
Analgesics, such as aspirin or ibuprofen, are given to help ease the pain of this process and reduce inflammation. No specific drug is used to treat dracunculiasis. Metronidazole or thiabendazole (in adults) is usually adjunctive to stick therapy and somewhat facilitates the extraction process.
What are the treatment options for dracunculiasis?
Dracunculiasis Treatment & Management 1 Medical Care. The mainstay of treatment is the extraction of the adult worm from the patient using a stick at the skin surface and wrapping or winding the worm a ... 2 Surgical Care. The worm also can be excised surgically where such facilities are available. 3 Consultations. ... 4 Diet. ... 5 Activity. ...
What is dracunculiasis disease?
Dracunculiasis (guinea worm disease), caused by the nematode parasite Dracunculiasis medinensis, is a painful, disabling disease of impoverished, rural villagers in 13 sub-Saharan African countries that do not have access to safe drinking water.
Is the elimination of dracunculiasis an indicator of success?
In May 1981, the Interagency Steering Committee for Cooperative Action for the International Drinking Water Supply and Sanitation Decade (1981–1990) proposed the elimination of dracunculiasis as an indicator of success of the Decade.
How is dracunculiasis (guinea worm disease) prevented?
Prevention of Dracunculiasis (Guinea worm disease) is based on the following: Surveillance (case detection) and case containment (preventing contamination of drinking water sources by infected persons or animals) Provision of safe drinking water.

How is dracunculiasis eliminated?
Dracunculiasis, Guinea-worm disease, can be prevented by boiling drinking water or filtering it through a cloth to remove the larvae's copepod hosts, by educating villagers not to contaminate their sources, by providing clean drinking water from underground sources such as borehole wells which cannot be contaminated, ...
What is the only cure for Guinea worm?
Management of Guinea Worm Disease There is no specific drug to treat or prevent GWD. There is also no vaccine to prevent GWD.
What is the treatment for Dracunculus medinensis?
Treat dracunculiasis by slowly removing the adult worm over days to weeks by rolling it on a stick or sometimes by surgically removing it. Filtering drinking water through a piece of fine-mesh cloth, chlorination, or boiling effectively protects against dracunculiasis.
How is dracunculiasis diagnosed?
Dracunculiasis is usually diagnosed simply by seeing the worm exit the body through the blister on the skin. Once the worm is completely removed from the skin, the worm and its larvae can be examined under a microscope to ensure it is a D. medinensis worm.
Is Guinea worm removal painful?
In addition to the pain of the blister, removing the worm is also very painful. Furthermore, without proper care the wound often becomes infected by bacteria. These wound infections can then result in one or more of the following complications: Redness and swelling of the skin (cellulitis)
What causes worms in Virgina?
Causes of threadworms A threadworm infection is passed from person to person by swallowing threadworm eggs. A female threadworm can lay thousands of tiny eggs around the anus or vagina.
What is the work of albendazole tablet?
Albendazole is used to treat infections caused by worms. It works by keeping the worm from absorbing sugar (glucose), so that the worm loses energy and dies. This medicine is available only with your doctor's prescription.
How do you get rid of worms under your skin?
There are two medications that can be used to treat the infection and manage the symptoms. The treatment of choice is diethylcarbamazine (DEC), which kills the microfilariae and adult worms. Albendazole is sometimes used in patients who are not cured with multiple DEC treatments.
What is the best treatment for dracunculiasis?
No specific drug is used to treat dracunculiasis. Metronidazole or thiabendazole (in adults) is usually adjunctive to stick therapy and somewhat facilitates the extraction process.
Can worms be excised surgically?
Therefore, such medications should be used with caution. The worm also can be excised surgically where such facilities are available.
What are the symptoms of dracunculiasis?
One or more worms may be seen at a time, with the legs and feet being the most commonly infected areas. Symptoms include pruritus, nausea, vomiting, diarrhoea, or asthmatic attacks.
What is a lack of accepted safety for use under medical supervision?
There is a lack of accepted safety for use under medical supervision. 2. Has a high potential for abuse. Has a currently accepted medical use in treatment in the United States or a currently accepted medical use with severe restrictions. Abuse may lead to severe psychological or physical dependence.
Dracunculiasis causes
Today, Dracunculiasis (Guinea worm disease) affects poor communities in remote parts of Africa that do not have safe water to drink.
Dracunculiasis life cycle
Recent research has shown that certain aquatic animals can become infected by eating copepods (tiny “water fleas” too small to be clearly seen without a magnifying glass) that have been infected with Guinea worm larvae 15). Larvae are immature forms of the Guinea worm that contaminate water.
Dracunculiasis prevention
Teaching people to follow these simple control measures can prevent the spread of the Guinea worm disease:
Dracunculiasis eradication
Many federal, private, and international agencies are helping with the eradication of Dracunculiasis (Guinea worm disease). During 2018, Angola and South Sudan reported human cases; Chad and Ethiopia reported both human and animal cases; and Mali reported animal cases. Human cases have fallen from 3.5 million per year in 1986 to 28 in 2018.
Dracunculiasis symptoms
People with Dracunculiasis or Guinea worm disease have no symptoms for about 1 year. Then, the person begins to feel ill. Symptoms can include:
Dracunculiasis complications
In addition to the pain of the blister, removing the Dracunculus medinensis worm is also very painful. Furthermore, without proper care the wound often becomes infected by bacteria. These wound infections can then result in one or more of the following complications:
Dracunculiasis treatment
When the Guinea worm is ready to come out of the body, it creates a painful burning blister on the skin. The blister eventually ruptures, exposing the worm. Management of Guinea worm disease or Dracunculiasis involves removing the whole worm and caring for the wound in general.
How many cases of dracunculiasis were there in the 1980s?
During the mid-1980s an estimated 3.5 million cases of dracunculiasis occurred in 20 countries worldwide, 17 countries of which were in Africa. The number of reported cases fell to fewer than 10 000 cases for the first time in 2007, dropping further to 542 cases (2012). Over the past eight years, human cases have stayed at double digits (28 in 2018 ...
How many dogs have Dracunculus medinensis?
Dracunculus medinensis infection in dogs continues to pose a challenge to the global eradication campaign. In 2019, Chad reported 1935 infected dogs and 46 infected cats; Ethiopia reported two infected dogs, and six infected baboons; Mali reported infections in nine dogs and Angola in one dog.
How to prevent worms?
There is no vaccine to prevent the disease, nor is there any medication to treat patients. Prevention is possible, however, and successful implementation of preventive strategies have driven the disease to the verge of eradication. Prevention strategies include: 1 heightening surveillance to detect every case within 24 hours of worm emergence; 2 preventing transmission from each worm by treatment, and regular cleaning and bandaging of affected areas of skin until the worm is completely expelled from the body; 3 preventing contamination of drinking-water by preventing infected people with emerging worms from wading into water; 4 ensuring wider access to improved drinking-water supplies to prevent infection; 5 filtering water from open water bodies before drinking; 6 implementing vector control by using the larvicide temephos; and 7 promoting health education and behavioural change.
How long should guinea worm surveillance be?
WHO recommends active surveillance in a country and/or area that has recently interrupted guinea-worm disease transmission to be maintained for a minimum of 3 consecutive years. Ongoing surveillance is essential to ensure that no cases have been missed and to prevent reoccurrence of the disease.
How to prevent contamination of drinking water?
preventing contamination of drinking-water by preventing infected people with emerging worms from wading into water; ensuring wider access to improved drinking-water supplies to prevent infection; filtering water from open water bodies before drinking; implementing vector control by using the larvicide temephos; and.
What was the goal of the International Drinking Water Supply and Sanitation Decade?
In the same year, WHO’s decision-making body, the World Health Assembly, adopted resolution WHA 34.25, recognizing that the International Drinking Water Supply and Sanitation Decade presented an opportunity to eliminate dracunculiasis. This led to WHO and the United States Centers for Disease Control and Prevention formulating the strategy and technical guidelines for an eradication campaign.
Is dracunculiasis fatal?
Dracunculiasis is rarely fatal, but infected people become non-functional for weeks. It affects people in rural, deprived and isolated communities who depend mainly on open surface water sources such as ponds for drinking water.
Causal Agents
Dracunculiasis (Guinea worm disease) is caused by the nematode (roundworm) Dracunculus medinensis.
Life Cycle
Humans become infected by drinking unfiltered water containing copepods (small crustaceans) which are infected with larvae of D. medinensis. Following ingestion, the copepods die and release the larvae, which penetrate the host stomach and intestinal wall and enter the abdominal cavity and retroperitoneal space.
Geographic Distribution
An ongoing eradication campaign has dramatically reduced the incidence of dracunculiasis, which is now restricted to rural, isolated areas in a narrow belt of African countries.
Clinical Presentation
The clinical manifestations are localized but incapacitating. The worm emerges as a whitish filament (duration of emergence: 1 to 3 weeks) in the center of a painful ulcer, accompanied by inflammation and frequently by secondary bacterial infection.
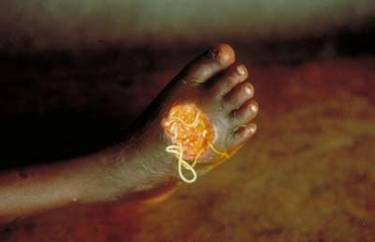
Transmission, Life-Cycle and Incubation Period
The Road to Eradication
- In May 1981, the Interagency Steering Committee for Cooperative Action for the International Drinking Water Supply and Sanitation Decade (1981–1990) proposed the elimination of dracunculiasis as an indicator of success of the Decade. In the same year, WHO’s decision-making body, the World Health Assembly, adopted resolution WHA 34.25, recognizing that the In…
Ongoing Surveillance
- WHO recommends active surveillance in a country and/or area that has recently interrupted guinea-worm disease transmission to be maintained for a minimum of 3 consecutive years. Ongoing surveillance is essential to ensure that no human cases and infected animals have been missed and to prevent reoccurrence of the disease. As the incubation period of the worm takes …