ongoing for CLL.
Why do doctors recommend stem cell transplants?
Your doctor may recommend a stem cell transplant if your cancer doesn’t respond to other treatments. A stem cell transplant allows you to receive higher doses of chemotherapy to kill more cancer cells.
What is the treatment for CLL?
Until recently, the standard regimen for initial treatment has been a combination of: chemotherapy (fludarabine and cyclophosphamide (FC)) an antibody immunotherapy (rituximab), known as FCR, for patients younger than 65 . and bendamustine and rituximab if older than 65.
What is the FCR for CLL?
an antibody immunotherapy (rituximab), known as FCR, for patients younger than 65. and bendamustine and rituximab if older than 65. These regimens were developed because the combination of fludarabine and cyclophosphamide kills CLL cells synergistically in the laboratory, and the addition of rituximab to FC in a randomized clinical trial improved ...
Why is treatment with new drugs and combinations enabling patients to live longer?
So far, this survival improvement is most noticeable in patients whose disease has high-risk characteristics, because those with low-risk features have always done very well, Brown says.
Is CLL a mutated gene?
Young, fit patients without significant medical problems, who have the lower risk subtype of CLL — in other words, whose CLL is considered IGHV mutated based on the presence of mutations in the immunoglobulin variable region gene — should generally still receive the standard treatment: chemoimmunotherapy with FCR.
What is the target of ibrutinib?
Ibrutinib targets the Bruton tyrosine kinase, or BTK, which is crucial to signaling downstream of the B cell receptor and is now known to be a lynchpin in CLL cell survival. After multiple studies in relapsed CLL, in 2016, ibrutinib was approved as a single agent given continuously for first-line treatment of CLL, ...
Does ibrutinib affect TP53?
The benefits of ibrutinib frontline increase the greater the disease risk, such that patients with 17p deletion or TP53 mutation should not receive chemoimmu notherapy but rather ibrutinib or another targeted agent, while mutated IGHV patients have similar outcomes with chemoimmunotherapy or ibrutinib.
Is CLL a first line treatment?
Updated: October 21, 2019. Medically reviewed by Jennifer Brown, MD. Most patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) now have several options for first-line therapy, thanks to new clinical trial results and novel targeted agents. Many patients with CLL, a slowly progressive blood cancer in which the bone marrow makes too many white blood ...
MRD Status Not Associated With PFS in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia Patients on Ibrutinib
Undetectable MRD was not associated with significantly better PFS at any time point.
Changes in Clinical Trial Conduct Prompted by the COVID-19 Pandemic Should Persist
The AACR COVID-19 and Cancer Task Force recommends keeping changes to clinical trial practices that were prompted by the pandemic.
Acalabrutinib Seems Safe and Efficacious in Patients With Treatment-Naïve Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia
Researchers sought to determine whether acalabrutinib would be safe and effective in patients with treatment-naïve CLL who declined or were in ineligible for chemotherapy.
ASCO and Friends: Cancer Patients Should Be Included in COVID-19 Vaccine Trials
A statement recommends including cancer patients and survivors in COVID-19 vaccine trials.
The Past, Present, and Future of GRASP: Connecting Cancer Researchers, Clinicians, and Patient Advocates
GRASP co-founder Julia Maués explains how the initiative came about and reveals plans for the future.
How to Manage Venetoclax Resistance in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia
Experts outline treatment options for patients with venetoclax resistance.
Underdosing in Patients With Cancer and Obesity: A Thing of the Past?
New guidelines recommend using the full approved doses of immunotherapy and targeted therapies for patients with cancer and obesity.