
What is the treatment for megaloblastic anemia?
Megaloblastic anemia secondary to folate deficiency is generally treated with oral folate, as it is most often caused by dietary deficiency rather than malabsorption. For supplementation and treatment, it is available as either of the following: The synthetic form, known as folic acid or pteroylglutamic acid.
What is the name of the vitamin B drug that is used to treat megaloblastic anemia?
Cyanocobalamin (vitamin B12) is used to correct vitamin B12 deficiency and folic acid is used to treat folic acid deficiencies. Cyanocobalamin does not naturally occur.
What happens if you have megaloblastic anemia?
Megaloblastic anemia is a type of anemia characterized by very large red blood cells. In addition to the cells being large, the inner contents of each cell are not completely developed. This malformation causes the bone marrow to produce fewer cells, and sometimes the cells die earlier than the 120-day life expectancy.
How long does it take to recover from megaloblastic anemia?
While most mild neurologic abnormalities that may have arisen in the past 3 months can be expected to improve in up to 90% of patients within about 6 months, those with more prolonged symptoms could take a year to recover completely.
How do you increase B12 absorption?
To increase the amount of vitamin B12 in your diet, eat more of foods that contain it, such as:Beef, liver, and chicken.Fish and shellfish such as trout, salmon, tuna fish, and clams.Fortified breakfast cereal.Low-fat milk, yogurt, and cheese.Eggs.
Why does metformin cause megaloblastic anemia?
Metformin can cause megaloblastic anemia, due to vitamin B12 deficiency; therefore, we would advise annual blood panels to be required by the prescribing physician for all patients undergoing treatment with metformin.
Can megaloblastic anemia be cured?
The treatment of megaloblastic anemia depends upon the underlying cause of the disorder. Dietary insufficiency of cobalamin and folate can be treated with appropriate changes to the diet and the administration of supplements.
Which infection causes megaloblastic anemia?
The common causative agent (D. latum) is a large tapeworm that can reach a length of 20 meters. One of its more conspicuous clinical manifestations in humans is megaloblastic anemia, which is caused by the parasite intake of vitamin B12 or folic acid within the host.
What medications cause megaloblastic anemia?
II. Causes: Megaloblastic Macrocytic AnemiaOral Contraceptive Use.Pyrimethamine (Daraprim)Triamterene.Alcohol.Biguanides. Methotrexate. Cholestyramine (Questran)Anticonvulsants. Phenytoin (Dilantin) ... Antibiotics. Sulfasalazine (Azulfidine) ... Reverse transcriptase inhibitors (HIV Medications) Stavudine (Zerit)
What is the fastest way to increase red blood cells?
5 nutrients that increase red blood cell countsred meat, such as beef.organ meat, such as kidney and liver.dark, leafy, green vegetables, such as spinach and kale.dried fruits, such as prunes and raisins.beans.legumes.egg yolks.
Is megaloblastic anemia rare?
Megaloblastic anemia is a rare blood disorder characterized by the presence of abnormal white blood cells, low white blood cell counts, and abnormally low levels of circulating platelets.
How is megaloblastic anemia diagnosed?
Megaloblastic anemia is diagnosed through a physical exam and other tests, including:complete blood count.reticulocyte count.blood tests to measure of vitamin B12, methylmalonic acid (MMA) or homocysteine levels.blood tests to detect the antibodies toward intrinsic factor or the cells that produce it.More items...
What are the causes of megaloblastic anemia?
Causes of megaloblastic anemia. The two most common causes of megaloblastic anemia are deficiencies of vitamin B12 and folate. These two nutrients are necessary for producing healthy RBCs. When you don’t get enough of them, it affects the makeup of your RBCs.
What is anemia in blood?
Anemia is a blood disorder in which the number of red blood cells (RBCs) is lower than usual. RBCs transport oxygen through the body. When your body doesn’t have enough RBCs, your tissues and organs don’t get enough oxygen. There are many types of anemia with different causes and characteristics. Megaloblastic anemia is characterized by RBCs ...
What is the gene that converts B12 to folate?
Some individuals have a genetic mutation on the methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase ( MTHFR) gene. This gene is responsible for the conversion of certain B vitamins, including B12 and folate, into their usable forms within the body. Supplemental methylcobalamin is recommended for individuals with the MTHFR mutation.
What is the condition called when you don't have enough B12?
Megaloblastic anemia caused by vitamin B12 deficiency is known as vitamin B12 deficiency anemia. One rare type of vitamin B12 deficiency anemia is pernicious anemia. Pernicious anemia is an autoimmune condition and is due to the lack of a protein in the stomach called intrinsic factor.
What is the name of the disorder in which the number of red blood cells is lower than usual?
Megaloblastic Anemia . Anemia is a blood disorder in which the number of red blood cells (RBCs) is lower than usual. RBCs transport oxygen through the body. When your body doesn’t have enough RBCs, your tissues and organs don’t get enough oxygen. There are many types of anemia with different causes and characteristics.
What test is used to determine if you have vitamin B12?
Another test that your doctor may use to help with diagnosis is the Schilling test . The Schilling test is a blood test that evaluates your ability to absorb vitamin B12.
Can you get anemia from lack of B12?
It’s possible to develop vitamin B12 deficiency anemia because there simply isn’t enough vitamin B12 in your diet. Since B12 isn’t naturally found in any plant-based products, vitamin B12 deficiency is common in people following a vegetarian or vegan diet.
What is the treatment for megaloblastic anemia?
Once drug-induced megaloblastic changes and myelodysplasia-related megaloblastosis have been ruled out, most patients are treated with cobalamin or folate. Since megaloblastic anemias usually develop gradually, many patients adjust to low hemoglobin levels and do not require transfusions. Transfusion therapy should be restricted to patients with severe, uncompensated, and life-threatening anemia.
What is the treatment for blind loop syndrome?
Blind loop syndrome should be treated with antibiotics. Patients with transcobalamin II (TCII) deficiency may require higher doses of cobalamin. Tropical sprue should be treated with both cobalamin and folate. Acute megaloblastic anemias due to nitrous oxide exposure can be treated with folate and cobalamin.
What foods should I eat if I have a folate deficiency?
Patients should have diets rich with folic acid. Examples of such foods include asparagus, broccoli, spinach, lettuce, lemons, bananas, melons, liver, and mushrooms.
What is the best supplement for kidney failure?
Fortification of foods and folic acid supplements have been recommended to reduce the risk of pancreatic, cervical, and colon cancers. Folic acid supplements are indicated in patients with kidney failure. Folate supplementation is indicated in elderly persons.
How much should hemoglobin rise?
The hemoglobin should rise approximately 1 g/dL each week. This rise is valuable for monitoring a complete response. If the hemoglobin does not rise appropriately and is not normal within 2 months, other causes of anemia, such as iron deficiency, should be considered.
Can potassium be taken with iron deficiency?
Therefore, potassium should be monitored and supplements may be indicated. Iron deficiency can occur in the course of treatment due to the consumption of iron stores for red blood cell production.
Can folic acid be used for megaloblastic anemia?
Folate therapy should not be instituted in a patient with megaloblastic anemia if cobalamin deficiency has not been definitively ruled out. The danger is that folic acid will improve the anemia but not the neurological complications of cobalamin deficiency, and the neurological disorder will worsen.
A Type of Anemia With Large Red Blood Cells
Heidi Moawad is a neurologist and expert in the field of brain health and neurological disorders. Dr. Moawad regularly writes and edits health and career content for medical books and publications.
Types
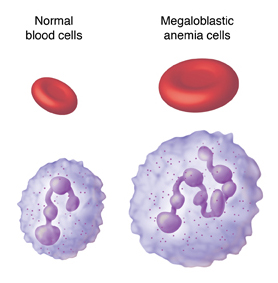
Megaloblastic anemia is a type of macrocytic anemia. Macrocytic anemia includes all types of anemia with larger than normal red blood cells. They can be megaloblastic (with enlarged and unusual red blood cell precursors in the bone marrow) or non-megaloblastic, and the causes of each type differ. 1
What Are the Symptoms of Megaloblastic Anemia?
You can have symptoms that range from mild to severe with megaloblastic anemia. The symptoms often develop gradually and may be accompanied by other effects of vitamin B12 or folate deficiency.
What Causes Megaloblastic Anemia?
Megaloblastic anemia develops due to vitamin B12 or folate deficiency. You can develop a deficiency of one or both vitamins for many reasons.
How Is Megaloblastic Anemia Diagnosed?
Megaloblastic anemia is diagnosed with blood tests. Often, an evaluation to identify the cause relies on additional tests.
How Megaloblastic Anemia Is Treated
Treatment for megaloblastic anemia involves correcting the vitamin deficiency. This can be done with diet and sometimes with oral supplements or injections.
Prognosis: What to Expect
Megaloblastic anemia should improve with treatment. It takes weeks—possibly months—to notice an improvement of symptoms and for blood tests to reflect the changes.
What are the causes of megaloblastic anemia?
Megaloblastic anemia has several different causes – deficiencies of either cobalamin (vitamin B12) or folate (vitamin B9) are the two most common causes. These vitamins play an essential role in the production of red blood cells.
What blood test can show megaloblastic anemia?
Blood tests may reveal the abnormally large, misshapen red blood cells that characterize megaloblastic anemia. Blood tests can also confirm cobalamin or folate deficiency as the cause of megaloblastic anemia. Additional tests such as a Schilling test, which confirms poor absorption as the cause of cobalamin deficiency, may be necessary.
What is the condition where the bone marrow produces red blood cells?
Megaloblastic anemia is a condition in which the bone marrow produces unusually large, structurally abnormal, immature red blood cells (megaloblasts). Bone marrow, the soft spongy material found inside certain bones, produces the main blood cells of the body -red cells, white cells, and platelets. Anemia is a condition characterized by the low levels of circulating, red blood cells. Red blood cells are released from the marrow into the bloodstream where they travel throughout the body delivering oxygen to tissue. A deficiency in healthy, fully-matured red blood cells can result in fatigue, paleness of the skin (pallor), lightheadedness and additional findings. Megaloblastic anemia has several different causes – deficiencies of either cobalamin (vitamin B12) or folate (vitamin B9) are the two most common causes. These vitamins play an essential role in the production of red blood cells.
What happens when you don't have enough red blood cells?
Red blood cells are released from the marrow into the bloodstream where they travel throughout the body delivering oxygen to tissue. A deficiency in healthy, fully-matured red blood cells can result in fatigue, paleness of the skin (pallor), lightheadedness and additional findings.
What are the symptoms of anemia?
Symptoms common to anemia usually develop at some point and may include fatigue, paleness of the skin (pallor), shortness of breath, lightheadedness, dizziness and a fast or irregular heartbeat. The specific symptoms present in each individual can vary greatly.
Can megaloblastic anemia be asymptomatic?
Because the causes of megaloblastic anemia vary and because some individuals may not exhibit any obvious symptoms (asymptomatic), determining its true frequency in the general population is difficult.
Can anemia cause cobalamin deficiency?
Pernicious anemia may also cause cobalamin deficiency. This form of anemia is characterized by a lack of intrinsic factor, a protein that binds with cobalamin and aids in its absorption by the small intestines. Without enough intrinsic factor, the body cannot absorb enough cobalamin.
What is the treatment for anemia?
Treatment for this anemia can include blood transfusions to boost levels of red blood cells. You might need a bone marrow transplant if your bone marrow can't make healthy blood cells. Anemias associated with bone marrow disease. Treatment of these various diseases can include medication, chemotherapy or bone marrow transplantation.
What is the treatment for hemolytic anemia?
Sickle cell anemia. Treatment might include oxygen, pain relievers, and oral and intravenous fluids to reduce pain and prevent complications. Doctors might also recommend blood transfusions, folic acid supplements and antibiotics.
What is the treatment for folic acid deficiency?
This might involve surgery. Vitamin deficiency anemias. Treatment for folic acid and vitamin C deficiency involves dietary supplements and increasing these nutrients in your diet. If your digestive system has trouble absorbing vitamin B-12 from the food you eat, you might need vitamin B-12 shots.
What is CBC in anemia?
A CBC is used to count the number of blood cells in a sample of your blood . For anemia, your doctor will be interested in the levels of the red blood cells contained in your blood (hematocrit) and the hemoglobin in your blood. Normal adult hematocrit values vary among medical practices but are generally between 40% and 52% for men and 35% ...
How to treat iron deficiency?
Iron deficiency anemia. Treatment for this form of anemia usually involves taking iron supplements and changing your diet. If the cause of iron deficiency is loss of blood — other than from menstruation — the source of the bleeding must be located and the bleeding stopped. This might involve surgery. Vitamin deficiency anemias.
Overview
- Megaloblastic anemia is a type of anemia, a blood disorder in which the number of red blood cells is lower than normal. Red blood cells transport oxygen through the body. When your body doesnt have enough red blood cells, your tissues and organs dont get enough oxygen. Folate is another nutrient thats important for the development of healthy red blood cells. Folate is found in foods li…
Treatment
- How you and your doctor decide to treat megaloblastic anemia depends on whats causing it. Your treatment plan can also depend on your age and overall health as well as your response to treatments and how severe the disease is. Treatment to manage anemia is often ongoing. In the case of megaloblastic anemia caused by vitamin B-12 deficiency, you may need monthly injectio…
Causes
- There are many types of anemia with different causes and characteristics. Megaloblastic anemia is characterized by red blood cells that are larger than normal. There also arent enough of them. Its known as vitamin B-12 or folate deficiency anemia, or macrocytic anemia, as well. Megaloblastic anemia is caused when red blood cells arent produced properly. Because the cell…
- Megaloblastosis can be associated with severe anemia and pancytopenia, gastrointestinal dysfunction and glossitis, personality changes, psychosis, and neurological disorders. [2] Megaloblastic changes can occur in HIV infections and myelodysplastic disorders as a result of interference of DNA synthesis. [1, 2, 3] Vitamin B-12 and folic acid deficiencies and certain medi…
Diagnosis
- One test used to diagnose many forms of anemia is the complete blood count (CBC). This test measures the different parts of your blood. Your doctor can check the number and appearance of your red blood cells. They will appear larger and underdeveloped if you have megaloblastic anemia. Your doctor will also gather your medical history and perform a physical exam to rule ou…
- See 21 Hidden Clues to Diagnosing Nutritional Deficiencies, a Critical Images slideshow, to help identify clues to conditions associated with malnutrition.
Pathophysiology
- Megaloblastic changes are most apparent in rapidly dividing cells such as blood cells and gastrointestinal cells. [1, 2] 3 In addition to large nucleated red blood cells (megaloblasts), hypersegmented neutrophils can be seen on peripheral smears, and giant bands occur in bone marrow.
Symptoms
- The most common symptom of megaloblastic anemia is fatigue. Symptoms can vary from person to person. Common symptoms include:
Morphology
- Megaloblastosis describes a heterogeneous group of disorders that share common morphologic characteristics: large cells with an arrest in nuclear maturation. Nuclear maturation is immature relative to cytoplasmic maturity. Hence, these cells, which can be seen in bone marrow aspirates and in peripheral smears, have been called megaloblasts. These abnormalities are due to impai…
Prognosis
- In the past, megaloblastic anemia was difficult to treat. Today, people with megaloblastic anemia due to either vitamin B-12 or folate deficiency can manage their symptoms and feel better with ongoing treatment and nutrient supplements.
Prevention
- Some individuals have a genetic mutation on the MTHFR (methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase) gene. This MTHFR gene is responsible for the conversion of certain B vitamins, including B-12 and folate, into their usable forms within the body. Individuals with the MTHFR mutation are recommended to take supplemental methylcobalamin. Regular intake of vitamin B-12-rich foods…
Scope
- The objectives of this article are to review the pathophysiology, clinical presentation, diagnosis, and management of megaloblastic anemias. An overview of the physiology and biochemistry of vitamin B-12 and folate under normal and pathological conditions are discussed.