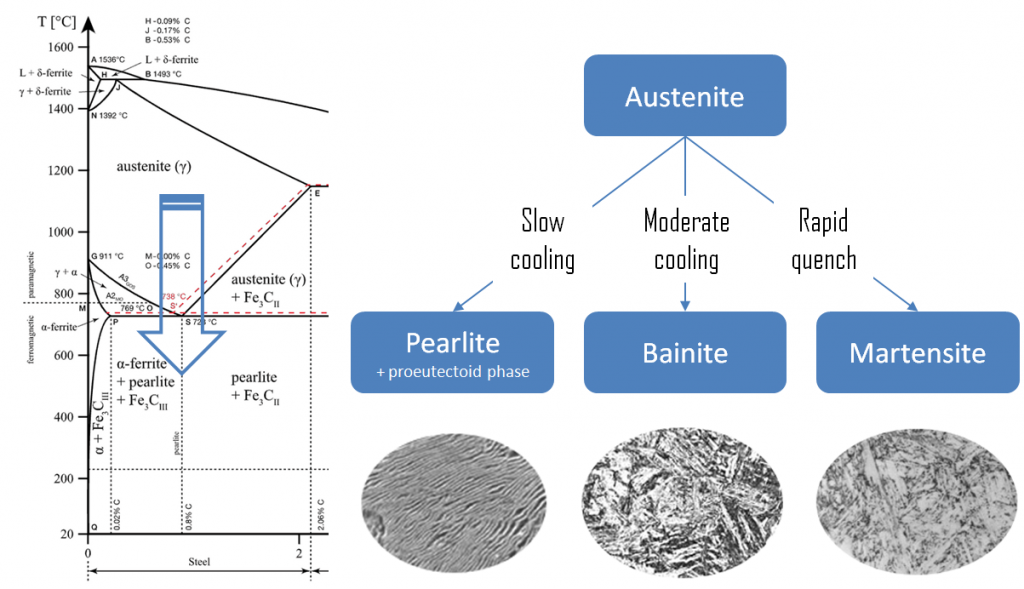
The steel is allowed to cool in air to room temperature, resulting tin fine pearlite What is the most important heat treatment for hardening steels? The most important heat treatment for steels is martensite formation by heating steel into the austenite region and quenching.
What is the most important heat treatment for steels?
Induction heating is the most important heat treatment for hardening steels and it involves application of electromagnetically induced energy supplied by an induction coil to an electrically conductive work part. Induction heating is widely used in industry for processes such as brazing, soldering, adhesive curing, and various heat treatments.
What is hardening of steel?
Answer (1 of 3): Heat Treatment Steel: Annealing The purpose of annealing is to do the opposite of hardening. You anneal metals to relieve stress, soften the metal, increase ductility, and improve their grain structures. Without an appropriate preheating stage, welding can lead to a metal with ...
Does heat treatment affect the hardness of metal?
Expert Answer 100% (1 rating) 4-1). The most important heat treatment for steels is martensite formation by heating steel into the austenite region and quenching. Heat treating via the oil quenching process involves immersing already appropriately heated steel in an oil, dependi … View the full answer Transcribed image text: 4-1.
What happens when steel is allowed to cool to room temperature?
Aug 21, 2018 · Chap 26 26.3 What is the most important heat treatment for hardening steels? I’d have to say martensite formation is the most important, because it is the phase that gives the steel its ability to reach high levels of strength.

What is the most significant in heat treatment of steels?
Normalising. One of the most important methods for heat treatment is normalising, giving the steel an even, fine-grained structure with homogeneous properties. This method is applied particularly for carbon steels or low-alloyed steel types. Their structures are normalised after hot-rolling or casting.
What heat treatments are used on steel?
In this post, we'll cover the four basic types of heat treatment steel undergoes today: annealing, normalizing, hardening, and tempering.Jul 14, 2020
What heat treatment produces the hardest steel?
The DPH of martensite is about 1,000; it is the hardest and most brittle form of steel. Tempering martensitic steel—i.e., raising its temperature to a point such as 400° C and holding it for a time—decreases the hardness and brittleness and produces a strong and tough steel.
Which heat treatment is used to improve hardness?
Tempering can be used to change the hardness, ductility, and strength of metal, which usually makes it easier to machine. The metal will be heated to a temperature below the critical point as lower temperatures reduce brittleness while maintaining hardness.
How does heat treating hardened steel?
Hardening: When a metal is hardened, it's heated to a point where the elements in the material transform into a solution. Defects in the structure are then transformed by creating a reliable solution and strengthening the metal. This increases the hardness of the metal or alloy, making it less malleable.
Can all steels be heat treated?
All steel has to be treated in order to be used in commercial products. The heat treatment of steel generally always involves annealing, quenching, and tempering.
Why is heat treatment very necessary to steel?
Heat treating can improve wear resistance by hardening the material. Metals (including steel, titanium, inconel, and some copper alloys) can be hardened either on the surface (case hardening) or all the way through (through hardening), to make the material stronger, tougher, more durable and more resistant to wear.Sep 25, 2020
Why is heat treatment performed in steels?
The Benefits of Steel Heat Treatment. Steel parts often require some form of heat treatment to achieve an increase in hardness and obtain maximum strength and durability. Through the many different processes of heat treatment, the properties of steel are changed via physical and mechanical channels.Nov 23, 2016
How do you heat harden steel?
5:3717:29Intro to heat treatment of steel (hardening and tempering) - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipSo the weight a hardened steel is to heat it up until it's glowing red and then very quickly reduceMoreSo the weight a hardened steel is to heat it up until it's glowing red and then very quickly reduce the temperature. By plunging it in water or oil typically.
How does heat treatment affect hardness?
As conclusion, the heat treatment done to the 22MnB5 with different type of quenching process has portrayed an encouraging result, particularly in the hardness of the 22MnB5. The higher the cooling rate of the quenching, the smaller the size of the grain size. Hence, it will increase the hardness of the steel.
Which heat treatment process is used to improve the machinability of steel?
In annealing, the metal is heated beyond the upper critical temperature and then cooled at a slow rate. Annealing is carried out to soften the metal. It makes the metal more suitable for cold working and forming. It also enhances the metal's machinability, ductility and toughness.Feb 13, 2020
What are the two types of heat treatments used for hardening aluminum alloys?
The typical aluminum heat treatments are annealing, homogenizing, solution heat treatment, natural aging, and artificial aging (also known as precipitation hardening). Depending on the exact process being used, furnace temperatures can range from 240 to 1000°F.Nov 2, 2018
How to harden steel?
To harden most steels, you would use the first two stages of heat treatment (slow temperature heat followed by soaking by a specified time to a uniform temperature), the third stage is different. When you harden metals, you rapidly cool them by plunging them into water, oil, or brine.
Why is steel hard?
The answer may be to temper the steel to reduce that brittleness and remove or relieve the internal stresses.
Why is steel normalized?
The purpose of normalizing is to remove any internal stresses from heat treatment, machining, forging, forming, welding, or casting. Metal failure can result from uncontrolled stress, so normalizing steel before any hardening can help ensure the success of projects.
What is the purpose of annealing steel?
Heat Treatment Steel: Annealing. The purpose of annealing is to do the opposite of hardening. You anneal metals to relieve stress, soften the metal, increase ductility, and improve their grain structures. Without an appropriate preheating stage, welding can lead to a metal with uneven temperatures, even molten areas next to areas ...
What happens when you add alloys to steel?
When you add alloys to steel to increase its hardness, you also increase the carbon’s ability to harden and strengthen. That means that the carbon content needed to produce the highest level of hardness is lower in alloyed steels versus plain carbon steels.
Does hardening steel make it stronger?
The intent of hardening is not just to harden the steel, but also to make it stronger. Unfortunately, there aren’t just plusses to hardening. While hardening does increase strength, it also decreases ductility, making the metal more brittle.
What is the difference between carbon steel and alloy steel?
Typically, carbon steels are quenched in brine or water, whereas alloy steels are quenched in oil. Unfortunately, quenching is a process that produces high internal stress and, to relieve the steel, one option is to temper it.
What is the purpose of hardening steel?
Hardening is carried to accomplish the following: To reduce the grain size. Obtain maximum hardness.
Why is heat treatment important?
It is very important manufacturing process that can not only help the manufacturing process but can also improve the product, its performance, and its characteristics in many ways. By Heat Treatment process, Example: The plain carbon steel. The following changes may be achieved: The hardness of Steel may be increased or decreased.
What are the changes in steel?
The following changes may be achieved: The hardness of Steel may be increased or decreased. Internal stresses that are set up due to cold or hot working may be relieved. The machinability of Steel may be enhanced. The mechanical properties like tensile strength the Talati shock resistance toughness etc may be improved.
Who is Amrit Kumar?
Amrit Kumar is the founder of Learn Mechanical, an Advisor at The Mechanical Engineering- a content-based website in Mechanical Engineering based in Delhi. He has 5+ years of teaching experience in the Core Mechanical Field.
What temperature does annealing take place?
Annealing consists of heating of steel parts to a temperature at or near the critical temperature 900 degree Celsius hold it at that temperature for a suitable time and when allowed to cool slowly in the Furnace itself. The heating done during annealing affects the metal in two stages of recovery and recrystallization.
What is annealing in metal?
Annealing is carried out for accomplishing one or more of the following: Softening of a metal or alloy. This may be done due to improving machinability. Relieving internal residual stresses caused by the various manufacturing process. Refining the grain size of the metal or alloy.
What is recrystallization in steel?
This causes complete recrystallization in steel to form New grain structure. This will release the internal stresses previously the strip in the steel and improve the machinability.
Why is carburized steel good?
Another major benefit of carburized steel is that it possesses a soft interior. Because it possesses a soft interior, it’s easy to manipulate into different shapes. This makes it especially useful for when you’re trying to manufacture intricate metal items with hard surfaces (ie. internal machine components).
How are steel alloys put in the environment?
First is the process of vacuum carburization. In this process, steel alloys are put in an oxygen-free, low-pressure environment. Then, a gas such as hydrocarbon is pumped into the environment, allowing carbon molecules to attach to said alloys.
What is liquid carburization?
Liquid carburization is a form of carburization which takes place in a sort of liquid vat. This vat is filled with a mixture of substances, typically including cyanide and salt.
Is carburized steel cheaper than steel?
If you’re buying a steel alloy simply for its surface hardness, carburized steel is easily the most affordable option. The carburization process is much cheaper than the production of certain steel alloys.
