Medication
Treatments for A-fib involve a variety of surgical procedures or medications to restore your heartbeat to its normal rhythm and blood-thinners to prevent blood clots from forming. More natural treatments may include dietary supplements, exercise, and more.
Procedures
Top 10 foods for AFib:
- Dark green leafy vegetables Dark green leafy vegetables such as kale, arugula or spinach are rich in dietary nitrates. ...
- Wild-caught salmon Fatty fish, such as salmon, is the single best source of essential omega 3 fatty acids. ...
- Avocado Avocados are arguably one of the most important foods for heart health, especially for AFib. ...
Nutrition
“I hear a lot about atrial fibrillation. What exactly is it ... Your provider can help decide what is the best option for you. The WATCHMAN Implant could be a life-changing alternative to the lifelong use of blood thinners for those who need one.
Are there any natural cures for AFIB?
February is heart month, and all month, we’ll be bringing you stories on different aspects of heart health. Tonight (Feb. 7), we’re focusing on new research involving a condition called Atrial Fibrillation Or A-Fib for short.
What diet is best for AFIB?
What is the best treatment for atrial fibrillation?
Can you cure AFIB naturally?
What is the newest medication for AFib?
Newly Approved Treatments A new medicine called edoxaban has been cleared to prevent blood clots and stroke in patients with AFib. Edoxoban is also a NOAC (non-vitamin K oral anticoagulant).
What is the most successful treatment for AFib?
Blood thinners (Aspirin and Heparin) can thin the blood and lower the risk of serious complications. Heart rate controlling medicines, such as beta-blockers that include Coreg (Carvedilol) and Lopressor and Toprol (Metoprolol), is the best way to treat AFib.
How do you permanently fix AFib?
When you have atrial fibrillation, or AFib, your heart has an irregular, sometimes quick rhythm. The condition can boost your chances for a stroke, heart failure, or other heart problems. Right now, there's no cure for it.
How successful is ablation for AFib 2021?
Results from the multicentre investigator-initiated trial found that cryoablation was superior in maintaining freedom from AF, atrial tachycardia and atrial flutter, with 57.1% of patients in the catheter ablation group versus 32.2% in the antiarrhythmic drug group achieving treatment success at 12 months.
Which is better cardioversion or ablation?
Conclusion: In patients with AF, there is a small periprocedural stroke risk with ablation in comparison to cardioversion. However, over longer-term follow-up, ablation is associated with a slightly lower rate of stroke.
What is the first drug of choice for atrial fibrillation?
Amiodarone as a first-choice drug for restoring sinus rhythm in patients with atrial fibrillation: a randomized, controlled study. Chest.
Is a pacemaker better than ablation?
Conclusions: In patients with paroxysmal AF-related tachycardia-bradycardia syndrome, AF ablation seems to be superior to a strategy of pacing plus AAD. Pacemaker implantation can be waived in the majority of patients after a successful ablation.
How many years does an ablation last?
Long-term success of AF ablation procedures, defined as freedom from arrhythmia recurrence for a minimum of 36 months off antiarrhythmic therapy, can be achieved in many patients.
What is the best sleep position for AFib?
A left lateral recumbent position increases the dimensions of the left atrium and the right pulmonary veins and thereby increases local myocardial stress (Wieslander et al., 2019).
What is the alternative to cardiac ablation?
The Mini-Maze procedure provides an alternative to conventional catheter ablation for atrial fibrillation (AF). It may be used in patients with chronic, persistent AF.
Is cardiac ablation worth it?
Ablation can relieve symptoms and improve the quality of life in people with atrial fibrillation. But it doesn't work for everyone. If atrial fibrillation happens again after the first ablation, you may need to have it done a second time. Repeated ablations have a higher chance of success.
Who is a good candidate for cardiac ablation?
Good Candidates for Cardiac Ablation Likely candidates for the cardiac ablation procedure include: People who cannot have a procedure called cardioversion. One type of cardioversion uses medication, but some people cannot take these drugs. Others experience severe side effects from them.
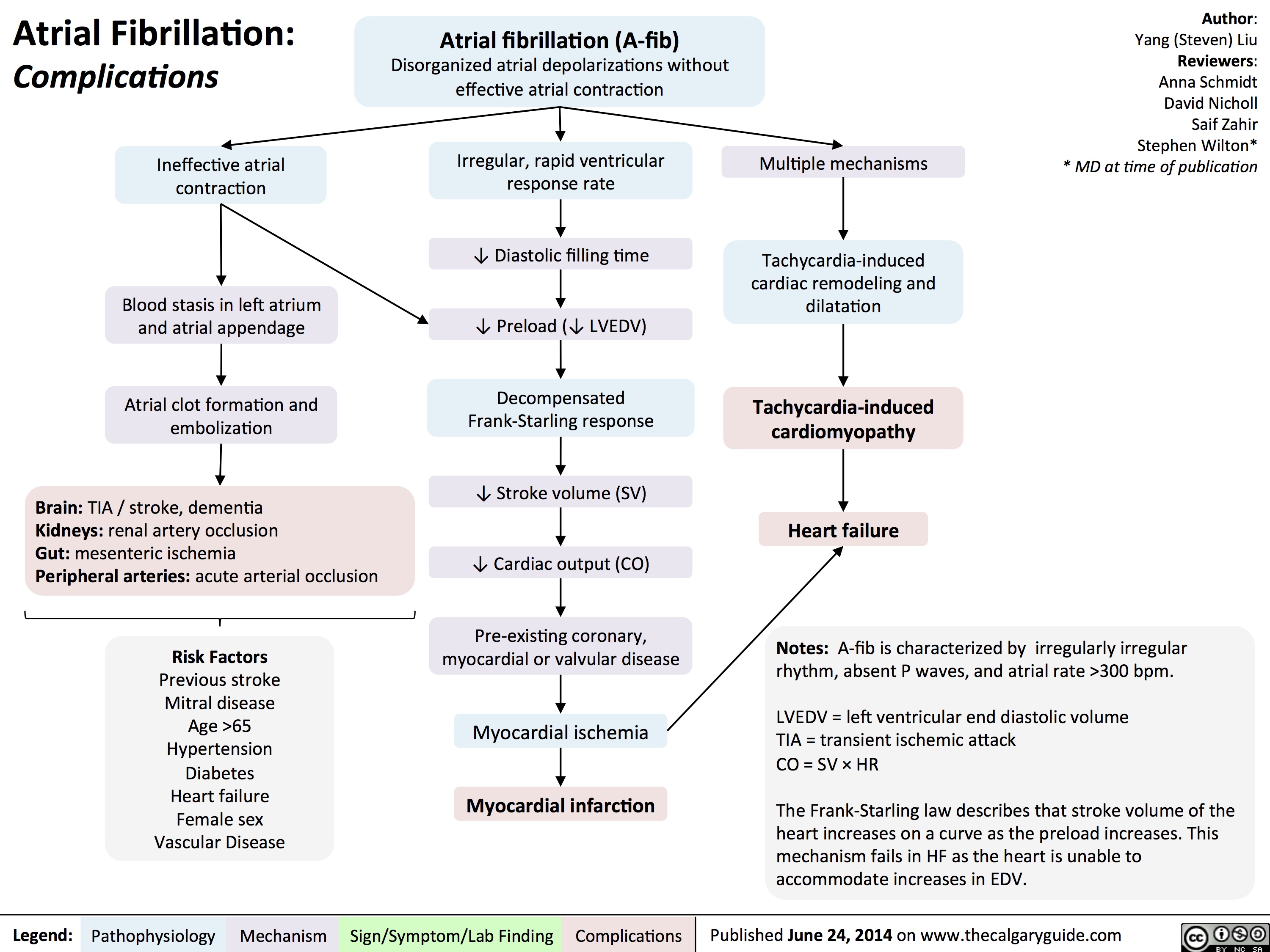
Treatment With Medications
There are two components of AF that need management: heart rate and heart rhythm.
Heart Rate Management
Beta-blockers decrease resting and exercise heart rates, reducing the workload on the heart. Common drugs in this class used for AF rate control are:
Heart Rhythm Management
Heart rhythm drugs, called antiarrhythmics, restore the heart’s normal rhythm. The goal here is to decrease AF episode duration and frequency.
Anticoagulation
Some people with AF are candidates for anticoagulation therapy, which reduces the risk of blood clots forming that can lead to a stroke.
Electrical Cardioversion
Research shows that electrical cardioversion is an effective way to resolve AF and it can return the heart to its normal rhythm.
Surgical Intervention
Open-heart surgery is the best option for some individuals, especially if it is scheduled to address and correct another problem. The Maze procedure is the top choice because it restores heart rate and rhythm while reducing the risk of stroke.
Catheter Ablation
Catheter ablation is a non-surgical intervention option for people with AF that does not respond to medication therapy.
How to reduce the risk of AFIB?
These changes can help reduce your risk of complications from AFib. You should stop or refrain from smoking and limit your intake of alcohol and caffeine. Also, you should avoid cough and cold medications that contain stimulants. If you’re not sure which to avoid, ask your pharmacist.
What are the goals of AFIB treatment?
Your treatment plan will likely address three goals: restore your normal heart rate. restore your normal heart rhythm. Medications can help achieve all three of these goals.
How does AFIB work?
Two types of medication can help with this. They work by slowing down electrical signals in your heart. These medications are: Sodium channel blockers such as flecainide (Tambocor) and quinidine.
How to slow down heart rate?
Slowing down your heart rate is another important step in treatment. Your doctor may prescribe medications for this purpose. Three types of medications can be used to restore your normal heart rate: 1 Beta-blockers such as atenolol (Tenormin), carvedilol (Coreg), and propranolol (Inderal) 2 Calcium channel blockers such as diltiazem (Cardizem) and verapamil (Verelan) 3 Digoxin (Lanoxin)
What is the best medicine for slowing down heart rate?
Three types of medications can be used to restore your normal heart rate: Beta-blockers such as atenolol (Tenormin), carvedilol (Coreg), and propranolol (Inderal) Calcium channel blockers such as diltiazem (Cardizem) ...
Why are NOACs recommended over warfarin?
These NOACs are now recommended over the traditionally prescribed warfarin (Coumadin) because they have no known food interactions and don’t require frequent monitoring. People who take warfarin require frequent blood testing and need to monitor their intake of foods rich in vitamin K.
How to restore sinus rhythm?
Another option for restoring sinus rhythm when medications fail is called catheter ablation. A narrow catheter is threaded through a blood vessel into your heart. The catheter uses radiofrequency energy to destroy a small number of tissue cells in your heart that send out signals that cause your abnormal heart rhythm.
What is the best medication for atrial fibrillation?
These medications include dabigatran, rivaroxaban, apixaban and edoxaban. They are shorter acting than warfarin and usually don't require regular blood tests or monitoring by your doctor.
What to do if you think you have atrial fibrillation?
If you think you may have atrial fibrillation, it is critical that you make an appointment with your family doctor. If atrial fibrillation is found early, your treatment may be easier and more effective. However, you may be referred to a doctor trained in heart conditions (cardiologist).
How does catheter ablation help with atrial fibrillation?
Atrial fibrillation is often caused by rapidly discharging triggers, or "hot spots." In catheter ablation to treat atrial fibrillation, a doctor inserts long, thin tubes (catheters) into your groin and guides them through blood vessels to your heart. The electrodes at the tips of the catheters help your doctor determine where these triggers are located. Electrodes at the catheter tips can use radiofrequency energy, extreme cold (cryotherapy) or heat to destroy these triggers, scarring the tissue so that the erratic signals are normalized.
What is the procedure called when a catheter is placed in the left atrium?
Left atrial appendage closure. Your doctor may also consider a procedure called left atrial appendage closure. In this procedure, doctors insert a catheter through a vein in the leg and eventually guide it to the upper left heart chamber (left atrium).
How to diagnose atrial fibrillation?
To diagnose atrial fibrillation, your doctor may review your signs and symptoms, review your medical history, and conduct a physical examination. Your doctor may order several tests to diagnose your condition, including:
How does cardioversion work?
In this brief procedure, an electrical shock is delivered to your heart through paddles or patches placed on your chest. The shock stops your heart's electrical activity for a short moment. The goal is to reset your heart's normal rhythm.
What is the best medication to slow your heart rate?
Digoxin. This medication may control the heart rate at rest, but not as well during activity. Most people need additional or alternative medications, such as calcium channel blockers or beta blockers. Beta blockers. These medications can help to slow the heart rate at rest and during activity.
What is the best medication for atrial fibrillation?
Among the medications typically prescribed to treat atrial fibrillation, the most common is the anticoagulant drug warfarin. AFib causes a higher risk of stroke and other related cardiovascular events, so one of the primary treatment goals is protecting against the formation of blood clots.
What is permanent AFIB?
Permanent AFib, in which symptoms are chronic and typically unresponsive to normal treatment. Atrial fibrillation frequently occurs alongside one or more other health conditions, and it may lead to a greater risk of heart failure, stroke, coronary heart disease, heart attack, and other serious cardiovascular complications.
How many cases of atrial fibrillation will there be in 2050?
The number of cases of atrial fibrillation in the United States is expected to double by the year 2050, making safe and effective treatment options a major priority. Though current treatments are generally effective and can improve the outlook and quality of life of most patients, the disorder remains complex and not well understood.
How does atrial fibrillation affect the heart?
Affecting between two and six million people in the United States, atrial fibrillation is caused by malfunctioning of the upper chambers of the heart, also known as the atria. This creates an irregular heartbeat, impairing the normal flow of blood through the heart. If you have atrial fibrillation, you may notice symptoms ...
What are the different types of AFIB?
Atrial fibrillation often occurs briefly and intermittently, but it may also become a permanent or semi-permanent condition that requires medical intervention. The disorder is divided into the following categories: 1 Paroxysmal fibrillation, in which symptoms last seven days or less. 2 Persistent AFib, in which symptoms persist for longer than seven days. 3 Permanent AFib, in which symptoms are chronic and typically unresponsive to normal treatment.
Is AFIB resistant to treatment?
There are also a number of new treatments that may offer greater effectiveness, particularly for AFib that is resistant to standard treatment options. If you suffer from AFib, here's what you need to know about the latest research and treatment options.
Where is the epicardial ablation?
Epicardial ablation treats the outside of the heart, on the back (posterior) of the atrium, another known trigger area for AF. Endocardial radiofrequency (RF) ablation treats the inside of the heart at the pulmonary veins. This is a key trigger area for atrial fibrillation.
Is there a PMA approved treatment for atrial fibrillation?
If your atrial fibrillation has lasted for more than a year, there's new hope for effective treatment. Hybrid AF™ Therapy is the first and only FDA PMA approved minimally invasive ablation therapy for long-standing persistent atrial fibrillation patients. Hybrid AF Therapy combines two types of ablation therapy to treat two key trigger areas for AF:

Diagnosis
Treatment
Clinical Trials
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
Specialist to consult
Preparing For Your Appointment